Abstract
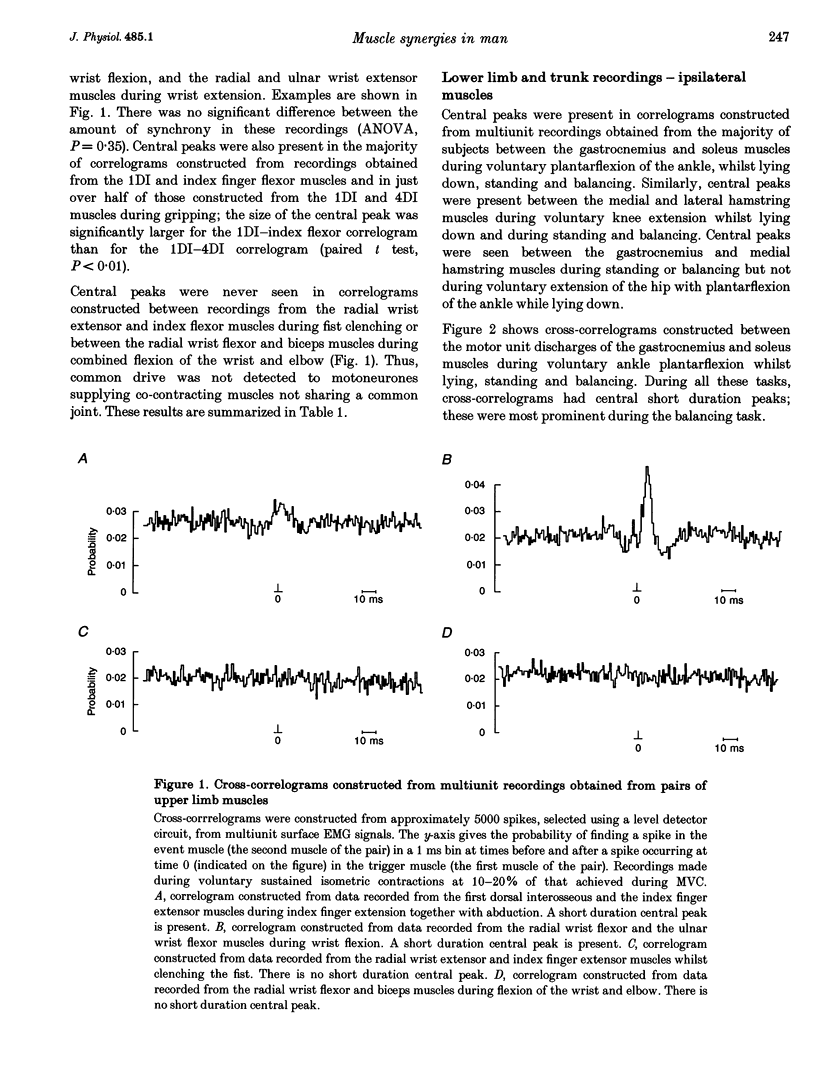
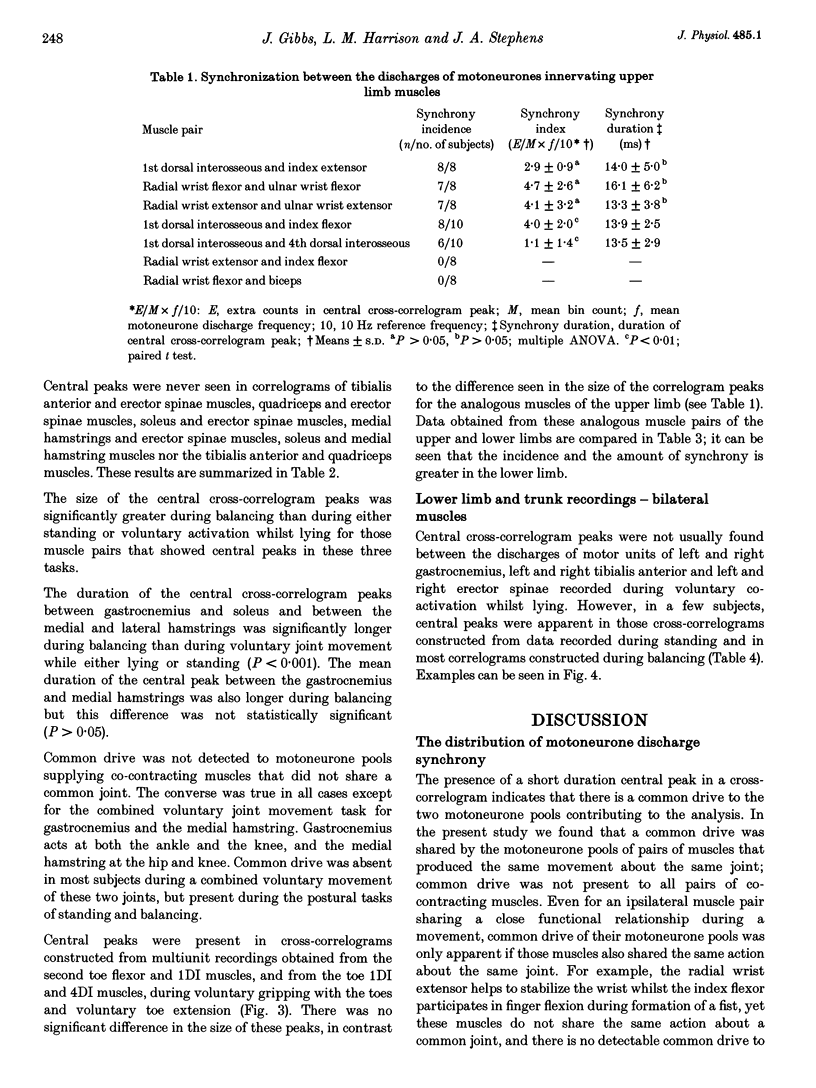
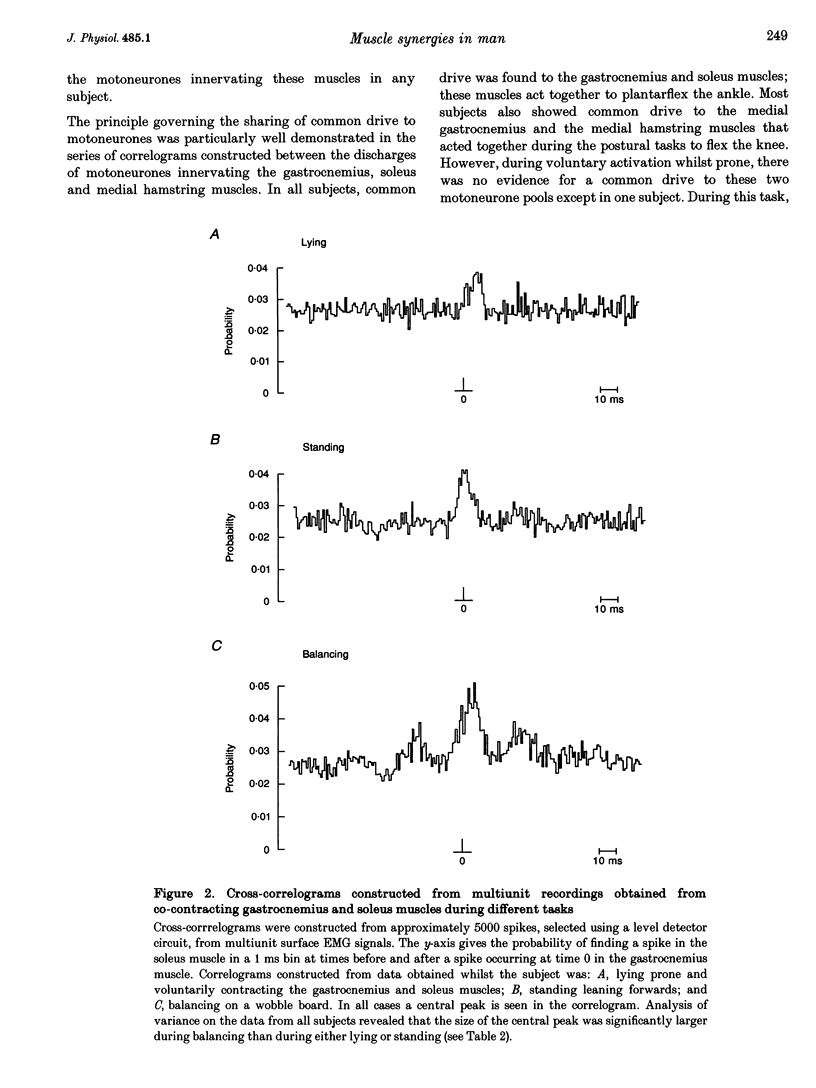
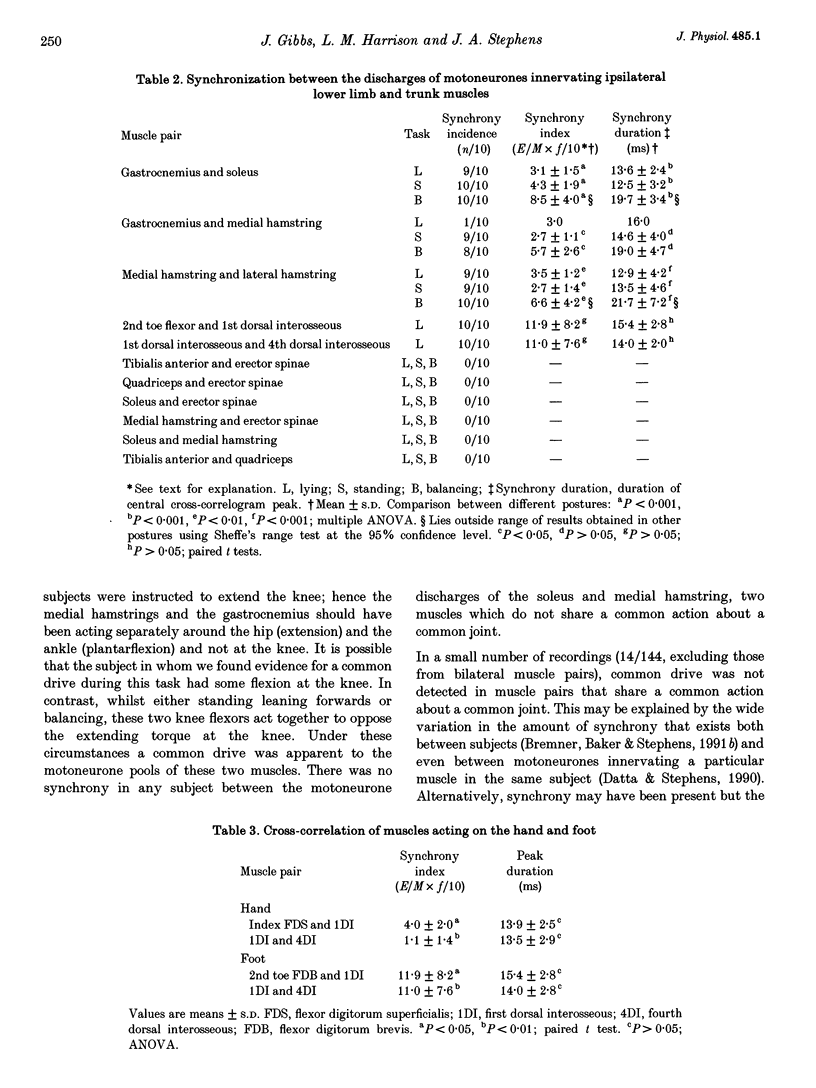
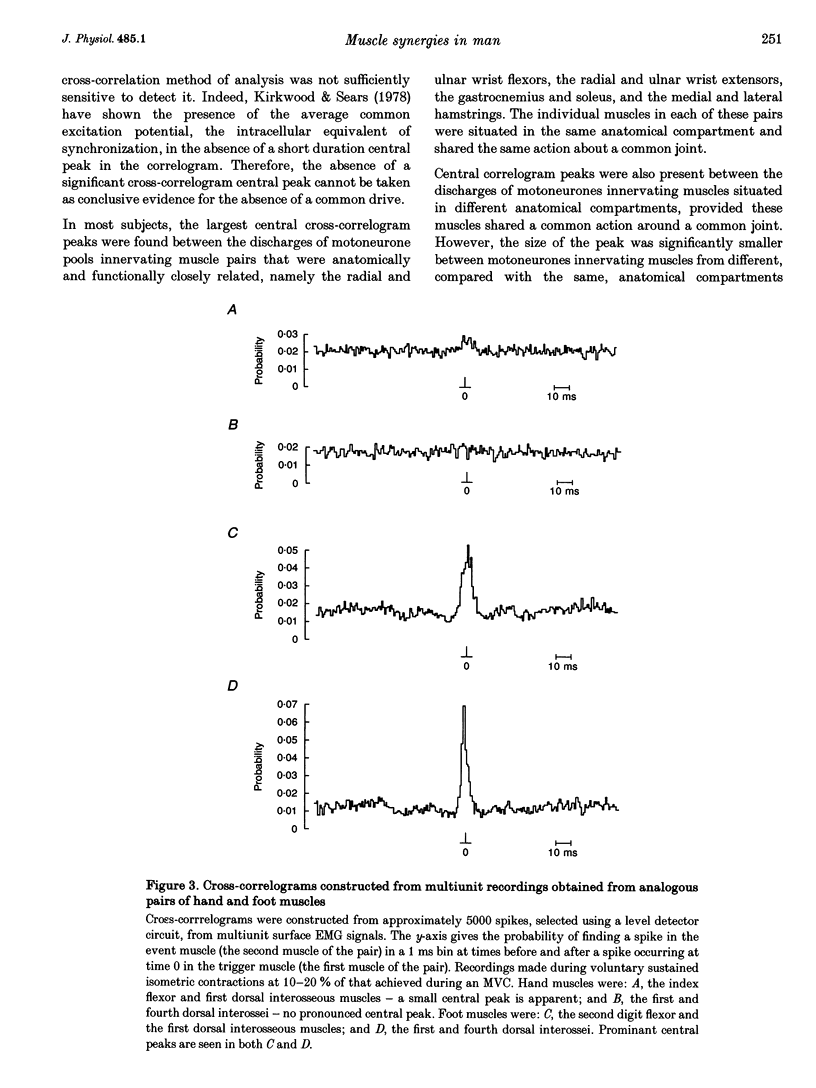
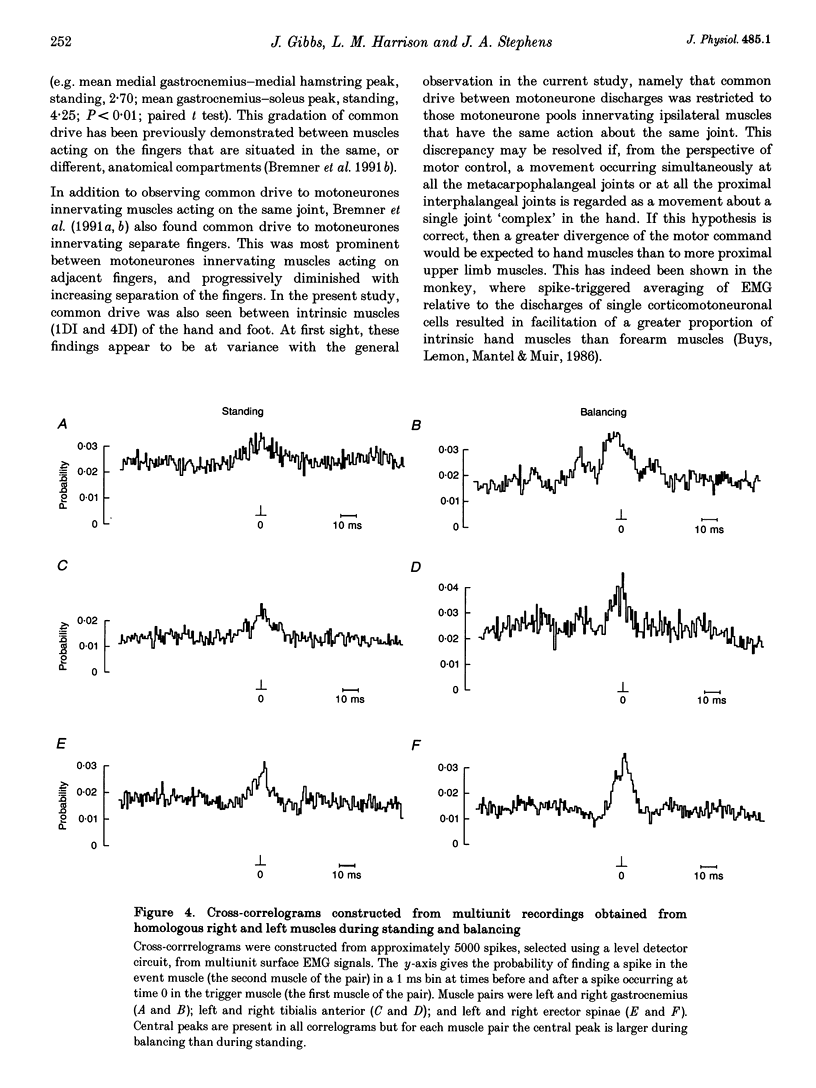
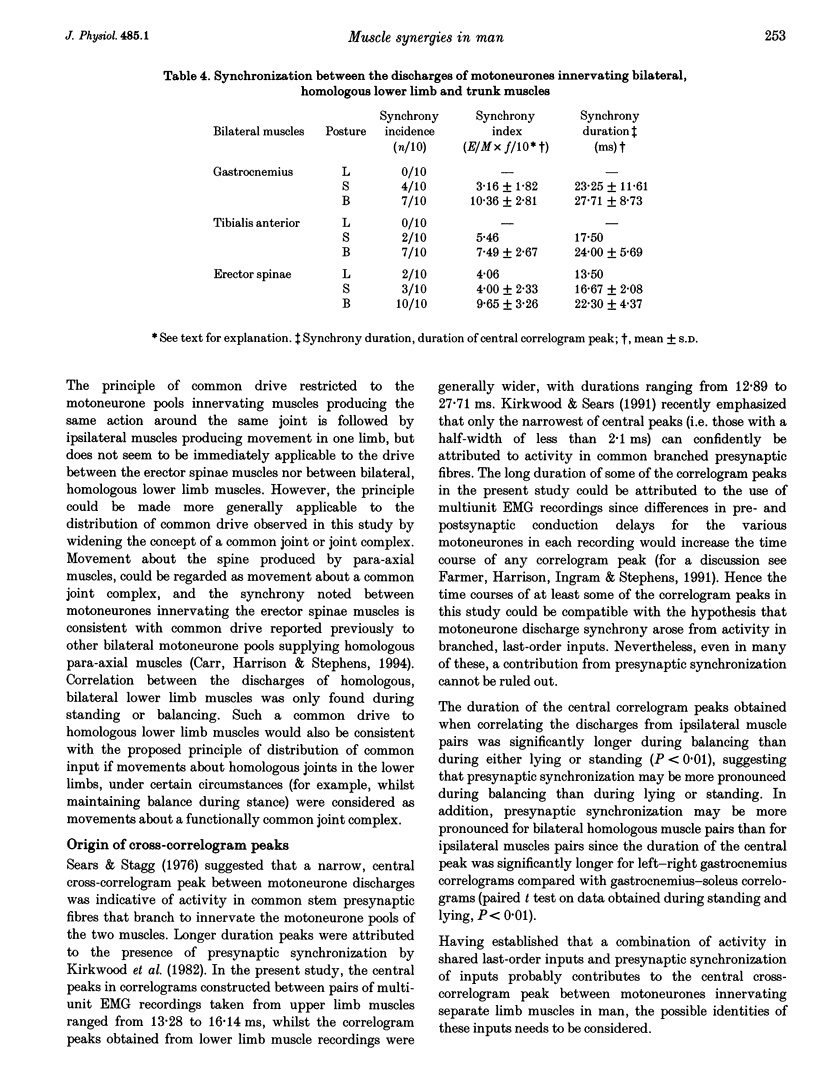
1. Surface EMGs were recorded from pairs of muscles involved in movements of the wrist and/or digits in the upper limb and from pairs of intrinsic foot muscles in the lower limb during voluntary isometric contractions. 2. EMGs were also recorded from lower limb and trunk muscles during three different tasks: lying, standing and balancing. 3. To investigate if the co-contraction of muscles was due to the presence of a common drive to each of the two motoneurone pools, cross-correlation analysis of the two multiunit EMG signals was used. 4. Evidence for a common drive was seen between pairs of muscles that share a common joint or joint complex (such as the metacarpophalangeal joints); no evidence was found for a common drive to co-contracting muscles that did not share a common joint. 5. When considering analogous hand and foot muscle pairs, the degree of synchrony was significantly greater for lower limb pairs. 6. Where a common drive was detected with lower limb muscle pairs, the degree of synchrony was significantly larger during balancing than during either lying or standing. 7. The origin of the common drive is discussed. It is concluded that activity in both last-order branched presynaptic fibers and presynaptic synchronization is involved.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allum J. H., Hepp-Reymond M. C., Gysin R. Cross-correlation analysis of interneuronal connectivity in the motor cortex of the monkey. Brain Res. 1982 Jan 14;231(2):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90369-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner F. D., Baker J. R., Stephens J. A. Correlation between the discharges of motor units recorded from the same and from different finger muscles in man. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:355–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner F. D., Baker J. R., Stephens J. A. Variation in the degree of synchronization exhibited by motor units lying in different finger muscles in man. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:381–399. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buys E. J., Lemon R. N., Mantel G. W., Muir R. B. Selective facilitation of different hand muscles by single corticospinal neurones in the conscious monkey. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:529–549. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr L. J., Harrison L. M., Stephens J. A. Evidence for bilateral innervation of certain homologous motoneurone pools in man. J Physiol. 1994 Mar 1;475(2):217–227. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney P. D., Fetz E. E., Mewes K. Neural mechanisms underlying corticospinal and rubrospinal control of limb movements. Prog Brain Res. 1991;87:213–252. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough J. F., Kernell D., Phillips C. G. The distribution of monosynaptic excitation from the pyramidal tract and from primary spindle afferents to motoneurones of the baboon's hand and forearm. J Physiol. 1968 Sep;198(1):145–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. K., Stephens J. A. Synchronization of motor unit activity during voluntary contraction in man. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:397–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey N. J., Ellaway P. H., Friedland C. L., Short D. J. Motor unit discharge characteristics and short term synchrony in paraplegic humans. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 Sep;53(9):764–769. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.9.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey N. J., Ellaway P. H., Stein R. B. Statistical limits for detecting change in the cumulative sum derivative of the peristimulus time histogram. J Neurosci Methods. 1986 Aug;17(2-3):153–166. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(86)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz V., Berger W. Spinal coordination of bilateral leg muscle activity during balancing. Exp Brain Res. 1982;47(2):172–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00239376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz V., Mauritz K. H., Dichgans J. Body oscillations in balancing due to segmental stretch reflex activity. Exp Brain Res. 1980;40(1):89–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00236666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H. Cumulative sum technique and its application to the analysis of peristimulus time histograms. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1978 Aug;45(2):302–304. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(78)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. F., Harrison L. M., Ingram D. A., Stephens J. A. Plasticity of central motor pathways in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Neurology. 1991 Sep;41(9):1505–1510. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.9.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Cheney P. D. Postspike facilitation of forelimb muscle activity by primate corticomotoneuronal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Oct;44(4):751–772. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.44.4.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. M., Ironton R., Stephens J. A. Cross-correlation analysis of multi-unit EMG recordings in man. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 Dec;40(2-3):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Padel Y., Tanaka R. Projections of pyramidal tract cells to alpha-motoneurones innervating hind-limb muscles in the monkey. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):637–667. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang Y., Endo K., Araki T. Differential connections by intracortical axon collaterals among pyramidal tract cells in the cat motor cortex. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:243–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. The synaptic connexions to intercostal motoneurones as revealed by the average common excitation potential. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:103–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A., Tuck D. L., Westgaard R. H. Variations in the time course of the synchronization of intercostal motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:105–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers H. G. A new look at the organization of the motor system. Prog Brain Res. 1982;57:381–403. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon R. N., Mantel G. W., Muir R. B. Corticospinal facilitation of hand muscles during voluntary movement in the conscious monkey. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:497–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. F., Cabana T., Humbertson A. O., Jr Evidence for collateral innervation of the cervical and lumbar enlargements of the spinal cord by single reticular and raphe neurons. Studies using fluorescent markers in double-labeling experiments on the North American opossum. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jun 12;24(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. P., Segundo J. P., Perkel D. H., Levitan H. Statistical signs of synaptic interaction in neurons. Biophys J. 1970 Sep;10(9):876–900. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86341-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nashner L. M. Adapting reflexes controlling the human posture. Exp Brain Res. 1976 Aug 27;26(1):59–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00235249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears T. A., Stagg D. Short-term synchronization of intercostal motoneurone activity. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(3):357–381. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda Y., Ohgaki T., Futami T., Sugiuchi Y. Vestibular projections to the spinal cord: the morphology of single vestibulospinal axons. Prog Brain Res. 1988;76:17–27. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64488-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda Y., Ohgaki T., Futami T. The morphology of single lateral vestibulospinal tract axons in the lower cervical spinal cord of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jul 8;249(2):226–241. doi: 10.1002/cne.902490208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda Y., Yamaguchi T., Futami T. Multiple axon collaterals of single corticospinal axons in the cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Mar;55(3):425–448. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda Y., Yokota J., Futami T. Divergent projection of individual corticospinal axons to motoneurons of multiple muscles in the monkey. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Apr 9;23(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. S., Fetz E. E. Effects of synchrony between primate corticomotoneuronal cells on post-spike facilitation of muscles and motor units. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jan 2;96(1):76–81. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90246-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


