Abstract
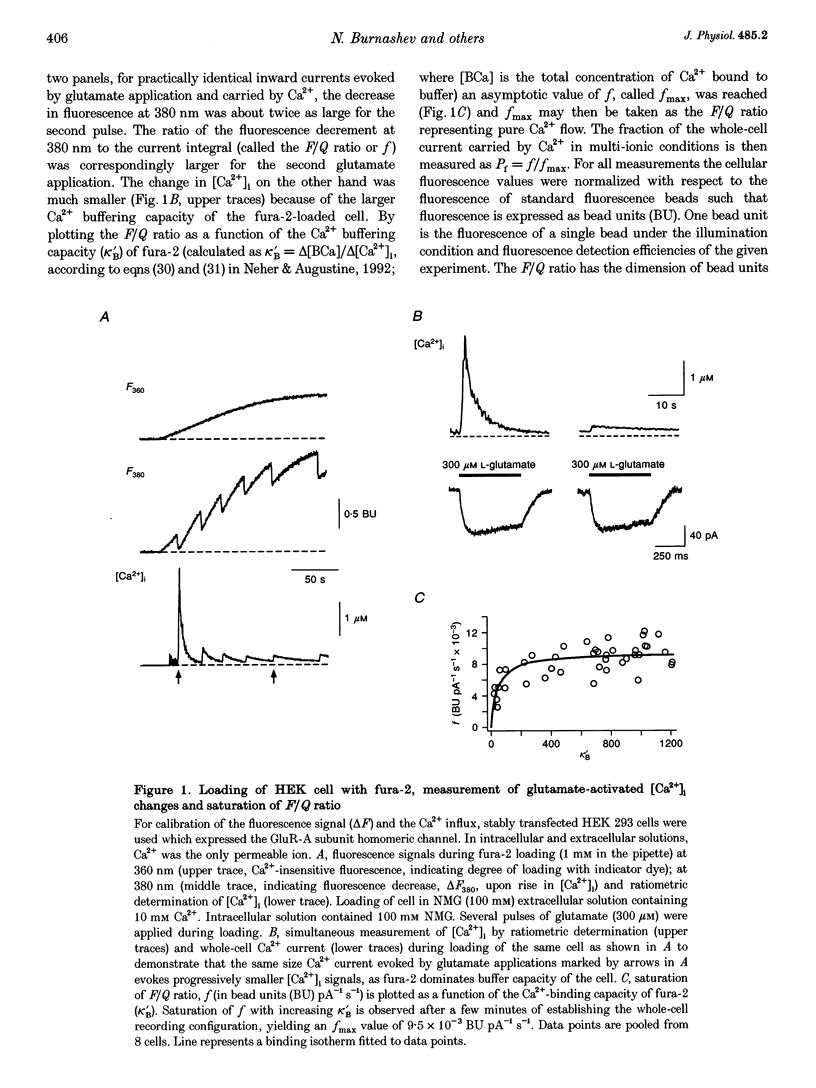
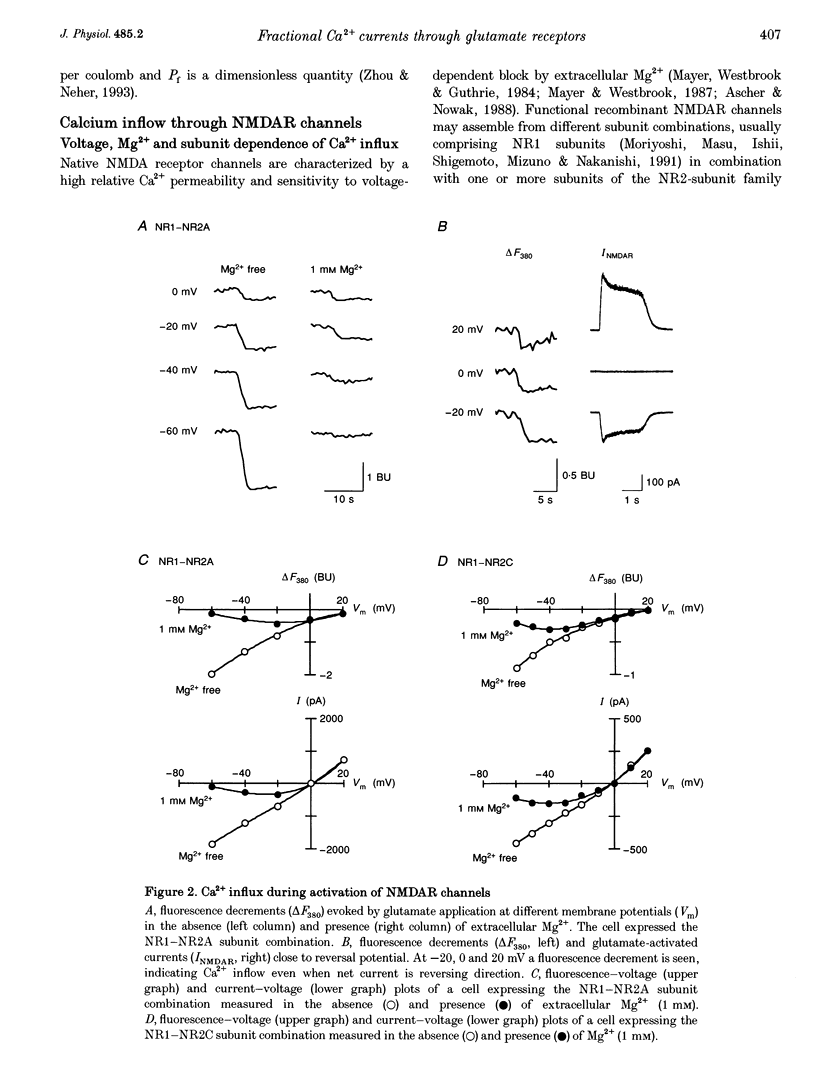
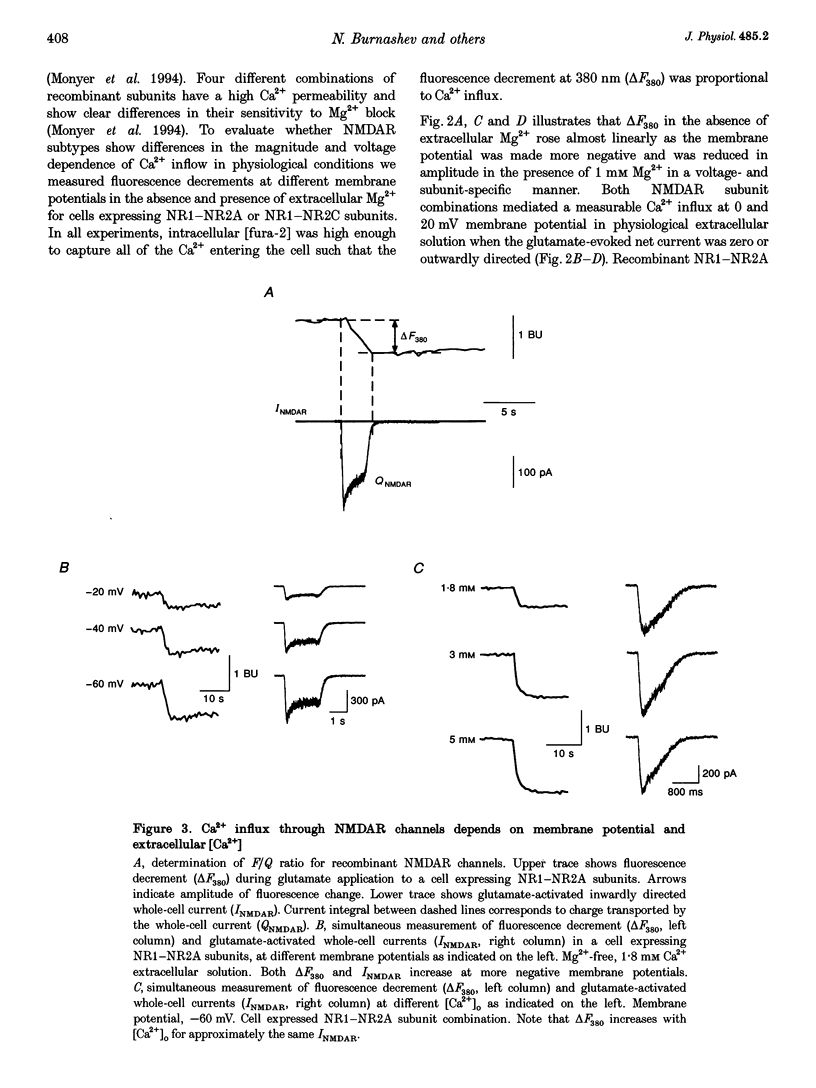
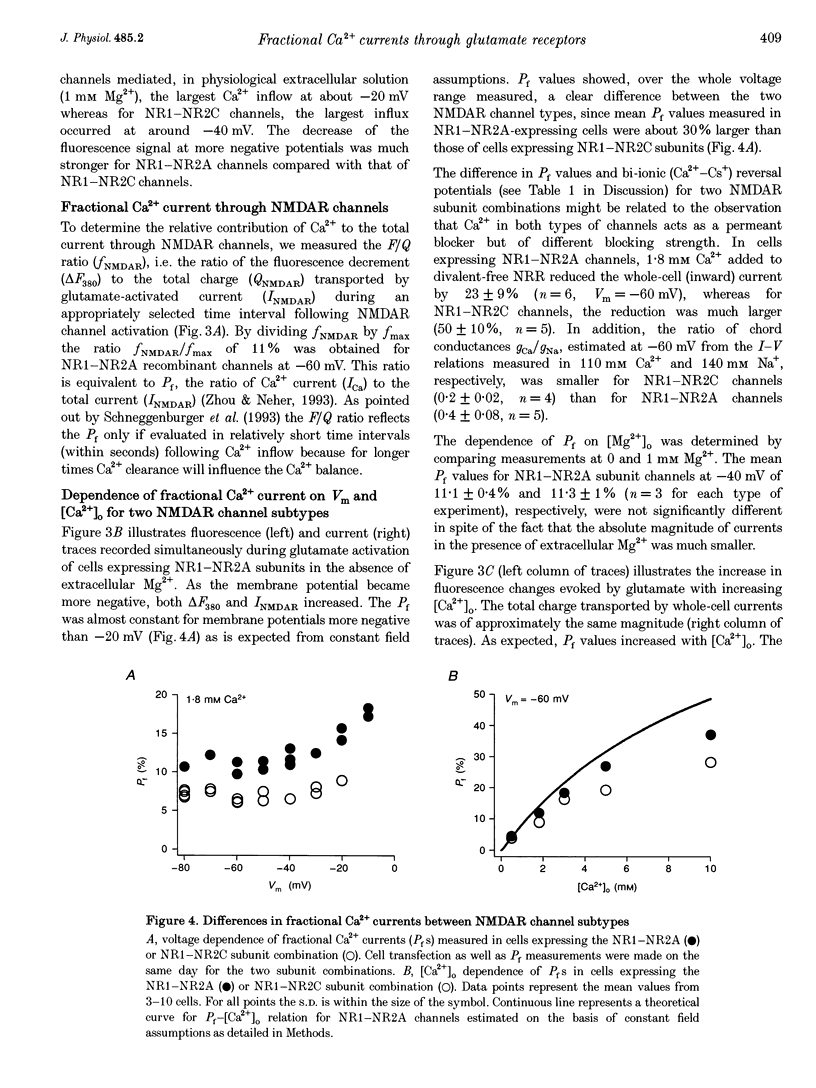
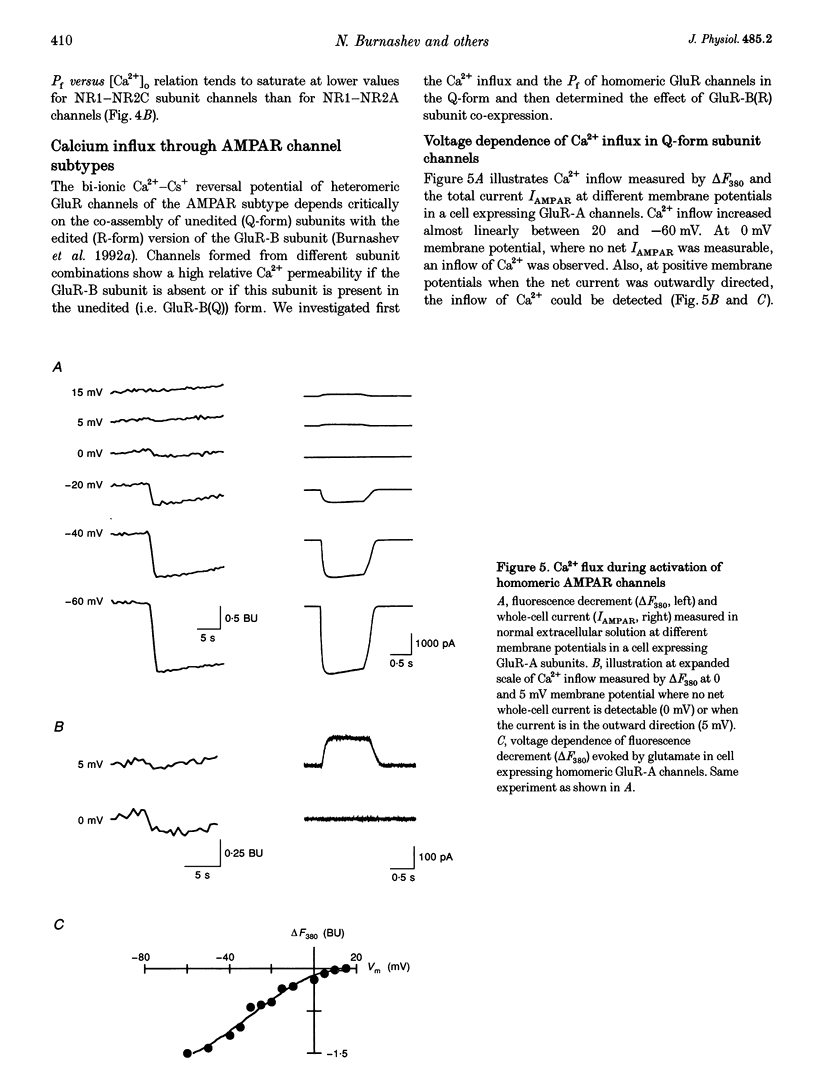
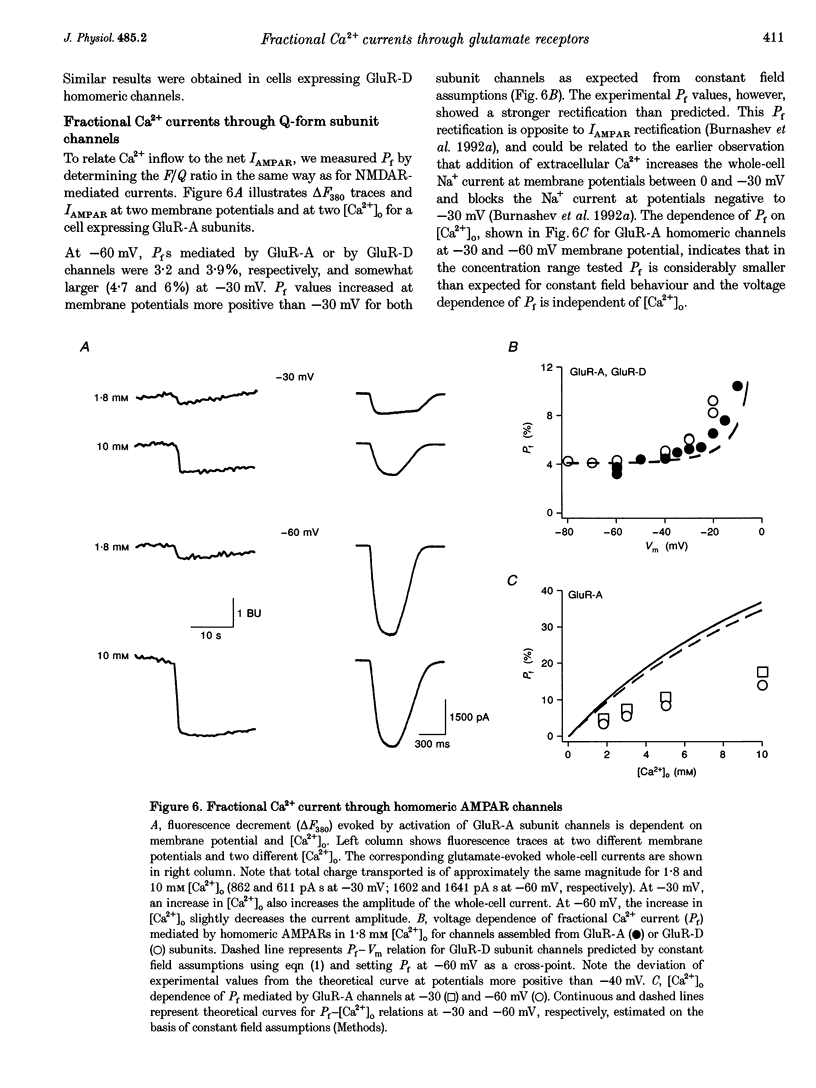
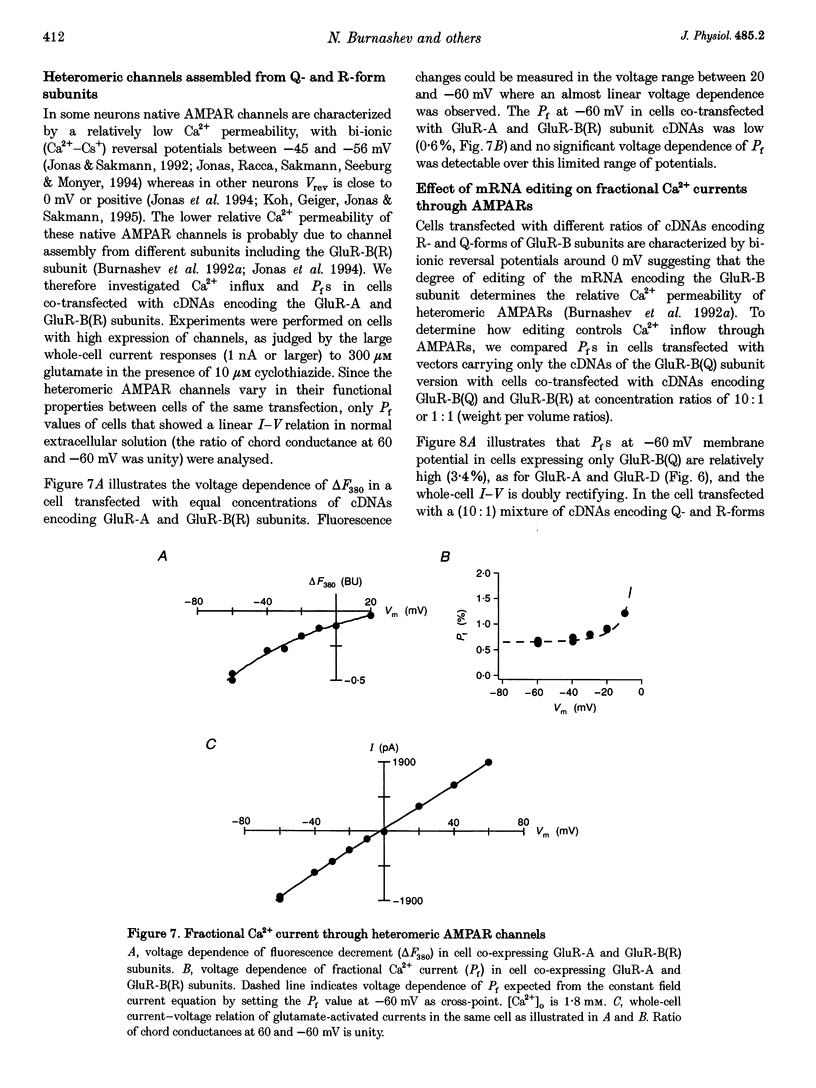
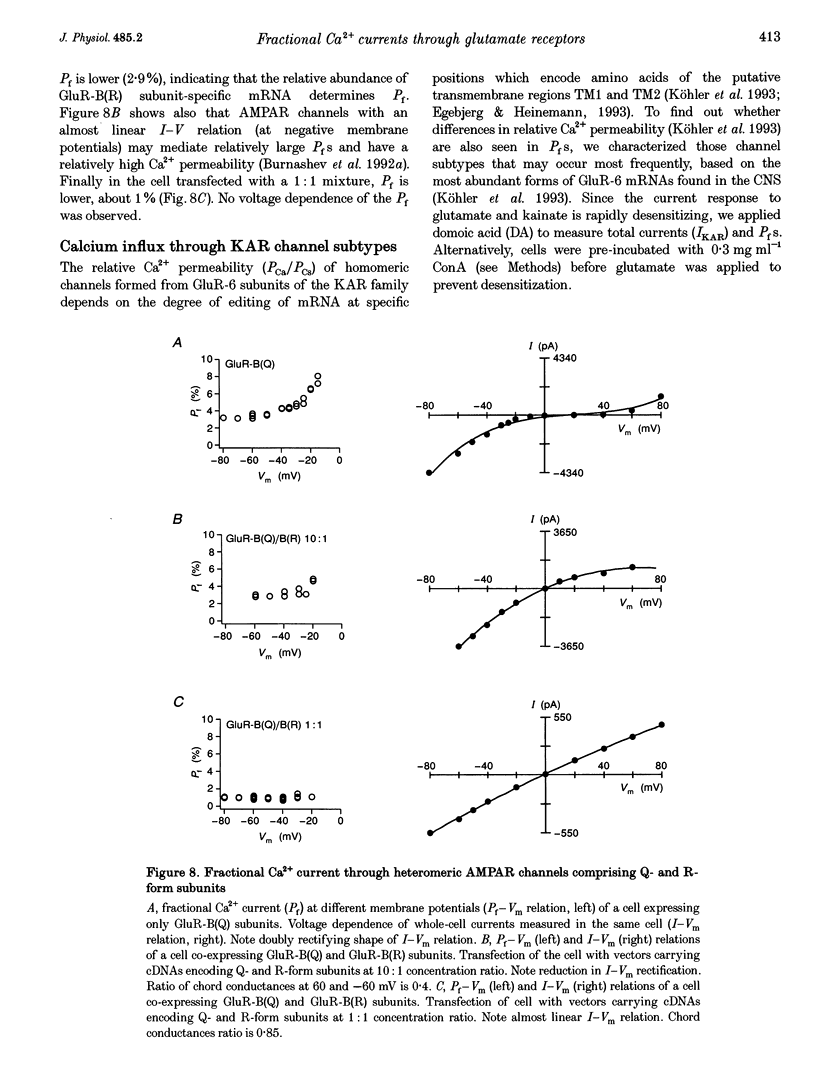
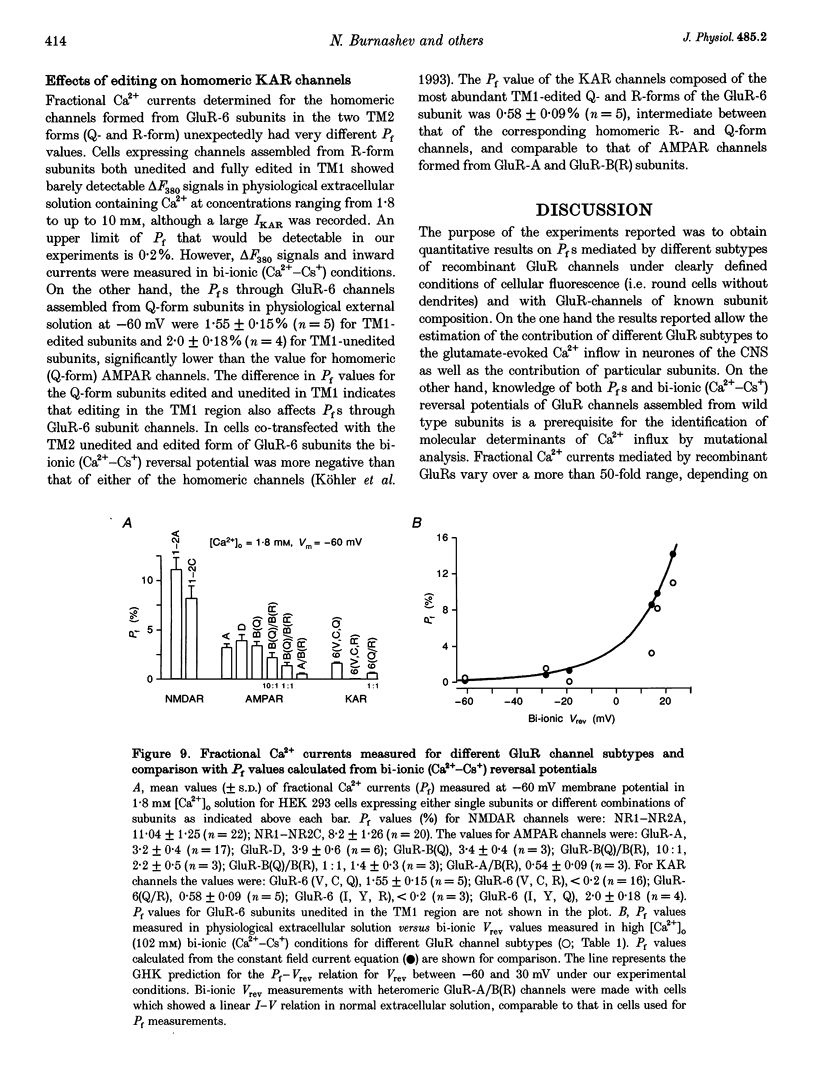
1. Simultaneous fluorescence and whole-cell current measurements using the calcium indicator dye fura-2 were made in HEK 293 cells expressing recombinant glutamate receptor (GluR) channels, and fractional Ca2+ currents (the proportion of whole-cell current carried by Ca2+; Pf) were determined. 2. Cells expressing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) channels showed glutamate activated Ca2+ inflow in the voltage range -60 to 40 mV in normal extracellular solution. Ca2+ inflow decreased in a voltage-dependent manner at membrane potentials more negative than -30 mV due to Mg2+ block. Voltage dependence of block at negative potentials was stronger in cells expressing the NR1-NR2A as compared with cells expressing NR1-NR2C subunits. 3. Fractional Ca2+ currents through NMDARs were independent of extracellular Mg2+ and varied between 8.2% (NR1-NR2C subunits) and 11% (NR1-NR2A subunits) in normal extracellular solution (1.8 mM Ca2+) at -60 mV membrane potential. Pf values increased with increasing [Ca2+]o in the range of 0.5-10mM [Ca2+]o in a saturating fashion. 4. In cells expressing alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate receptor (AMPAR) subunits which were unedited at the Q/R site of the putative transmembrane segment TM2 (Q-form), or in cells coexpressing unedited and edited subunits (R-form), the glutamate-evoked Ca2+ inflow increased from 20 to -80 mV in an almost linear way. 5. Fractional Ca2+ currents through AMPAR channels depended on subunit composition. Pf values of Q-form homomeric channels at -60 mV and 1.8 mM [Ca2+]o were between 3.2 and 3.9%. They were slightly voltage dependent and increased with [Ca2+]o in the range 1.8-10mM. Pf values in cells co-expressing Q- and R-form subunits were almost one order of magnitude smaller (0.54%). 6. Relative concentrations of Q-form and R-form GluR-B subunit-specific cDNAs used for cell transfection determined the expression of functionally different heteromeric AMPARS. Pf decreased with increasing relative concentration of R-form encoding CDNAs from 3.4 to 1.4%, demonstrating that editing of the Q/R site of GluR-B subunits decreases Ca2+ inflow through heteromeric AMPARs. 7. Cells expressing the GluR-6 subunit of the kainate receptor (KAR) family were characterized by Pf values which depended on the editing in the TM1 and TM2 segments. Pf values were largest for the Q-form (1.55-2.0%) and lowest for R-form channels (< 0.2%), suggesting that Q/R site editing also decreases Ca2+ inflow through KAR channels. Cells co-expressing both subunit forms showed an intermediate value (0.58%).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascher P., Nowak L. The role of divalent cations in the N-methyl-D-aspartate responses of mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:247–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Nicoll R. Molecular machines integrate coincident synaptic signals. Cell. 1993 Jan;72 (Suppl):65–75. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Divalent ion permeability of AMPA receptor channels is dominated by the edited form of a single subunit. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Schoepfer R., Monyer H., Ruppersberg J. P., Günther W., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Control by asparagine residues of calcium permeability and magnesium blockade in the NMDA receptor. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1415–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1382314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Singer W. Excitatory amino acid receptors and synaptic plasticity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jul;11(7):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90011-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Heinemann S. F. Ca2+ permeability of unedited and edited versions of the kainate selective glutamate receptor GluR6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Hartley M., Heinemann S. Ca2+ permeability of KA-AMPA--gated glutamate receptor channels depends on subunit composition. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):851–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1709304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Ozawa S., Tsuzuki K. Permeation of calcium through excitatory amino acid receptor channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:151–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Calcium permeability of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel in hippocampal neurons in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11573–11577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas P., Racca C., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H., Monyer H. Differences in Ca2+ permeability of AMPA-type glutamate receptor channels in neocortical neurons caused by differential GluR-B subunit expression. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90444-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas P., Sakmann B. Glutamate receptor channels in isolated patches from CA1 and CA3 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1992 Sep;455:143–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh D. S., Geiger J. R., Jonas P., Sakmann B. Ca(2+)-permeable AMPA and NMDA receptor channels in basket cells of rat hippocampal dentate gyrus. J Physiol. 1995 Jun 1;485(Pt 2):383–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler M., Burnashev N., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Determinants of Ca2+ permeability in both TM1 and TM2 of high affinity kainate receptor channels: diversity by RNA editing. Neuron. 1993 Mar;10(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90336-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Permeation and block of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor channels by divalent cations in mouse cultured central neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Bridges R. J., Cotman C. W. The excitatory amino acid receptors: their classes, pharmacology, and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:365–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monyer H., Burnashev N., Laurie D. J., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors. Neuron. 1994 Mar;12(3):529–540. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90210-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyoshi K., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Molecular cloning and characterization of the rat NMDA receptor. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):31–37. doi: 10.1038/354031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Augustine G. J. Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Kauer J. A., Malenka R. C. The current excitement in long-term potentiation. Neuron. 1988 Apr;1(2):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneggenburger R., Zhou Z., Konnerth A., Neher E. Fractional contribution of calcium to the cation current through glutamate receptor channels. Neuron. 1993 Jul;11(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90277-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Keinänen K., Verdoorn T. A., Wisden W., Burnashev N., Herb A., Köhler M., Takagi T., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Flip and flop: a cell-specific functional switch in glutamate-operated channels of the CNS. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1580–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.1699275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern P., Edwards F. A., Sakmann B. Fast and slow components of unitary EPSCs on stellate cells elicited by focal stimulation in slices of rat visual cortex. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:247–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Honoré T. Structure-activity relationships in the development of excitatory amino acid receptor agonists and competitive antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jan;11(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90038-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. Mammalian ionotropic glutamate receptors. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Jun;3(3):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90120-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Neher E. Calcium permeability of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channels in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Dec;425(5-6):511–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00374879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


