Abstract
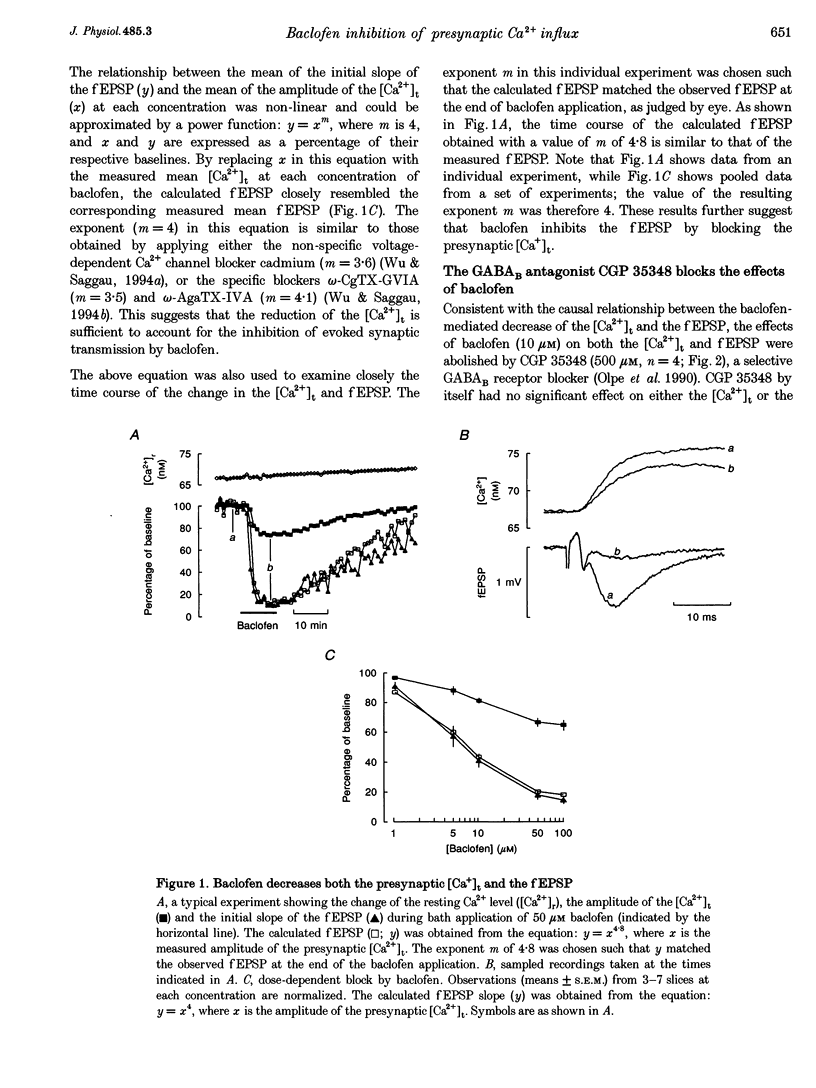
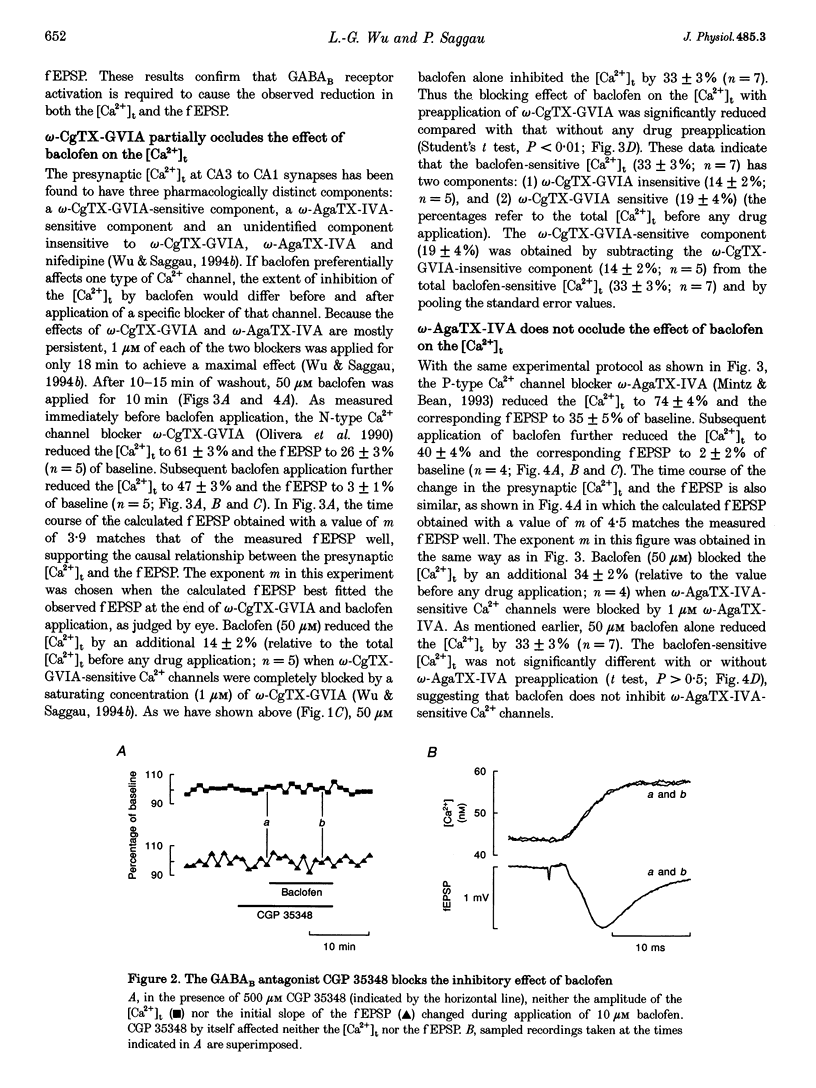
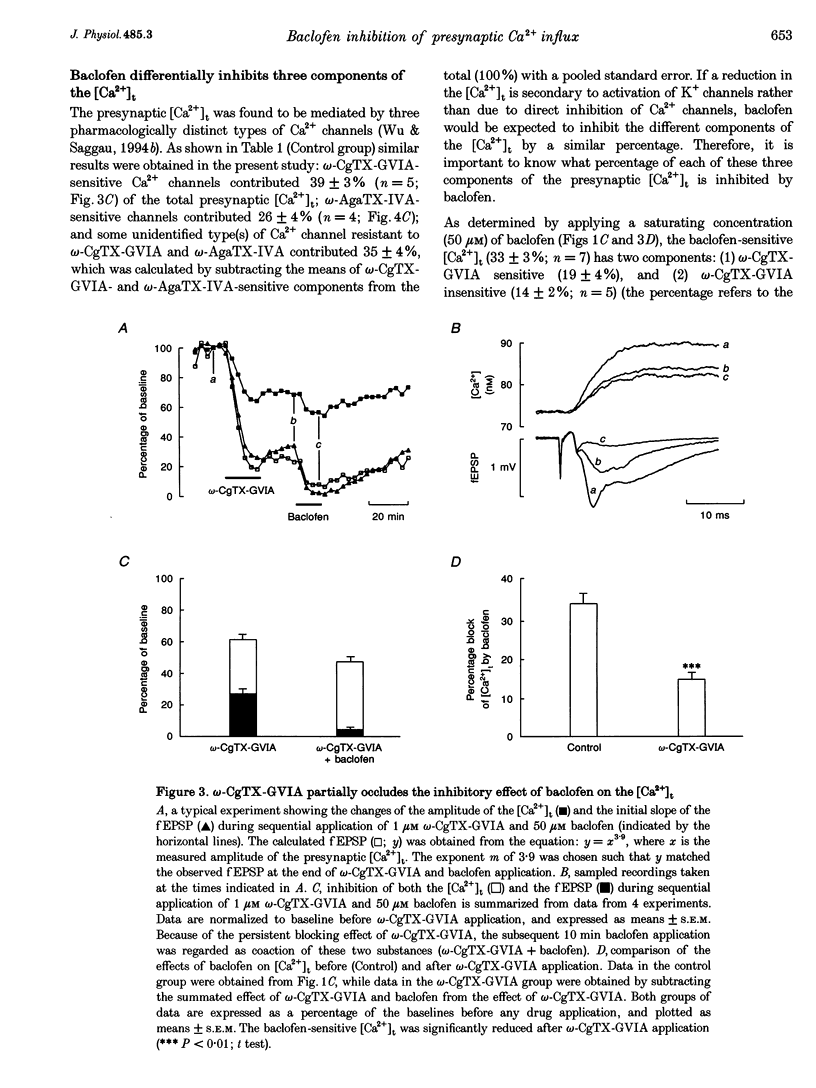
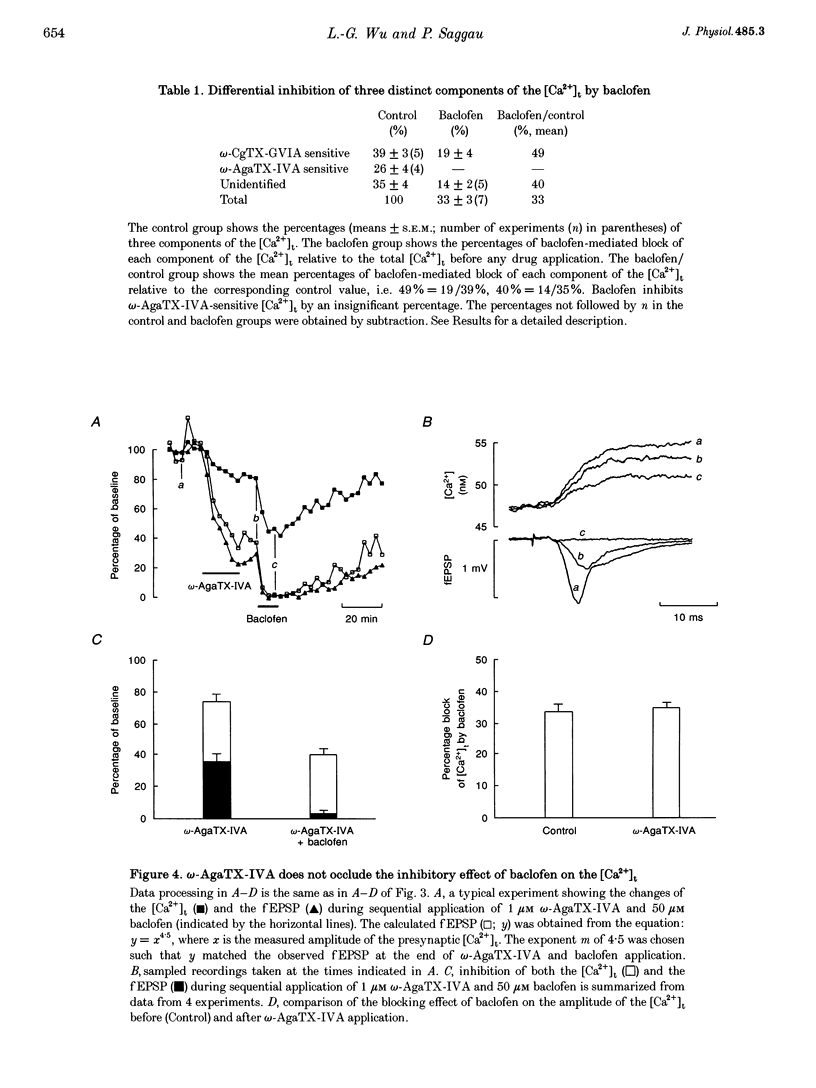
1. The hypothesis that activation of GABAB receptors inhibits evoked synaptic transmission by reducing the presynaptic Ca2+ influx was tested using a recently developed technique for simultaneously recording the presynaptic Ca2+ transient ([Ca2+]t) and the field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) evoked by a single electrical stimulus at CA3 to CA1 synapses of guinea-pig hippocampus. 2. The GABAB receptor agonist baclofen reversibly blocked, in a dose-dependant manner, both the fEPSP and the presynaptic [Ca2+]t with similar time courses. During application of baclofen, the fEPSP was proportional to about the fourth power of the presynaptic [Ca2+]t, and the presynaptic fibre volley and the resting Ca2+ level did not change. These results are similar to those we previously observed following application of several voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel blockers, suggesting that baclofen inhibits the fEPSP by blocking the presynaptic Ca2+ influx. 3. The inhibition by baclofen of both the fEPSP and the presynaptic [Ca2+]t was blocked by the GABAB receptor antagonist CGP 35348, consistent with the causal relationship between the GABAB receptor-mediated presynaptic inhibition of the [Ca2+]t and the fEPSP. 4. The inhibition by baclofen of the [Ca2+]t was partially occluded by application of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel blocker omega-conotoxin-GVIA (omega-CgTX-GVIA), but not omega-agatoxin-IVA (omega-AgaTX-IVA), suggesting that baclofen reduces the presynaptic [Ca2+]t by blocking Ca2+ channels including the omega-CgTX-GVIA-sensitive type. 5. We conclude that baclofen inhibits evoked transmitter release by reducing presynaptic Ca2+ influx.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustine G. J., Charlton M. P., Smith S. J. Calcium entry and transmitter release at voltage-clamped nerve terminals of squid. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:163–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Nadler J. V. Baclofen selectively inhibits transmission at synapses made by axons of CA3 pyramidal cells in the hippocampal slice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. W., Jones O. T., Angelides K. J. Distribution of Ca2+ channels on frog motor nerve terminals revealed by fluorescent omega-conotoxin. J Neurosci. 1991 Apr;11(4):1032–1039. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-04-01032.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W. Activation and modulation of neuronal K+ channels by GABA. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Feb;15(2):46–51. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H., Brown D. A. GABAB-receptor-activated K+ current in voltage-clamped CA3 pyramidal cells in hippocampal cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1558–1562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Hamon B., Konnerth A. GABA and baclofen reduce changes in extracellular free calcium in area CA1 of rat hippocampal slices. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Jun 29;47(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90529-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson J. S., Solís J. M., Nicoll R. A. Local and diffuse synaptic actions of GABA in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90308-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanthorn T. H., Cotman C. W. Baclofen selectively inhibits excitatory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 23;225(1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton J. T., Stern M., Schulze K., Perin M., Bellen H. J. Mutational analysis of Drosophila synaptotagmin demonstrates its essential role in Ca(2+)-activated neurotransmitter release. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1125–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90733-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Silver R. B. Microdomains of high calcium concentration in a presynaptic terminal. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1350109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Bean B. P. Block of calcium channels in rat neurons by synthetic omega-Aga-IVA. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Nov;32(11):1161–1169. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90010-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. Direct hyperpolarizing action of baclofen on hippocampal pyramidal cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):450–452. doi: 10.1038/308450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Malenka R. C., Kauer J. A. Functional comparison of neurotransmitter receptor subtypes in mammalian central nervous system. Physiol Rev. 1990 Apr;70(2):513–565. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.2.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Rivier J., Clark C., Ramilo C. A., Corpuz G. P., Abogadie F. C., Mena E. E., Woodward S. R., Hillyard D. R., Cruz L. J. Diversity of Conus neuropeptides. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):257–263. doi: 10.1126/science.2165278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olpe H. R., Karlsson G., Pozza M. F., Brugger F., Steinmann M., Van Riezen H., Fagg G., Hall R. G., Froestl W., Bittiger H. CGP 35348: a centrally active blocker of GABAB receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct 2;187(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90337-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfrieger F. W., Gottmann K., Lux H. D. Kinetics of GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of calcium currents and excitatory synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons in vitro. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regehr W. G., Delaney K. R., Tank D. W. The role of presynaptic calcium in short-term enhancement at the hippocampal mossy fiber synapse. J Neurosci. 1994 Feb;14(2):523–537. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-02-00523.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robitaille R., Adler E. M., Charlton M. P. Strategic location of calcium channels at transmitter release sites of frog neuromuscular synapses. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):773–779. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90336-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanziani M., Capogna M., Gähwiler B. H., Thompson S. M. Presynaptic inhibition of miniature excitatory synaptic currents by baclofen and adenosine in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):919–927. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz K. P., Miller R. J. GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of Ca2+ currents and synaptic transmission in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:669–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silinsky E. M. On the mechanism by which adenosine receptor activation inhibits the release of acetylcholine from motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1984 Jan;346:243–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. Quantal release of neurotransmitter and long-term potentiation. Cell. 1993 Jan;72 (Suppl):55–63. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Capogna M., Scanziani M. Presynaptic inhibition in the hippocampus. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Jun;16(6):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90160-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toselli M., Taglietti V. Baclofen inhibits high-threshold calcium currents with two distinct modes in rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Dec 24;164(1-2):134–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90875-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. G., Saggau P. Adenosine inhibits evoked synaptic transmission primarily by reducing presynaptic calcium influx in area CA1 of hippocampus. Neuron. 1994 May;12(5):1139–1148. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90321-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. G., Saggau P. Pharmacological identification of two types of presynaptic voltage-dependent calcium channels at CA3-CA1 synapses of the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1994 Sep;14(9):5613–5622. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-09-05613.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. G., Saggau P. Presynaptic calcium is increased during normal synaptic transmission and paired-pulse facilitation, but not in long-term potentiation in area CA1 of hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1994 Feb;14(2):645–654. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-02-00645.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S., Delaney K. R., Mulkey R., Tank D. W. Presynaptic calcium in transmitter release and posttetanic potentiation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:191–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gersdorff H., Matthews G. Dynamics of synaptic vesicle fusion and membrane retrieval in synaptic terminals. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):735–739. doi: 10.1038/367735a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



