Abstract
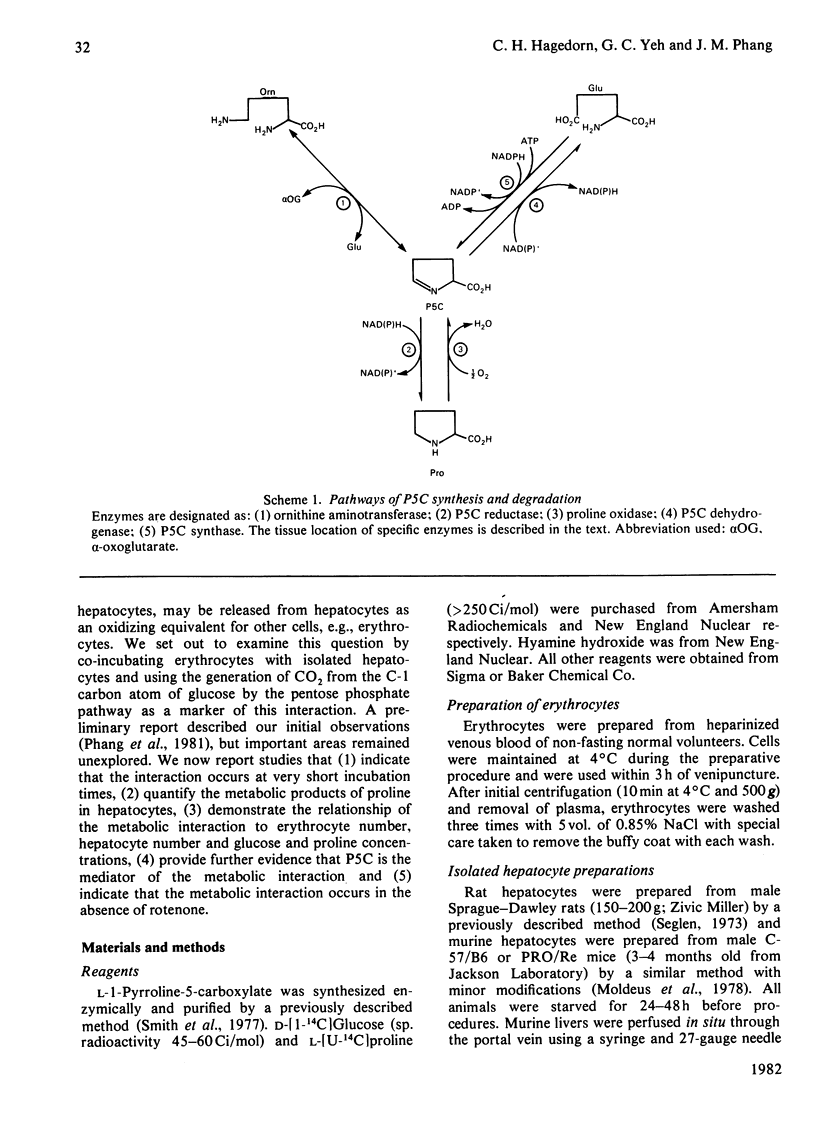
The interconversions of proline and 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate form an intercellular cycle that is the basis of a metabolic interaction between hepatocytes and erythrocytes. The cycle transfers oxidizing potential from hepatocytes to erythrocytes, which stimulates pentose phosphate pathway in erythrocytes. This interaction depends on the differential metabolism of proline and 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate in erythrocytes and hepatocytes and consists of the following: in hepatocytes proline oxidase converts proline into 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, which is released into the medium and taken up by erythrocytes; erythrocyte 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase converts 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate into proline and concomitantly generates NADP+; the generated oxidizing potential drives glucose metabolism through the pentose phosphate pathway in erythrocytes; finally, erythrocytes release proline into the medium, enabling it to re-enter hepatocytes and repeat the cycle. The increased activity of the pentose phosphate pathway in erythrocytes may enhance the production of 5-phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate, a necessary moiety for the processing of purines.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams E., Frank L. Metabolism of proline and the hydroxyprolines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1005–1061. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams E. Metabolism of proline and of hydroxyproline. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1970;5:1–91. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363705-5.50007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwyn D. H., Launder W. J., Parikh H. C., Wise E. M., Jr Roles of plasma and erythrocytes in interorgan transport of amino acids in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1972 May;222(5):1333–1342. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.5.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITCH W. M., CHAIKOFF I. L. Extent and patterns of adaptation of enzyme activities in livers of normal rats fed diets high in glucose and fructose. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:554–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITCH W. M., HILL R., CHAIKOFF I. L. The effect of fructose feeding on glycolytic enzyme activities of the normal rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1048–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Räf L. Evidence of inter-organ amino-acid transport by blood cells in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1775–1779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. I., Mace J. W., Miles B. S., Teng C. C., Brown S. B. Defective hydroxyproline metabolism in type II hyperprolinemia. Biochem Med. 1974 Aug;10(4):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourdji D., Tixier-Vidal A., Morin A., Pradelles P., Morgat J. L., Fromageot P., Kerdelhue B. Binding of a tritiated thyrotropin-releasing factor to a prolactin secreting clonal cell line (GH3). Exp Cell Res. 1973 Nov;82(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90242-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens H. E., Meijer A. J., Williamson J. R., Gimpel J. A., Tager J. M. Prolone metabolism in isolated rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):699–707. doi: 10.1042/bj1700699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzfeld A., Mezl V. A., Knox W. E. Enzymes metabolizing delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate in rat tissues. Biochem J. 1977 Jul 15;166(1):95–103. doi: 10.1042/bj1660095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON A. B., STRECKER H. J. The interconversion of glutamic acid and proline. IV. The oxidation of proline by rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1876–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi Y., Ichihara A. Transfer of purines from liver to erythrocytes. In vivo and in vitro studies. J Biochem. 1979 Jan;85(1):295–301. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramar R. Studies on the proline oxidase complex. Enzymologia. 1967 Jul 31;33(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., Eggleston L. V. The regulation of the pentose phosphate cycle in rat liver. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1974;12:421–434. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(74)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. Proline transport in rat liver mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 30;178(2):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldéus P., Högberg J., Orrenius S. Isolation and use of liver cells. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:60–71. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W. The biological significance of purine salvage. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:811–826. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.004115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEISACH J., STRECKER H. J. The interconversion of glutamic acid and proline. V. The reduction of delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid to proline. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2255–2260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phang J. M., Downing S. J., Valle D. L., Kowaloff E. M. A radioisotopic assay for proline oxidase activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):312–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phang J. M., Downing S. J., Valle D. A radioisotopic assay for delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):266–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90312-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phang J. M., Downing S. J., Yeh G. C., Smith R. J., Williams J. A. Stimulation of the hexose-monophosphate pentose pathway by delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid in human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 30;87(2):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91805-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phang J. M., Yeh G. C., Hagedorn C. H. The intercellular proline cycle. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 5;28(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard J. B., Chavez-Peon F., Berlin R. D. Purines: supply by liver to tissues. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1263–1267. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG L. E., WEINBERG A. N., SEGAL S. The effect of high galactose diets on urinary excretion of amino acids in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 15;48:500–505. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Wice B. M., Kennell D. The pentose cycle. Control and essential function in HeLa cell nucleic acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5616–5626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH M. E., GREENBERG D. M. Preparation and properties of partially purified glutamic semialdehyde reductase. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):317–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Buchanan J. M. Nucleotide and pentose synthesis after serum-stimulation of resting 3T6 fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Nov;101(2):293–309. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041010210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Downing S. J., Phang J. M. Enzymatic synthesis and purification of L-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid. Anal Biochem. 1977 Sep;82(1):170–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veech R. L., Eggleston L. V., Krebs H. A. The redox state of free nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate in the cytoplasm of rat liver. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):609–619. doi: 10.1042/bj1150609a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh G. C., Harris S. C., Phang J. M. Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase in human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1042–1046. doi: 10.1172/JCI110115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh G. C., Phang J. M. The function of pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase in human erythrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 30;94(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


