Abstract
1. A new rapid method for the purification of fat-cell acetyl-CoA carboxylase is described; the key step is sedimentation after specific polymerization by citrate. 2. Incubation of epididymal fat-pads or isolated fat-cells with insulin or adrenaline leads to a rapid increase or decrease respectively in the activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase measured in fresh tissue extracts. The persistence of the effect of insulin through high dilution of tissue extracts and through purification involving precipitation with (NH4)2SO4 suggests that the enzyme undergoes a covalent modification after exposure of intact tissue to the hormone. The opposed effects of insulin and adrenaline are not adequately explained through modification of a common site on acetyl-CoA carboxylase, since these hormones bring about qualitatively different alterations in the kinetic properties of the enzyme measured in tissue extracts. 3. The state of phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase within intact fat-cells exposed to insulin was determined, and results indicate a small but consistent rise in overall phosphorylation of the Mr-230000 subunit after insulin treatment. 4. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase from fat-cells previously incubated in medium containing [32P]phosphate was purified by immunoprecipitation and then digested with performic acid and trypsin before separation of the released phosphopeptides by two-dimensional analysis. Results obtained show that the exposure of fat-cells to insulin leads to a 5-fold increase in incorporation of 32P into a peptide which is different from those most markedly affected after exposure of fat-cells to adrenaline. 5. These studies indicate that the activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in cells incubated with insulin is brought about by the increased phosphorylation of a specific site on the enzyme, possibly catalysed by the membrane-associated cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase described by Brownsey, Belsham & Denton [(1981) FEBS Lett. 124, 145-150].
Full text
PDF





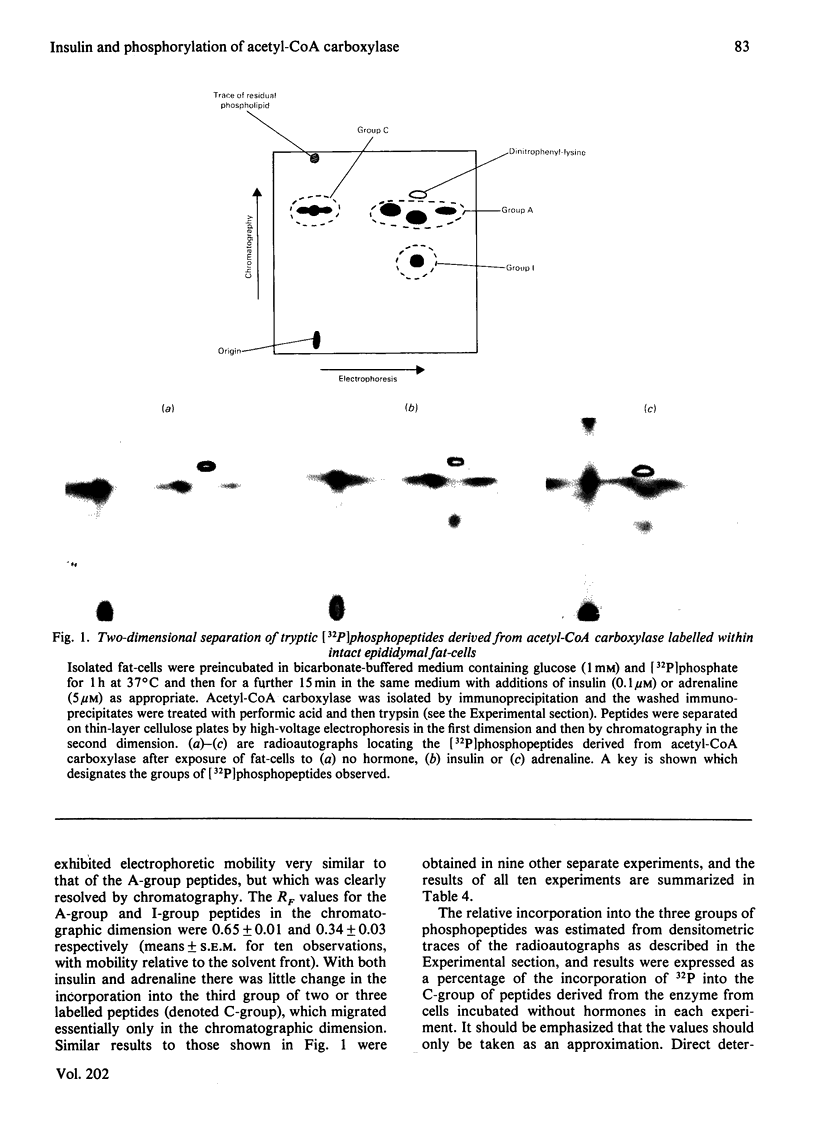



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. C., Kowaloff E. M., Witters L. A., Dennihy D. T., Avruch J. Purification of a hepatic 123,000-dalton hormone-stimulated 32P-peptide and its identification as ATP-citrate lyase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):8052–8056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Witters L. A., Alexander M. C., Bush M. A. Effects of glucagon and insulin on cytoplasmic protein phosphorylation in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4754–4761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsham G. J., Brownsey R. W., Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Anti-insulin receptor antibodies mimic the effects of insulin on the activities of pyruvate dehydrogenase and acetylCoA carboxylase and on specific protein phosphorylation in rat epididymal fat cells. Diabetologia. 1980 Apr;18(4):307–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00251011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsham G. J., Denton R. M. The effect of insulin and adrenaline on the phosphorylation of a 22 000-molecular weight protein within isolated fat cells; possible identification as the inhibitor-1 of the 'general phosphatase' [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):382–383. doi: 10.1042/bst0080382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin W. B., Singer I. Actions of insulin, epinephrine, and dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate on fat cell protein phosphorylations. Cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate dependent and independent mechanisms. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 29;14(15):3301–3309. doi: 10.1021/bi00686a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Belsham G. J., Denton R. M. Evidence for phosphorylation and activation of acetyl CoA carboxylase by a membrane-associated cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase. Relationship to the activation of acetyl CoA carboxylase by insulin. FEBS Lett. 1981 Feb 23;124(2):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Hardie D. G. Regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase: identity fo sites phosphorylated in intact cells treated with adrenaline and in vitro by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 20;120(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Adrenaline and the regulation of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Inactivation of the enzyme is associated with phosphorylation and can be reversed on dephosphorylation. Biochem J. 1979 Oct 15;184(1):23–32. doi: 10.1042/bj1840023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Demonstration of the phosphorylation of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase within intact rat epididymal fat-cells. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):441–445. doi: 10.1042/bj1680441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Brownsey R. W., Belsham G. J. A partial view of the mechanism of insulin action. Diabetologia. 1981 Oct;21(4):347–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00252681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Richards D. A., Chin J. G. Calcium ions and the regulation of NAD+-linked isocitrate dehydrogenase from the mitochondria of rat heart and other tissues. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):899–906. doi: 10.1042/bj1760899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen M. J., Beynen A. C., Christiansen R. Z., Lepreau-Jose M. J., Gibson D. M. Short-term effects of insulin and glucagon on lipid synthesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. Covariance of acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity and the rate of 3H2O incorporation into fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 1978 Nov 15;95(2):326–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Hormonal regulation of adipose-tissue acetyl-Coenzyme A carboxylase by changes in the polymeric state of the enzyme. The role of long-chain fatty acyl-Coenzyme A thioesters and citrate. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;142(2):365–377. doi: 10.1042/bj1420365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Insulin and the regulation of adipose tissue acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1320509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G., Cohen P. Dephosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase from lactating rabbit mammary gland. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G., Cohen P. Purification and physicochemical properties of fatty acid synthetase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase from lactating rabbit mammary gland. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):25–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G., Cohen P. The regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis: simple procedure for the purification of acetyl CoA carboxylase from lactating rabbit mammary gland, and its phosphorylation by endogenous cyclic AMP-dependent and -independent protein kinase activities. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jul 1;91(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie D. G., Guy P. S. Reversible phosphorylation and inactivation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase from lactating rat mammary gland by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(1):167–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. A., Brownsey R. W., Denton R. M. Studies on the incorporation of [32P]phosphate into pyruvate dehydrogenase in intact rat fat-cells. Effects of insulin. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):469–481. doi: 10.1042/bj1920469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Incorporation of 32Pi into pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate in mitochondria from control and insulin-treated adipose tissue. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):471–473. doi: 10.1038/264471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue H., Lowenstein J. M. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase from rat liver. Purification and demonstration of different subunits. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 10;247(15):4825–4832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakower G. R., Kim K. H. Dephosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by phosphorylase phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90345-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. D., Moss J., Polakis S. E. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):139–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastick S. M., McConkey E. H. HeLa ribosomal protein S6. Insulin and dibutyryl cyclic AMP affect different phosphopeptides. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):583–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Kim K. H. Effect of epinephrine on acetyl-CoA carboxylase in rat epididymal fat tissue. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8157–8161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Kim K. H. Regulation of rat liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. Evidence for interconversion between active and inactive forms of enzyme by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1748–1751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Kim K. H. Stimulation by epinephrine of in vivo phosphorylation and inactivation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase of rat epididymal adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1450–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Thrall T., Kim K. H. Hormonal regulation of acetyl CoA carboxylase effect of insulin and epinephrine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):1133–1140. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90810-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lent B. A., Lee K. H., Kim K. H. Regulation of rat liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Stimulation of phosphorylation and subsequent inactivation of liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase by cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate and effect on the structure of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8149–8156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Srere P. A. Identification of ATP citrate lyase as a phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1691–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Denton R. M. Evidence that fatty acid synthesis in the interscapular brown adipose tissue of cold-adapted rats is increased in vivo by insulin by mechanisms involving parallel activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 15;166(3):627–630. doi: 10.1042/bj1660627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo H. G., Proud C. G., Cohen P. The purification and properties of rabbit skeletal muscle glycogen synthase. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep;68(1):21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogiwara H., Tanabe T., Nikawa J., Numa S. Inhibition of rat-liver acetyl-coenzyme-A carboxylase by palmitoyl-coenzyme A. Formation of equimolar enzyme-inhibitor complex. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):33–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna S., Benjamin W. B. Fat cell protein phosphorylation. Identification of phosphoprotein-2 as ATP-citrate lyase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9232–9236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna S., Benjamin W. B. Phosphorylation of ATP-citrate lyase by a cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1981 Feb 23;124(2):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Insulin-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes and cell-free extracts derived from them incorporate 32P into ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2641–2645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Wejksnora P. J., Warner J. R., Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Insulin-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2725–2729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansbie D., Brownsey R. W., Crettaz M., Denton R. M. Acute effects in vivo of anti-insulin serum on rates of fatty acid synthesis and activities of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase in liver and epididymal adipose tissue of fed rats. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):413–416. doi: 10.1042/bj1600413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Randle P. J. Regulation of pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase by phosphorylation. Studies on the subunit and phosphorylation stoicheiometries. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):659–668. doi: 10.1042/bj1730659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas O., Walaas E., Lystad E., Alertsen A. R., Horn R. S., Fossum S. A stimulatory effect of insulin on phosphorylation of a peptide in sarcolemma-enriched membrane preparation from rat skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 15;80(2):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80489-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas O., Walaas E., Lystad E., Alertsen A. R., Horn R. S. The effect of insulin and guanosine nucleotides on protein phosphorylations by sarcolemma membranes from skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Oct;16(1):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. H., Betts S. A., Manning R., Mayer R. J. Absorption of antisera for studies on specific enzyme turnover. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):355–362. doi: 10.1042/bj1590355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):872–878. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Kowaloff E. M., Avruch J. Glucagon regulation of protein phosphorylation. Identification of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase as a substrate. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):245–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Moriarity D., Martin D. B. Regulation of hepatic acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by insulin and glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6644–6649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Vogt B. A new method for the isolation of rat liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase. J Lipid Res. 1981 Feb;22(2):364–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman S. J., Hutcheson E. T., Roche T. E., Pettit F. H., Brown J. R., Reed L. J., Watson D. C., Dixon G. H. Sites of phosphorylation on pyruvate dehydrogenase from bovine kidney and heart. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2364–2370. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh L. A., Song C. S., Kim K. H. Coenzyme A activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2289–2296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




