Abstract
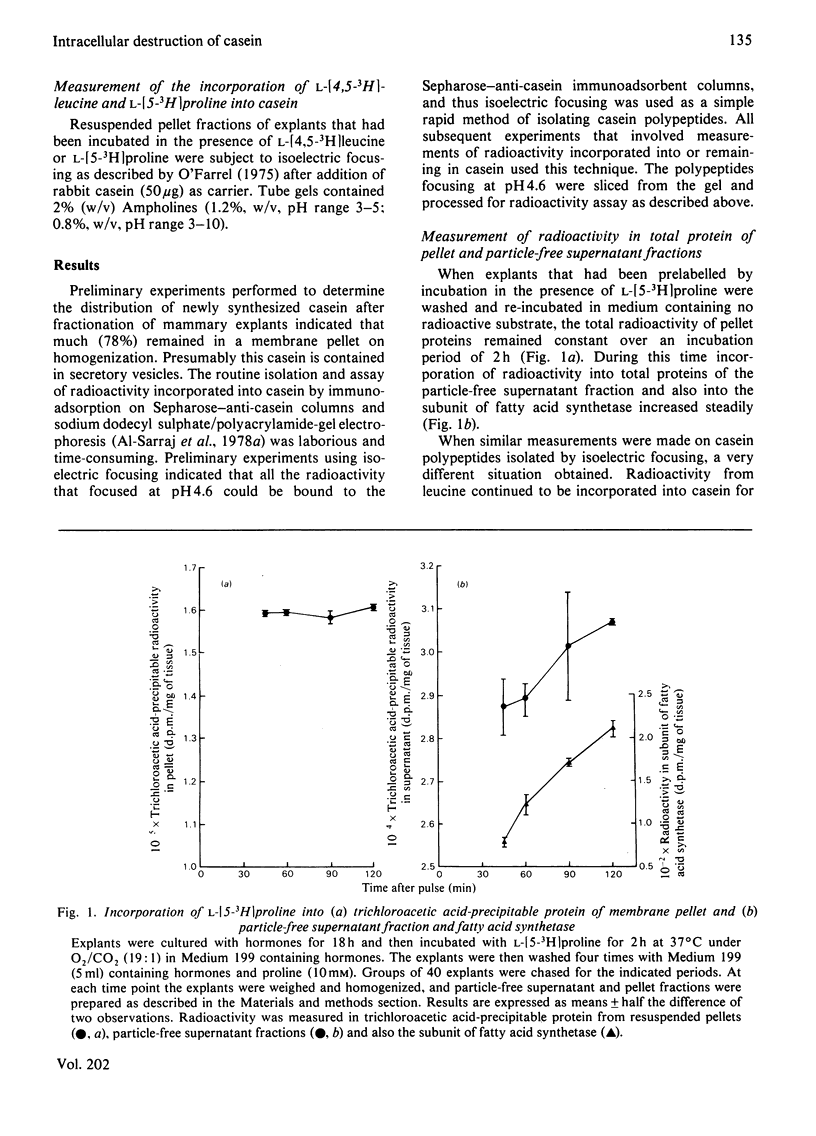
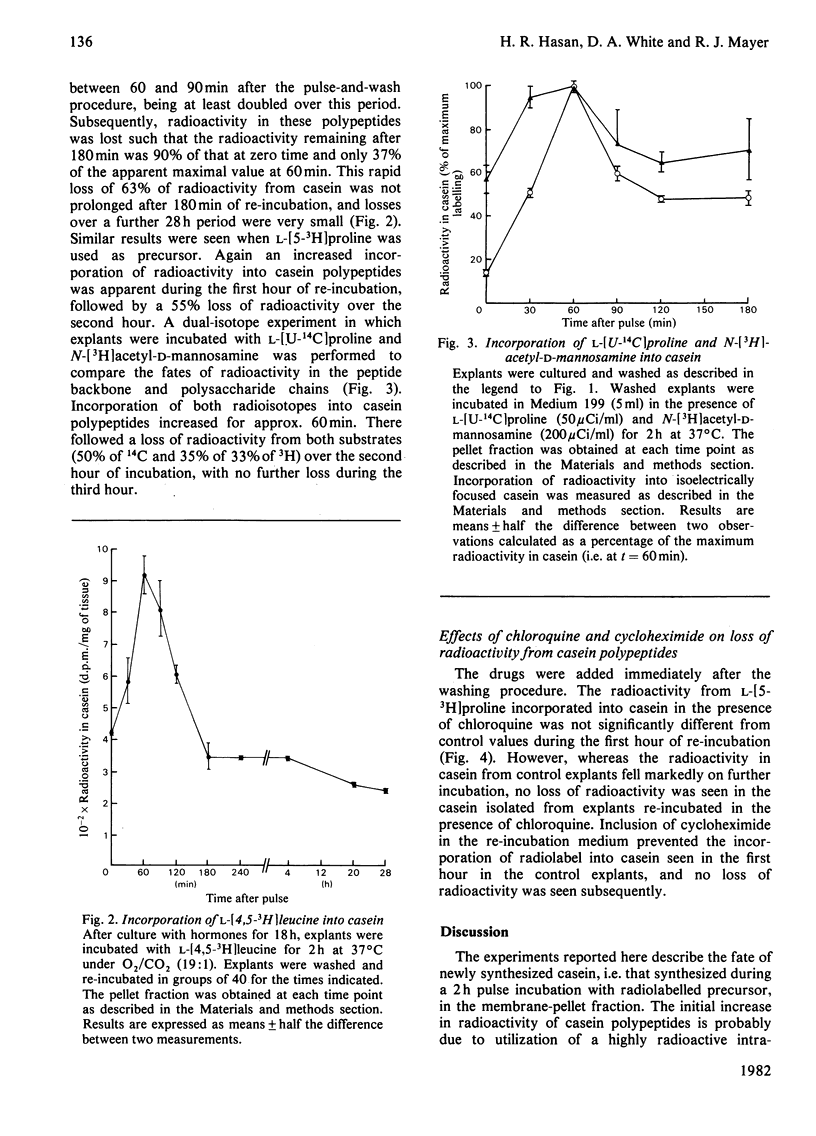
1. Explants of mammary glands of mid-pregnant rabbits that had been cultured for 18h in the presence of insulin, prolactin and cortisol were incubated at 37°C for 2h in Medium 199 containing l-[4,5-3H]leucine. After a wash procedure at 4°C, explants were re-incubated at 37°C in fresh medium and the radioactivity of casein polypeptides isolated by isoelectric focusing (at pH 4.6) was followed with time. Casein radioactivity rose during the first hour of re-incubation, but fell markedly during the subsequent hour. 2. Loss of radioactivity represented casein degradation, since less than 10% of newly synthesized casein was found in the incubation medium. 3. Such a loss of radioactivity was not due solely to hydrolysis of signal peptides, since similar results were obtained when l-[5-3H]proline, which is not part of casein signal peptides, was the radiolabelled precursor. 4. A dual-isotope experiment using l-[U-14C]proline and N-[3H]acetyl-d-mannosamine gave similar profiles of radioactivity loss from isoelectrically focused casein, indicating that degradation of mature casein was occurring. 5. Analysis of total pellet and particle-free-supernatant fractions prepared by centrifugation of explant homogenates at 115000gav. for 1h did not show loss of radioactivity on re-incubation. Total pellet-protein radioactivity remained constant, whereas total soluble-protein radioactivity increased during the 2h re-incubation period. 6. Radioactivity in a specific particle-free-supernatant polypeptide, the subunit of fatty acid synthetase, mimicked that of the total soluble protein. 7. Addition of cycloheximide (20μg/ml) during the re-incubation period completely blocked the incorporation of radioactivity from l-[5-3H]proline into casein and the subsequent fall, indicating that observations were being made on newly synthesized casein. 8. Addition of chloroquine (50μm) did not prevent the increase in radioactivity from l-[5-3H]proline into casein during the first hour of re-incubation, but did prevent the loss of radioactivity in the second hour. 9. The intracellular degradation of a newly synthesized milk protein is discussed in relation to the known intracellular degradation of other secretory polypeptides.
Full text
PDF

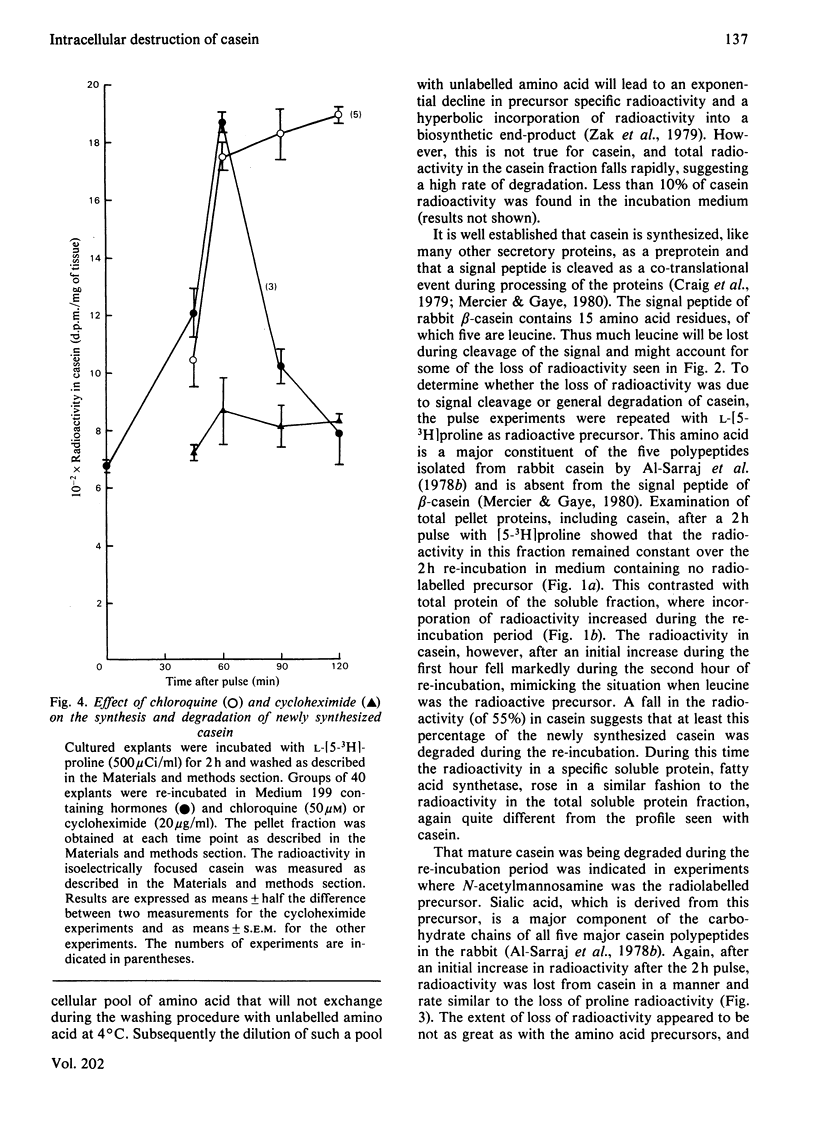

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Sarraj K., Newbury J., White D. A., Mayer R. J. Casein turnover in rabbit mammary explants in organ culture. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):837–845. doi: 10.1042/bj1820837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sarraj K., White D. A., Mayer R. J. Immunochemical characterization of casein from rabbit mammary gland. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):877–883. doi: 10.1042/bj1730877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sarraj K., White D. A., Mayer R. J. Purification and properties of casein from mammary gland of lactating rabbits. Int J Biochem. 1978;9(4):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(78)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowski R. S., Baum B. J., Crystal R. G. Fibroblasts degrade newly synthesised collagen within the cell before secretion. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):413–416. doi: 10.1038/276413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. K., Perera P. A., Mellor A., Smith A. E. Initiation and processing in vitro of the primary translation products of guinea-pig caseins. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):261–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1840261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth I. A., Myres R. P. Human prolactin. Evidence obtained by the bioassay of human plasma. J Endocrinol. 1971 Sep;51(1):157–168. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0510157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B. Intracellular degradation of insulin stores by rat pancreatic islets in vitro. An alternative pathway for homeostasis of pancreatic insulin content. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6003–6006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison O. S., Craig R. K., Campbell P. N. Isolation and characterization of messenger ribonucleic acid species for guinea-pig milk proteins from free and membrane-bound polyribosomes. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(2):340–341. doi: 10.1042/bst0040340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdebine L. M., Gaye P. Absence of mRNA for casein in free polysomes of lactating ewe mammary gland. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Feb;2(2):165–178. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN J. F., MORTON H. J., PARKER R. C. Nutrition of animal cells in tissue culture; initial studies on a synthetic medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Jan;73(1):1–8. doi: 10.3181/00379727-73-17557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier J. C., Gaye P. Study of secretory lactoproteins: primary structures of the signals and enzymatic processing. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:232–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. J., Cohn D. V. Secretion and degradation of parathormone as a function of intracellular maturation of hormone pools. Modulation by calcium and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):521–528. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paskin N., Mayer R. J. A method for the analysis of protein turnover characteristics. Indirect estimation of rates of protein degradation. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):153–161. doi: 10.1042/bj1740153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenai R., Wallis M. Biosynthesis and degradation of prolactin in the rat anterior pituitary gland. Time course of incorporation of label in vitro and evidence for rapid degradation. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):735–743. doi: 10.1042/bj1820735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speake B. K., Dils R., Mayer R. J. Regulation of enzyme turnover during tissue differention. Studies on the effects of hormones on the turnover of fatty acid synthetase in rabbit mammary gland in organ culture. Biochem J. 1975 May;148(2):309–320. doi: 10.1042/bj1480309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. A., Speake B. K. The effect of cycloheximide on the glycosylation of lactating-rabbit mammary glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):297–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1920297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. J., Paskin N., Saxton J., Mayer R. J. Protein degradation during terminal cytodifferentiation. Studies on mammary gland in organ culture. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):311–320. doi: 10.1042/bj1920311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak R., Martin A. F., Blough R. Assessment of protein turnover by use of radioisotopic tracers. Physiol Rev. 1979 Apr;59(2):407–447. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


