Abstract
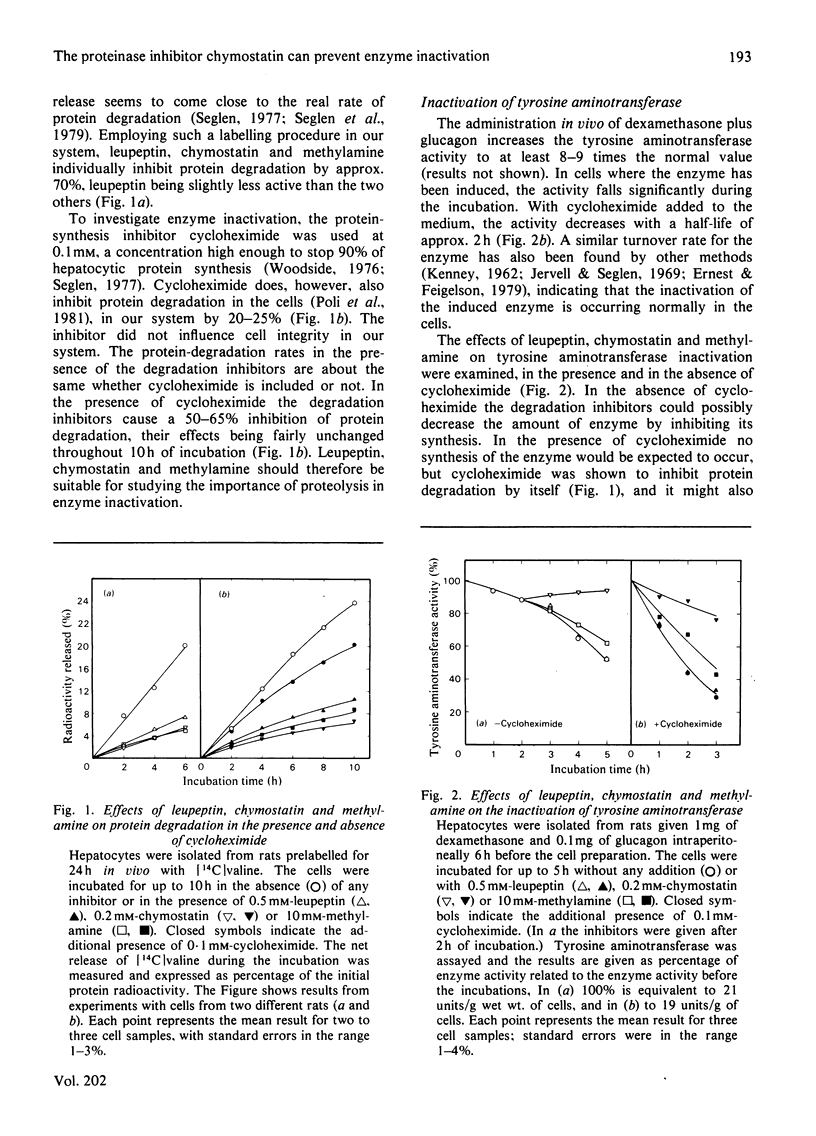
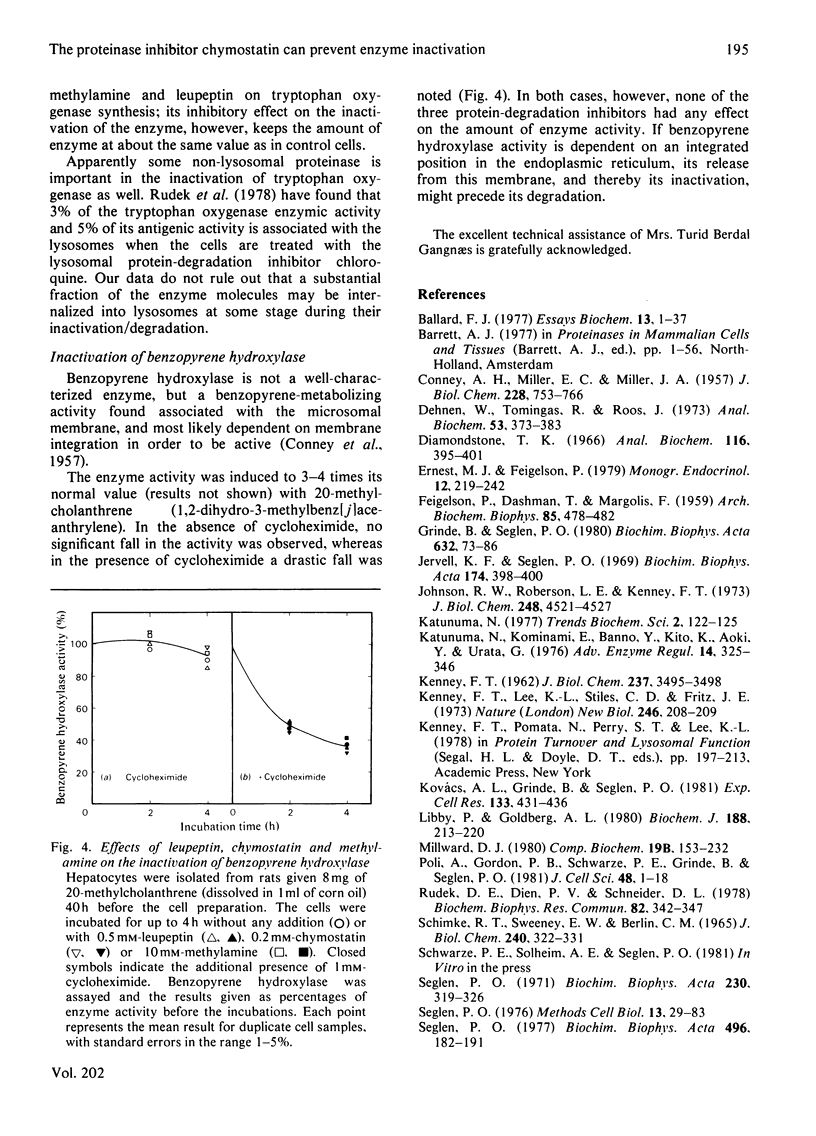
The following three potent inhibitors of hepatocytic proteolysis were investigated to see if they would inhibit the intracellular inactivation of enzymes: chymostatin and leupeptin (proteinase inhibitors) and methylamine (a lysosomotropic weak base). Chymostatin inhibited the inactivation of two of the three enzymes tested: tyrosine aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.5) and tryptophan oxygenase (tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase, EC 1.13.11.11). Leupeptin had no effect on any of the enzymes, whereas methylamine had only a weak inhibitory effect on tyrosine aminotransferase inactivation. Apparently proteolytic cleavage (probably by a non-lysosomal proteinase, since only chymostatin is effective) is involved in the inactivation of tyrosine aminotransferase and tryptophan oxygenase. The third enzyme, benzopyrene hydroxylase (flavoprotein-linked mono-oxygenase, EC 1.14.14.1), is probably inactivated by a non-proteolytic mechanism.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CONNEY A. H., MILLER E. C., MILLER J. A. Substrate-induced synthesis and other properties of benzpyrene hydroxylase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):753–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehnen W., Tomingas R., Roos J. A modified method for the assay of benzo(a)pyrene hydroxylase. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernest M. J., Feigelson P. Multihormonal control of tyrosine aminotransferase in isolated liver cells. Monogr Endocrinol. 1979;12:219–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81265-1_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEIGELSON P., DASHMAN T., MARGOLIS F. The half-life-time of induced tryptophan peroxidase in vivo. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Dec;85:478–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90514-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinde B., Seglen P. O. Differential effects of proteinase inhibitors and amines on the lysosomal and non-lysosomal pathways of protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 17;632(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90250-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. W., Roberson L. E., Kenney F. T. Regulation of tyrosine aminotransferase in rat liver. X. Characterization and interconversion of the multiple enzyme forms. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4521–4527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEY F. T. Induction of tyrosine-alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase in rat liver. IV. Evidence for an increase in the rate of enzyme synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3495–3498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katunuma N., Kominami E., Banno Y., Kito K., Aoki Y., Urata G. Concept on mechanism and regulation of intracellular enzyme degradation in mammalian tissues. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1976;14:325–345. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(76)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney F. T., Lee K. L., Stiles C. D., Fritz J. E. Further evidence against post-transcriptional control of inducible tyrosine aminotransferase synthesis in cultured hepatoma cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 19;246(155):208–210. doi: 10.1038/newbio246208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács A. L., Grinde B., Seglen P. O. Inhibition of autophagic vacuole formation and protein degradation by amino acids in isolated hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Jun;133(2):431–436. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90336-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Goldberg A. L. Effects of chymostatin and other proteinase inhibitors on protein breakdown and proteolytic activities in muscle. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):213–220. doi: 10.1042/bj1880213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli A., Gordon P. B., Schwarze P. E., Grinde B., Seglen P. O. Effects of insulin and anchorage on hepatocytic protein metabolism and amino acid transport. J Cell Sci. 1981 Apr;48:1–18. doi: 10.1242/jcs.48.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudek D. E., Dien P. Y., Schneider D. L. Identification of tryptophan pyrrolase in liver lysosomes after treatment of rats with hydrocortisone and chloroquine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 15;82(1):342–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90615-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., SWEENEY E. W., BERLIN C. M. THE ROLES OF SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION IN THE CONTROL OF RAT LIVER TRYPTOPHAN PYRROLASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:322–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Effects of amino acids, ammonia and leupeptin on protein synthesis and degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):469–474. doi: 10.1042/bj1740469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O., Grinde B., Solheim A. E. Inhibition of the lysosomal pathway of protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes by ammonia, methylamine, chloroquine and leupeptin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr 2;95(2):215–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O., Jervell K. F. A simple perfusion technique applied to glucocorticoid regulation of tryptophan oxygenase turnover and bile production in the isolated rat liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Mar;350(3):308–316. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1969.350.1.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O., Jervell K. F. Tryptophan oxygenase activation and ascorbate oxidation in whole homogenates from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 7;171(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:29–83. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Protein-catabolic stage of isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 24;496(1):182–191. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Regulation of tyrosine transaminase degradation in the isolated perfused rat liver by cycloheximide and insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 23;230(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O., Solheim A. E., Grinde B., Gordon P. B., Schwarze P. E., Gjessing R., Poli A. Amino acid control of protein synthesis and degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;349:1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb29510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Everitt M., Sanada Y., Katunuma N., Lagunoff D., Neurath H. A major serine protease in rat skeletal muscle: evidence for its mast cell origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5311–5313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Gruzenski G. M., Lagunoff D. Immunofluorescent localization of a serine protease in rat small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodside K. H. Effects of cycloheximide on protein degradation and gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 14;421(1):70–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


