Abstract
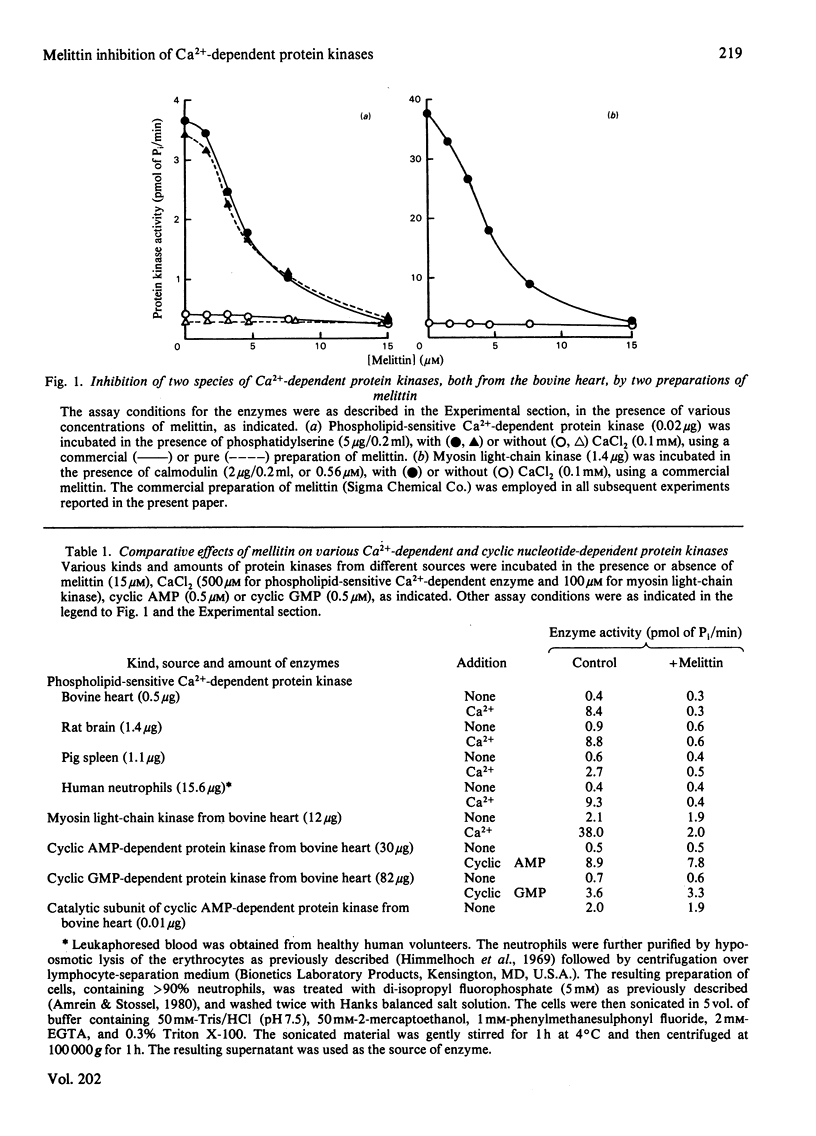
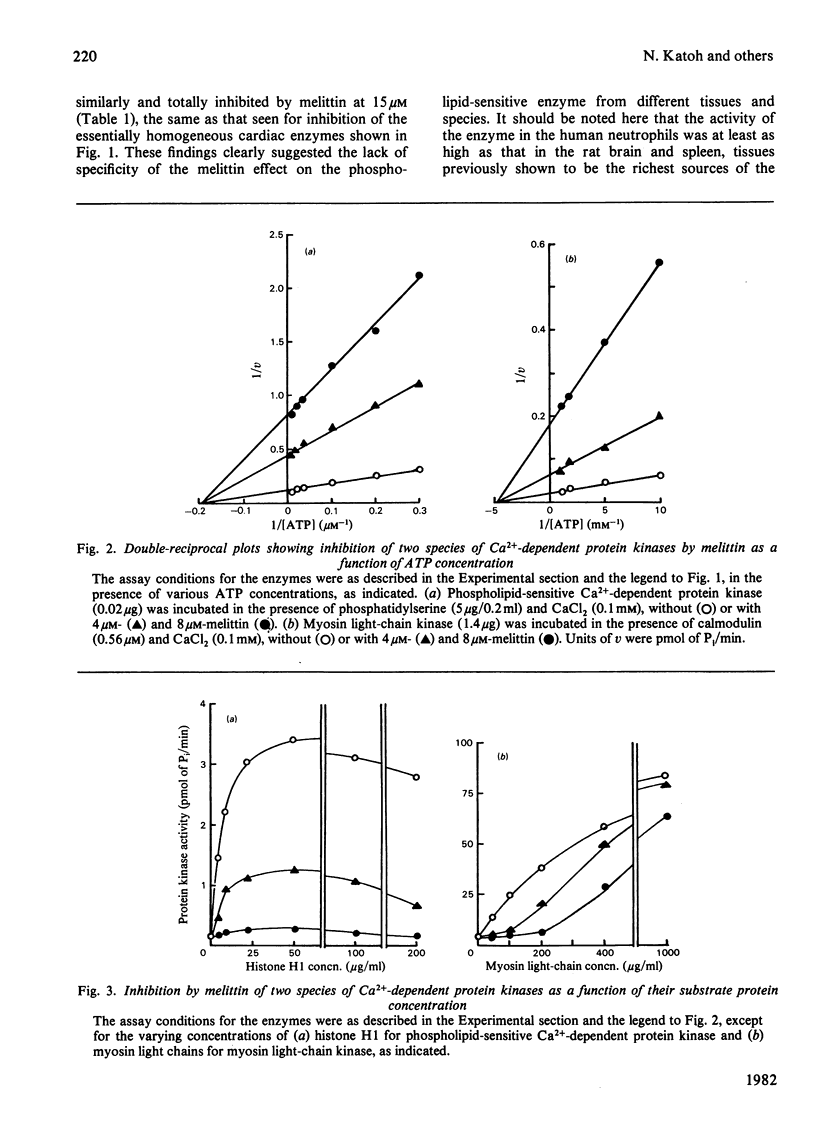
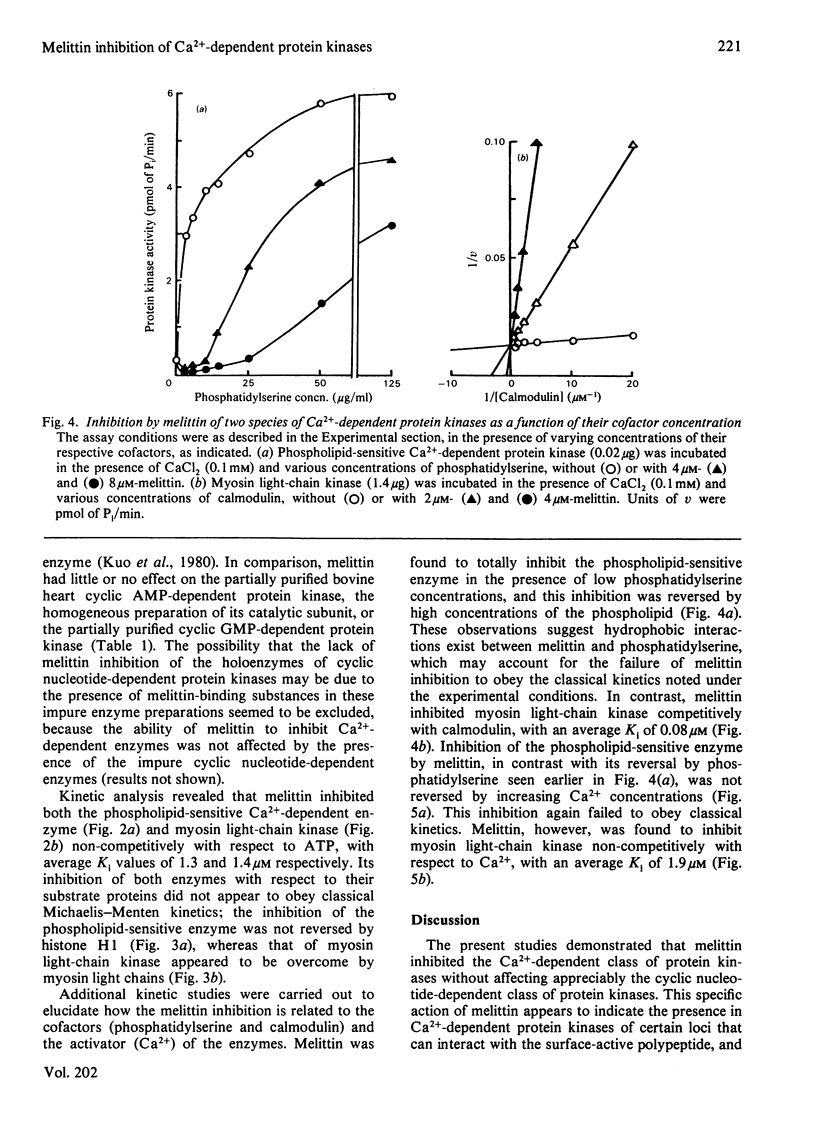
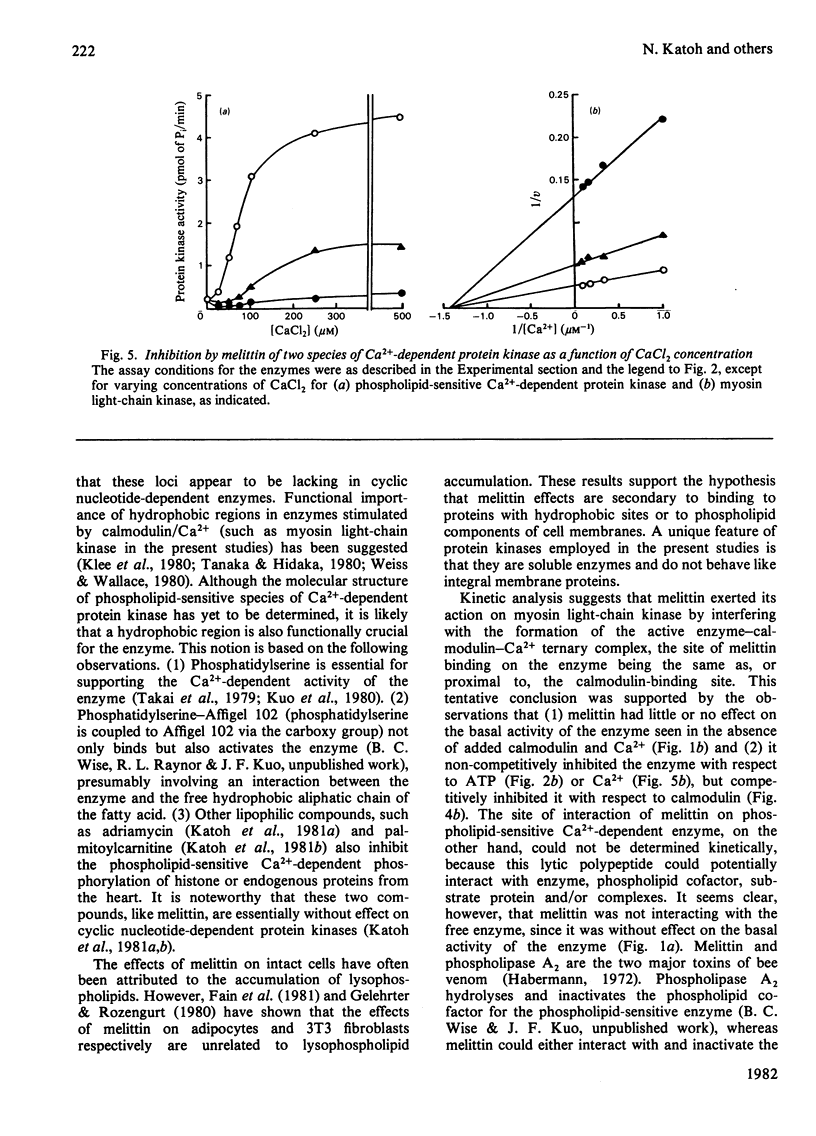
Effects of melittin, an amphipathic polypeptide, on various species of protein kinases were investigated. It was found that melittin inhibited the newly identified phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase (from heart, brain, spleen and neutrophils) and the cardiac myosin light-chain kinase, a calmodulin-sensitive Ca2+-dependent enzyme. In contrast, melittin had little or no effect on either the holoenzymes of the cardiac cyclic AMP-dependent and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinases or the catalytic subunit of the former. Kinetic analysis indicated that melittin inhibited phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase non-competitively with respect to ATP (Ki = 1.3 microM); although exhibiting complex kinetics, its inhibition of the enzyme was overcome by phosphatidylserine (a phospholipid cofactor), but not by protein substrate (histone H1) or Ca2+. On the other hand, melittin inhibited myosin light-chain kinase non-competitively with respect to ATP (Ki = 1.4 microM) or Ca2+ (Ki = 1.9 microM), and competitively with respect to calmodulin (Ki = 0.08 microM); although exhibiting complex kinetics, its inhibition of the enzyme was reversed by myosin light chains (substrate protein). The present findings indicate the presence of functionally important hydrophobic or hydrophilic loci on the Ca2+-dependent protein kinases, but not on the cyclic nucleotide-dependent class of protein kinase, with which melittin can interact. Moreover, the kinetic data suggest that melittin inhibited myosin light-chain kinase by interacting with a site on the enzyme the same as, or proximal to, the calmodulin-binding site, thus interfering with the formation of active enzyme-calmodulin-Ca2+ complex.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein P. C., Stossel T. P. Prevention of degradation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte proteins by diisopropylfluorophosphate. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):442–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel P. J., Beavo J. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and characterization of catalytic subunit of skeletal muscle adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2691–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Cormier M. J. Purification of plant calmodulin by fluphenazine-Sepharose affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):1039–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91931-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelehrter T. D., Rozengurt E. Stimulation of monovalent ion fluxes and DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells by melittin and vasopressin is not mediated by phospholipid deacylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 28;97(2):716–724. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georghiou S., Thompson M., Mukhopadhyay A. K. Melittin-phospholipid interaction: evidence for melittin aggregation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 6;642(2):429–432. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Bee and wasp venoms. Science. 1972 Jul 28;177(4046):314–322. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4046.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Yamaki T., Naka M., Tanaka T., Hayashi H., Kobayashi R. Calcium-regulated modulator protein interacting agents inhibit smooth muscle calcium-stimulated protein kinase and ATPase. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):66–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelhoch S. R., Evans W. H., Mage M. G., Peterson E. A. Purification of myeloperoxidases from the bone marrow of the guinea pig. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):914–921. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Kubo S., Takahashi H. Immunological studies on the light chains of myosin with special reference to the relationship between light chain components. J Biochem. 1973 Oct;74(4):771–778. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Andersson R. G., Wise B. C., Mackerlova L., Salomonsson I., Brackett N. L., Katoh N., Shoji M., Wrenn R. W. Calcium-dependent protein kinase: widespread occurrence in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom and comparison of effects of phospholipid, calmodulin, and trifluoperazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Krueger B. K., Sanes J. R., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. V. Preparation and properties of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from various bovine tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 15;212(1):79–91. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. J., Shier W. T. Activation of microsomal guanylate cyclase by a cytotoxic polypeptide: melittin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90980-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollay C., Kreil G., Berger H. Action of phospholipases on the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Stimulation by melittin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 5;426(2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90340-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollay C., Kreil G. Enhancement of bee venom phospholipase A2 activity by melittin, direct lytic factor from cobra venom and polymyxin B. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 15;46(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80354-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollay C., Kreil G. Fluorometric measurements on the interaction of melittin with lecithin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 23;316(2):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Yu B., Nishizuka Y. Inhibitory action of chlorpromazine, dibucaine, and other phospholipid-interacting drugs on calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8378–8380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Perry S. V. An electrophoretic study of the low-molecular-weight components of myosin. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):31–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1190031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pires E. M., Perry S. V. Purification and properties of myosin light-chain kinase from fast skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1670137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Wise B. C., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase: inhibition by antipsychotic drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 12;98(3):669–676. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa G., Freer J. H., Colacicco G., Weissmann G. Interaction of alytic polypeptide, melittin, with lipid membrane systems. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3575–3582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji M., Patrick J. G., Davis C. W., Kuo J. F. Guanosine cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from foetal calf heart. Purification, general properties and catalytic subunit. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):213–221. doi: 10.1042/bj1610213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Hidaka H. Hydrophobic regions function in calmodulin-enzyme(s) interactions. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11078–11080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt W., Patzer P., Lege L., Oldigs H. D., Wille G. Synergism between phospholipase A and various peptides and SH-reagents in causing haemolysis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1970;265(5):442–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00997079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Vallet B., Autric F., Demaille J. G. Purification and characterization of bovine cardiac calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12136–12144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Andersson R. G., Mackerlova L., Raynor R. L., Solomonsson I., Kuo J. F. Ontogenetic aspects of phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase in guinea pig tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 31;99(2):407–413. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91760-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn R. W., Katoh N., Wise B. C., Kuo J. F. Stimulation by phosphatidylserine and calmodulin of calcium-dependent phosphorylation of endogenous proteins from cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12042–12046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



