Abstract
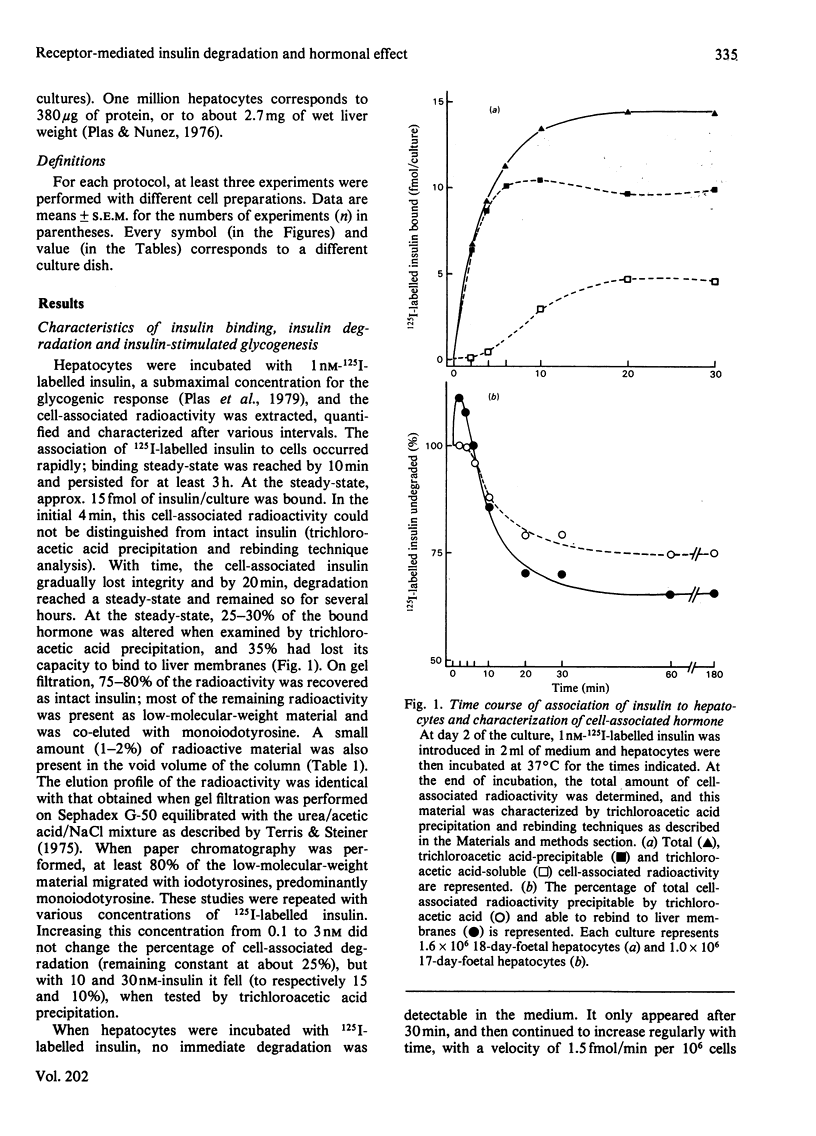
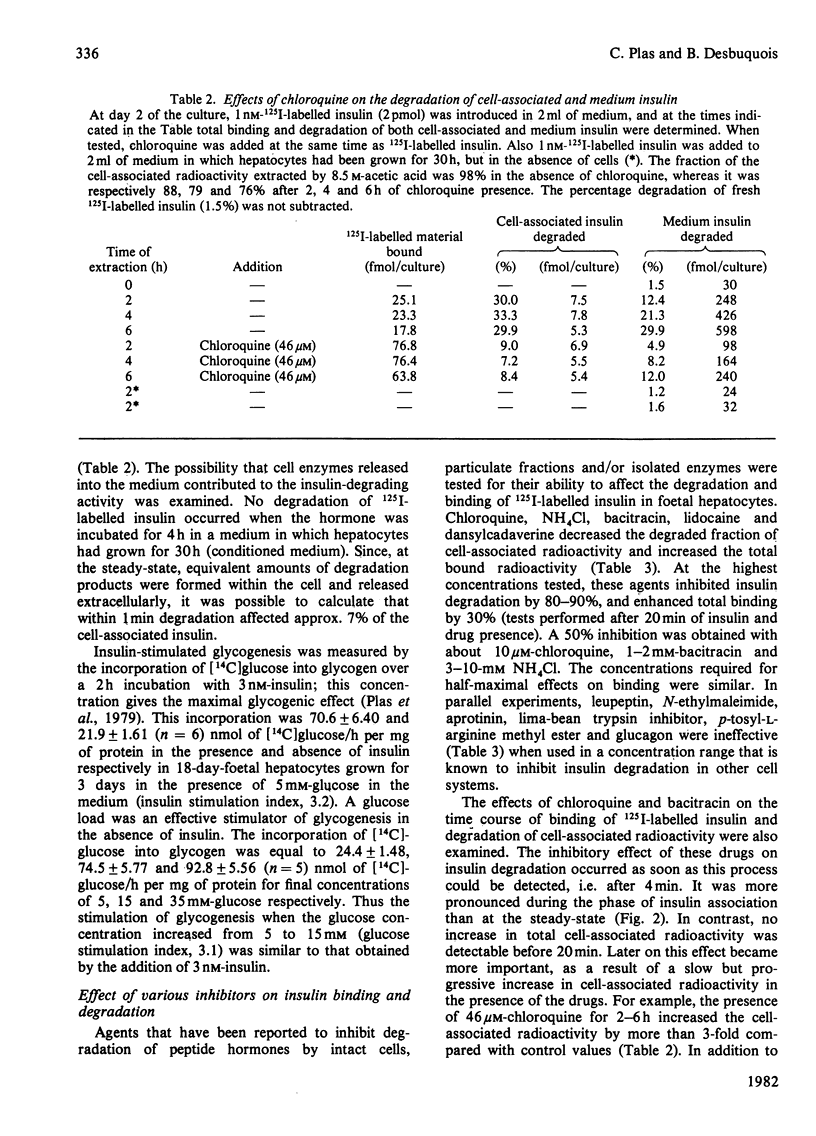
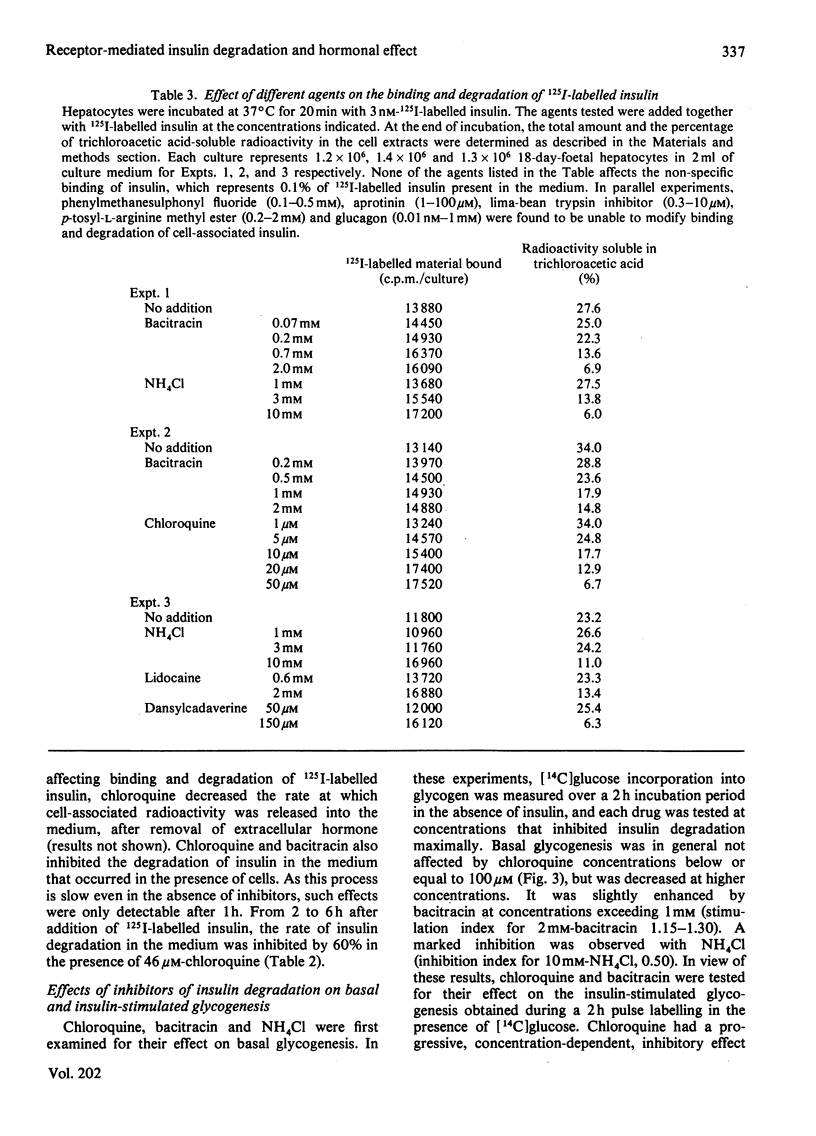
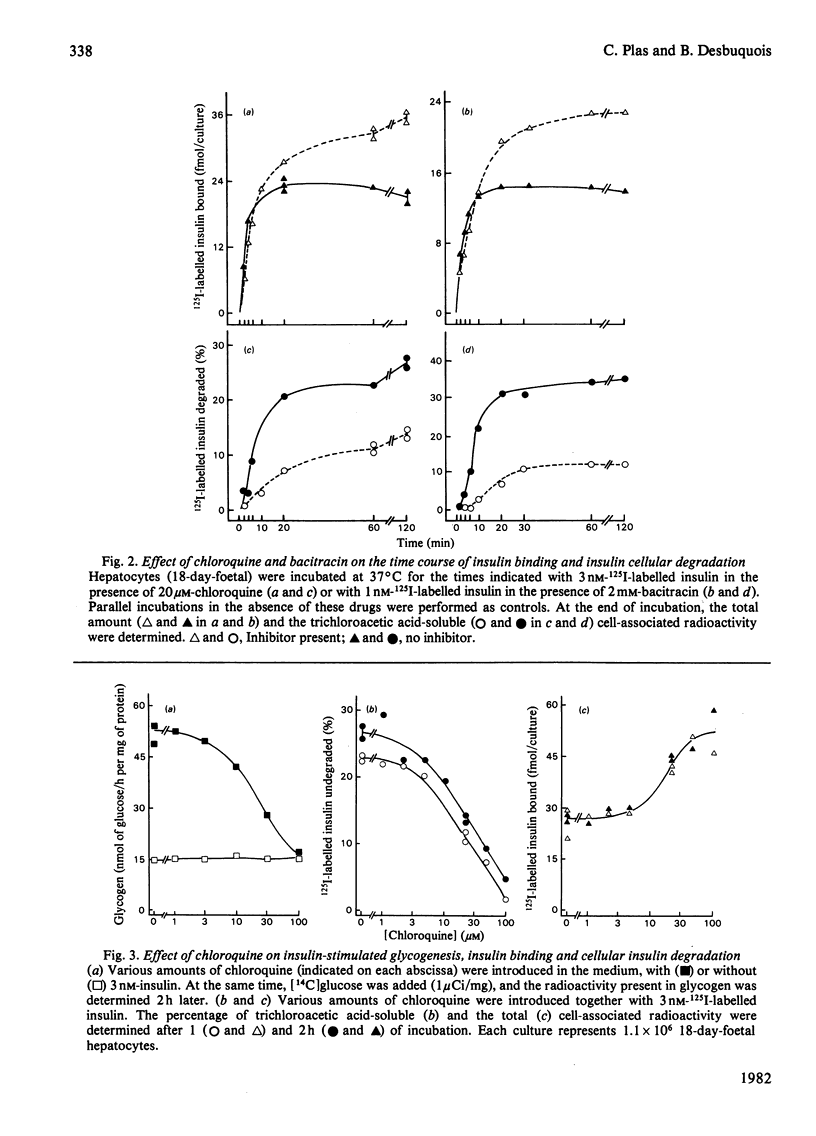
Insulin-stimulated glycogenesis and insulin degradation were studied simultaneously at 37 degrees C in cultured foetal hepatocytes grown for 2-3 days in the presence of cortisol. Degradation of cell-associated insulin, as measured by trichloroacetic acid precipitation, was significant after 4 min in the presence of 1-3 nM-125I-labelled insulin. This process became maximal (30% of insulin degraded) after 20 min, a time when binding-state conditions were achieved. No insulin-degradative activity was detected in a medium that had been exposed to cells. At steady-state, the appearance of insulin degradation products in the medium was linearly dependent on time (1.5 fmol/min per 10(6) cells at 1nM-125I-labelled insulin). Chloroquine (3-50 microM), bacitracin (0.1-10 mM) and NH4Cl (1-10 mM) inhibited insulin degradation as soon as this became detectable and caused an increase in the association of insulin to hepatocytes after 20 min. Lidocaine and dansylcadaverine had similar effects, whereas N-ethylmaleimide, aprotinin, phenylmethanesulphonyl fluoride and leupeptin were found to be ineffective. Chloroquine, and also bacitracin, at concentrations that inhibited insulin degradation, decreased the insulin-stimulated incorporation of [14C]glucose into glycogen over 2 h. This effect of chloroquine was specific, since it did not modify the basal glycogenesis, or the glycogenic effect of a glucose load in the absence of insulin. It therefore appears that the receptor-mediated insulin degradation (or some associated pathway) is functionally related to the glycogenic effect of insulin in foetal hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin D., Jr, Terris S., Steiner D. F. Characterization of insulin-like actions of anti-insulin receptor antibodies. Effects on insulin binding, insulin degradation, and glycogen synthesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4028–4034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron J. J., Sikstrom R., Hand A. R., Posner B. I. Binding and uptake of 125I-insulin into rat liver hepatocytes and endothelium. An in vivo radioautographic study. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):427–443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghen G. A., Kitabchi A. E., Brush J. S. Characterization of a rat liver protease with specificity for insulin. Endocrinology. 1972 Sep;91(3):633–642. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-3-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Amatruda J. M. Functional relationships between insulin binding, action, and degradation. A reassessment. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10052–10055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Barazzone P., Freychet P., Le Cam A., Orci L. Intracellular localization of 125I-labeled insulin in hepatocytes from intact rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2803–2807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Freychet P., Le Cam A., Orci L. Lysosomal association of internalized 125I-insulin in isolated rat hepatocytes. Direct demonstration by quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1249–1261. doi: 10.1172/JCI109420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Krug F., Cuatrecasas P. Inhibitors of glucagon inactivation. Effect on glucagon--receptor interactions and glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in liver cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):101–120. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Willeput J., Huet de Froberville A. Receptor-mediated internalisation of insulin in intact rat liver. A biochemical study. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):338–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C. Insulin degradation by liver cell membranes. Endocrinology. 1979 Jun;104(6):1758–1764. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-6-1758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS V. J., BRYANT J. C., KERR H. A., SCHILLING E. L. CHEMICALLY DEFINED MEDIA FOR CULTIVATION OF LONG-TERM CELL STRAINS FROM FOUR MAMMALIAN SPECIES. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Dec;36:439–474. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fussganger R. D., Kahn C. R., Roth J., De Meyts P. Binding and degradation of insulin by human peripheral granulocytes. Demonstration of specific receptors with high affinity. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2761–2769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Kristensen L. O., Sestoft L. Insulin receptors in isolated rat hepatocytes. Reassessment of binding properties and observations of the inactivation of insulin at 37 degrees C. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8406–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Dansylcadaverine inhibits internalization of 125I-epidermal growth factor in BALB 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1239–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammons G. T., Jarett L. Lysosomal degradation of receptor-bound 125I-labeled insulin by rat adipocytes: its characterization and dissociation from the short-term biologic effects of insulin. Diabetes. 1980 Jun;29(6):475–486. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.6.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann C., Marsh J. W., Miller B., Steiner D. F. Cultured hepatoma cells as a model system for studying insulin processing and biologic responsiveness. Diabetes. 1980 Nov;29(11):865–874. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.11.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Seals J. R. Pyruvate dehydrogenase activation in adipocyte mitochondria by an insulin-generated mediator from muscle. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1407–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.505013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K., Filier J. S., Jarrett D. B. Effects of autoantibodies to the insulin receptor on isolated adipocytes. Studies of insulin binding and insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1094–1106. doi: 10.1172/JCI108861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J., Galasko G., Cheng K., DePaoli-Roach A. A., Huang L., Daggy P., Kellogg J. Generation by insulin of a chemical mediator that controls protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1408–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.228395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P., Lenoir P. Degradation of insulin by isolated rat liver cells. Diabetes. 1975 Jun;24(6):566–573. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.6.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Gorden P., Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Freychet P. Anti-insulin receptor antibodies inhibit insulin binding and stimulate glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle. Diabetologia. 1978 May;14(5):311–317. doi: 10.1007/BF01223022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Olefsky J. M. Effects of lysosomotropic agents on insulin interactions with adipocytes. Evidence for a lysosomal pathway for insulin processing and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10153–10160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Olefsky J. M. The endocytotic-internalization pathway of insulin metabolism: relationship to insulin degradation and activation of glucose transport. Endocrinology. 1980 Dec;107(6):1937–1945. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-6-1937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Davies P. J., Klempner L., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Epidermal growth factor stimulation of DNA synthesis is potentiated by compounds that inhibit its clustering in coated pits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5731–5735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKanna J. A., Haigler H. T., Cohen S. Hormone receptor topology and dynamics: morphological analysis using ferritin-labeled epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5689–5693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menuelle P., Plas C. Relationship between insulin binding and glycogenesis in cultured fetal hepatocytes. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):647–653. doi: 10.1007/BF00257435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps B. H., Varandani P. T. Stimulation by insulin of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase. Role of glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 21;75(2):302–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plas C., Chapeville F., Jacquot R. Development of glycogen storage ability under cortisol control in primary cultures of rat fetal hepatocytes. Dev Biol. 1973 May;32(1):82–91. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plas C., Menuelle P., Moncany M. L., Fulchignoni-Lataud M. C. Time dependence of the glycogenic effect of insulin in cultured fetal hepatocytes. Diabetes. 1979 Aug;28(8):705–712. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.8.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plas C., Nunez J. Role of cortisol on the glycogenolytic effect of glucagon and on the glycogenic response to insulin in fetal hepatocyte culture. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1431–1437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner B. I., Patel B., Verma A. K., Bergeron J. J. Uptake of insulin by plasmalemma and Golgi subcellular fractions of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):735–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A. Bacitracin: an inhibitor of the insulin degrading activity of glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jan 30;98(2):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90858-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouer E., Desbuquois B., Postel-Vinay M. C. Interactions of glucagon with isolated rat-liver cells. Fate and subcellular localization of cell-associated hormone. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1980 Aug;19(2):143–164. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(80)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., Czech M. P. Evidence that insulin activates an intrinsic plasma membrane protease in generating a secondary chemical mediator. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6529–6531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., Jarett L. Activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by direct addition of insulin to an isolated plasma membrane/mitochondria mixture: evidence for generated of insulin's second messenger in a subcellular system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):77–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonne O., Gliemann J. Insulin receptors of cultured human lymphocytes (IM-9). Lack of receptor-mediated degradation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7449–7454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F. The Banting Memorial Lecture 1976. Insulin today. Diabetes. 1977 Apr;26(4):322–340. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.4.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Internalization and degradation of fat cell-bound insulin. Separation and partial characterization of subcellular vesicles associated with iodoinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9786–9794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Hofmann C., Steiner D. F. Mode of uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated hepatocytes and H4 hepatoma cells. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):459–468. doi: 10.1139/o79-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Retention and degradation of 125I-insulin by perfused livers from diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):885–896. doi: 10.1172/JCI108365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Spooner P. M., Kahn C. R., Chernick S. S., Garrison M. M., Karlsson F. A., Grunfeld C. Insulin-receptor antibodies mimic a late insulin effect. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):500–502. doi: 10.1038/280500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. X. Identification of insulin degrading activity of rat liver plasma membrane as glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T., Nafz M. A., Chandler M. L. Interaction of insulin analogs, glucagon, growth hormone, vasopressin, oxytocin, and scrambled forms of ribonuclease and lysozyme with glytathione-insulin transhydrogenase (thiol: protein-disulfide oxidoreductase): dependence upon conformation. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2115–2120. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzel G., Eisele K., Stock W. Structure and activity of insulin, XIII. Specificity of the arginine-guanidino group in biologically active tetrapeptides of the insulin sequence B 22-25 (Arg-Gly-Phe-Phe). Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 May;356(5):583–590. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.1.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


