Abstract
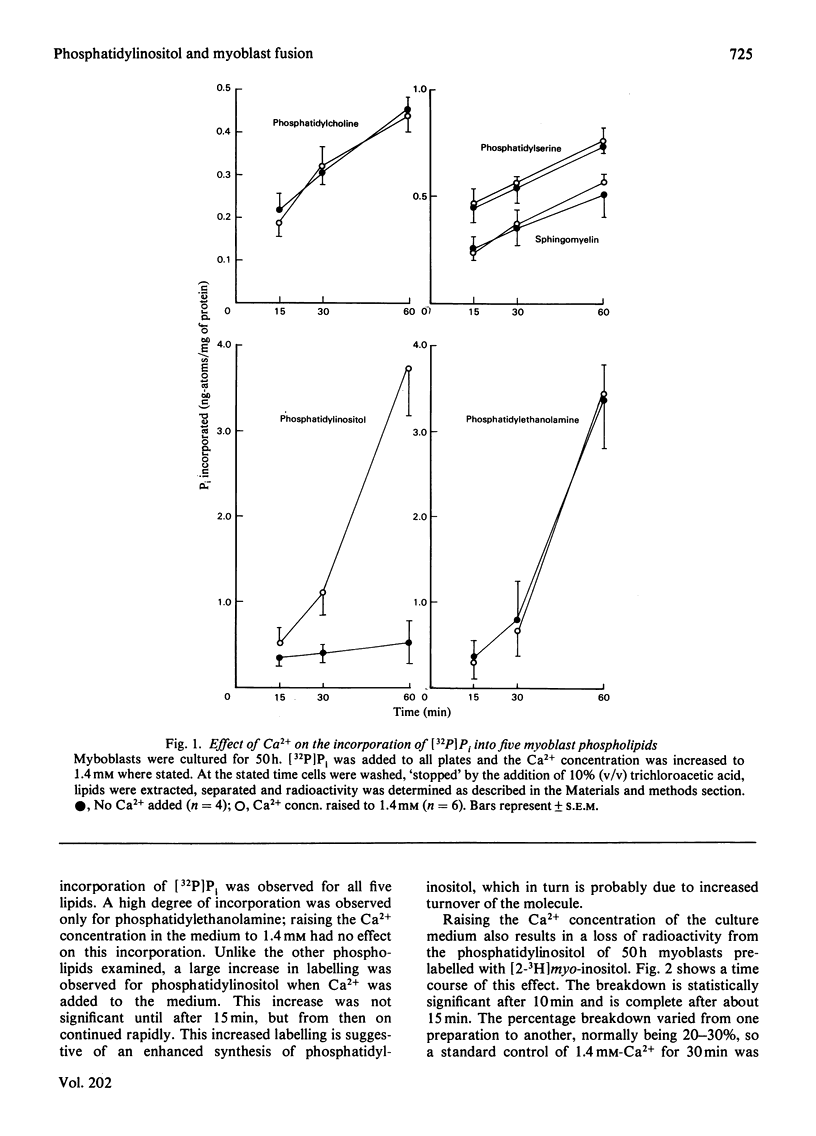
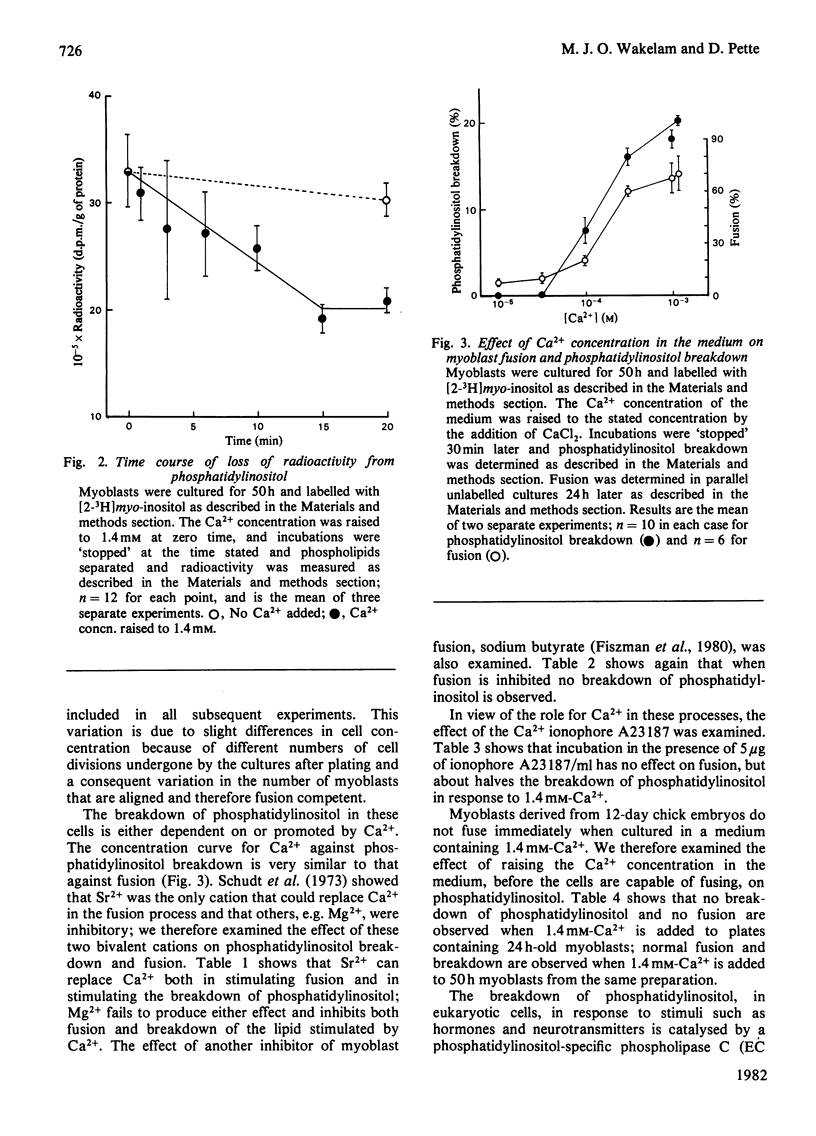
1. The fusion of chick-embryo myoblasts to produce myotubes was studied. The myoblasts were grown for 50 h in medium containing 10--20 microM-Ca2+; during this period they achieve fusion competence. 2. A rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol is also observed on addition of 1.4 mM-Ca2+ to these cells. This Ca2+ concentration also stimulates rapid myoblast fusion. 3. The breakdown is complete within 15 min and shows the same dependence on Ca2+ concentration as the fusion process. 4. Fusion-incompetence myoblasts and cells where fusion is inhibited by sodium butyrate exhibit no phosphatidylinositol breakdown on Ca2+ addition. 5. The Ca2+ ionophore A23187 inhibits the Ca2+-stimulated breakdown by about 50%, but has no effect on fusion. 6. A concomitant increase in 1,2-diacylglycerol labelled and fall in phosphatidylinositol labelling was observed when the lipids were labelling with [14C]glycerol on increasing the Ca2+ concentration in the medium to 1.4 mM. 7. We propose that the breakdown of phosphatidylinositol with a resultant increase in 1,2-diacylglycerol content of the cell membrane promotes myoblast fusion.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON D., BLECHER M. QUANTITATIVE TWO-DIMENSIONAL THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF NATURALLY OCCURRING PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:628–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Michell R. H. The possible role of lipids in control of membrane fusion during secretion. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1979;33:323–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl G., Schudt C., Gratzl M. Fusion of isolated myoblast plasma membranes. An approach to the mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 4;514(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. D., See W. M., Higginbotham C. A. Fusion of chick embryo skeletal myoblasts: role of calcium influx preceding membrane union. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90453-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiszman M. Y., Montarras D., Wright W., Gros F. Expression of myogenic differentiation and myotube formation by chick embryo myoblasts in the presence of sodium butyrate. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Mar;126(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90467-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman C. P., West D. Complete separation of lipid classes on a single thin-layer plate. J Lipid Res. 1966 Mar;7(2):324–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman B. A., Fernandez S. M. Changes in membrane dynamics associated with myogenic cell fusion. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Mar;94(3):253–263. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040940303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon N., Gilula N. B. Membrane events involved in myoblast fusion. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):411–425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Michell R. H., Hems D. A. Phosphatidylinositol metabolism in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):155–165. doi: 10.1042/bj1940155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Michell R. H. Stimulation by acetylcholine of phosphatidylinositol labelling. Subcellular distribution in rat cerebral-cortex slices. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1141–1147. doi: 10.1042/bj1261141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Vail W. J., Pangborn W. A., Poste G. Studies on membrane fusion. II. Induction of fusion in pure phospholipid membranes by calcium ions and other divalent metals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 5;448(2):265–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives J., Shinitzky M. Increased membrane fluidity precedes fusion of muscle cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):761–763. doi: 10.1038/268761a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCKDALE F. E., HOLTZER H. DNA synthesis and myogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Sep;24:508–520. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90450-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schudt C., van der Bosch J., Pette D. Inhibition of muscle cell fusion in vitro by Mg2+ and K+ ions. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 1;32(2):296–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80857-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schudt O., Pette D. Influence of the ionophore A 23 187 on myogenic cell fusion. FEBS Lett. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):36–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainberg A., Yagil G., Yaffe D. Alterations of enzymatic activities during muscle differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1971 May;25(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidekamm E., Schudt C., Brdiczka D. Physical properties of muscle cell membranes during fusion. A fluorescence polarization study with the ionophore A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 16;443(2):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D. Developmental changes preceding cell fusion during muscle differentiation in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1971 May;66(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bosch J., Schudt C., Pette D. Quantitative investigation on Ca++-and pH-dependence of muscle cell fusion in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 25;48(2):326–332. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


