Abstract
Monoclonal antibody has been obtained to the human complement control protein C3b inactivator after immunization of mice with the enzyme prepared by conventional methods. Antibody from ascitic fluid was purified and coupled to Sepharose-CL-4B to give a specific affinity column, which was used to isolate C3b inactivator from human serum in 70% yield. The product was characterized by size, chain structure, amino acid analysis and proteolytic activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlaud G. J., Gagnon J., Porter R. R. The catalytic chain of human complement subcomponent C1r. Purification and N-terminal amino acid sequences of the major cyanogen bromide-cleavage fragments. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):49–59. doi: 10.1042/bj2010049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. D., Gagnon J., Porter R. R. Amino acid sequence around the thiol and reactive acyl groups of human complement component C4. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 1;199(2):359–370. doi: 10.1042/bj1990359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie D. L., Gagnon J. Isolation, characterization and N-terminal sequences of the CNBr-cleavage peptides from human complement Factor B. Localization of a free thiol group and a sequence defining the site cleaved by factor D. Biochem J. 1982 Mar 1;201(3):555–567. doi: 10.1042/bj2010555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie D. L., Gagnon J., Porter R. R. Partial sequence of human complement component factor B: novel type of serine protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4923–4927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley L. G., Porter R. R. Purification of the human complement control protein C3b inactivator. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):173–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1910173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Purification of C3b inactivator and demonstration of its two polypeptide chain structure. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1248–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. A., Lachmann P. J. The physiological breakdown of the third component of human complement. Mol Immunol. 1980 Jan;17(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The demonstration in human serum of "conglutinogen-activating factor" and its effect on the third component of complement. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):691–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernhardt W., Andersson J., Coutinho A., Melchers F. Cloning of murine transformed cell lines in suspension culture with efficiencies near 100%. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Feb;111(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole J. E., Niemann M. A. Structural evidence that complement factor B constitutes a novel class of serine protease. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8472–8476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
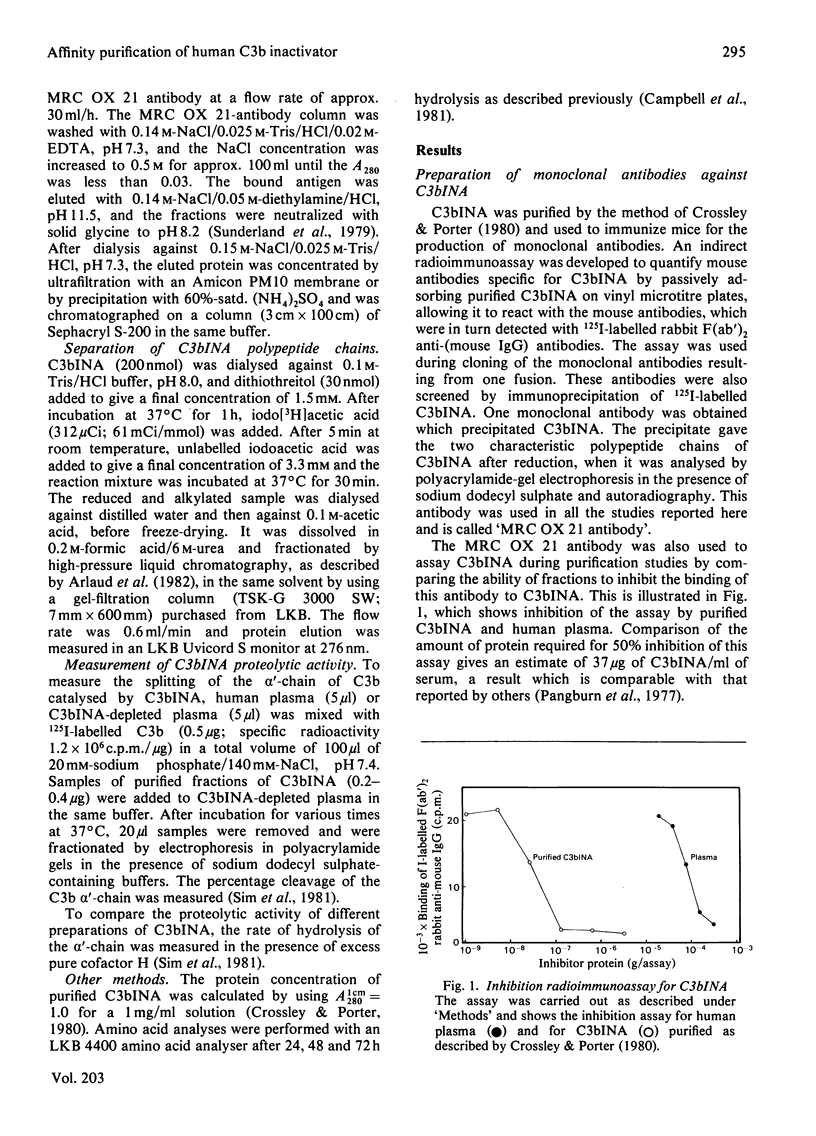
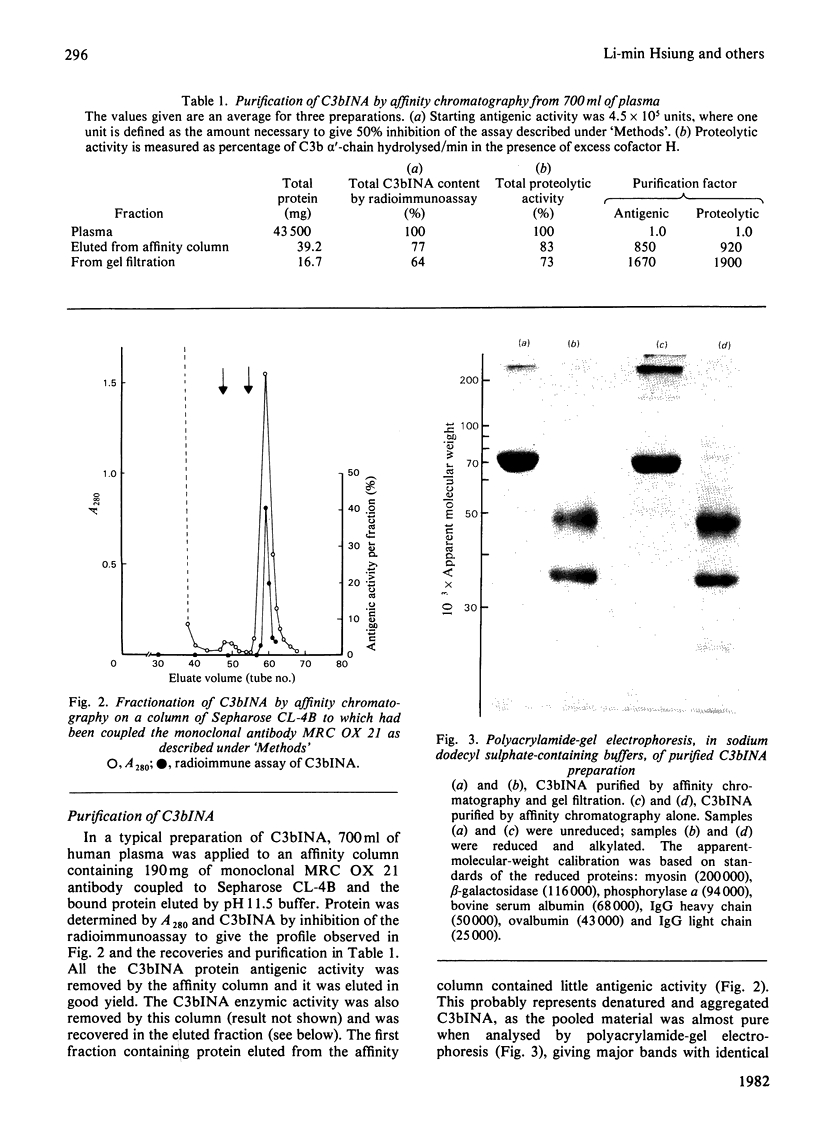
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Human complement C3b inactivator: isolation, characterization, and demonstration of an absolute requirement for the serum protein beta1H for cleavage of C3b and C4b in solution. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press E. M., Gagnon J. Human complement component C4. Structural studies on the fragments derived from C4b by cleavage with C3b inactivator. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 1;199(2):351–357. doi: 10.1042/bj1990351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. The proteolytic activation systems of complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:433–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
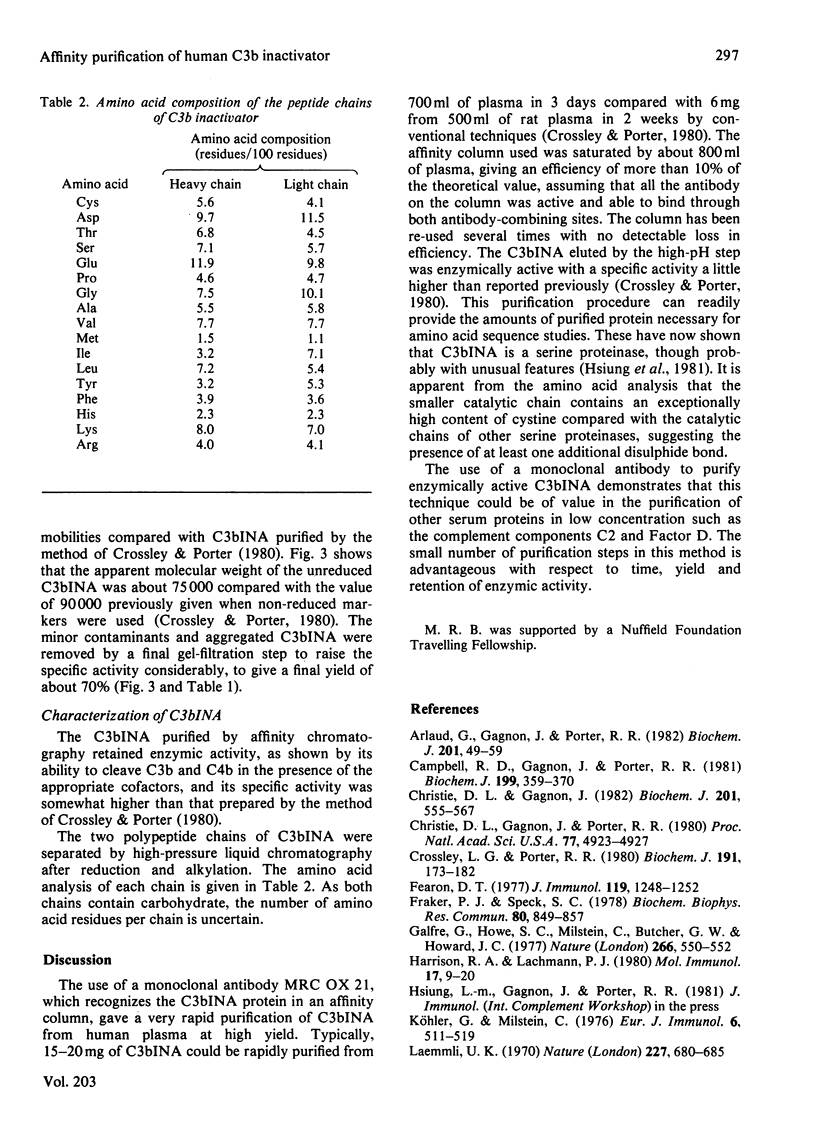
- Sim E., Wood A. B., Hsiung L. M., Sim R. B. Pattern of degradation of human complement fragment, C3b. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 14;132(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80426-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland C. A., McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Purification with monoclonal antibody of a predominant leukocyte-common antigen and glycoprotein from rat thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Feb;9(2):155–159. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura N., Nelson R. A., Jr Three naturally-occurring inhibitors of components of complement in guinea pig and rabbit serum. J Immunol. 1967 Sep;99(3):582–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Galfrè G., Milstein C. Analysis of cell surfaces by xenogeneic myeloma-hybrid antibodies: differentiation antigens of rat lymphocytes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]