Abstract
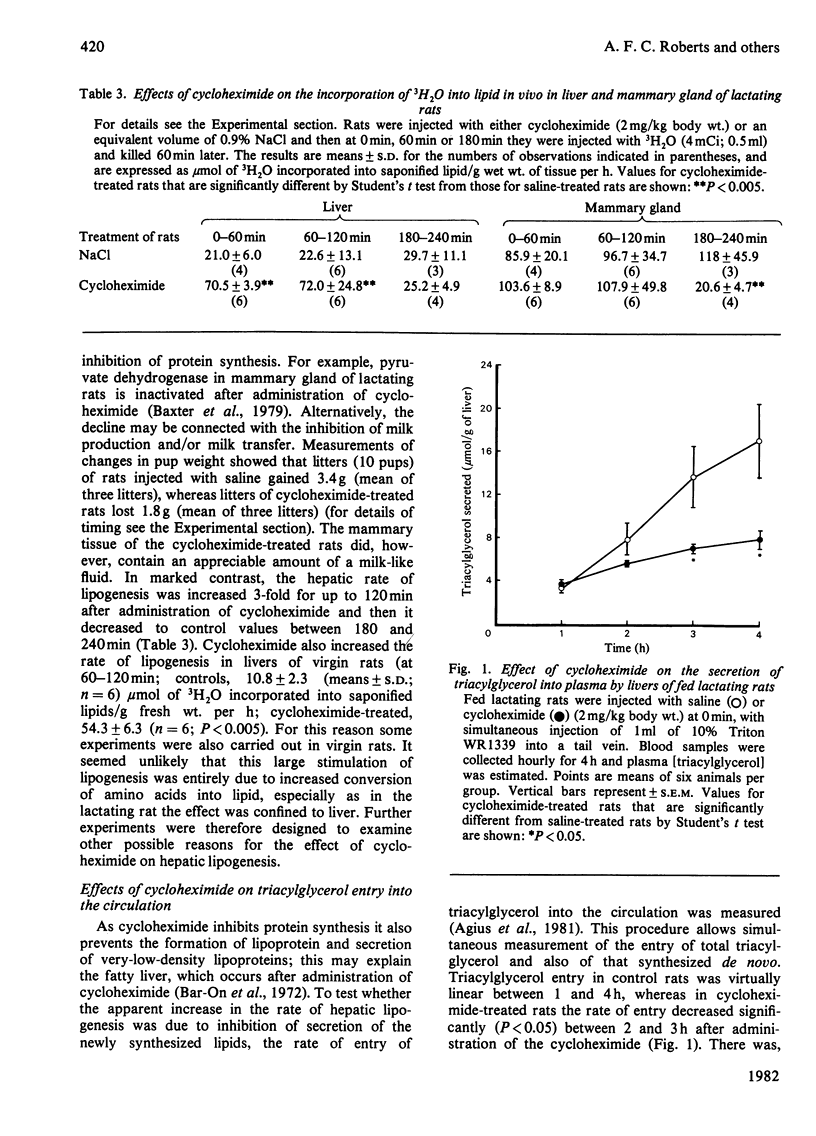
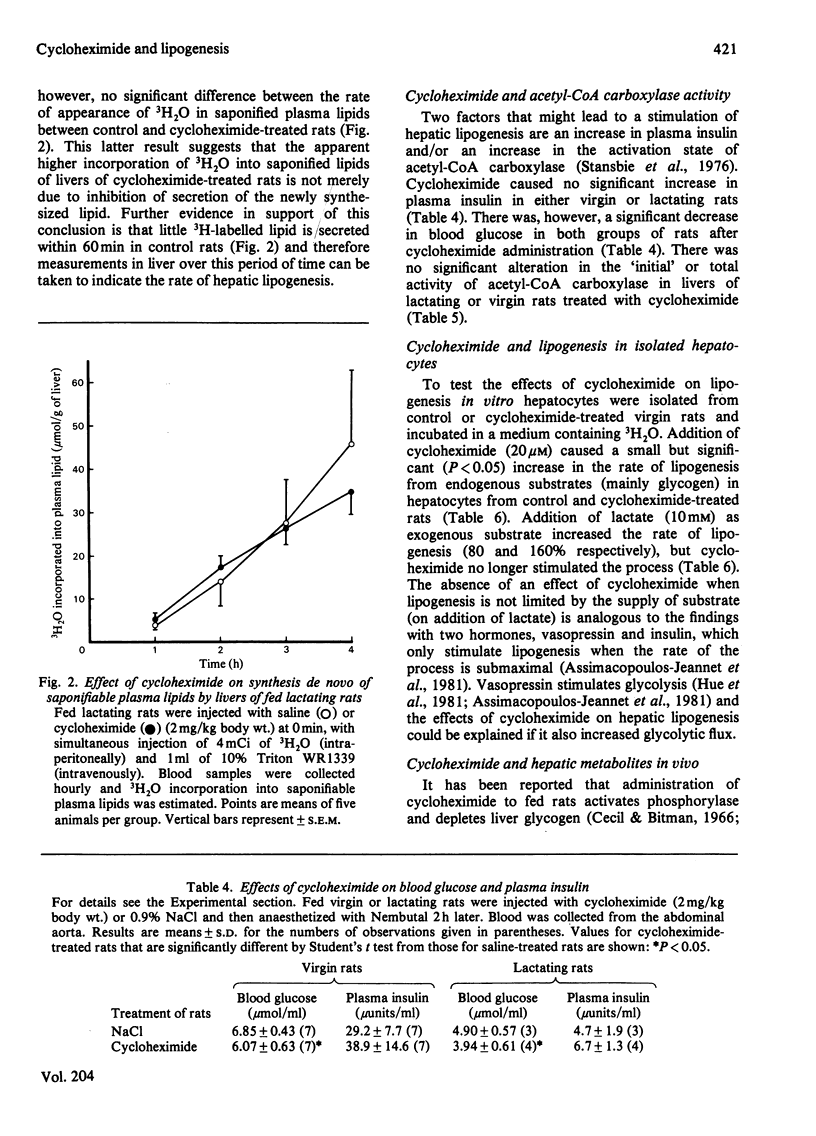
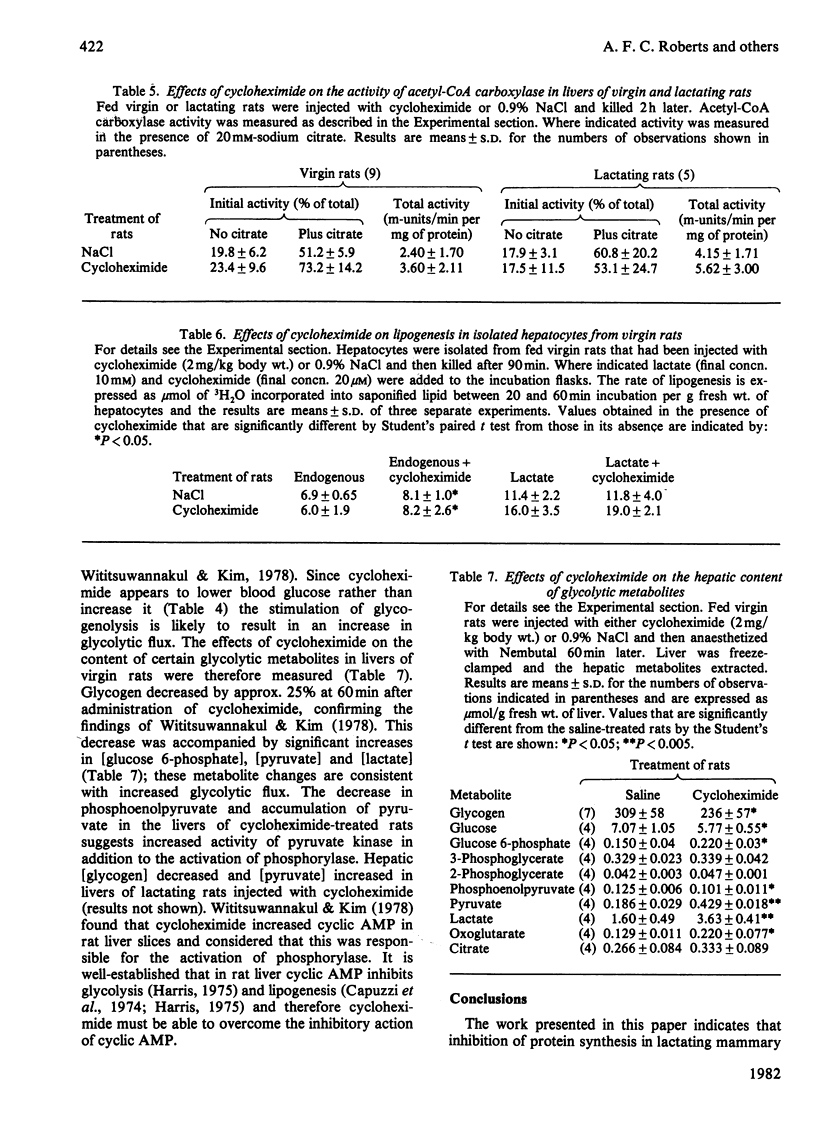
1. Administration of cycloheximide (an inhibitor of protein synthesis) to lactating rats raised the concentrations of amino acids, and in particular, the branched-chain amino acids (valine, leucine and isoleucine) in blood, liver and mammary gland. 2. Inhibition of protein synthesis increased the incorporation in vivo of L-[U-14C]leucine into lipids of mammary gland and liver. 3. Cycloheximide treatment caused no immediate change in the overall rate of lipogenesis in vivo (measured with 3H2O) in mammary gland but increased the rate in liver 3-fold; this latter effect also occurred in livers of virgin rats. 4. The increased rate of hepatic lipogenesis was not accompanied by significant changes in the plasma insulin concentration or the activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. 5. Although cycloheximide decreased the entry of total triacylglycerol into the circulation it did not alter the rate of secretion of newly synthesized saponifiable lipid. 6. Cycloheximide slightly stimulated lipogenesis from endogenous substrates in isolated hepatocytes, but this effect was abolished when lactate was the exogenous substrate. 7. Administration of cycloheximide to virgin rats decreased liver glycogen and increased the hepatic content of glucose 6-phosphate, pyruvate and lactate. 8. It is concluded that (a) there is no short-term link between the rate of protein synthesis and lipogenesis in the lactating mammary gland and (b) the increased rate of hepatic lipogenesis in cycloheximide-treated rats is mainly due to stimulation of glycogenolysis, glycolytic flux and consequent increased availability of pyruvate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agius L., Blackshear P. J., Williamson D. H. Rates of triacylglycerol entry into the circulation in the lactating rat. Biochem J. 1981 May 15;196(2):637–640. doi: 10.1042/bj1960637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Maritz G., Turner R. C. A sensitive, precise radioimmunoassay of serum insulin relying on charcoal separation of bound and free hormone moieties. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Jul;70(3):487–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., Denton R. M., Jeanrenaud B. Stimulation of hepatic lipogenesis and acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase by vasopressin. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):485–490. doi: 10.1042/bj1980485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-On H., Stein O., Stein Y. Mulitiple effects of cycloheximide on the metabolism of triglycerides in the liver of male and female rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 11;270(4):444–452. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter M. A., Goheer M. A., Coore H. G. Absent pyruvate inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase in lactating rat mammary gland following various treatments. Removal of circulating insulin and prolactin and exposure to protein synthesis inhibitors. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 1;97(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capuzzi D. M., Rothman V., Margolis S. The regulation of lipogenesis by cyclic nucleotides in intact hepatocytes prepared by a simplified technique. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1286–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecil H. C., Bitman J. Inhibition of estrogen-induced glycogen synthesis in the rat uterus by cycloheximide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Mar;119(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90434-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOHORST H. J., KREUTZ F. H., BUECHER T. [On the metabolite content and the metabolite concentration in the liver of the rat]. Biochem Z. 1959;332:18–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Insulin and the regulation of adipose tissue acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1320509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. A. Studies on the inhibition of hepatic lipogenesis by N-6,O-2'-dibutyryl adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jul;169(1):168–180. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90330-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. A., Williamson D. H. Measurements of substrate uptake by mammary gland of the rat. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(5):1171–1173. doi: 10.1042/bj1291171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L., Van Schaftingen E., Blackmore P. F. Stimulation of glycolysis and accumulation of a stimulator of phosphofructokinase in hepatocytes incubated with vasopressin. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 15;194(3):1023–1026. doi: 10.1042/bj1941023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Jacobs R., Smith M. B., Morris H. P. The regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis in rat hepatomas. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3588–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otway S., Robinson D. S. The use of a non-ionic detergent (Triton WR 1339) to determine rates of triglyceride entry into the circulation of the rat under different physiological conditions. J Physiol. 1967 May;190(2):321–332. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. M., Girard J. R., Williamson D. H. Evidence for a role of insulin in the regulation of lipogenesis in lactating rat mammary gland. Measurements of lipogenesis in vivo and plasma hormone concentrations in response to starvation and refeeding. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):343–346. doi: 10.1042/bj1760343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. M., Williamson D. H. Comparison of glucose metabolism in the lactating mammary gland of the rat in vivo and in vitro. Effects of starvation, prolactin or insulin deficiency. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):153–159. doi: 10.1042/bj1640153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M. Factors affecting lipoprotein metabolism. Adv Lipid Res. 1965;3:63–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansbie D., Brownsey R. W., Crettaz M., Denton R. M. Acute effects in vivo of anti-insulin serum on rates of fatty acid synthesis and activities of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase in liver and epididymal adipose tissue of fed rats. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):413–416. doi: 10.1042/bj1600413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLLENBERGER A., RISTAU O., SCHOFFA G. [A simple technic for extremely rapid freezing of large pieces of tissue]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;270:399–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., McKeown S. R., Ilic V. Interactions of glucose, acetoacetate and insulin in mammary-gland slices of lactating rats. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;150(2):145–152. doi: 10.1042/bj1500145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wititsuwannakul D., Kim K. H. Mechanism of glycogenolytic action of cycloheximide in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):1007–1012. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



