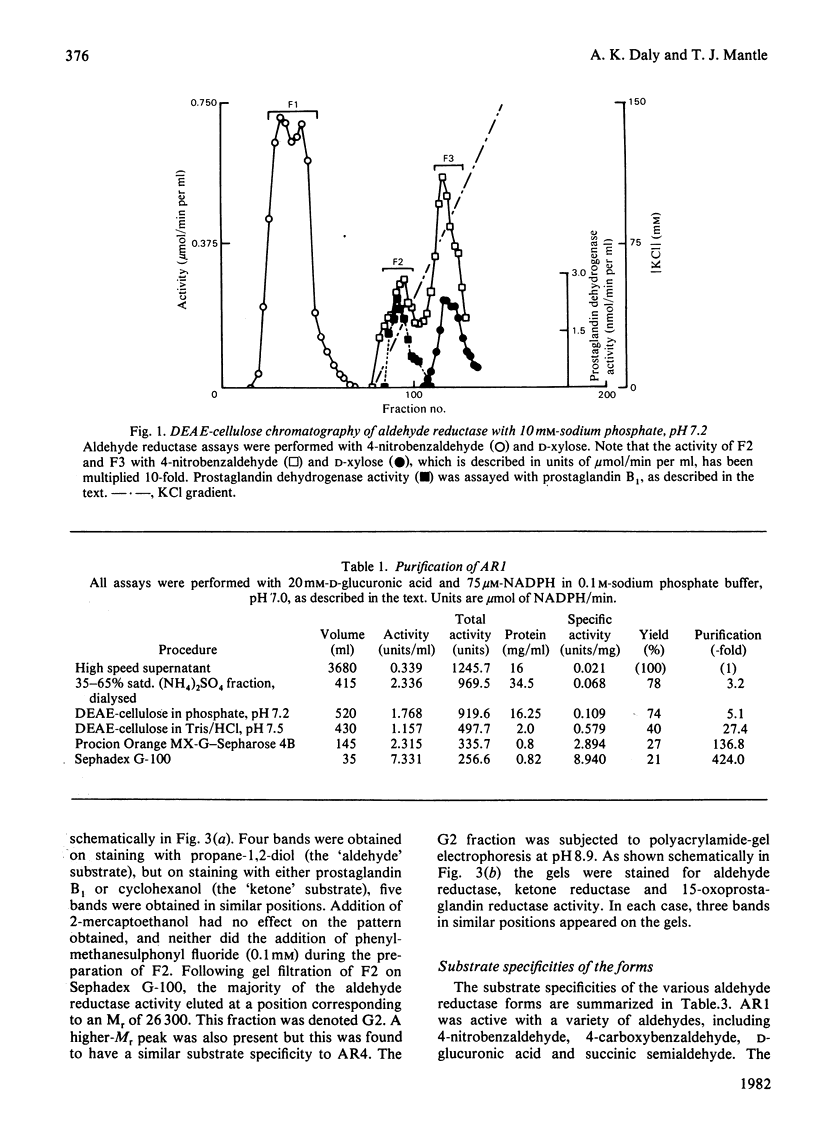
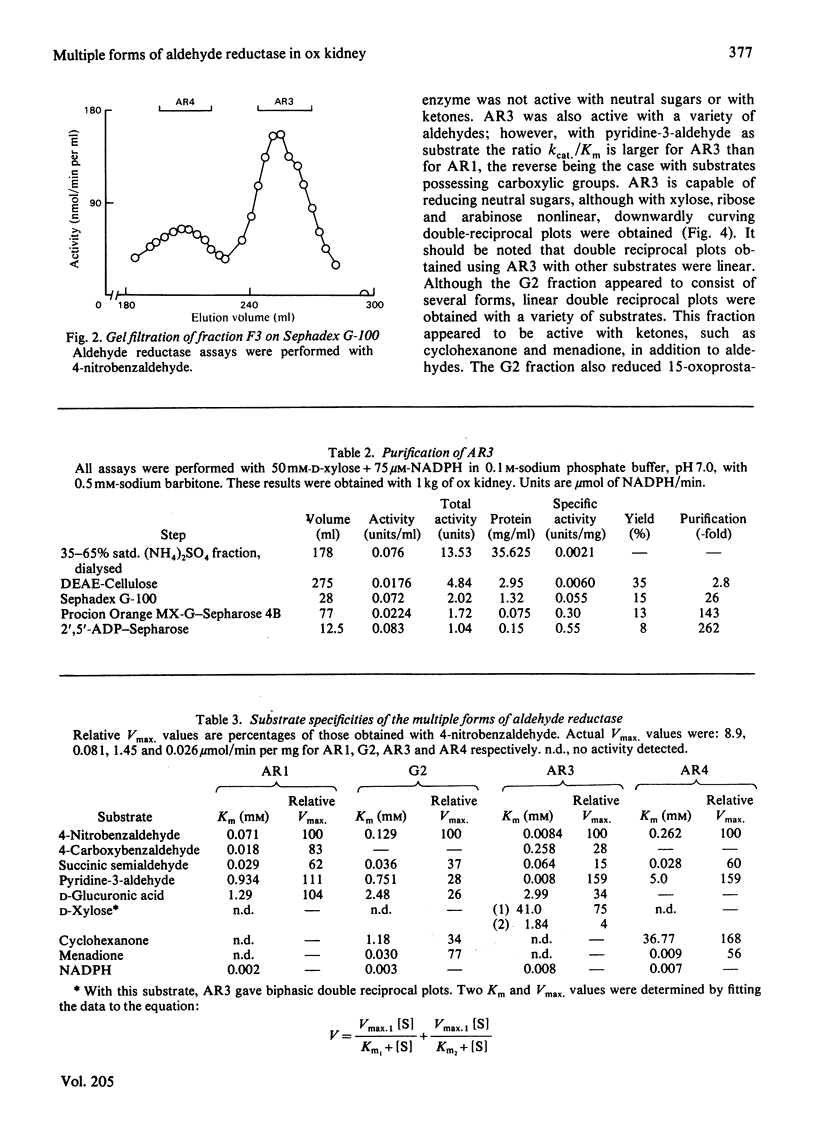
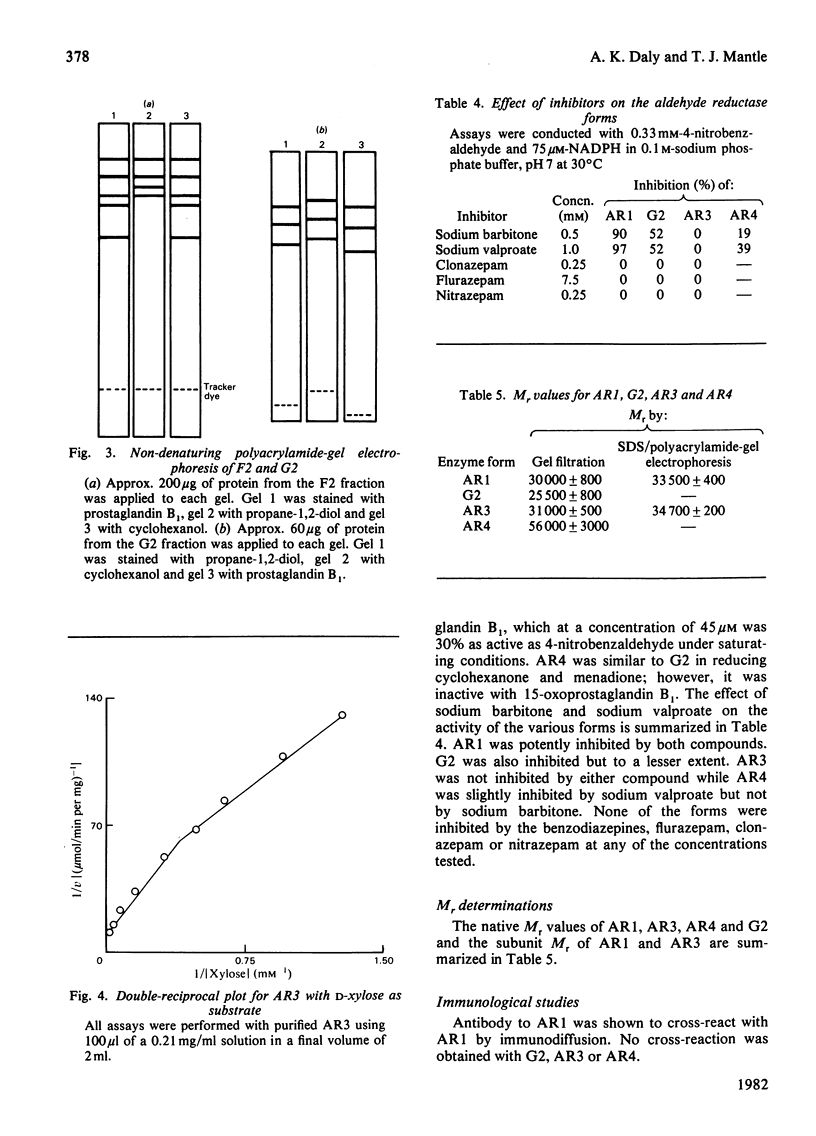
Abstract
Aldehyde reductase from ox kidney cytosol has been fractionated into four forms, two of which have been purified to apparent homogeneity. One of the minor forms is shown to be heterogenous on polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. The substrate specificities of the four forms using a variety of aldehydes and ketones are presented. The sensitivity of the various forms to inhibition by sodium valproate, sodium barbitone and various benzodiazepines has been determined. The relationship of these forms to the previously described hexonate dehydrogenase, aldose reductase and prostaglandin dehydrogenase is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachur N. R. Cytoplasmic aldo-keto reductases: a class of drug metabolizing enzymes. Science. 1976 Aug 13;193(4253):595–597. doi: 10.1126/science.959821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird J. K., Sherwood R. F., Carr R. J., Atkinson A. Enzyme purification by substrate elution chromatography from procion dye-polysaccharide matrices. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80726-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosron W. F., Prairie R. L. Reduced triphosphopyridine-liked aldehyde reductase. II. Species and tissue distribution. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):166–172. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosron W. F., Prairie R. L. Triphosphopyridine nucleotide-linked aldehyde reductase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme from pig kidney cortex. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4480–4485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite S. S., Jarabak J. Studies on a 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase from human placenta. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2315–2318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant G., Biellmann J. F. Purification and some properties of aldehyde reductases from pig liver. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(3):611–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash C. D., Maitre M., Mandel P. Purification from human brain and some properties of two NADPH-linked aldehyde reductases which reduce succinic semialdehyde to 4-hydroxybutyrate. J Neurochem. 1979 Dec;33(6):1169–1175. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. G., Tai H. H. Prostaglandin 9-ketoreductase/type II 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase is not a prostaglandin specific enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Aug 14;101(3):898–904. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91834-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee I. B. Evolution and the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid. Science. 1973 Dec 21;182(4118):1271–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4118.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbe M. J., Halder A. B. Affinity chromatography of bovine lens aldose reductase, and a comparison of some kinetic properties of the enzyme from lens and human erythrocyte [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Apr;8(2):194–195. doi: 10.1042/bst0080194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. S., Flynn T. G. Kinetics and mechanism of action of aldehyde reductase from pig kidney. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 1;177(2):595–601. doi: 10.1042/bj1770595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. S., Walton D. J., Flynn T. G. A comparative study of the tissue and species distribution of NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1978;60(3):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(78)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dons R. F., Doughty C. C. Isolation and characterization of aldose reductase from calf brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 8;452(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn T. G., Shires J., Walton D. J. Properties of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent aldehyde reductase from pig kidney. Amino acid composition, reactivity of cysteinyl residues, and stereochemistry of D-glyceraldehyde reduction. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2933–2940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbay K. H., O'Sullivan J. B. The sorbitol pathway in diabetes and galactosemia: enzyme and sobstrate localization and changes in kidney. Diabetes. 1968;17:300–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G. [Aldose reductase]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jan 1;37:120–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. L., Wermuth B., von Wartburg J. P. Human brain aldehyde reductases: relationship to succinic semialdehyde reductase and aldose reductase. J Neurochem. 1980 Aug;35(2):354–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb06272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morpeth F. F., Dickinson F. M. Kinetic studies of the mechanism of pig kidney aldehyde reductase. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):485–492. doi: 10.1042/bj1930485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morpeth F. F., Dickinson F. M. Some properties of pig kidney-cortex aldehyde reductase. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):619–626. doi: 10.1042/bj1910619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips O., Mantle T. J. Some kinetic and physical properties of biliverdin reductase. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Aug;9(4):275–278. doi: 10.1042/bst0090275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ris M. M., von Wartburg J. P. Heterogeneity of NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase from human and rat brain. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 1;37(1):69–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J., Smith I. L., Tipton K. F. Purification of the high-Km aldehyde reductase from rat brain and liver and from ox brain. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):473–481. doi: 10.1042/bj1970473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Hara A., Kato F., Nakayama T. Purification and properties of reductases for aromatic aldehydes and ketones from guinea pig liver. J Biochem. 1979 Oct;86(4):871–881. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Hara A., Nakayama T., Kato F. Reductases for aromatic aldehydes and ketones from rabbit liver. Purification and characterization. J Biochem. 1980 Apr;87(4):1153–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Hara A. The presence of two NADPH-linked aromatic aldehyde-ketone reductases different from aldehyde reductase in rabbit liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 1;28(7):1089–1094. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheaff C. M., Doughty C. C. Physical and kinetic properties of homogenous bovine lens aldose reductase. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2696–2702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabakoff B., Erwin V. G. Purification and characterization of a reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked aldehyde reductase from brain. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabakoff B., von Wartburg J. P. Separation of aldehyde reductases and alcohol dehydrogenase from brain by affinity chromatography: metabolism of succinic semialdehyde and ethanol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90662-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Touster Resolution and partial characterization of two aldehyde reductases of mammalian liver. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2545–2550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner A. J., Tipton K. F. The characterization of two reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked aldehyde reductases from pig brain. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):765–772. doi: 10.1042/bj1300765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wermuth B. Purification and properties of an NADPH-dependent carbonyl reductase from human brain. Relationship to prostaglandin 9-ketoreductase and xenobiotic ketone reductase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1206–1213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


