Abstract
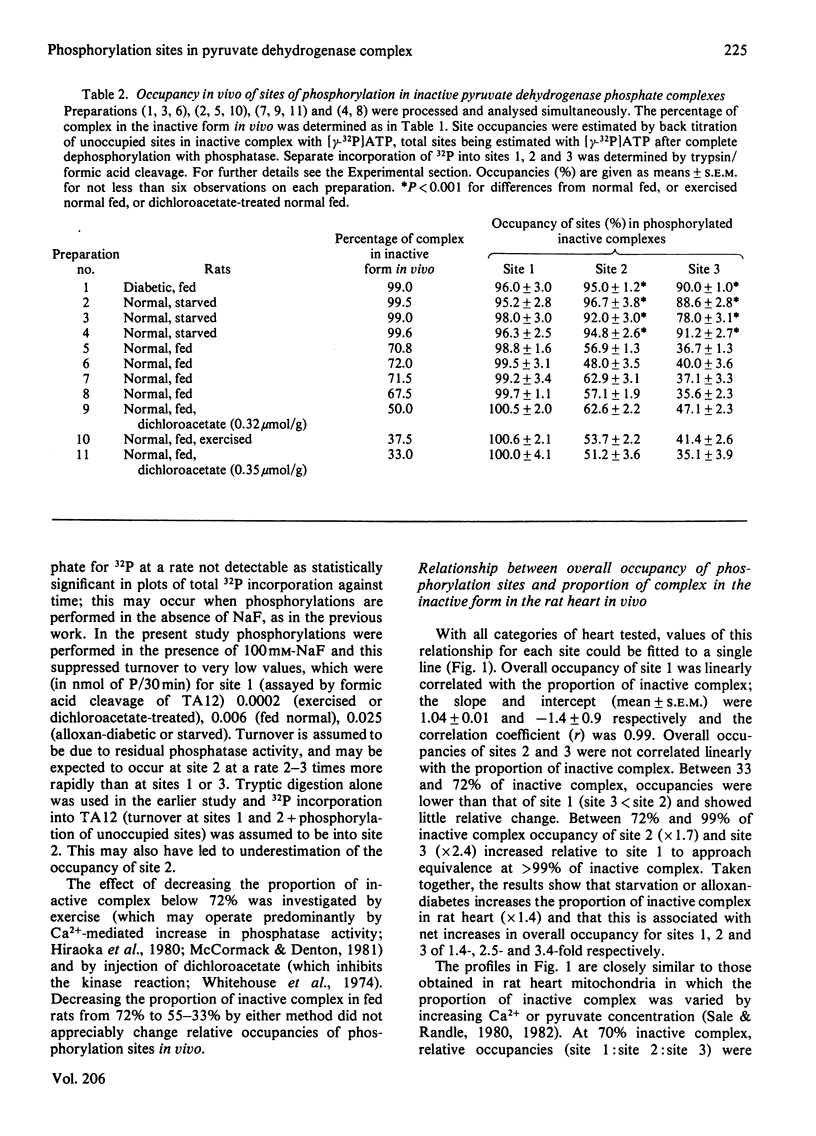
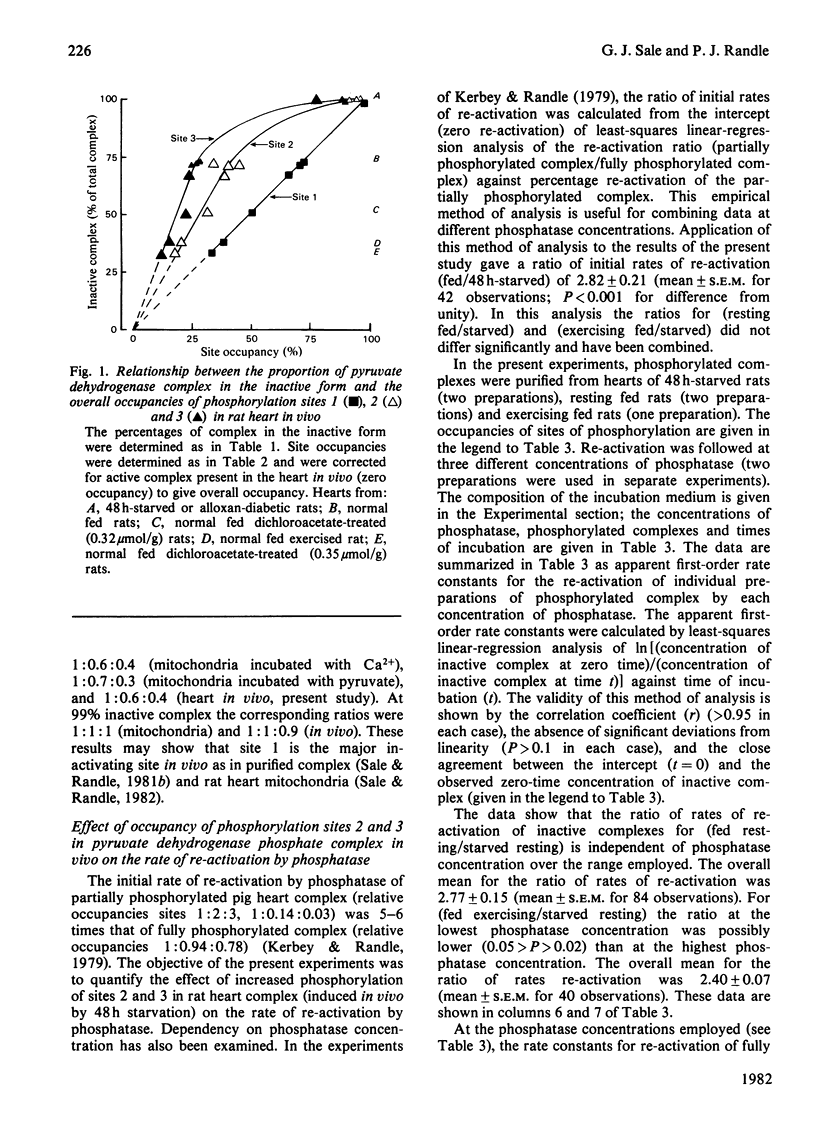
The [gamma-32P]ATP-back-titration method of estimating occupancy in vivo of the three phosphorylation sites in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex was improved in precision by specific analysis with trypsin/formic acid, by more effective prevention of site-2 dephosphorylation during purification with NaF, and by other refinements. Disproportionation of phosphorylated complexes during purification was excluded. With this improved method it was shown that the relationship between occupancy of sites and the proportion of complex in the inactive form in rat heart in vivo is closely similar to that measured directly in heart mitochondria by incorporation of [32P]Pi. In the heart in vivo (as in mitochondria), occupancy of site 1 correlated linearly with the proportion of inactive complex. Occupancy of sites 2 and 3 only approached equivalence to that of site 1 when 99% of the complex was inactive (starved or diabetic rats). When 70% or less of the complex was inactive (resting or exercising fed normal rats), occupancy of sites 2 and 3 was minimal (3 less than 2) relative to site 1. The initial rate of re-activation by phosphatase of phosphorylated complex from hearts of resting or exercising fed normal rats was approximately three times that of complex from 48 h-starved rats.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arce C. A., Barra H. S., Rodriguez J. A., Caputto R. Tentative identification of the amino acid that binds tyrosine as a single unit into a soluble brain protein. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 15;50(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka T., DeBuysere M., Olson M. S. Studies of the effects of beta-adrenergic agonists on the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in the perfused rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7604–7609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. A., Brownsey R. W., Denton R. M. Studies on the incorporation of [32P]phosphate into pyruvate dehydrogenase in intact rat fat-cells. Effects of insulin. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):469–481. doi: 10.1042/bj1920469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson N. J., Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J., Sugden P. H. Conversion of inactive (phosphorylated) pyruvate dehydrogenase complex into active complex by the phosphate reaction in heart mitochondria is inhibited by alloxan-diabetes or starvation in the rat. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):669–680. doi: 10.1042/bj1730669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson N. J., Randle P. J. Enhanced activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase in rat heart mitochondria in alloxan-diabetes or starvation. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 1;92(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80724-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Radcliffe P. M., Randle P. J., Sugden P. H. Regulation of kinase reactions in pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):427–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1810427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J., Cooper R. H., Whitehouse S., Pask H. T., Denton R. M. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat heart. Mechanism of regulation of proportions of dephosphorylated and phosphorylated enzyme by oxidation of fatty acids and ketone bodies and of effects of diabetes: role of coenzyme A, acetyl-coenzyme A and reduced and oxidized nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 15;154(2):327–348. doi: 10.1042/bj1540327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J., Kearns A. Dephosphorylation of pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate complexes by pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):51–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1950051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J. Role of multi-site phosphorylation in regulation of pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):485–488. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80594-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J. Thermolabile factor accelerates pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase reaction in heart mitochondria of starved or alloxan-diabetic rats. FEBS Lett. 1981 May 18;127(2):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresze G. B., Steber L. Inactivation and disassembly of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from bovine kidney by limited proteolysis with an enzyme from rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):569–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pettit F. H., Hucho F., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. XI. Comparative studies of regulatory properties of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes from kidney, heart, and liver mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):227–234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. X. Regulation of the activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from beef kidney mitochondria by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):234–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Denton R. M. The activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in the perfused rat heart by adrenaline and other inotropic agents. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 15;194(2):639–643. doi: 10.1042/bj1940639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe P. M., Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J. Inactivation of pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by adenosine-5'-O(3-thiotriphosphate). FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J., Denton R. M. Rate control by insulin and its mechanism. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1973;27:401–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. J., Randle P. J. Incorporation of [32P]phosphate into the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in rat heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1980 May 15;188(2):409–421. doi: 10.1042/bj1880409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. J., Randle P. J. Occupancy of sites of phosphorylation in inactive rat heart pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate in vivo. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):935–946. doi: 10.1042/bj1930935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. J., Randle P. J. Role of individual phosphorylation sites in inactivation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in rat heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):99–108. doi: 10.1042/bj2030099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Denton R. M., Pask H. T., Randle P. J. Calcium and magnesium ions as effectors of adipose-tissue pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):225–237. doi: 10.1042/bj1400225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. J., Perham R. N. Purification of 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes from ox heart by a new method. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):147–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1910147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Hutson N. J., Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J. Phosphorylation of additional sites on pyruvate dehydrogenase inhibits its re-activation by pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase. Biochem J. 1978 Feb 1;169(2):433–435. doi: 10.1042/bj1690433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J., Waller C. A., Reid K. B. Amino acid sequences around the sites of phosphorylation in the pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):419–426. doi: 10.1042/bj1810419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Simister N. E. Role of multisite phosphorylation in the regulation of ox kidney pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 10;111(2):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80814-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teague W. M., Pettit F. H., Yeaman S. J., Reed L. J. Function of phosphorylation sites on pyruvate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 15;87(1):244–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91672-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Kearns A., Randle P. J. Pig heart [35S]thiophosphoryl pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;122(3):549–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Cooper R. H., Randle P. J. Mechanism of activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by dichloroacetate and other halogenated carboxylic acids. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):761–774. doi: 10.1042/bj1410761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman S. J., Hutcheson E. T., Roche T. E., Pettit F. H., Brown J. R., Reed L. J., Watson D. C., Dixon G. H. Sites of phosphorylation on pyruvate dehydrogenase from bovine kidney and heart. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2364–2370. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


