Abstract
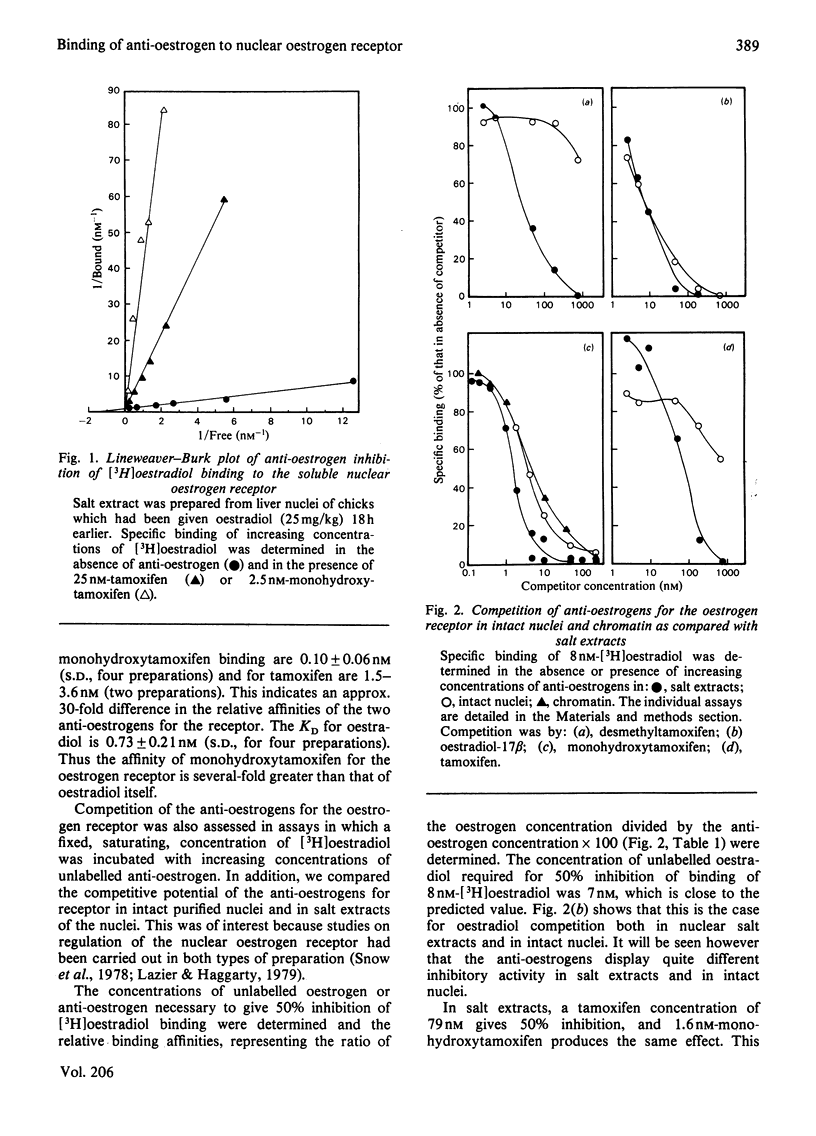
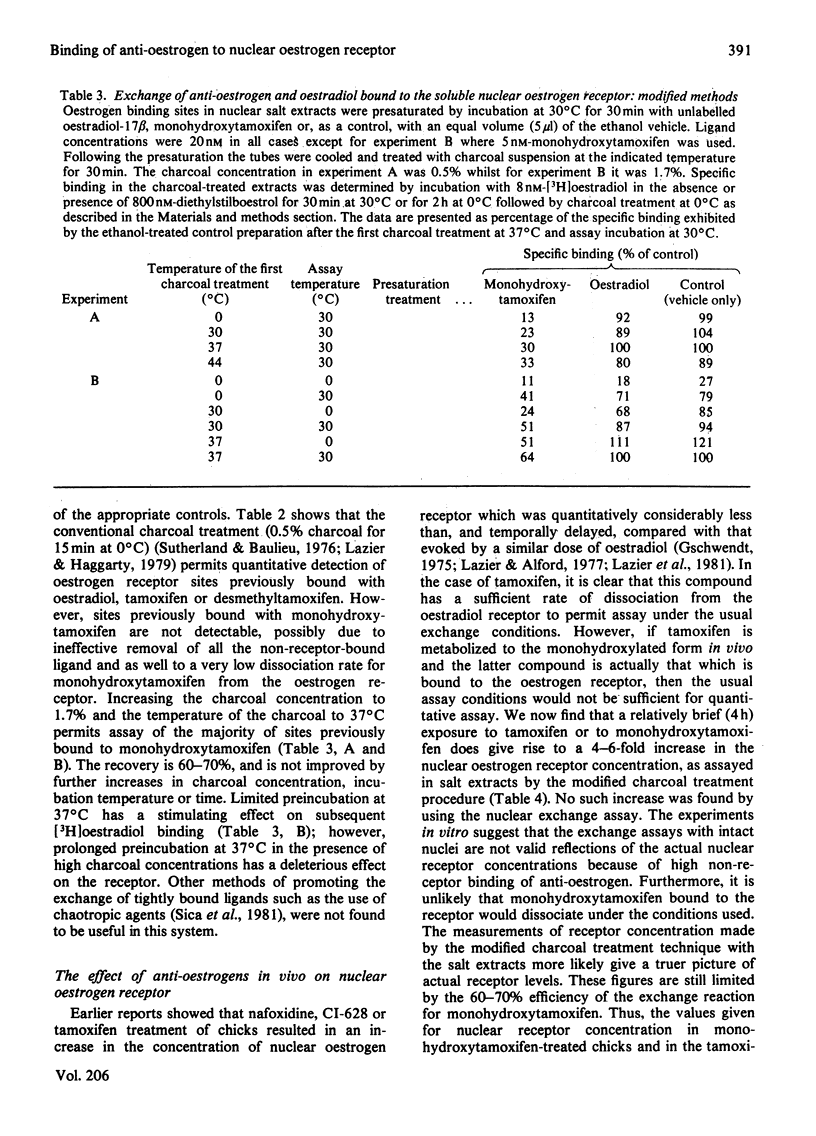
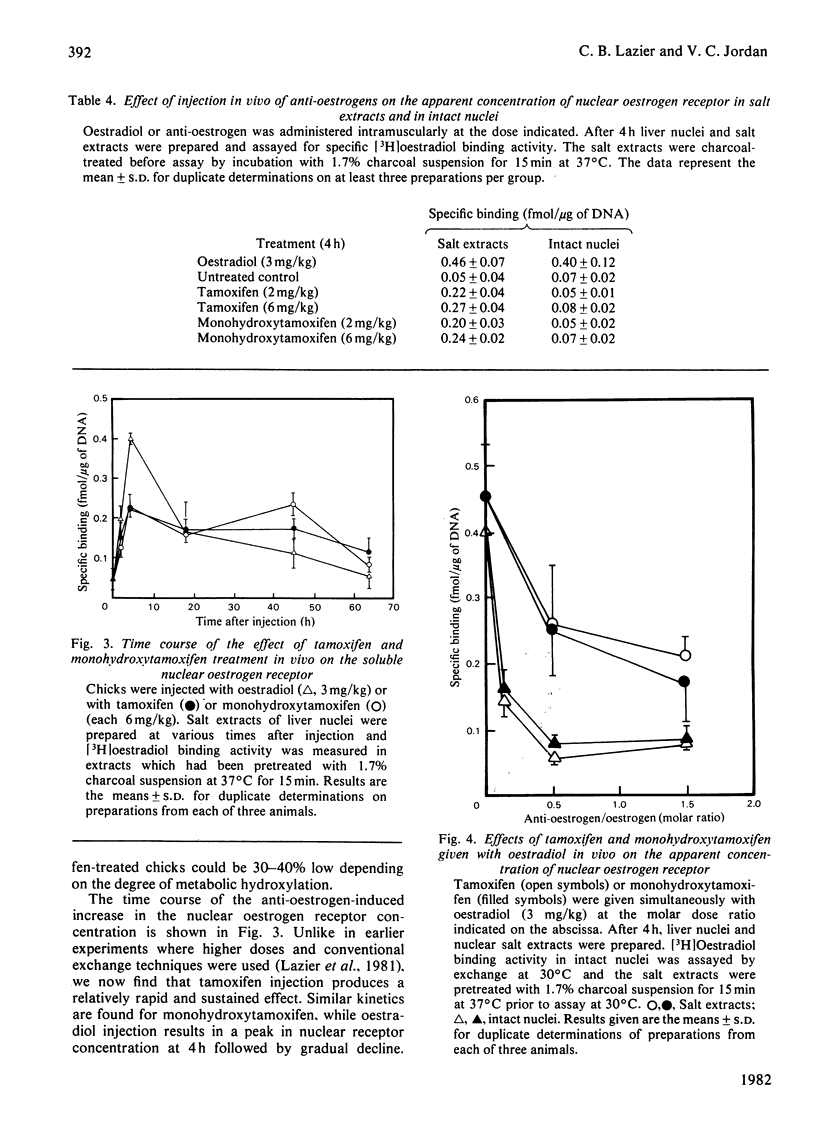
Tamoxifen is a potent inhibitor of specific oestrogen-induced yolk protein synthesis by chicken liver. The oestradiol receptor in salt extracts of liver nuclei from oestrogen-treated chicks has a Kd for oestradiol of 0.7±0.2nm. Tamoxifen and its metabolite, monohydroxytamoxifen, compete for binding to the salt-soluble nuclear receptor with Ki values of 2.6 and 0.1nm respectively. The anti-oestrogens show much less inhibition of [3H]oestradiol binding when assays are carried out using intact nuclei. The competition by unlabelled oestradiol for [3H]oestradiol binding to receptor is identical in both salt extracts and intact nuclei. This suggests that intact nuclei contain components which bind anti-oestrogens, but not oestradiol. While tamoxifen and desmethyltamoxifen will readily dissociate from the salt-soluble nuclear oestrogen receptor, monohydroxytamoxifen does not dissociate under the conditions generally used for exchange assays. A modified assay was developed in which 60–70% of monohydroxytamoxifen-bound sites were shown to be exchangeable for [3H]oestradiol. Soluble receptor preparations were first incubated in a 1.7% charcoal suspension at 37°C for 15min before assay of specific oestradiol binding. This technique was used in examining the effects of tamoxifen and monohydroxytamoxifen given in vivo on the nuclear oestrogen receptor concentration. Despite their 30-fold difference in binding affinity for the receptor, both anti-oestrogens increase nuclear receptor levels to about the same degree. When given with oestradiol, both compounds have the same apparent partial inhibitory effect on the oestrogen-induced increase in nuclear receptor. These data are consistent with the metabolic hydroxylation of tamoxifen before binding to the hepatic oestrogen receptor.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam H. K., Douglas E. J., Kemp J. V. The metabolism of tamoxifen in human. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979;28(1):145–147. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen K. E., Clark E. R., Jordan V. C. Evidence for the metabolic activation of non-steroidal antioestrogens: a study of structure-activity relationships. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(1):83–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10912.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binart N., Catelli M. G., Geynet C., Puri V., Hähnel R., Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Monohydroxytamoxifen: an antioestrogen with high affinity for the chick oviduct oestrogen receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):812–818. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91952-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgna J. L., Rochefort H. High-affinity binding to the estrogen receptor of [3H]4-hydroxytamoxifen, an active antiestrogen metabolite. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1980 Oct;20(1):71–85. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(80)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgna J. L., Rochefort H. Hydroxylated metabolites of tamoxifen are formed in vivo and bound to estrogen receptor in target tissues. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):859–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouton M. M., Raynaud J. P. The relevance of kinetic parameters in the determination of specific binding to the estrogen receptor. J Steroid Biochem. 1978 Jan;9(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(78)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capony F., Williams D. L. Antiestrogen action in avian liver: the interaction of estrogens and antiestrogens in the regulation of apolipoprotein B synthesis. Endocrinology. 1981 May;108(5):1862–1868. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-5-1862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capony F., Williams D. L. Apolipoprotein B of avian very low density lipoprotein: characteristics of its regulation in nonstimulated and estrogen-stimulated rooster. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2219–2226. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. H., Peck E. J., Jr, Anderson J. N. Oestrogen receptors and antagonism of steroid hormone action. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):446–448. doi: 10.1038/251446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M. The effect of antiestrogens on egg yolk protein synthesis and estrogen-binding to chromatin in the rooster liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 13;399(2):395–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. R., Rorke E. A., Robertson D. W., Katzenellenbogen B. S., Katzenellenbogen J. A. Biological potency and uterine estrogen receptor interactions of the metabolites of the antiestrogens CI628 and U23,469. Endocrinology. 1981 Jan;108(1):164–172. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-1-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., Koseki Y., McGuire W. L. Estrogen control of progesterone receptor in human breast cancer: role of estradiol and antiestrogen. Endocrinology. 1978 Nov;103(5):1742–1751. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-5-1742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., McGuire W. L. Nuclear mechanisms of estrogen action. Effects of estradiol and anti-estrogens on estrogen receptors and nuclear receptor processing. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8185–8191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan V. C., Collins M. M., Rowsby L., Prestwich G. A monohydroxylated metabolite of tamoxifen with potent antioestrogenic activity. J Endocrinol. 1977 Nov;75(2):305–316. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0750305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan V. C., Dix C. J. Effect of oestradiol benzoate, tamoxifen and monohydroxytamoxifen on immature rat uterine progesterone receptor synthesis and endometrial cell division. J Steroid Biochem. 1979 Jul;11(1A):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(79)90310-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan V. C., Dix C. J., Rowsby L., Prestwich G. Studies on the mechanism of action of the nonsteroidal antioestrogen tamoxifen (I.C.I. 46,474) in the rat. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1977 Apr;7(2):177–192. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(77)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan V. C., Prestwich G. Effect of non-steroidal anti-oestrogens on the concentration of rat uterine progesterone receptors. J Endocrinol. 1978 Feb;76(2):363–364. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0760363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen B. S., Pavlik E. J., Robertson D. W., Katzenellenbogen J. A. Interaction of a high affinity anti-estrogen (alpha-[4-pyrrolidinoethoxy]phenyl-4-hydroxy-alpha'-nitrostilbene, CI628M) with uterine estrogen receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2908–2915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazier C. B., Alford W. S. Interaction of the anti-oestrogen, nafoxidine hydrochloride, with the soluble nuclear oestradiol-binding protein in chick liver. Biochem J. 1977 Jun 15;164(3):659–667. doi: 10.1042/bj1640659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazier C. B., Haggarty A. J. A high-affinity oestrogen-binding protein in cockerel liver cytosol. Biochem J. 1979 May 15;180(2):347–353. doi: 10.1042/bj1800347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazier C. B. Ontogeny of the vitellogenic response to oestradiol and of the soluble nuclear oestrogen receptor in embryonic-chick liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):143–152. doi: 10.1042/bj1740143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochefort H., Borgna J. L. Differences between oestrogen receptor activation by oestrogen and antioestrogen. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):257–259. doi: 10.1038/292257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochefort H., Garcia M., Borgna J. L. Absence of correlation between antiestrogenic activity and binding affinity for the estrogen receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sica V., Weisz A., Petrillo A., Armetta I., Puca G. A. Assay of total estradiol receptor in tissue homogenate and tissue fractions by exchange with sodium thiocyanate at low temperature. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):686–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow L. D., Eriksson H., Hardin J. W., Chan L., Jackson R. L., Clark J. H., Means A. R. Nuclear estrogen receptor in the avian liver: correlation with biologic response. J Steroid Biochem. 1978 Nov;9(11):1017–1026. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(78)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R. L., Baulieu E. E. Quantitative estimates of cytoplasmic and nuclear oestrogen receptors in chick oviduct. Effect of oestrogen on receptor concentration and subcellular distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):531–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R. L. Estrogen antagonists in chick oviduct: antagonist activity of eight synthetic triphenylethylene derivatives and their interactions with cytoplasmic and nuclear estrogen receptors. Endocrinology. 1981 Dec;109(6):2061–2068. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-6-2061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R. L., Murphy L. C., San Foo M., Green M. D., Whybourne A. M., Krozowski Z. S. High-affinity anti-oestrogen binding site distinct from the oestrogen receptor. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):273–275. doi: 10.1038/288273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R., Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Tamoxifen is a potent "pure" anti-oestrogen in chick oviduct. Nature. 1977 Jun 2;267(5610):434–435. doi: 10.1038/267434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenius L. Structure-activity relationships of anti-oestrogens with regard to interaction with 17-beta-oestradiol in the mouse uterus and vagina. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1971 Mar;66(3):431–447. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0660431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



