Abstract
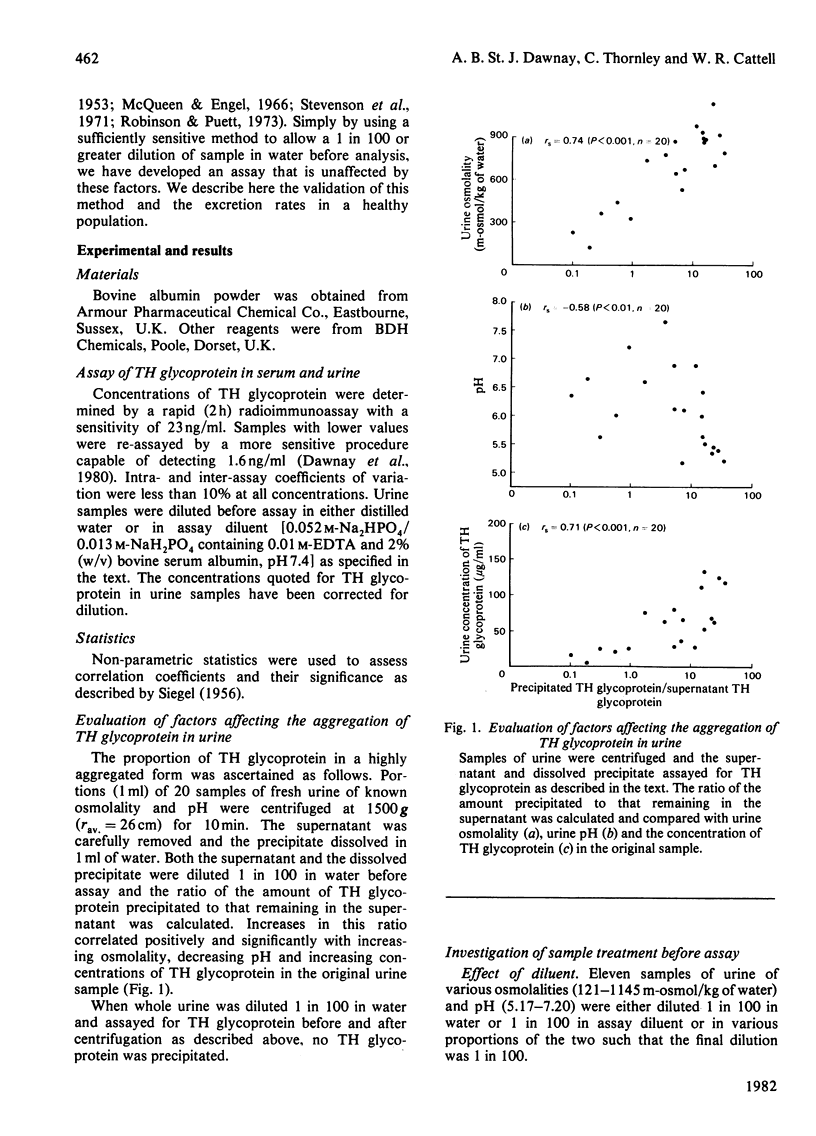
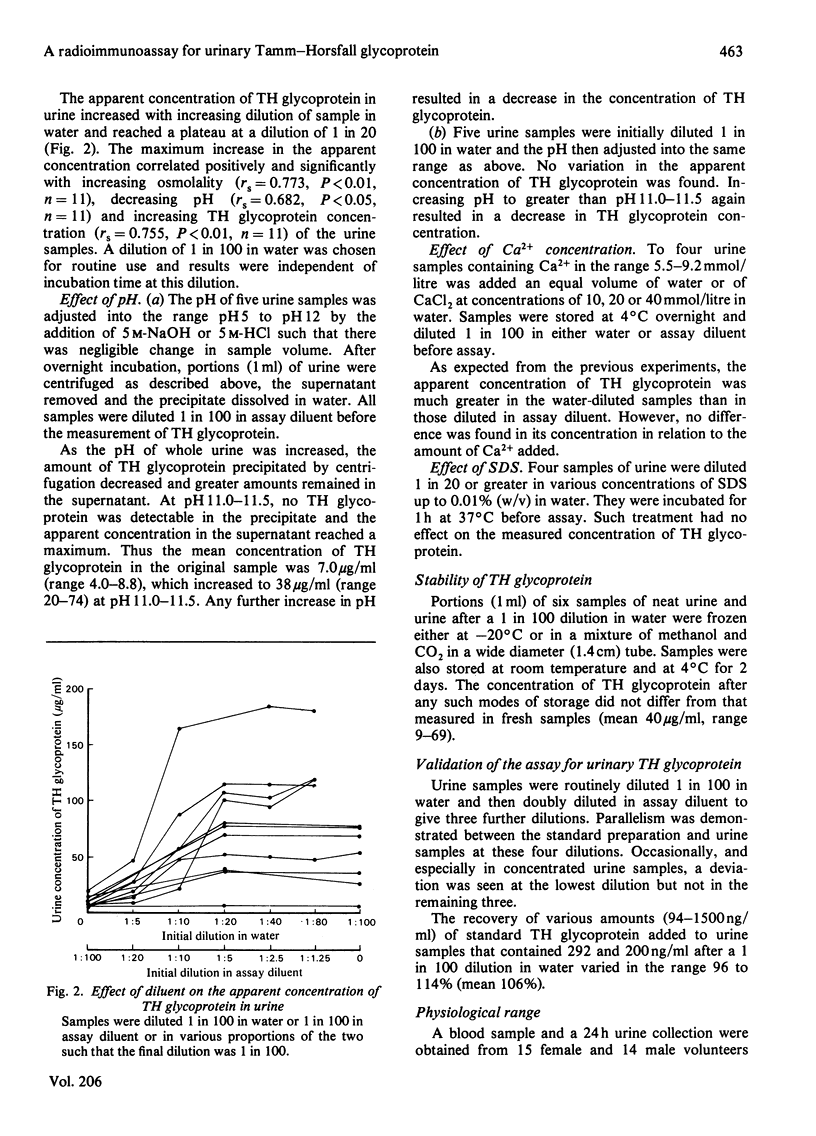
A rapid, specific radioimmunoassay has been used to measure Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein (TH glycoprotein) in urine. The apparent concentration increased with increasing dilution of urine in water, reaching a plateau at 1 in 20. This increase was greater the higher the osmolality and TH glycoprotein concentration and the lower the pH of the original sample. A dilution of 1 in 100 was chosen for routine assay. Whole urine was centrifuged and the dissolved precipitate and supernatant assayed to quantify the proportion of TH glycoprotein of TH glycoprotein initially present in highly aggregated form. This correlated positively and significantly with increasing osmolality, decreasing pH and increasing TH glycoprotein concentration. When the urine was diluted 1 in 100 in water, no TH glycoprotein was precipitated by centrifugation and the measured concentrations were unaffected by alterations of urine pH or calcium concentration or by addition of sodium dodecyl sulphate. Parallelism was demonstrated between the diluted samples and the disaggregated standard preparation. Recovery of added standard to diluted urine varied between 96 and 114%. The apparent concentration of TH glycoprotein in neat or diluted urine was not affected by freezing or by storage at 4 degrees C or room temperature for at least 2 days. A physiological range for the urinary excretion rate was established as 22--56 mg/24 h, based on samples from 29 individuals with normal renal function, as defined by their creatinine clearance. There was no significant correlation between serum concentrations of TH glycoprotein and its urinary excretion rate, nor between urinary excretion rate and creatinine clearance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akesson I., Haugen H., Enger E. Quantification of uromucoid: a simplified method. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1978 Feb;38(1):93–95. doi: 10.3109/00365517809108409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avis P. J. The development of a radioimmunoassay procedure for the estimation of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein in human serum. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Feb;52(2):183–191. doi: 10.1042/cs0520183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichler K. H., Haupt H., Uhlemann G., Schwick H. G. Human uromucoid. I. Quantitative immunoassay. Urol Res. 1973 May;1(2):50–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00256119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichler K. H., Kirchner C., Ideler V. Uromucoid excretion of normal individuals and stone formers. Br J Urol. 1975;47(7):733–737. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1975.tb04050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTAIN C. C. The viscometric behaviour of a mucoprotein isolated from human urine. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1953 Jun;31(3):255–265. doi: 10.1038/icb.1953.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawnay A., McLean C., Cattell W. R. The development of a radioimmunoassay for Tamm--Horsfall glycoprotein in serum. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 1;185(3):679–687. doi: 10.1042/bj1850679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall A. A., Marshall R. D. Effects of freezing on the estimated amounts of Tamm--Horsfall glycoprotein in urine, as determined by radioimmunoassay. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):533–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1890533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall A. A., Marshall R. D. Problems relating to the storage and treatment of urine samples before radioimmunoassay for Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(5):1043–1047. doi: 10.1042/bst0061043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant A. M., Baker L. R., Neuberger A. Urinary Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein in certain kidney diseases and its content in renal and bladder calculi. Clin Sci. 1973 Apr;44(4):377–384. doi: 10.1042/cs0440377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant A. M., Neuberger A. The development of a radioimmunoassay for the measurement of urinary Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate. Clin Sci. 1973 Feb;44(2):163–179. doi: 10.1042/cs0440163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallson P. C., Rose G. A. Uromucoids and urinary stone formation. Lancet. 1979 May 12;1(8124):1000–1002. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92755-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen H., Akesson I., Enger E., Meberg A. Uromucoid in normal urine. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1978 Feb;38(1):49–51. doi: 10.3109/00365517809108402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer J. R., Sisson S. P., Vernier R. L. Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein: ultrastructural immunoperoxidase localization in rat kidney. Lab Invest. 1979 Aug;41(2):168–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKENZIE J. K., PATEL R., MCQUEEN E. G. THE EXCRETION RATE OF TAMM-HORSFALL URINARY MUCOPROTEIN IN NORMALS AND IN PATIENTS WITH RENAL DISEASE. Australas Ann Med. 1964 Feb;13:32–39. doi: 10.1111/imj.1964.13.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzuchi N., Pecarovich R., Ross N., Rodríguez I., Sanguinetti C. M. Tamm-Horsfall urinary glycoprotein quantitation by radial immunodiffusion: normal patterns. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Nov;84(5):771–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen E. G., Engel G. B. Factors determining the aggregation of urinary mucoprotein. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jul;19(4):392–396. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.4.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATEL R., MCKENZIE J. K., MCQUEEN E. G. TAMM-HORSFALL URINARY MUCOPROTEIN AND TUBULAR OBSTRUCTION BY CASTS IN ACUTE RENAL FAILURE. Lancet. 1964 Feb 29;1(7331):457–461. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90794-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuell C. T. A modified electroimmunoassay technique for uromucoid in urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 May 2;85(3):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikri K. L., Foster C. L., Bloomfield F. J., Marshall R. D. Localization by immunofluorescence and by light- and electron-microscopic immunoperoxidase techniques of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein in adult hamster kidney. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 1;181(3):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1810525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikri K. L., Foster C. L., MacHugh N., Marshall R. D. Localization of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein in the human kidney using immuno-fluorescence and immuno-electron microscopical techniques. J Anat. 1981 Jun;132(Pt 4):597–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. K., Cleave A. J., Kent P. W. The effect of ions on the viscometric and ultracentrifugal behaviour of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 27;236(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., HORSFALL F. L., Jr Characterization and separation of an inhibitor of viral hemagglutination present in urine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 May;74(1):106–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander J., Bygren P., Heinegård D. Determination of the Tamm and Horsfall glycoprotein in human urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Aug 1;78(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


