Abstract
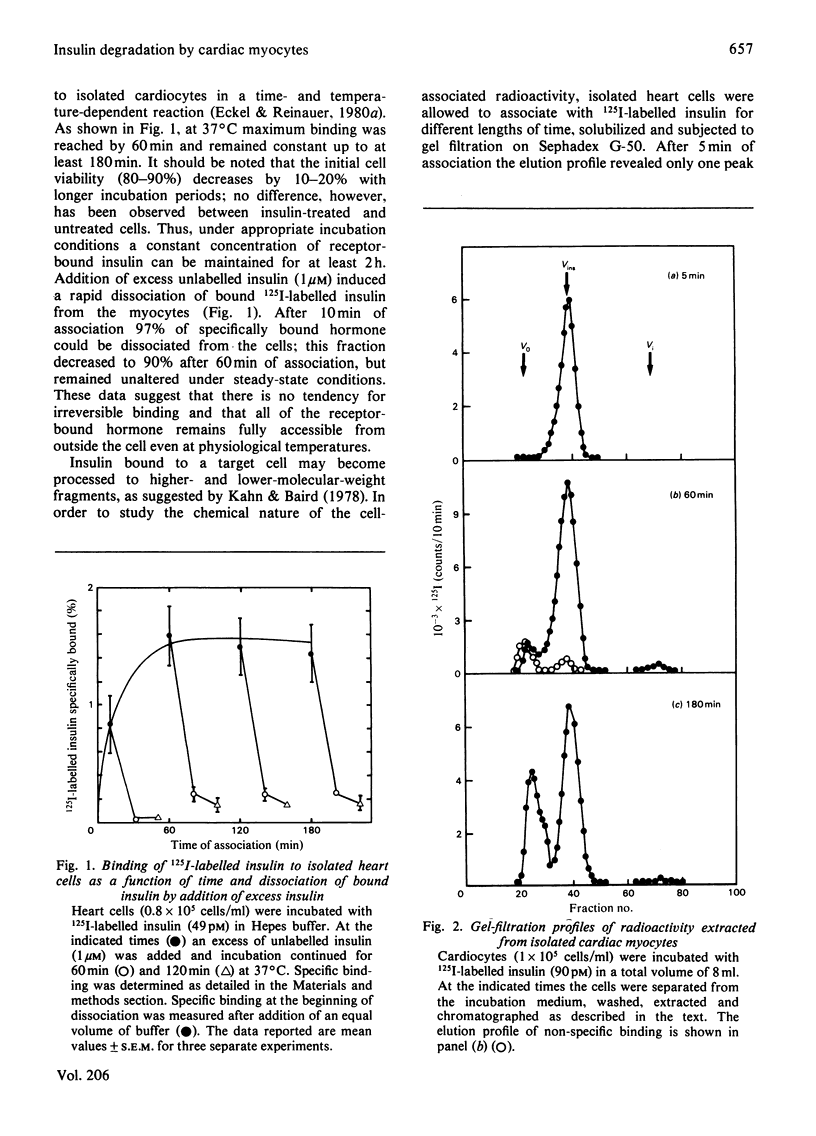
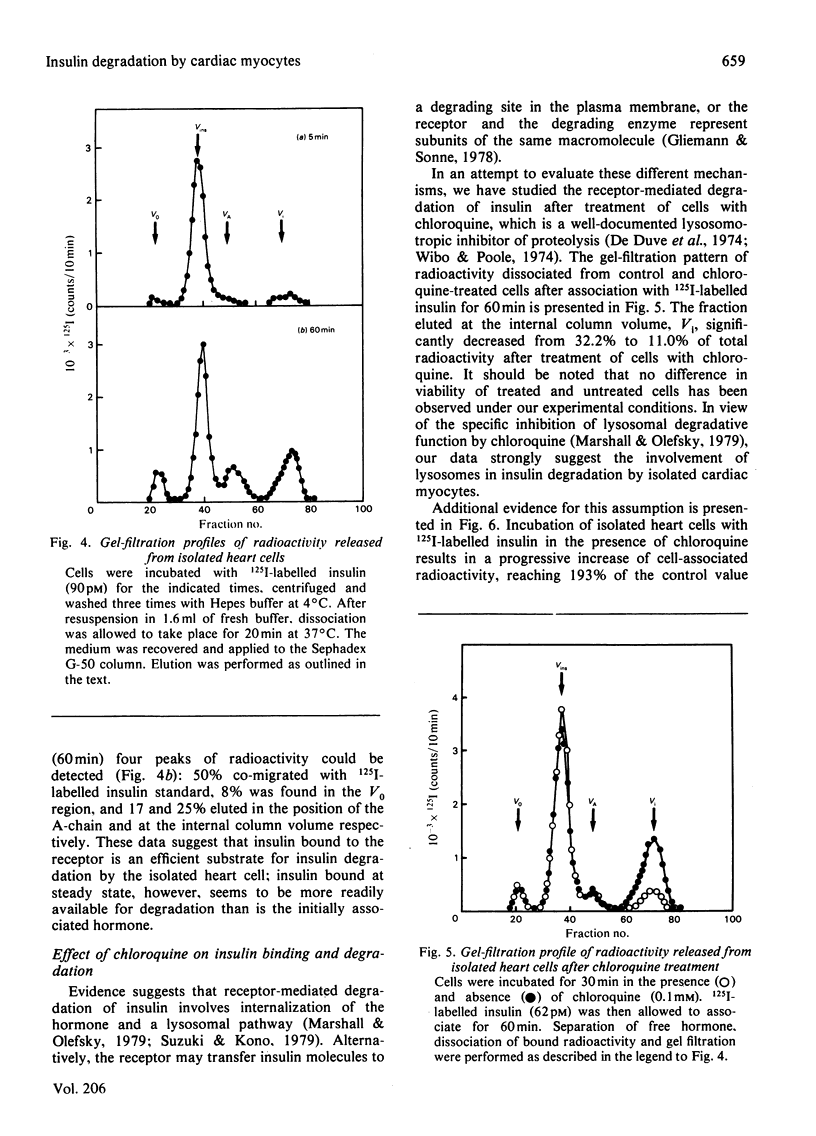
Isolated muscle cells from adult rat heart were used to study myocardial degradation of insulin and the reactions after the initial binding event. After 60 min of association at 37 degrees C, 90% of specifically bound insulin could be dissociated from the cells; this fraction remained unaltered under steady-state conditions (up to 180 min). To assess the nature of cell-associated radioactivity, cardiocytes were solubilized and filtered on Sephadex G-50. After 5 min of association only intact insulin was observed, whereas under steady-state conditions 4% of 125I-labelled insulin bound to the cells was degraded to iodotyrosine-containing fragments. The Km for insulin degradation by isolated heart cells was estimated to be 1.75 x 10(-7)M. Receptor-mediated insulin degradation was studied by examination of the nature of radioactivity released by the cells after different times of association. After 5 min 83% of dissociating material consisted of intact insulin, whereas this fraction decreased to 50% under steady-state conditions. Treatment of cells with the lysosomotropic agent chloroquine (0.1 mM) significantly decreased the fraction that was eluted at the internal column volume. This study demonstrates that insulin degradation by the heart cell occurs by a receptor-independent and a receptor-dependent mechanism. The latter may involve internalization and a lysosomal pathway.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschuld R., Gibb L., Ansel A., Hohl C., Kruger F. A., Brierley G. P. Calcium tolerance of isolated rat heart cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1980 Dec;12(12):1383–1395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(80)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron J. J., Posner B. I., Josefsberg Z., Sikstrom R. Intracellular polypeptide hormone receptors. The demonstration of specific binding sites for insulin and human growth hormone in Golgi fractions isolated from the liver of female rats. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):4058–4066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghen G. A., Kitabchi A. E., Brush J. S. Characterization of a rat liver protease with specificity for insulin. Endocrinology. 1972 Sep;91(3):633–642. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-3-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Amherdt M., Van Obberghen E., Kahn C. R., Orci L. 125I-insulin binding to cultured human lymphocytes. Initial localization and fate of hormone determined by quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1057–1070. doi: 10.1172/JCI109005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Barazzone P., Freychet P., Le Cam A., Orci L. Intracellular localization of 125I-labeled insulin in hepatocytes from intact rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2803–2807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Gorden P., Freychet P., Le Cam A., Orci L. Lysosomal association of internalized 125I-insulin in isolated rat hepatocytes. Direct demonstration by quantitative electron microscopic autoradiography. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1249–1261. doi: 10.1172/JCI109420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chain E. B., Mansford K. R., Opie L. H. Effects of insulin on the pattern of glucose metabolism in the perfused working and Langendorff heart of normal and insulin-deficient rats. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):537–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1150537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung J. Y., Conover C., Regen D. M., Whitfield C. F., Morgan H. E. Effect of insulin on kinetics of sugar transport in heart muscle. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):E70–E78. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.1.E70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C. Insulin and glucagon binding and degradation by kidney cell membranes. Endocrinology. 1978 Jun;102(6):1766–1774. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-6-1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C., Runyan K. R., Wright R. K., Halban P. A., Solomon S. S. Insulin degradation by hepatocytes in primary culture. Endocrinology. 1981 Apr;108(4):1142–1147. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-4-1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel J., Reinauer H. Characteristics of insulin receptors in the heart muscle: binding of insulin to isolated muscle cells from adult rat heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 22;629(3):510–521. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel J., Reinauer H. Effect of vinblastine on the insulin-receptor interaction in mammalian heart muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 27;92(4):1403–1408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90442-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer B. B., Harris R. A., Jolly W. W., Hathaway D. R., Katzberg A., Watanabe A. M., Whitlow A. L., Besch H. R., Jr Isolation and characterization of adult rat hearts cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Mar;179(2):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U. Die Insulinwirkung auf die transmembrane Glukosebilanz des iolierten perfundierten Rattenherzen. II. Die Wirkung von Insulin auf die kinetischen Parameter der Glukoseaufnahme. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1971;26(1):87–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Sonne O. Binding and receptor-mediated degradation of insulin in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7857–7863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D. Does insulin need a second messenger? Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):148–155. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Smith G. J. Binding of insulin to isolated nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1427–1431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. J., Livingston J. N. Insulin degradation by adipose tissue. Studies at several levels of cellular organization. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):351–360. doi: 10.1042/bj1860351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Carpentier J. L., Freychet P. O., Orci L. Internalization of polypeptide hormones: mechanism, intracellular localization and significance. Diabetologia. 1980 Apr;18(4):263–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00251003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond J. M., Jarett L. Insulin degradation by isolated fat cells and their subcellular fractions. Diabetes. 1975 Nov;24(11):1011–1019. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.11.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K. The fate of insulin bound to adipocytes. Evidence for compartmentalization and processing. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4900–4906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kones R. J., Phillips J. H. Insulin: fundamental mechanism of action and the heart. Cardiology. 1975;60(5):280–303. doi: 10.1159/000169727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Robinson F. W., Sarver J. A., Vega F. V., Pointer R. H. Actions of insulin in fat cells. Effects of low temperature, uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation, and respiratory inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2226–2233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P., Lenoir P. Degradation of insulin by isolated rat liver cells. Diabetes. 1975 Jun;24(6):566–573. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.6.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN H. E., RANDLE P. J., REGEN D. M. Regulation of glucose uptake by muscle. 3. The effects of insulin, anoxia, salicylate and 2:4-dinitrophenol on membrane transport and intracellular phosphorylation of glucose in the isolated rat heart. Biochem J. 1959 Dec;73:573–579. doi: 10.1042/bj0730573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahbouba M., Smith H. J. Thiolation and disulphide cross-linking of insulin to form macromolecules of potential therapeutic value. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;86A:247–260. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3282-4_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Olefsky J. M. Effects of lysosomotropic agents on insulin interactions with adipocytes. Evidence for a lysosomal pathway for insulin processing and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10153–10160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Kobayashi M., Chang H. Interactions between insulin and its receptors after the initial binding event. Functional heterogeneity and relationships to insulin degradation. Diabetes. 1979 May;28(5):460–471. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.5.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers A. C., Solomon S. S., Duckworth W. C. Insulin degradation by mononuclear cells. Diabetes. 1980 Jan;29(1):27–32. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonne O., Gliemann J. Insulin receptors of cultured human lymphocytes (IM-9). Lack of receptor-mediated degradation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7449–7454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Internalization and degradation of fat cell-bound insulin. Separation and partial characterization of subcellular vesicles associated with iodoinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9786–9794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. S., Seeman M. In vitro characterization of the mechanism of insulin degradation and the effect of chloroquine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 18;673(3):259–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahouny G. V., Wei R. W., Tamboli A., Albert E. N. Adult canine myocytes: isolation, morphology and biochemical characteristics. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1979 Apr;11(4):339–357. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(79)90422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wibo M., Poole B. Protein degradation in cultured cells. II. The uptake of chloroquine by rat fibroblasts and the inhibition of cellular protein degradation and cathepsin B1. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):430–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokono K., Imamura Y., Sakai H., Baba S. Insulin-degrading activity of plasma membranes from rat skeletal muscle: its isolation, characterization, and biologic significance. Diabetes. 1979 Sep;28(9):810–817. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.9.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


