Abstract
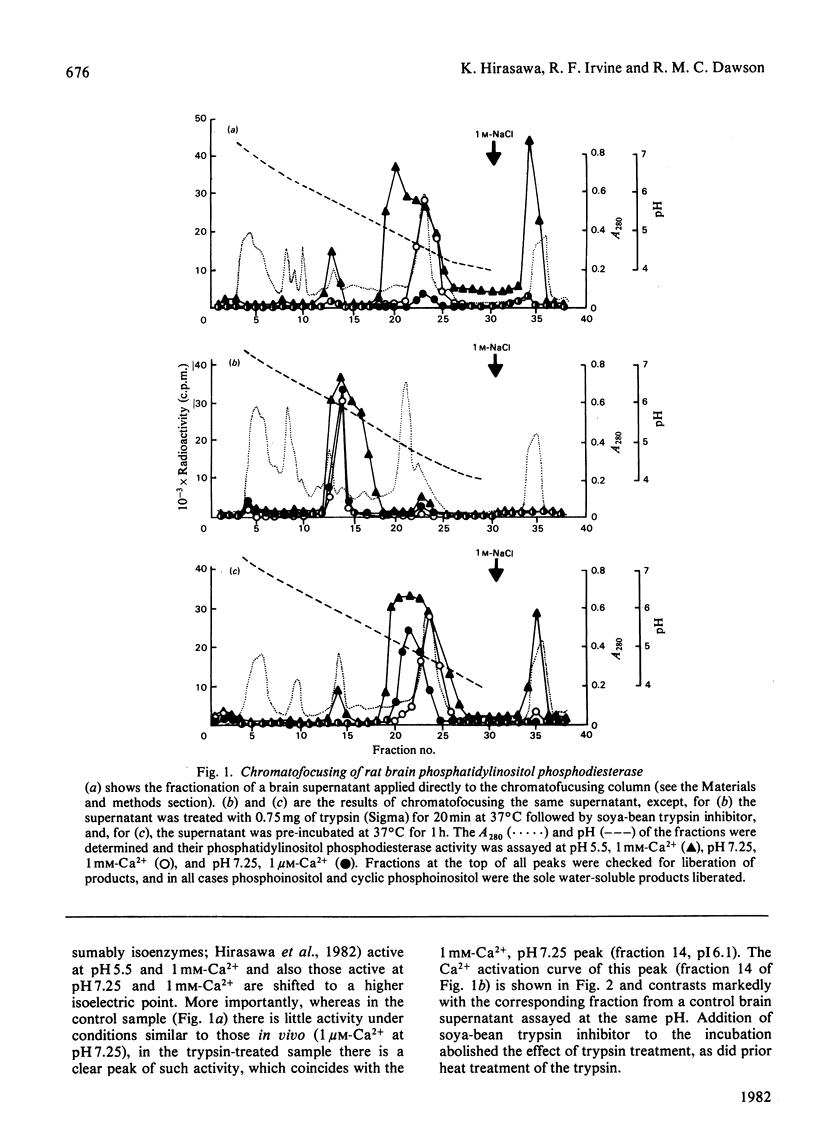
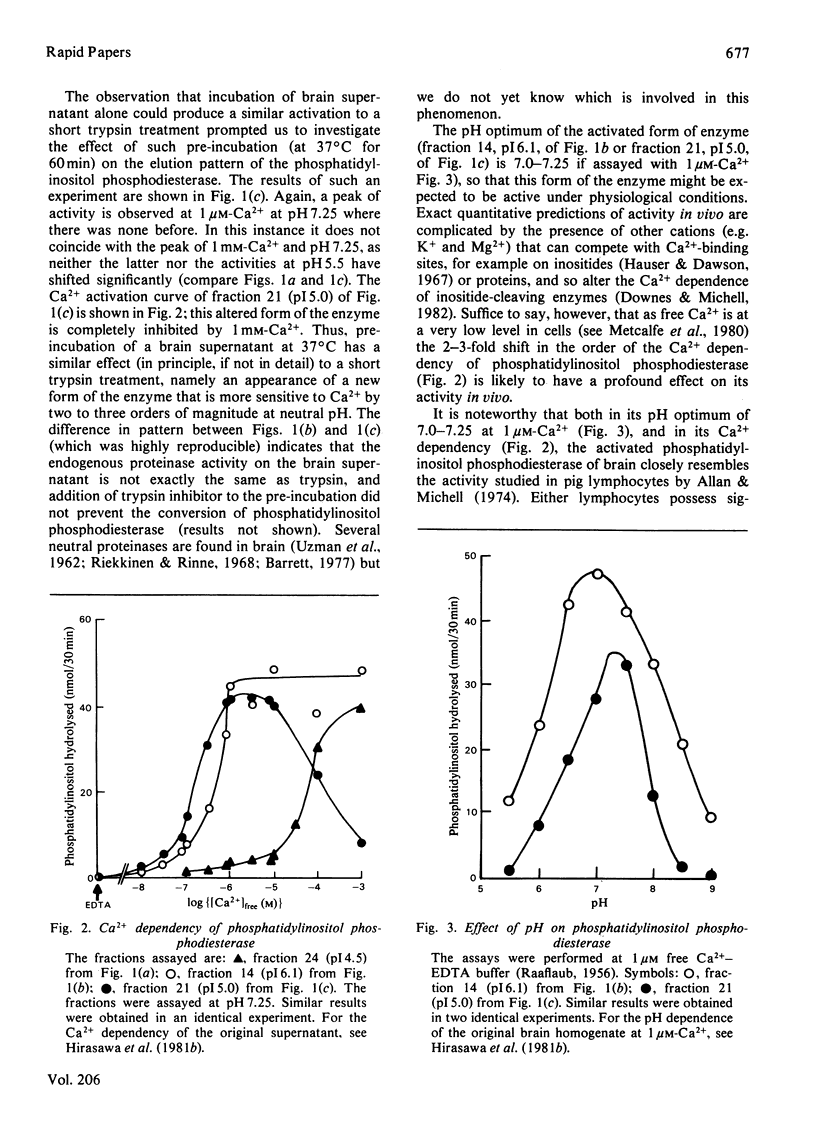
The phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase of rat brain shows little activity under conditions likely to pertain in vivo (neutral pH and micromolar Ca2+ concentrations). A short incubation of a brain supernatant with trypsin, or a longer pre-incubation of the supernatant alone, produce new forms of the enzyme, which are active under such conditions. A possible role of receptor-linked proteinases in initiating phosphatidylinositol catabolism is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan D., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol cleavage in lymphocytes. Requirement for calcium ions at a low concentration and effects of other cations. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):599–604. doi: 10.1042/bj1420599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. Studies on the enzymic hydrolysis of monophosphoinositide by phospholipase preparations from P. notatum and ox pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 May;33(1):68–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90499-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Hemington N., Irvine R. F. The inhibition and activation of Ca2+-dependent phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase by phospholipids and blood plasma. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Nov;112(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Thompson W. The triphosphoinositide phosphomonoesterase of brain tissue. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):244–250. doi: 10.1042/bj0910244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The control by Ca2+ of the polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and the Ca2+-pump ATPase in human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 15;202(1):53–58. doi: 10.1042/bj2020053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Dawson R. M. The binding of calcium at lipid-water interfaces. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):61–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa K., Irvine R. F., Dawson R. M. The catabolism of phosphatidylinisitol by an EDTA-insensitive phospholipase A1 and calcium-dependent phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase in rat brain. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):53–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa K., Irvine R. F., Dawson R. M. The hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol monolayers at an air/water interface by the calcium-ion-dependent phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase of pig brain. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):607–614. doi: 10.1042/bj1930607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Dynamic aspects of phospholipids during protein secretion. Int Rev Cytol. 1968;23:187–208. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Hemington N., Dawson R. M. The calcium-dependent phosphatidylinositol-phosphodiesterase of rat brain. Mechanisms of suppression and stimulation. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(3):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Hemington N., Dawson R. M. The hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol by lysosomal enzymes of rat liver and brain. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):475–484. doi: 10.1042/bj1760475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMP P., HUBSCHER G., HAWTHORNE J. N. Phosphoinositides. 3. Enzymic hydrolysis of inositol-containing phospholipids. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:193–200. doi: 10.1042/bj0790193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Guerrier P. Activation of calmodulin-dependent NAD+ kinase by trypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Mar 18;702(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe J. C., Pozzan T., Smith G. A., Hesketh T. R. A calcium hypothesis for the control of cell growth. Biochem Soc Symp. 1980;45:1–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Is phosphatidylinositol really out of the calcium gate? Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):492–493. doi: 10.1038/296492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaie C. R., Oliveira M. C., Juliano L., Paiva A. C. Inhibition of renin by conformationally restricted analogues of angiotensinogen. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 1;205(1):43–47. doi: 10.1042/bj2050043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAAFLAUB J. Applications of metal buffers and metal indicators in biochemistry. Methods Biochem Anal. 1956;3:301–325. doi: 10.1002/9780470110195.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riekkinen P. J., Rinne U. K. A new neutral proteinase from the rat brain. Brain Res. 1968 Jun;9(1):126–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D. Minireview. Phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipases C. Life Sci. 1982 Apr 19;30(16):1323–1335. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UZMAN L. L., VAN DEN NOORT S., RUMLEY M. K. Properties and classification of some brain peptidases. J Neurochem. 1962 May-Jun;9:241–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb09446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Intracellular phospholipases A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 30;604(2):191–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90574-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


