Abstract
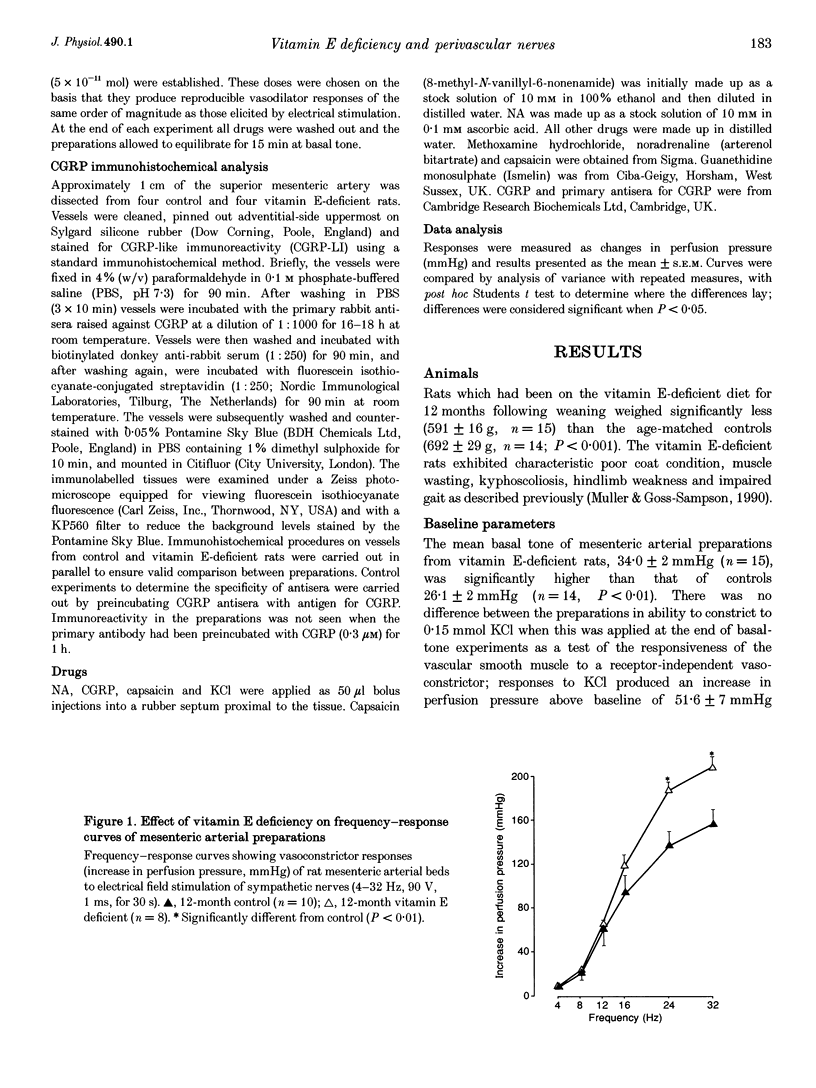
1. Mesenteric arterial beds from male rats deprived of vitamin E for 12 months postweaning were isolated and perfused at 5 ml min-1. 2. The basal perfusion pressure of vitamin E-deficient preparations was significantly higher (34.0 +/- 1.9 mmHg, n = 15) than in age-matched controls (26.1 +/- 2 mmHg, n = 14; P < 0.01). 3. At basal tone, vasoconstrictor responses to electrical field stimulation (EFS) were not attenuated by vitamin E deficiency; at high stimulation frequencies, responses were enhanced. According to dose-response curves, exogenous noradrenaline was significantly more efficacious in preparations from vitamin E-deficient rats (P < 0.05). 4. In preparations with tone raised by methoxamine (6-20 microM) and in the presence of guanethidine (5 microM), EFS of perivascular sensorimotor nerves elicited frequency-dependent vasodilatation which was significantly attenuated by vitamin E deficiency. There was no difference in relaxation to calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP; 1.5 x 10(-11) mol), or to the sensory neurotoxin capsaicin (5 x 10(-11) mol). 5. Immunohistochemical analysis of CGRP-containing nerves in the superior mesenteric artery showed no differences in density of innervation. 6. In conclusion, chronic vitamin E deficiency impairs sensorimotor vasodilatation in rat mesenteric arteries; this does not appear to be due to changes in postjunctional receptors, or to a depletion of transmitter (CGRP) content of the superior mesenteric artery. Sensorimotor nerves appear to be more vulnerable than sympathetic nerves to chronic vitamin E deficiency.
Full text
PDF

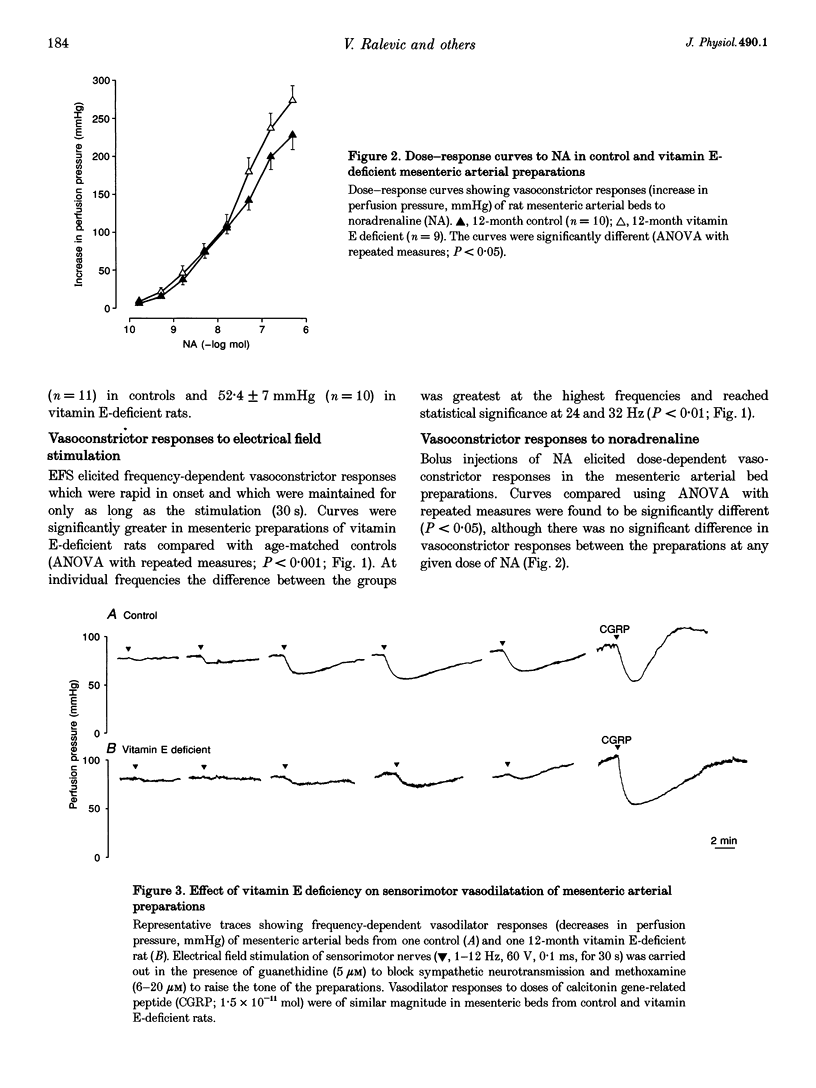
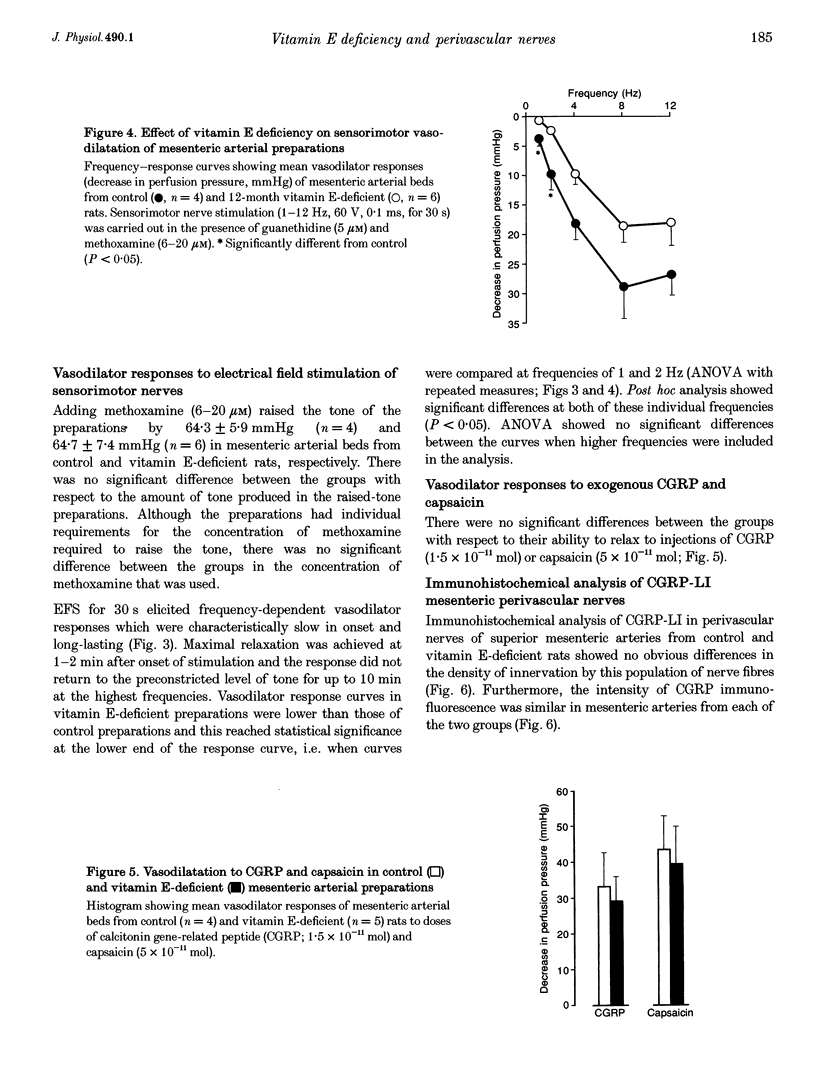
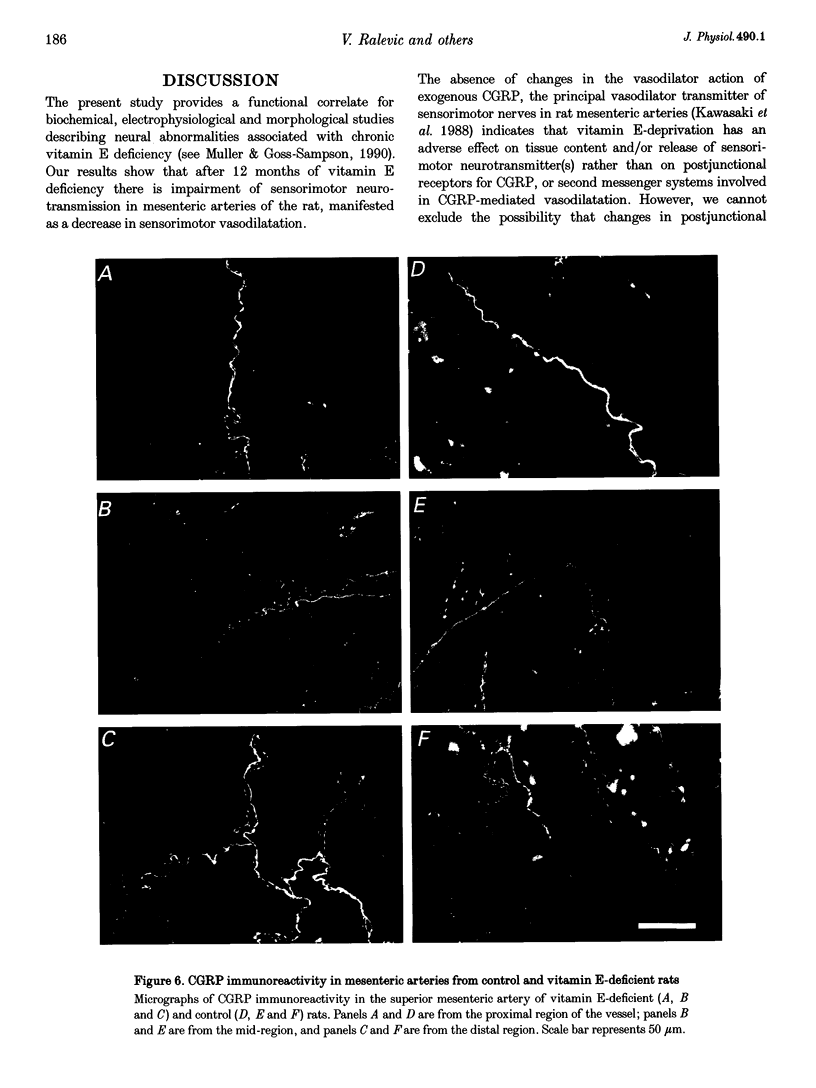



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belai A., Lincoln J., Burnstock G. Lack of release of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and calcitonin gene-related peptide during electrical stimulation of enteric nerves in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Gastroenterology. 1987 Nov;93(5):1034–1040. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90567-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belai A., Lincoln J., Milner P., Burnstock G. Progressive changes in adrenergic, serotonergic, and peptidergic nerves in proximal colon of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1234–1241. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belai A., Lincoln J., Milner P., Crowe R., Loesch A., Burnstock G. Enteric nerves in diabetic rats: increase in vasoactive intestinal polypeptide but not substance P. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):967–976. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. The fifth Heymans memorial lecture-Ghent, February 17, 1990. Co-transmission. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Mar-Apr;304:7–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton G. W., Joyce A., Ingold K. U. Is vitamin E the only lipid-soluble, chain-breaking antioxidant in human blood plasma and erythrocyte membranes? Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Feb 15;221(1):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh J. B. The problems of neurons with long axons. Lancet. 1984 Jun 9;1(8389):1284–1287. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92457-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori A., Saito A., Kimura S., Goto K. Release of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) from capsaicin-sensitive vasodilator nerves in the rat mesenteric artery. Neurosci Lett. 1990 May 4;112(2-3):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90198-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss-Sampson M. A., Kriss A., Muller D. P. A longitudinal study of somatosensory, brainstem auditory and peripheral sensory-motor conduction during vitamin E deficiency in the rat. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Dec;100(1-2):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90016-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss-Sampson M. A., MacEvilly C. J., Muller D. P. Longitudinal studies of the neurobiology of vitamin E and other antioxidant systems, and neurological function in the vitamin E deficient rat. J Neurol Sci. 1988 Oct;87(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(88)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S. P., Naes L., Westfall T. C. Inhibition of periarterial nerve stimulation-induced vasodilation of the mesenteric arterial bed by CGRP (8-37) and CGRP receptor desensitization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):786–791. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92390-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E. Vitamin E and the nervous system. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1987;3(1):89–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Ralevic V., Lincoln J., Knight G. E., Goss-Sampson M. A., Milla P. J., Burnstock G. Effects of vitamin E deficiency on autonomic neuroeffector mechanisms in the rat caecum, vas deferens and urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1995 Sep 15;487(Pt 3):773–786. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel C. A., Griggs K. C., McLaughlin M. K. Lipid peroxidation and altered vascular function in vitamin E-deficient rats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):H1539–H1545. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.6.H1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karanth S. S., Springall D. R., Francavilla S., Mirrlees D. J., Polak J. M. Early increase in CGRP- and VIP-immunoreactive nerves in the skin of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Histochemistry. 1990;94(6):659–666. doi: 10.1007/BF00271994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki H., Saito A., Takasaki K. Age-related decrease of calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing vasodilator innervation in the mesenteric resistance vessel of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Circ Res. 1990 Sep;67(3):733–743. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.3.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki H., Takasaki K., Saito A., Goto K. Calcitonin gene-related peptide acts as a novel vasodilator neurotransmitter in mesenteric resistance vessels of the rat. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):164–167. doi: 10.1038/335164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. J., Duckles S. P. Effect of endothelium on the actions of sympathetic and sensory nerves in the perfused rat mesentery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 7;210(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90647-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D. P., Goss-Sampson M. A. Neurochemical, neurophysiological, and neuropathological studies in vitamin E deficiency. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1990;5(3):239–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D. P., Lloyd J. K., Wolff O. H. Vitamin E and neurological function. Lancet. 1983 Jan 29;1(8318):225–228. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92598-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. S., Fitch C. D., Fischer V. W., Broun G. O., Jr, Chou A. C. Progressive neuropathologic lesions in vitamin E-deficient rhesus monkeys. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 Mar;40(2):166–186. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198103000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. A., Kobayashi S. Antioxidants in health and disease: overview. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1992 Jun;200(2):245–247. doi: 10.3181/00379727-200-43428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer L. Interactions among antioxidants in health and disease: vitamin E and its redox cycle. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1992 Jun;200(2):271–276. doi: 10.3181/00379727-200-43433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Karoon P., Burnstock G. Long-term sensory denervation by neonatal capsaicin treatment augments sympathetic neurotransmission in rat mesenteric arteries by increasing levels of norepinephrine and selectively enhancing postjunctional actions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jul;274(1):64–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum J. L., Keating J. P., Prensky A. L., Nelson J. S. A progressive neurologic syndrome in children with chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 26;304(9):503–508. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102263040902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. E., Coleman B. D., Nelson J. S. Differential effect of chronic vitamin E deficiency on the development of neuroaxonal dystrophy in rat gracile/cuneate nuclei and prevertebral sympathetic ganglia. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Feb 11;123(1):102–106. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90168-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöblom-Widfeldt N., Gustafsson H., Nilsson H. Transmitter characteristics of small mesenteric arteries from the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1990 Feb;138(2):203–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb08834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southam E., Thomas P. K., King R. H., Goss-Sampson M. A., Muller D. P. Experimental vitamin E deficiency in rats. Morphological and functional evidence of abnormal axonal transport secondary to free radical damage. Brain. 1991 Apr;114(Pt 2):915–936. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.2.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towfighi J. Effects of chronic vitamin E deficiency on the nervous system of the rat. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;54(4):261–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00696998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wichman A., Buchthal F., Pezeshkpour G. H., Gregg R. E. Peripheral neuropathy in abetalipoproteinemia. Neurology. 1985 Sep;35(9):1279–1289. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.9.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto R., Cline W. H., Jr, Takasaki K. Reassessment of the blocking activity of prazosin at low and high concentrations on sympathetic neurotransmission in the isolated mesenteric vasculature of rats. J Auton Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;8(4):303–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1988.tb00573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto R., Takasaki K., Nickols G. A. Purinergic vasoconstrictor component revealed by moderate cooling in the isolated mesenteric vasculature of Sprague-Dawley rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Sep;262(3):1133–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Acker S. A., Koymans L. M., Bast A. Molecular pharmacology of vitamin E: structural aspects of antioxidant activity. Free Radic Biol Med. 1993 Sep;15(3):311–328. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(93)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]