Abstract
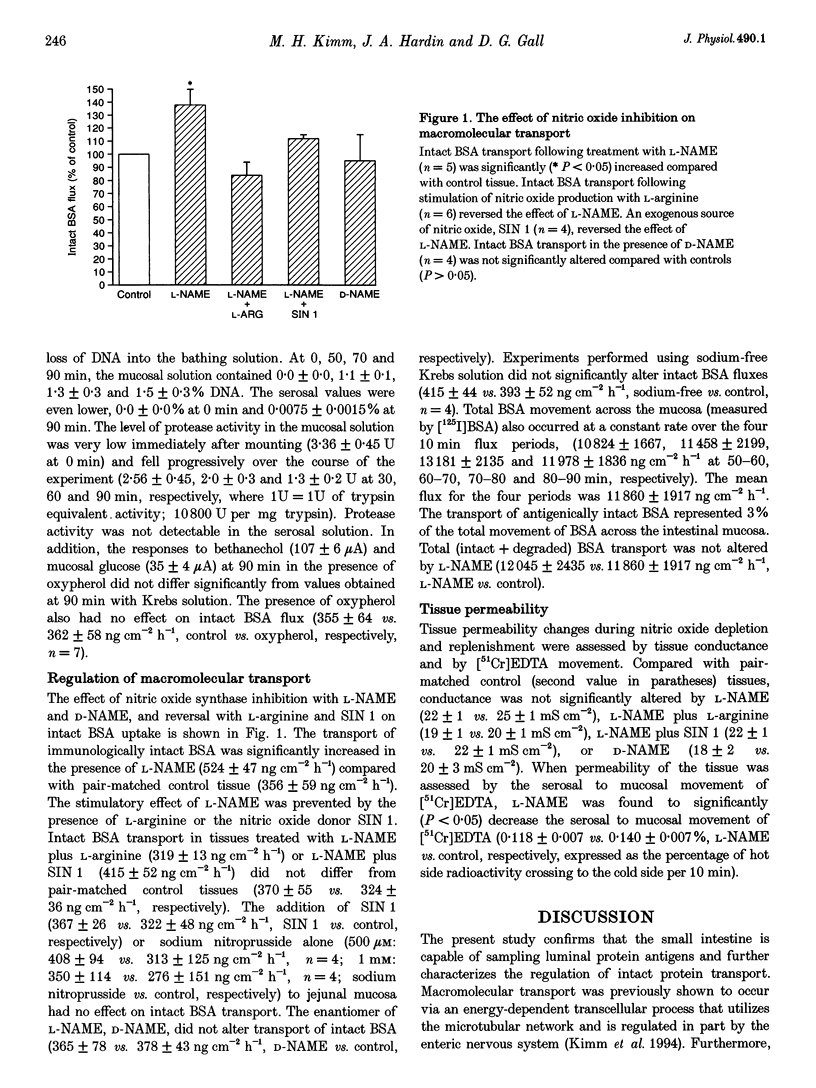
1. Nitric oxide is known to affect epithelial and microvascular permeability and is a major non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurotransmitter in the intestine. We have previously demonstrated neuronal regulation of macromolecular transport in the intestine. To define this regulation further the role of nitric oxide was investigated. 2. Stripped rat jejunum was mounted in Ussing chambers exposing the mucosal surface to bovine serum albumin (BSA; 2 mg ml-1), or BSA (2 mg ml-1) plus [125I]BSA (10 microCi). Following a 50 min equilibration, serosal fluids were sampled for four 10 min periods, and fluxes determined for intact BSA by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and total BSA by [125I]BSA under basal conditions, and after treatment with NG-nitro-L-arginine-methyl ester (L-NAME) alone or in conjunction with L-arginine or decarboxylated molsidomine (SIN 1). 3. L-NAME significantly increased intact BSA uptake. Total (intact + degraded) BSA flux was not altered. The L-NAME effect was reversed by L-arginine and SIN 1. Additional experiments were performed by adding the nitric oxide donors sodium nitroprusside and SIN 1 directly to control tissue. Nitric oxide donors did not further decrease intact BSA flux below levels obtained from control tissue. The L-NAME enantiomer D-NAME had no effect. Sodium-free bathing solutions also had no effect on intact BSA uptake. Non-specific permeability, as assessed by the serosal to mucosal movement of [51Cr]ethylene-diamine-tetraacetate ([51Cr]EDTA), was decreased with L-NAME. 4. The findings indicate that nitric oxide downregulates intact macromolecular flux in the small intestine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aimi Y., Kimura H., Kinoshita T., Minami Y., Fujimura M., Vincent S. R. Histochemical localization of nitric oxide synthase in rat enteric nervous system. Neuroscience. 1993 Mar;53(2):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90220-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel neuronal messenger. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90104-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christinck F., Jury J., Cayabyab F., Daniel E. E. Nitric oxide may be the final mediator of nonadrenergic, noncholinergic inhibitory junction potentials in the gut. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;69(10):1448–1458. doi: 10.1139/y91-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell R., Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J. Small intestinal absorption of horseradish peroxidase. A cytochemical study. Lab Invest. 1971 Jul;25(1):42–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinegardner R. T. An improved fluorometric assay for DNA. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biological actions and properties of endothelium-derived nitric oxide formed and released from artery and vein. Circ Res. 1989 Jul;65(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javed N. H., Wang Y. Z., Cooke H. J. Neuroimmune interactions: role for cholinergic neurons in intestinal anaphylaxis. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 1):G847–G852. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.6.G847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar S., Wallace J. L., Befus D., Kubes P. Nitric oxide synthesis inhibition increases epithelial permeability via mast cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Feb;266(2 Pt 1):G222–G229. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.266.2.G222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keljo D. J., Hamilton J. R. Quantitative determination of macromolecular transport rate across intestinal Peyer's patches. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):G637–G644. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.6.G637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan J. A. Degranulation of mast cells in the trachea and bronchi of the rat following stimulation of the vagus nerve. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;91(4):398–402. doi: 10.1159/000235149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacQueen G., Marshall J., Perdue M., Siegel S., Bienenstock J. Pavlovian conditioning of rat mucosal mast cells to secrete rat mast cell protease II. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):83–85. doi: 10.1126/science.2911721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newson B., Dahlström A., Enerbäck L., Ahlman H. Suggestive evidence for a direct innervation of mucosal mast cells. Neuroscience. 1983 Oct;10(2):565–570. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer J. R., Volpp K. Transmucosal impedance of small intestine: correlation with transport of sugars and amino acids. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):C480–C493. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.2.C480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe V., Levin R. J. Enterotoxin Escherichia coli STa activates a nitric oxide-dependent myenteric plexus secretory reflex in the rat ileum. J Physiol. 1994 Mar 15;475(3):531–537. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman A. L., Menconi M. J., Unno N., Ezzell R. M., Casey D. M., Gonzalez P. K., Fink M. P. Nitric oxide dilates tight junctions and depletes ATP in cultured Caco-2BBe intestinal epithelial monolayers. Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 1):G361–G373. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.268.2.G361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M., Ward S. M. Nitric oxide as a mediator of nonadrenergic noncholinergic neurotransmission. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):G379–G392. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.3.G379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


