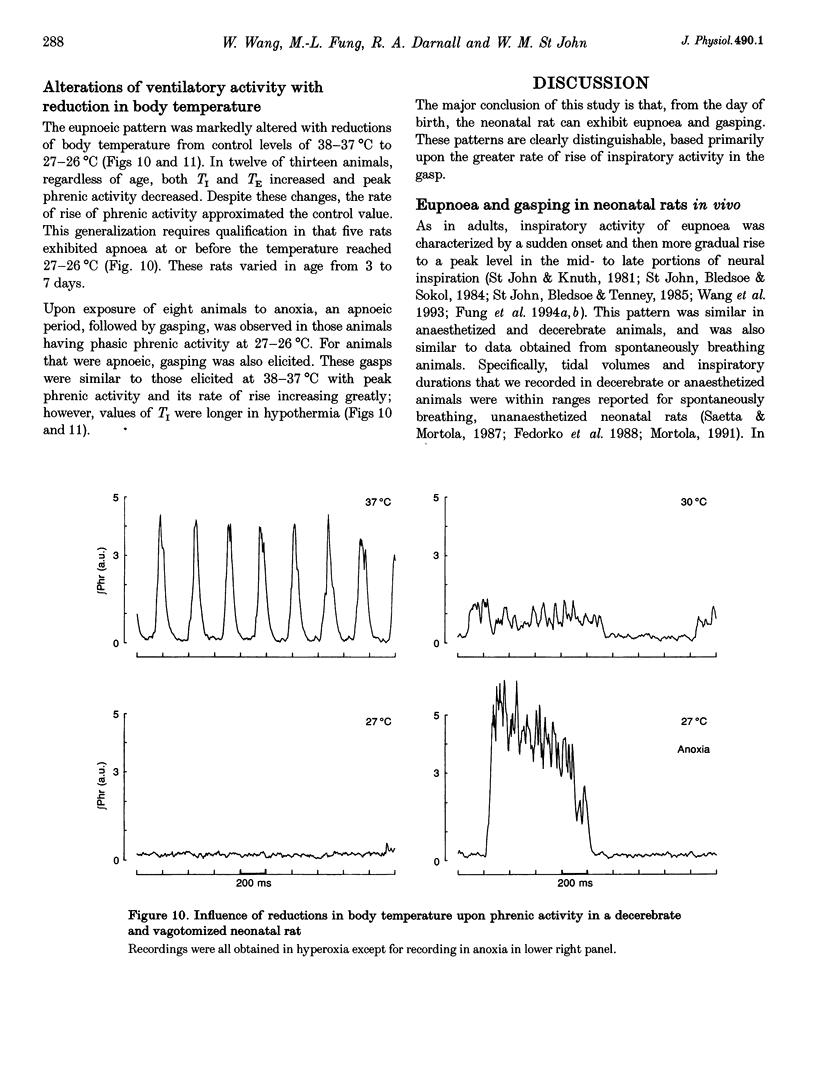
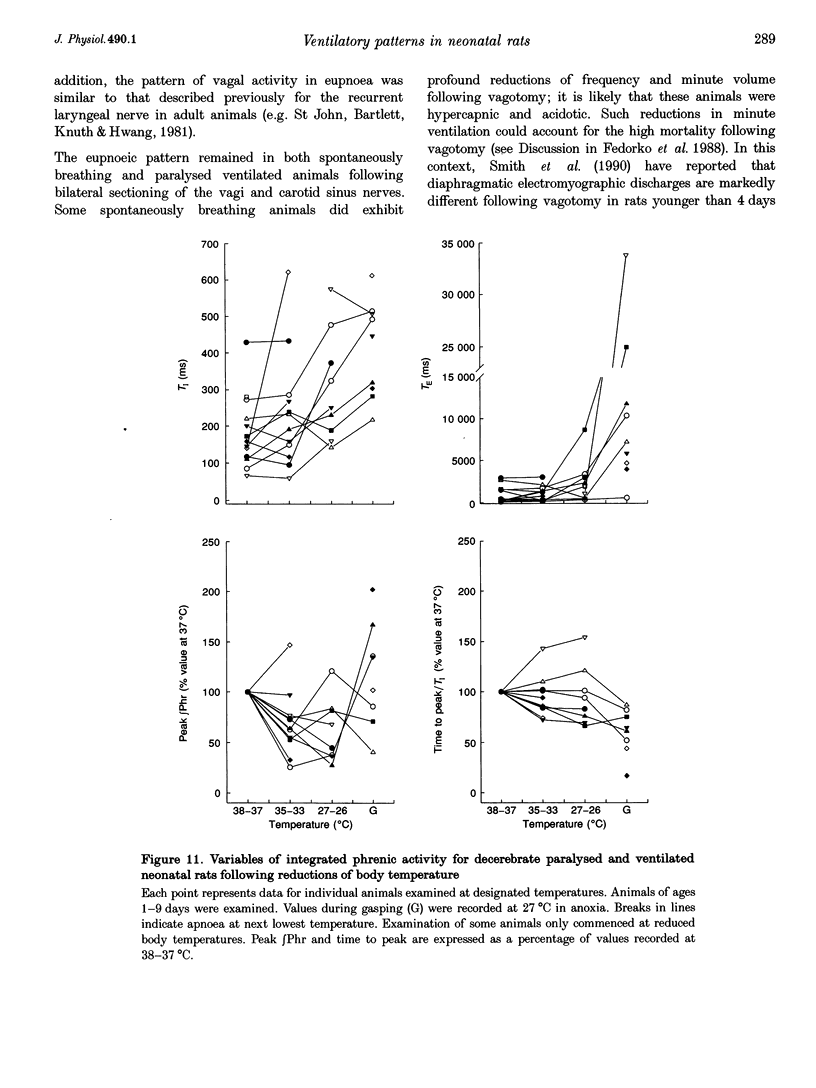
Abstract
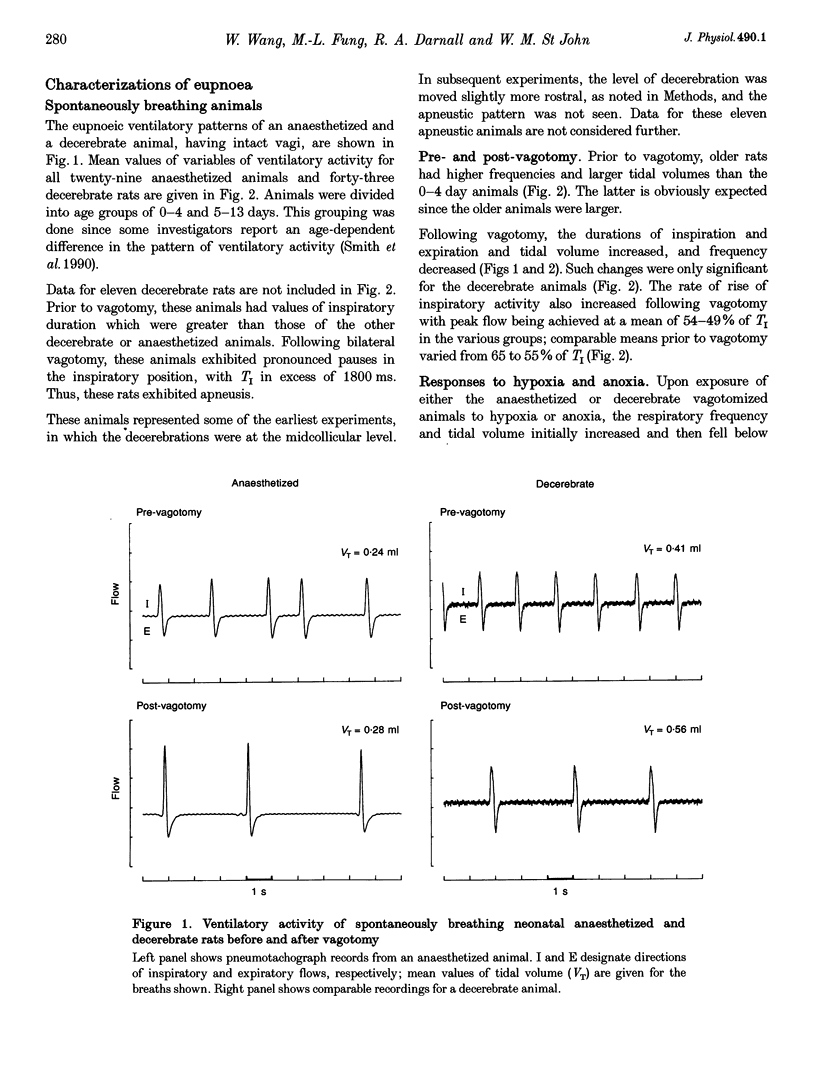
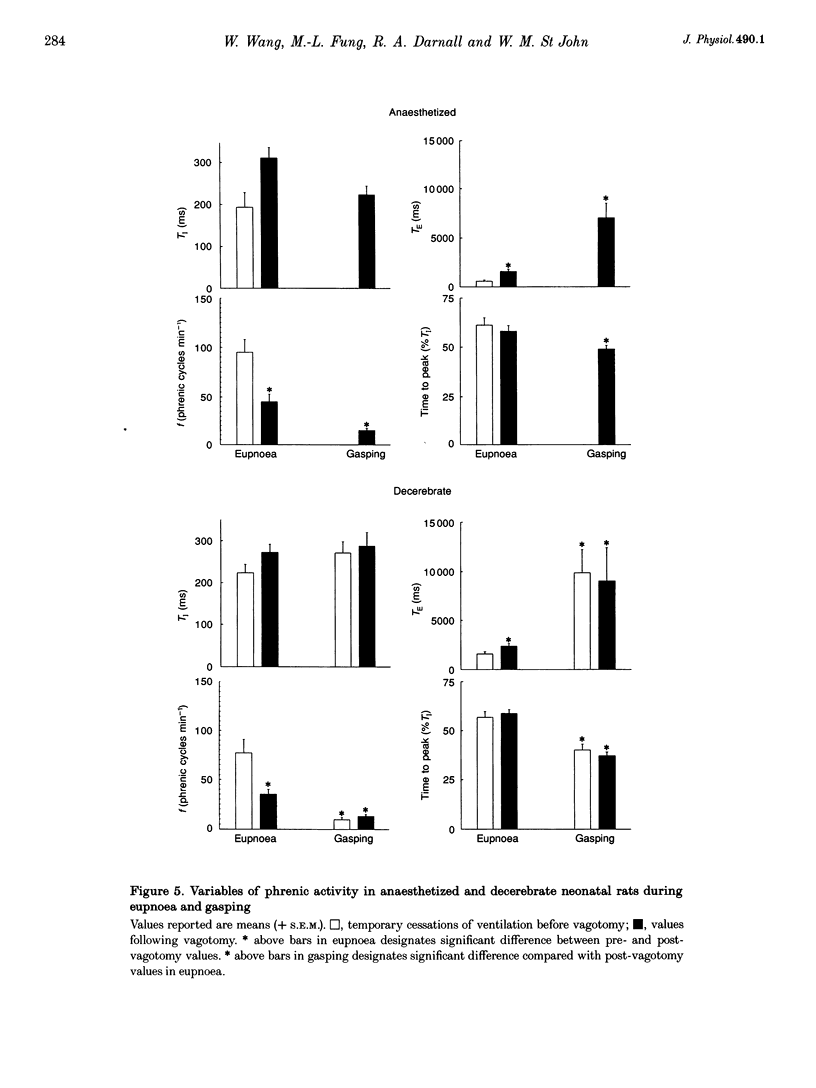
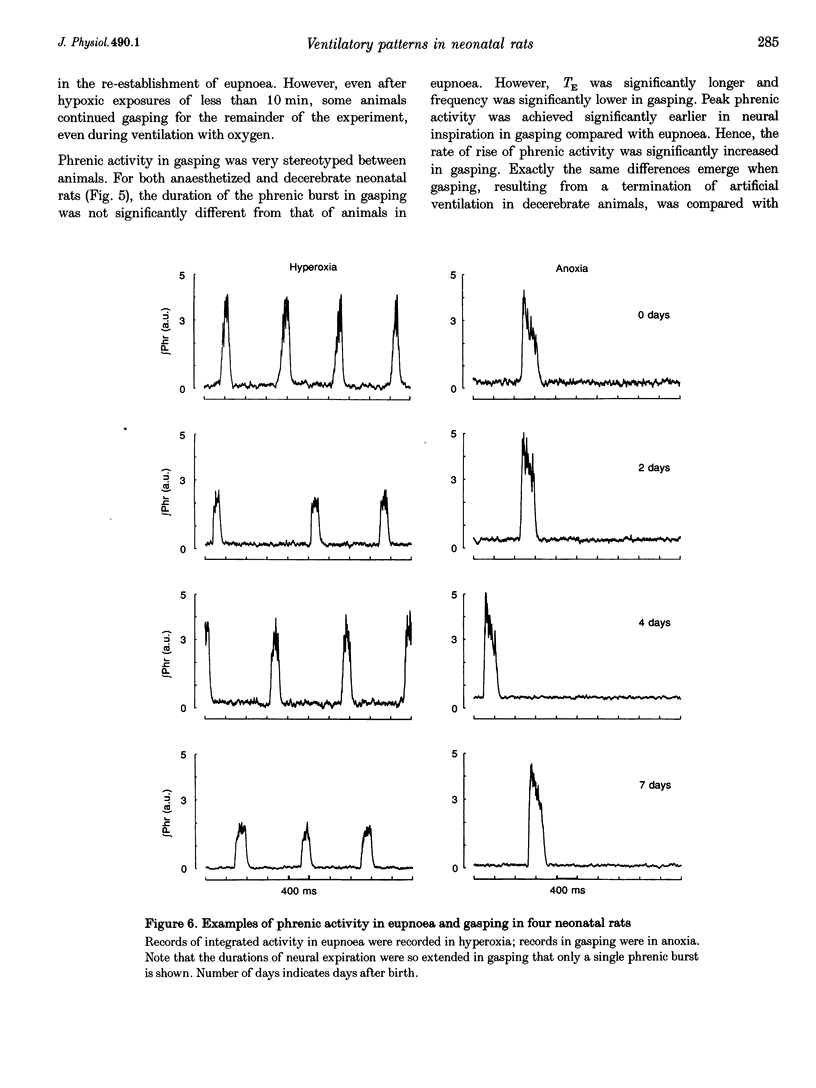
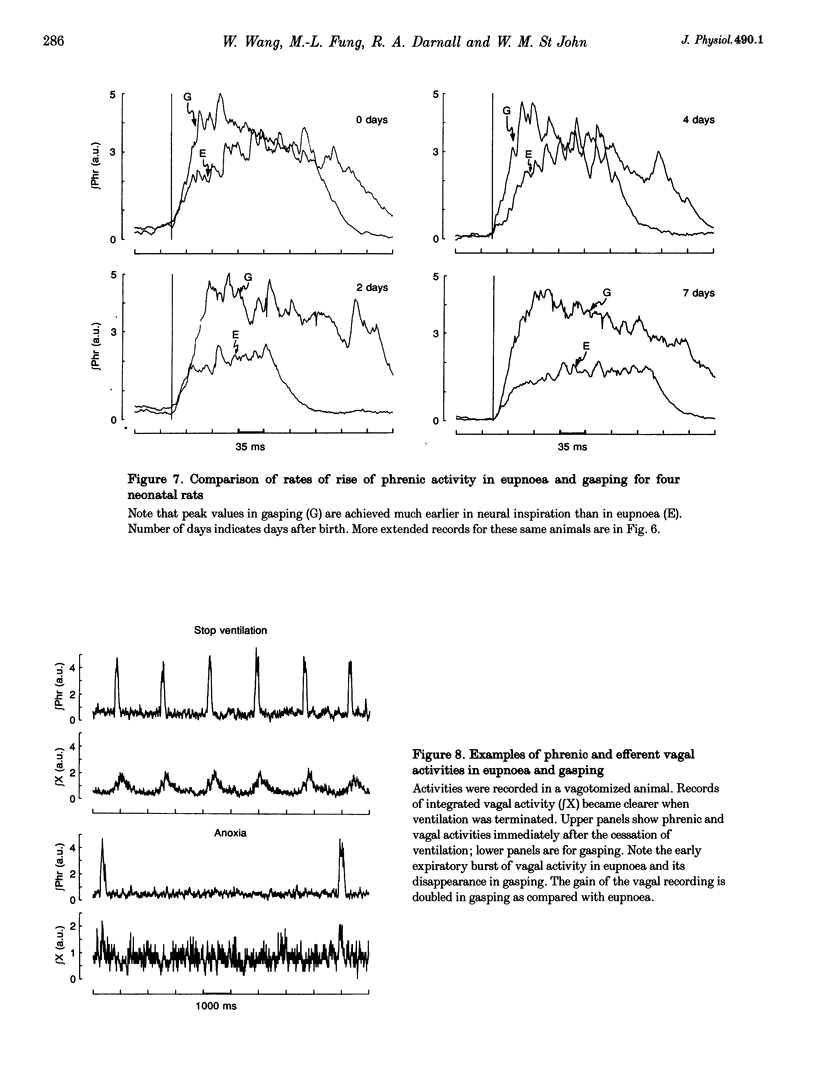
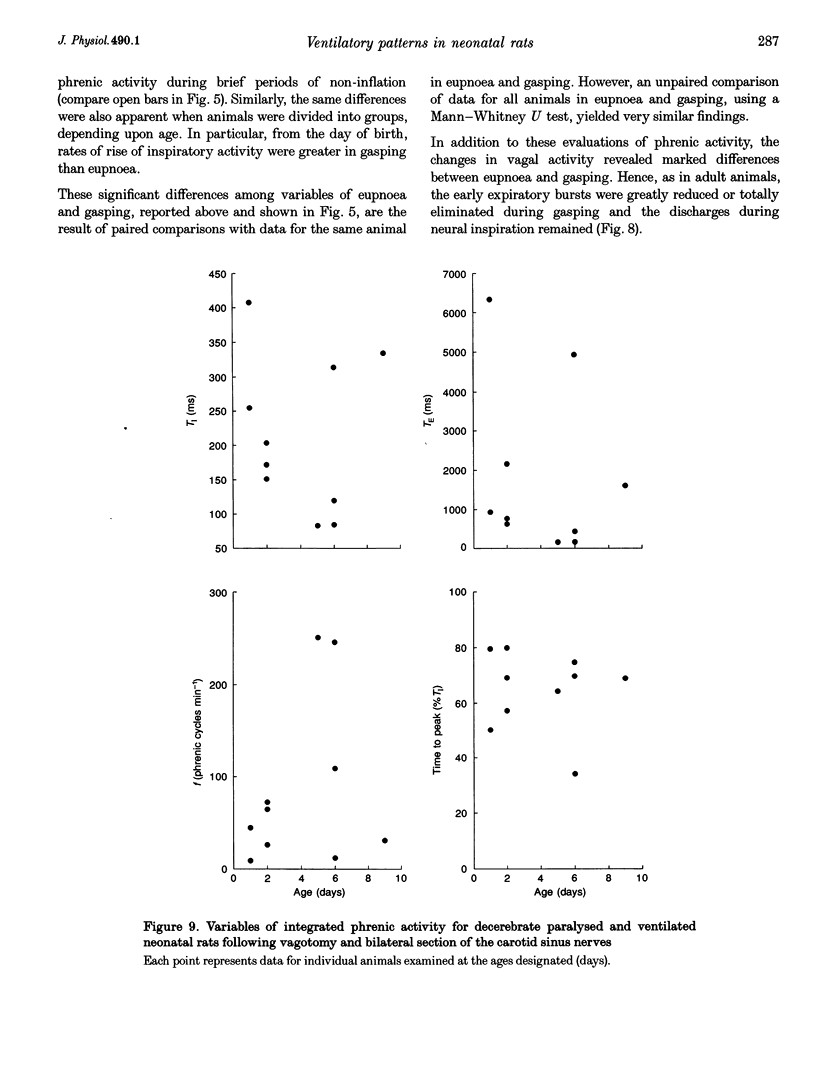
1. Our purpose was to characterize the ventilatory patterns of eupnoea and gasping in the neonatal rat. This study was precipitated by reports, using in vitro brainstem spinal cord preparations, that only a single pattern is present in neonatal rats. 2. In anaesthetized or decerebrate rat pups aged less than 13 days, eupnoea was characterized by a sudden onset of inspiratory activity and then a more gradual rise to peak levels. Following vagotomy, frequency fell and peak phrenic activity and tidal volume increased. The rate of rise of inspiratory activity also rose, but peak levels were still achieved during the latter half of inspiration. Vagal efferent activity exhibited bursts during both inspiration and the early expiration. This basic eupnoeic rhythm was not altered after sectioning of the carotid sinus nerves. 3. Upon exposure to hypoxia or anoxia, phrenic activity, tidal volume and frequency initially increased and then declined. In many animals, ventilatory activity then ceased, but later returned with a gasping pattern. 4. Gasping was characterized by a sudden onset of phrenic activity, which reached a peak intensity during the early portion of inspiration. The expiratory burst of vagal activity was eliminated. 5. Reductions of body temperature from 37 to 27 degrees C resulted in prolongations of inspiration and expiration and decreases of phrenic amplitude; phasic phrenic activity completely disappeared in some animals. Upon exposure to anoxia, gasping was observed, even in animals in which phrenic activity had disappeared in hyperoxia. 6. We conclude that, from the day of birth, rats can exhibit eupnoea and gasping patterns which are very similar to those of adult animals. 7. The rhythmic neural activities of the in vitro brainstem-spinal cord preparation, reported by others, differ markedly from eupnoea but are identical with gasping. We therefore conclude that this preparation is not suitable for investigation of the mechanisms that generate eupnoeic breathing.
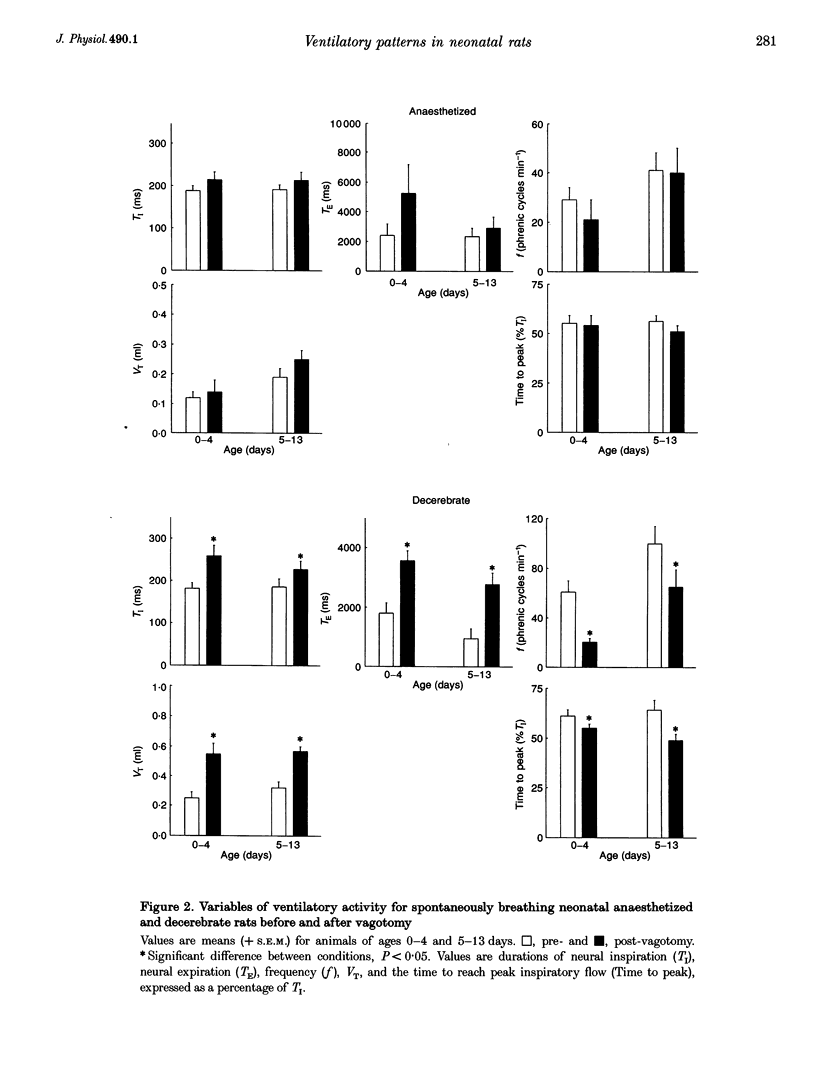
Full text
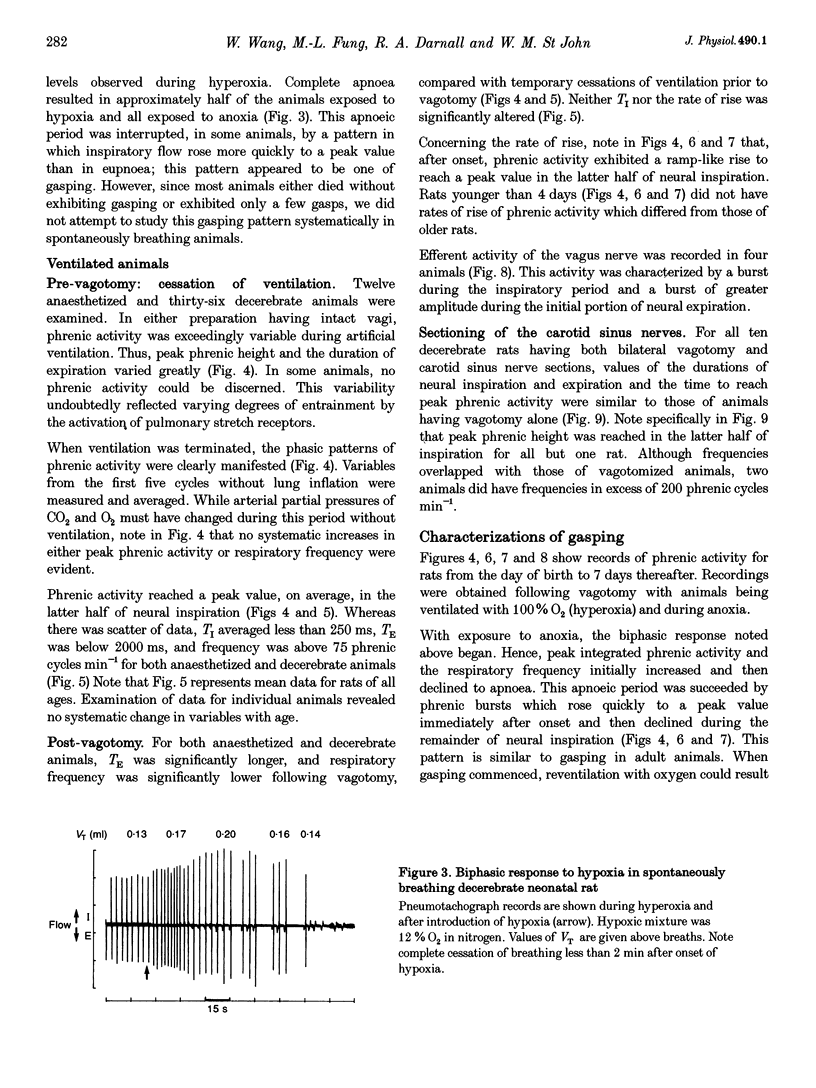
PDF


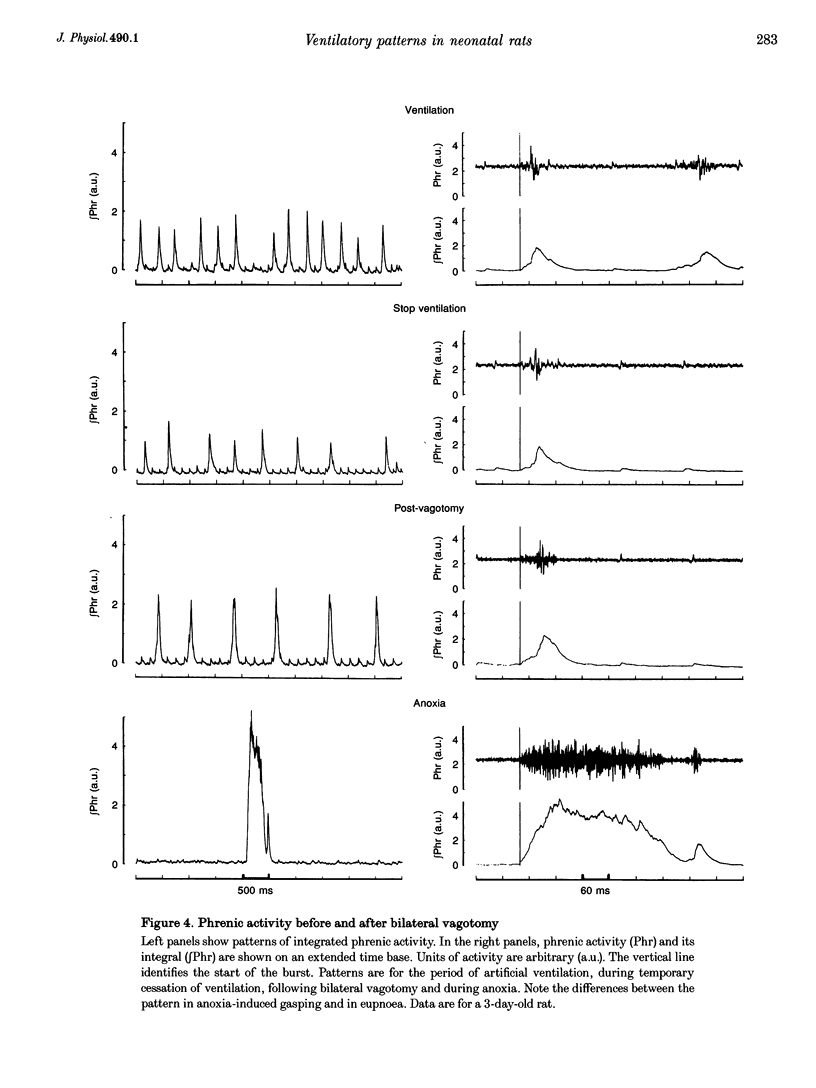



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballanyi K., Kuwana S., Völker A., Morawietz G., Richter D. W. Developmental changes in the hypoxia tolerance of the in vitro respiratory network of rats. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Dec 14;148(1-2):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90824-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus J., Ballanyi K., Smith J. C., Richter D. W. Microenvironment of respiratory neurons in the in vitro brainstem-spinal cord of neonatal rats. J Physiol. 1993 Mar;462:421–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. A. Changes in the tensions of CO(2) and O(2) in gases injected under the skin and into the abdominal cavity. J Physiol. 1924 Aug 12;59(1):1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1924.sp002157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly C. A., Dobbins E. G., Feldman J. L. Pre-Bötzinger complex in cats: respiratory neuronal discharge patterns. Brain Res. 1992 Sep 11;590(1-2):337–340. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Pasquale E., Monteau R., Hilaire G. Involvement of the rostral ventro-lateral medulla in respiratory rhythm genesis during the peri-natal period: an in vitro study in newborn and fetal rats. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1994 Apr 15;78(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(94)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins E. G., Feldman J. L. Brainstem network controlling descending drive to phrenic motoneurons in rat. J Comp Neurol. 1994 Sep 1;347(1):64–86. doi: 10.1002/cne.903470106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errchidi S., Monteau R., Hilaire G. Noradrenergic modulation of the medullary respiratory rhythm generator in the newborn rat: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:477–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorko L., Kelly E. N., England S. J. Importance of vagal afferents in determining ventilation in newborn rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Sep;65(3):1033–1039. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.3.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. L., Wang W., St John W. M. Involvement of pontile NMDA receptors in inspiratory termination in rat. Respir Physiol. 1994 May;96(2-3):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(94)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer J. J., Smith J. C., Feldman J. L. Role of excitatory amino acids in the generation and transmission of respiratory drive in neonatal rat. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:727–749. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Smith J. C., Funk G. D., Feldman J. L. Pacemaker behavior of respiratory neurons in medullary slices from neonatal rat. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Dec;72(6):2598–2608. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.6.2598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden T. Observations on the respiratory centres in the cat. J Physiol. 1923 Mar 21;57(3-4):153–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1923.sp002052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean H. A., Remmers J. E. Respiratory motor output of the sectioned medulla of the neonatal rat. Respir Physiol. 1994 Apr;96(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(94)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortola J. P. Hamsters versus rats: ventilatory responses in adults and newborns. Respir Physiol. 1991 Sep;85(3):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(91)90070-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakoshi T., Suzue T., Tamai S. A pharmacological study on respiratory rhythm in the isolated brainstem-spinal cord preparation of the newborn rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):95–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Mückenhoff K., Holtermann G., Acker H., Scheid P. Depth profiles of pH and PO2 in the isolated brain stem-spinal cord of the neonatal rat. Respir Physiol. 1993 Sep;93(3):315–326. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(93)90077-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onimaru H., Arata A., Homma I. Firing properties of respiratory rhythm generating neurons in the absence of synaptic transmission in rat medulla in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1989;76(3):530–536. doi: 10.1007/BF00248909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onimaru H., Arata A., Homma I. Inhibitory synaptic inputs to the respiratory rhythm generator in the medulla isolated from newborn rats. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Dec;417(4):425–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00370663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onimaru H., Arata A., Homma I. Primary respiratory rhythm generator in the medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparation from newborn rat. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 5;445(2):314–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilowsky P. M., Jiang C., Lipski J. An intracellular study of respiratory neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of the rat and their relationship to catecholamine-containing neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Nov 22;301(4):604–617. doi: 10.1002/cne.903010409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saetta M., Mortola J. P. Interaction of hypoxic and hypercapnic stimuli on breathing pattern in the newborn rat. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Feb;62(2):506–512. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.2.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzacher S. W., Smith J. C., Richter D. W. Pre-Bötzinger complex in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Apr;73(4):1452–1461. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.73.4.1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Ellenberger H. H., Ballanyi K., Richter D. W., Feldman J. L. Pre-Bötzinger complex: a brainstem region that may generate respiratory rhythm in mammals. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):726–729. doi: 10.1126/science.1683005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John W. M., Bledsoe T. A., Tenney S. M. Characterization by stimulation of medullary mechanisms underlying gasping neurogenesis. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Jan;58(1):121–128. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John W. M., Knuth K. V. A characterization of the respiratory pattern of gasping. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 May;50(5):984–993. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.5.984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John W. M. Neurogenesis, control, and functional significance of gasping. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Apr;68(4):1305–1315. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.4.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzue T. Respiratory rhythm generation in the in vitro brain stem-spinal cord preparation of the neonatal rat. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Fung M. L., St John W. M. Pontile regulation of ventilatory activity in the adult rat. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1993 Jun;74(6):2801–2811. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1993.74.6.2801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Wasicko M. J., Hu J. M., St John W. M. Differing activities of medullary respiratory neurons in eupnea and gasping. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Mar;70(3):1265–1270. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.70.3.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


