Abstract
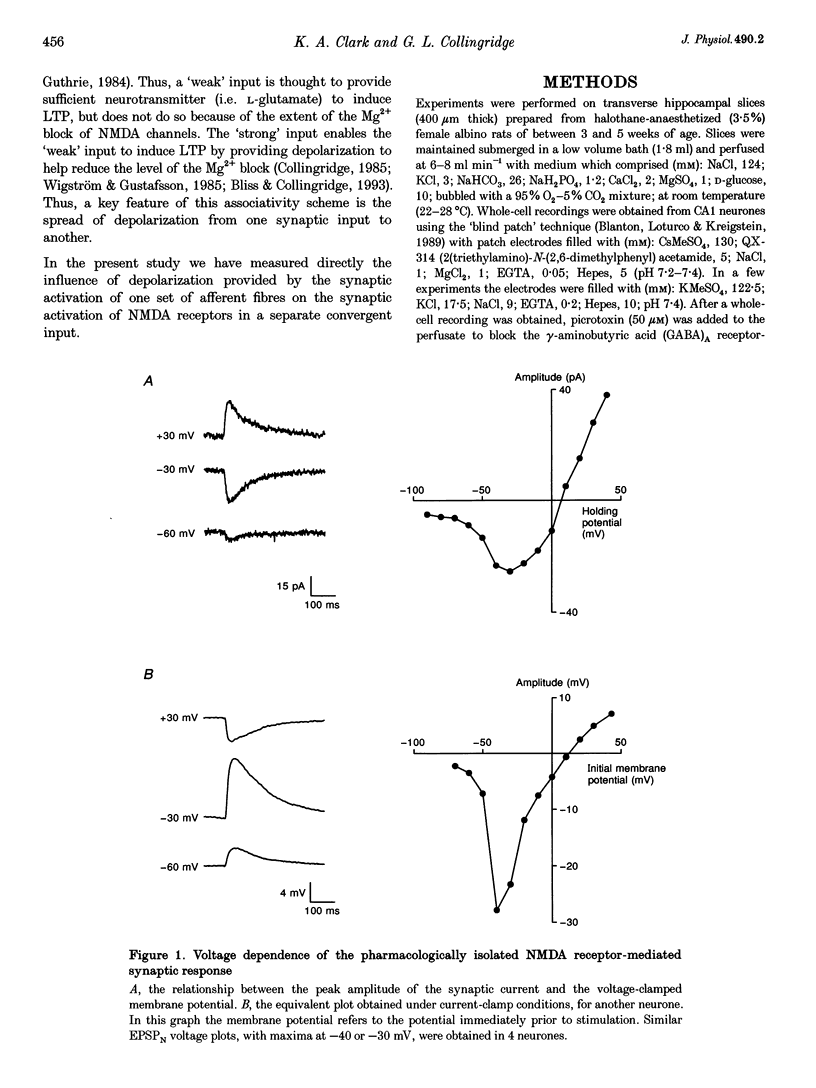
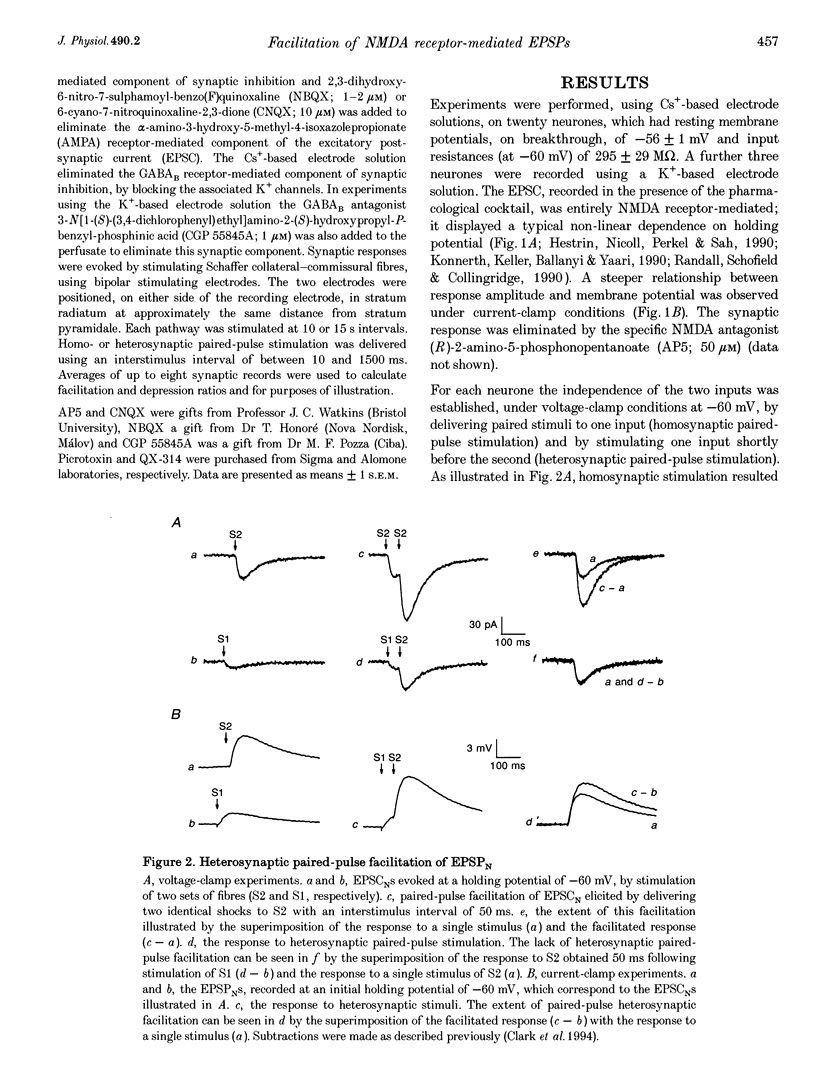
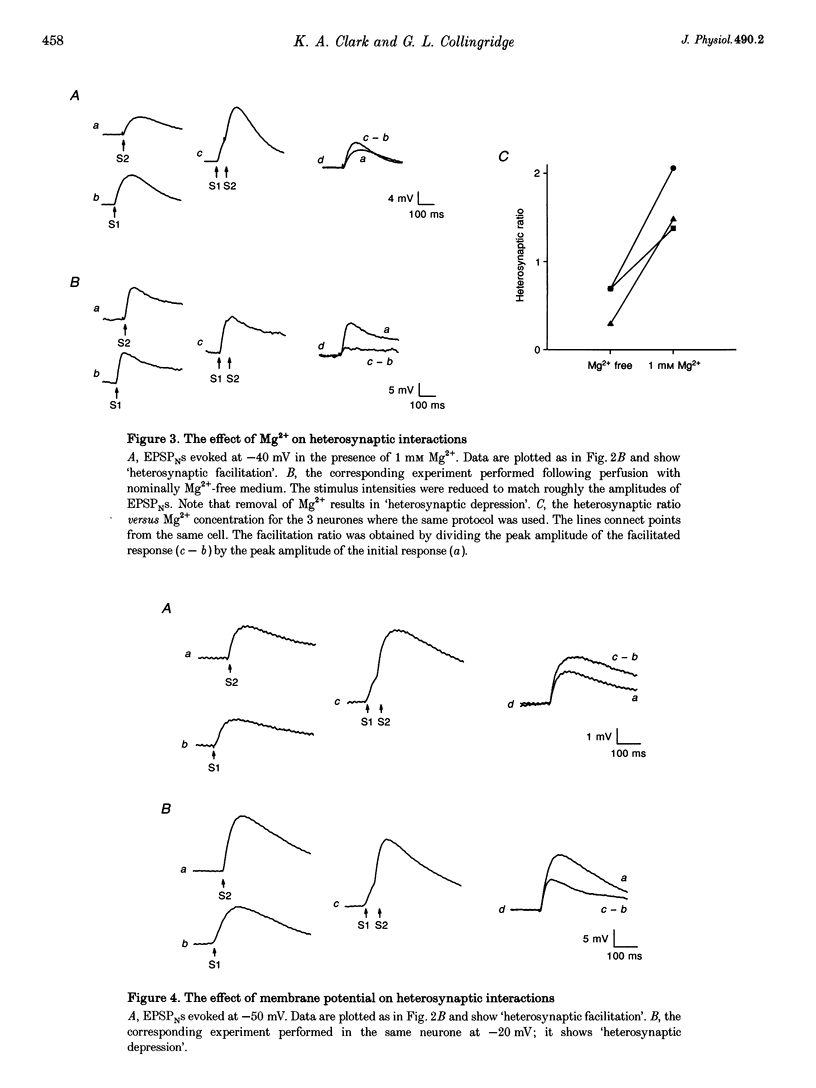
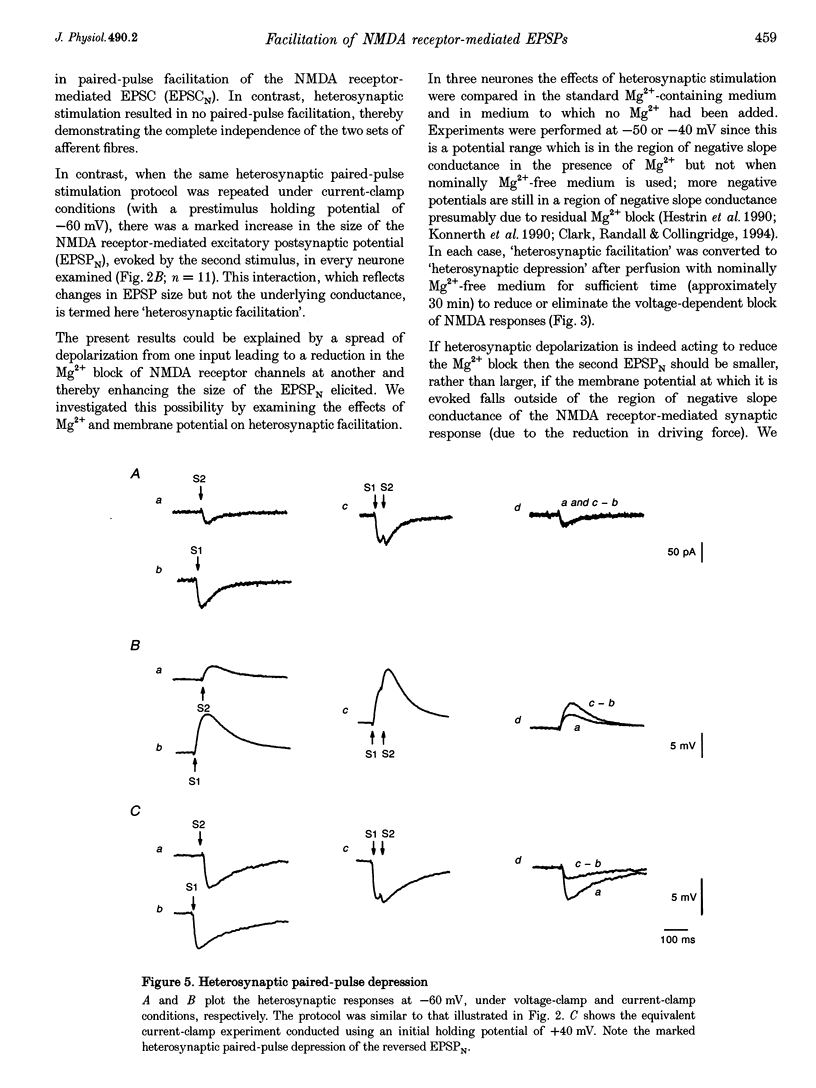
1. Whole-cell patch-clamp recording has been used to study the effect of heterosynaptic depolarization on pure N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices. 2. In neurones voltage clamped at -60 mV, paired-pulse stimulation of one set of Schaffer collateral-commissural fibres resulted in homosynaptic paired-pulse facilitation of the NMDA receptor-mediated excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSCN). In contrast, stimulation of one set of fibres prior to stimulation of a second set of fibres (i.e. heterosynaptic paired-pulse stimulation) did not result in any heterosynaptic interactions. 3. However, under current-clamp conditions, heterosynaptic paired-pulse stimulation resulted in heterosynaptic 'paired-pulse facilitation' of the NMDA receptor-mediated excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSPN). 4. In neurones held at -50 or -40 mV, perfusion of nominally Mg(2+)-free medium converted the response to heterosynaptic paired-pulse stimulation from 'heterosynaptic facilitation' to 'heterosynaptic depression' of EPSPN. 5. When neurones were held at potentials of between -30 and +40 mV then heterosynaptic paired-pulse stimulation, in normal Mg(2+)-containing medium, resulted in 'paired-pulse depression' of EPSPN. Under voltage-clamp conditions (tested at +40 mV) no heterosynaptic interactions were seen. 6. The time course of 'heterosynaptic facilitation' at -60 mV and of 'heterosynaptic depression' at +40 mV of EPSPN was similar to the time course of EPSCN. 7. We conclude, firstly, that the voltage clamp is able to prevent any voltage breakthrough associated with the synaptic activation of NMDA receptors from influencing neighbouring synapses. Secondly, when the neurone is not voltage clamped these same synapses are strongly influenced by the spreading depolarization generated by the synaptic activation of their neighbours. The time course and direction of this influence are compatible with the hypothesis that spreading synaptic depolarization, leading to a reduction of the voltage-dependent Mg2+ block of synaptic NMDA receptor channels, underlies the property of associativity.
Full text
PDF
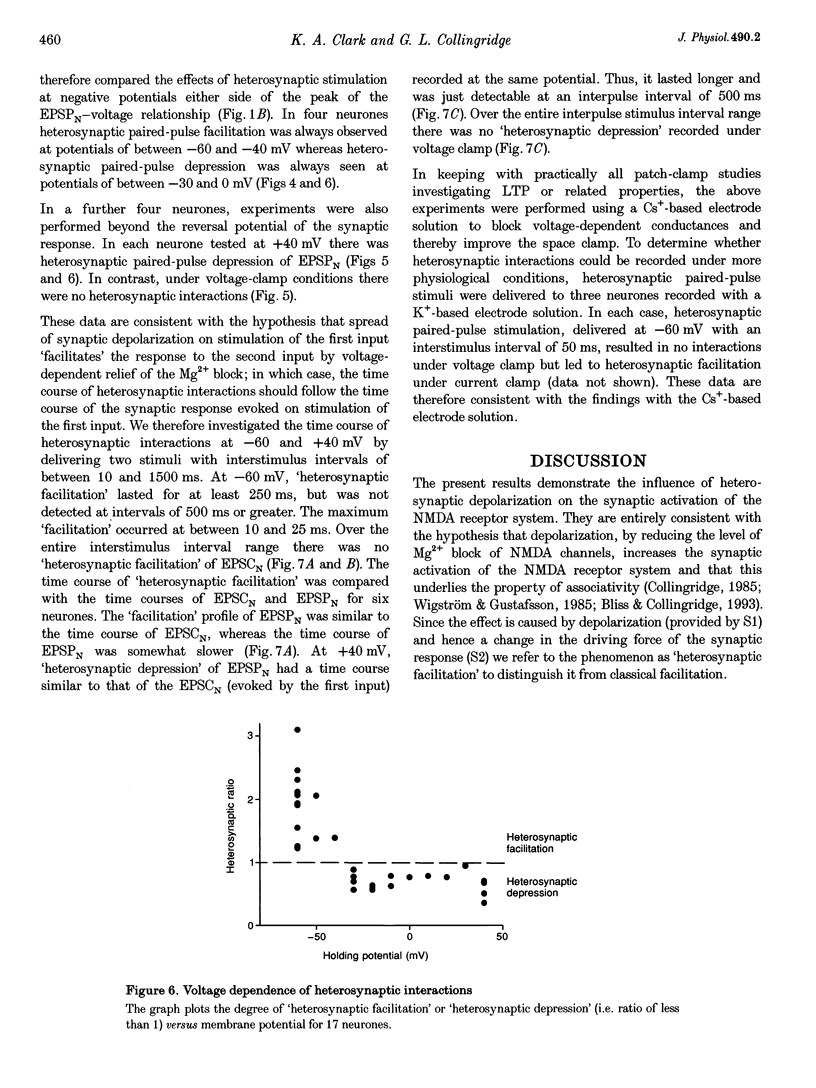

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
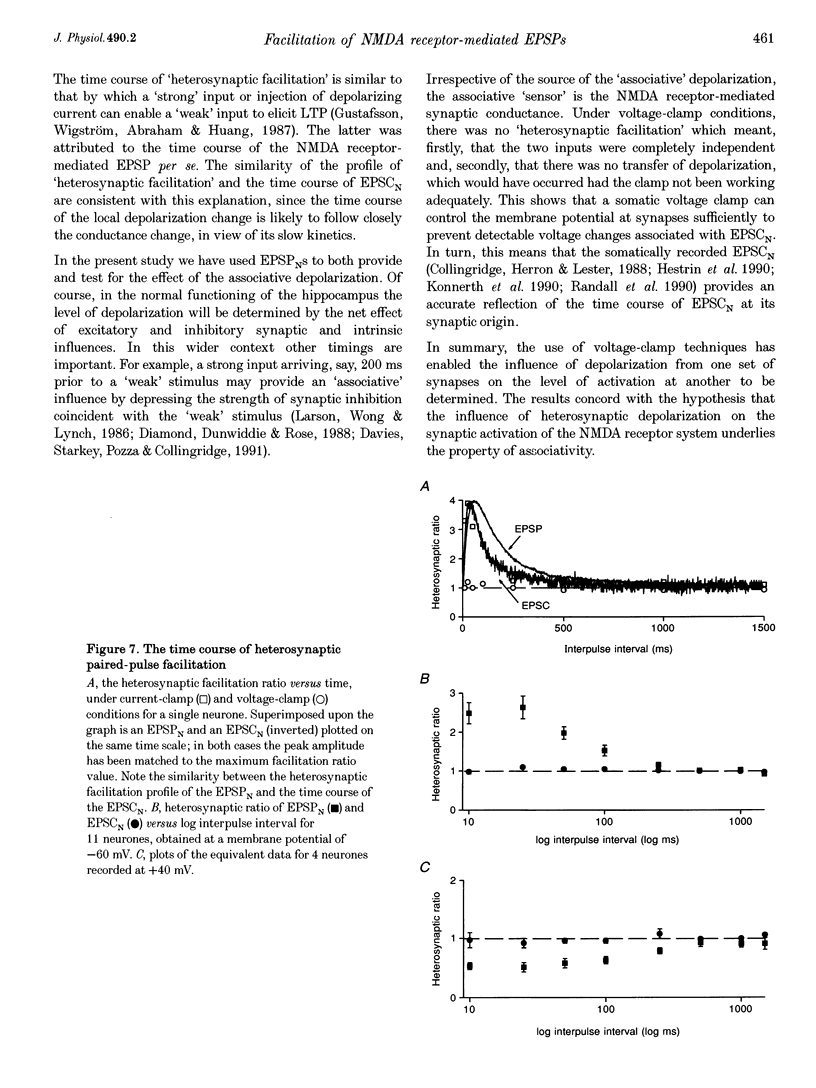
- Barrionuevo G., Brown T. H. Associative long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton M. G., Lo Turco J. J., Kriegstein A. R. Whole cell recording from neurons in slices of reptilian and mammalian cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Methods. 1989 Dec;30(3):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(89)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark K. A., Randall A. D., Collingridge G. L. A comparison of paired-pulsed facilitation of AMPA and NMDA receptor-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents in the hippocampus. Exp Brain Res. 1994;101(2):272–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00228747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Herron C. E., Lester R. A. Synaptic activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:283–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. Excitatory amino acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. H., Starkey S. J., Pozza M. F., Collingridge G. L. GABA autoreceptors regulate the induction of LTP. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):609–611. doi: 10.1038/349609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Wigström H., Abraham W. C., Huang Y. Y. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus using depolarizing current pulses as the conditioning stimulus to single volley synaptic potentials. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):774–780. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00774.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Wigström H. Hippocampal long-lasting potentiation produced by pairing single volleys and brief conditioning tetani evoked in separate afferents. J Neurosci. 1986 Jun;6(6):1575–1582. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-06-01575.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konnerth A., Keller B. U., Ballanyi K., Yaari Y. Voltage sensitivity of NMDA-receptor mediated postsynaptic currents. Exp Brain Res. 1990;81(1):209–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00230117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson J., Wong D., Lynch G. Patterned stimulation at the theta frequency is optimal for the induction of hippocampal long-term potentiation. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 19;368(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90579-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy W. B., Steward O. Synapses as associative memory elements in the hippocampal formation. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 19;175(2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)91003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton B. L., Douglas R. M., Goddard G. V. Synaptic enhancement in fascia dentata: cooperativity among coactive afferents. Brain Res. 1978 Nov 24;157(2):277–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall A. D., Schofield J. G., Collingridge G. L. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings of an NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic current in rat hippocampal slices. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Jul 3;114(2):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90070-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry B. R., Goh J. W., Auyeung A. Associative induction of posttetanic and long-term potentiation in CA1 neurons of rat hippocampus. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):988–990. doi: 10.1126/science.3010459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigström H., Gustafsson B. On long-lasting potentiation in the hippocampus: a proposed mechanism for its dependence on coincident pre- and postsynaptic activity. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Apr;123(4):519–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


