Abstract
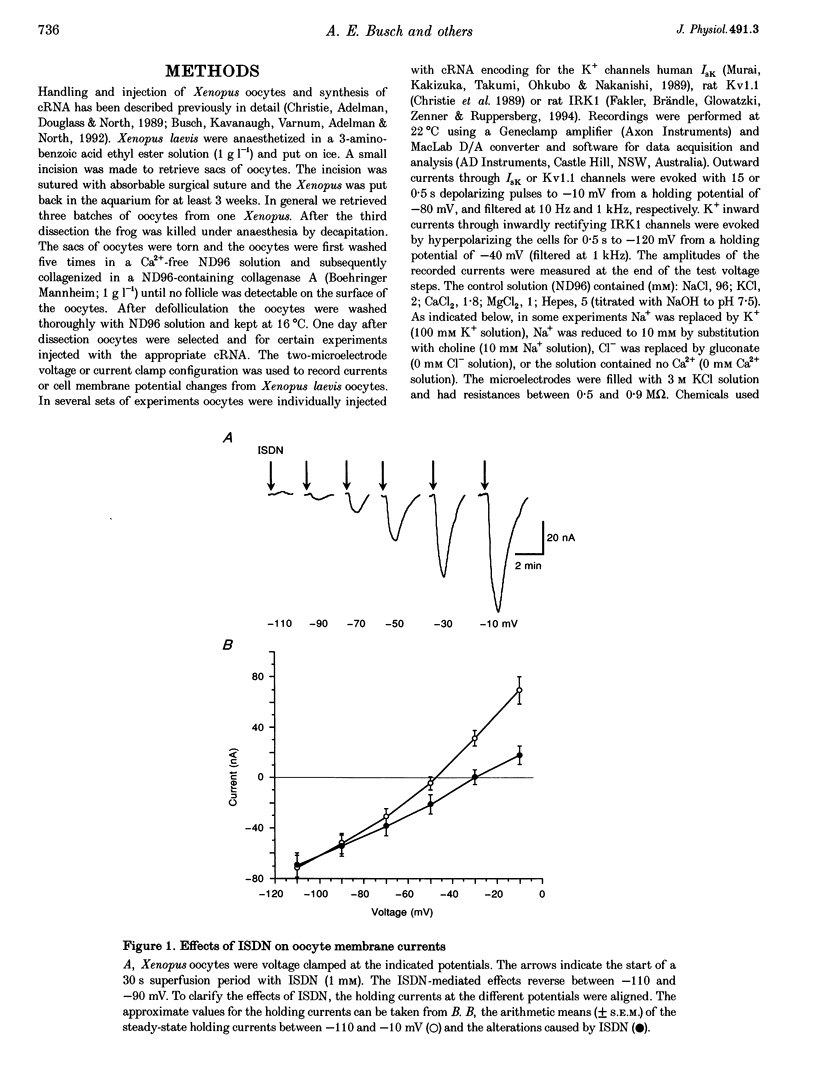
1. The effects of isosorbiddinitrate (ISDN) were tested on membrane currents and resting potential in Xenopus laevis oocytes which were either uninjected or injected with cRNA encoding for K+ channels from three distinct families (slowly activating IsK channels, delayed-rectifying Kv1.1 or inwardly rectifying IRK1 K+ channels). 2. In uninjected oocytes ISDN (1 mM) resulted in a decrease of the holding current at potentials more positive than -100 mV and in an increase at potentials below -100 mV. Increasing extracellular K+ to 100 mM shifted the reversal potential for ISDN-mediated effects to approximately -12 mV, suggesting an inhibition of a K+ conductance by ISDN. 3. In current clamp studies ISDN (1 mM) and Ba2+ (3 mM) depolarized cell membrane. ISDN and Ba2+ had no additive effects on membrane potential when applied simultaneously. In voltage clamp studies, corresponding results were observed for the effects of ISDN and Ba2+ on the holding current with an apparent K(m) of 0.21 and 0.08 mM, respectively. 4. In contrast to ISDN, the nitric oxide (NO) donors isosorbidmononitrate (ISMN) and S-nitrosocysteine (SNOC) had no effects on the holding currents in Xenopus oocytes. Moreover, the guanylate inhibitor LY 83583 did not affect ISDN-mediated holding current alterations, suggesting that ISDN acts independently of the second messenger NO. 5. ISDN inhibited exogenously expressed IsK channels with an apparent K(m) of 0.15 mM, but at 1 mM only weakly inhibited Kv1.1 and IRK1 channels. 6. It is concluded that ISDN inhibits an endogenous K+ conductance in Xenopus oocytes with a similar potency to that shown by expressed IsK channels. These effects are independent of the second messenger NO.
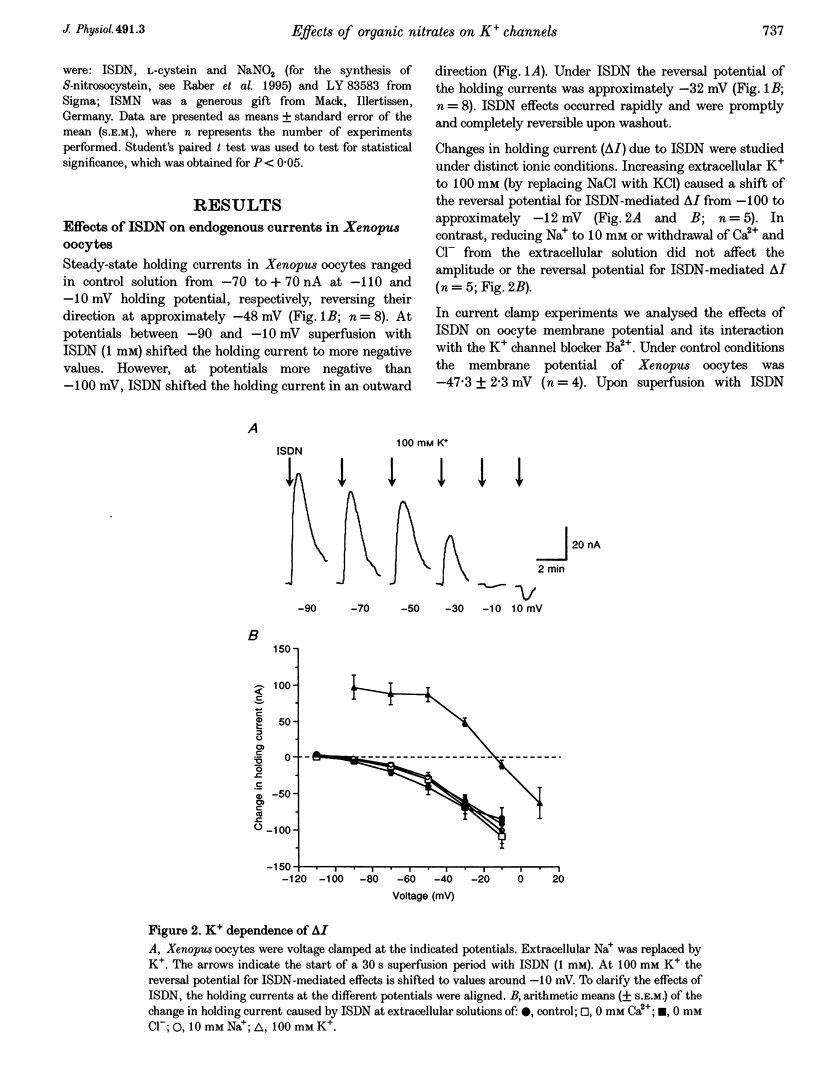
Full text
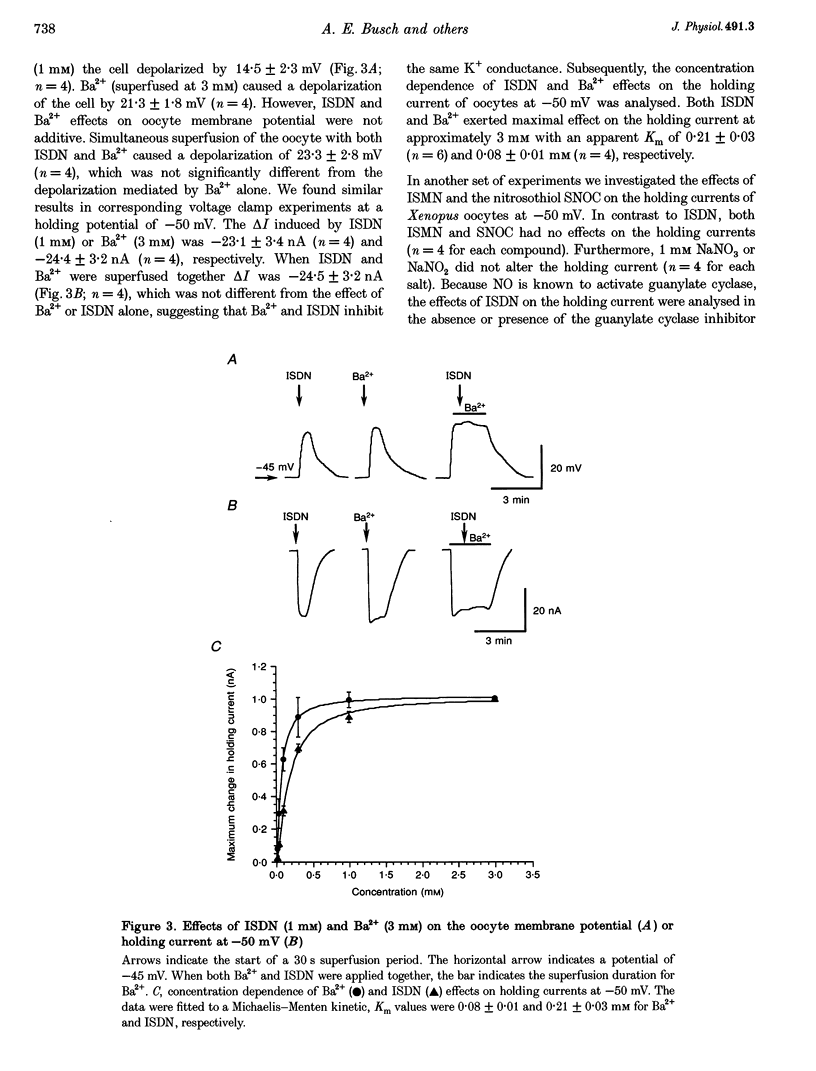
PDF

Selected References
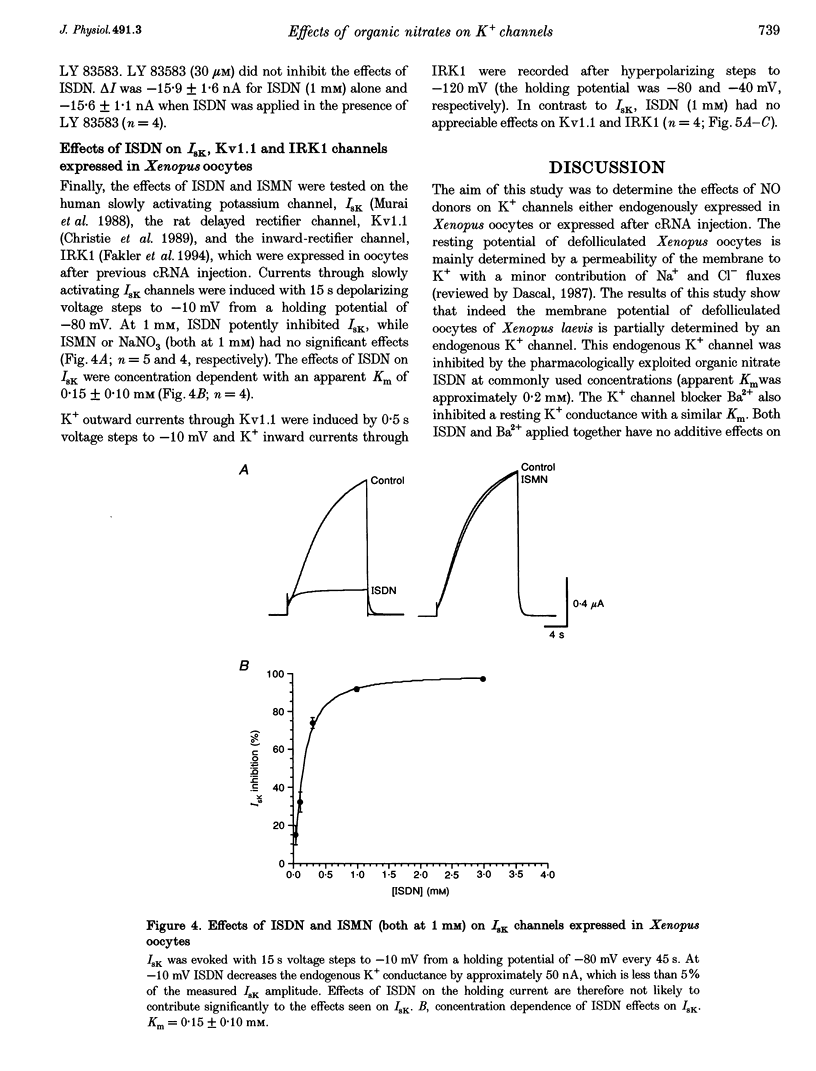
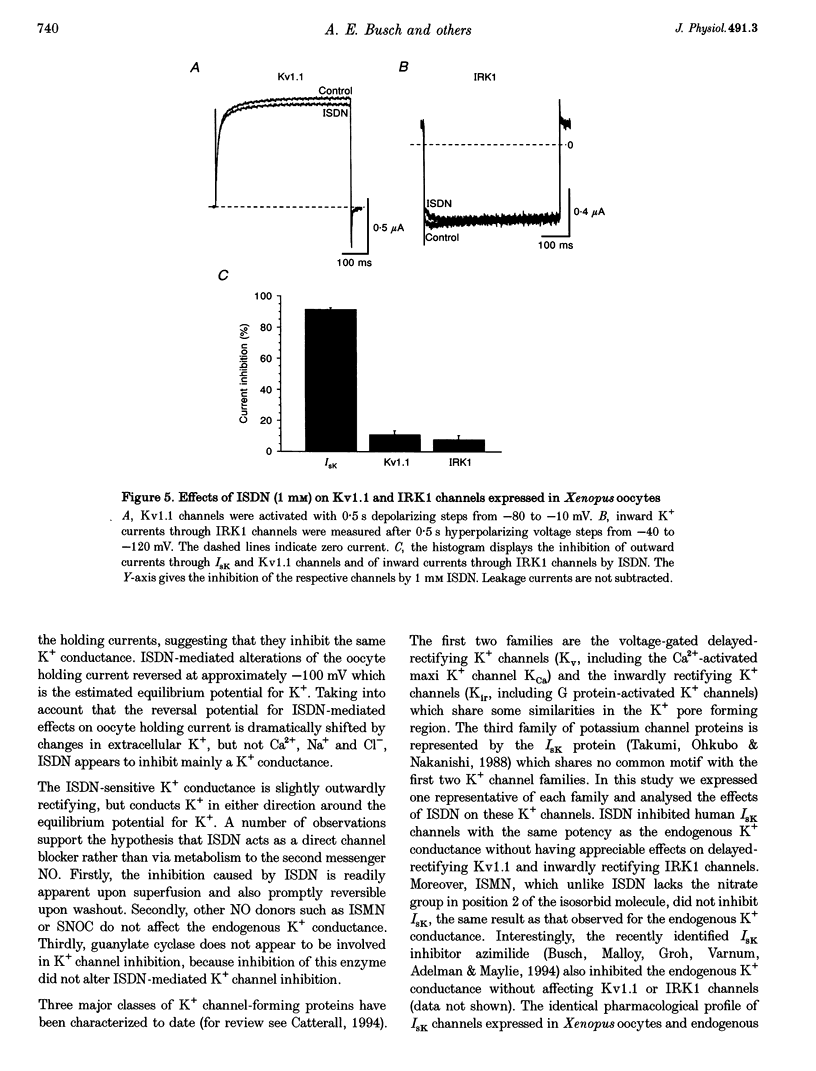
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolotina V. M., Najibi S., Palacino J. J., Pagano P. J., Cohen R. A. Nitric oxide directly activates calcium-dependent potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):850–853. doi: 10.1038/368850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch A. E., Kavanaugh M. P., Varnum M. D., Adelman J. P., North R. A. Regulation by second messengers of the slowly activating, voltage-dependent potassium current expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:491–502. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch A. E., Malloy K., Groh W. J., Varnum M. D., Adelman J. P., Maylie J. The novel class III antiarrhythmics NE-10064 and NE-10133 inhibit IsK channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes and IKs in guinea pig cardiac myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jul 15;202(1):265–270. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch A. E., Waldegger S., Herzer T., Raber G., Gulbins E., Takumi T., Moriyoshi K., Nakanishi S., Lang F. Molecular basis of IsK protein regulation by oxidation or chelation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 24;270(8):3638–3641. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.8.3638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Molecular properties of a superfamily of plasma-membrane cation channels. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;6(4):607–615. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerbai E., Ambrosio G., Porciatti F., Chiariello M., Giotti A., Mugelli A. Cellular electrophysiological basis for oxygen radical-induced arrhythmias. A patch-clamp study in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Circulation. 1991 Oct;84(4):1773–1782. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.4.1773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., Adelman J. P., Douglass J., North R. A. Expression of a cloned rat brain potassium channel in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):221–224. doi: 10.1126/science.2539643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascal N. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the study of ion channels. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;22(4):317–387. doi: 10.3109/10409238709086960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakler B., Brändle U., Glowatzki E., Zenner H. P., Ruppersberg J. P. Kir2.1 inward rectifier K+ channels are regulated independently by protein kinases and ATP hydrolysis. Neuron. 1994 Dec;13(6):1413–1420. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90426-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Lippton H., Edwards J. C., Baricos W. H., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J., Gruetter C. A. Mechanism of vascular smooth muscle relaxation by organic nitrates, nitrites, nitroprusside and nitric oxide: evidence for the involvement of S-nitrosothiols as active intermediates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):739–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei S. Z., Pan Z. H., Aggarwal S. K., Chen H. S., Hartman J., Sucher N. J., Lipton S. A. Effect of nitric oxide production on the redox modulatory site of the NMDA receptor-channel complex. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1087–1099. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. A pathway for the regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 1;38(11):1709–1715. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai T., Kakizuka A., Takumi T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human genomic DNA encoding a novel membrane protein which exhibits a slowly activating potassium channel activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 30;161(1):176–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raber G., Waldegger S., Herzer T., Gulbins E., Murer H., Busch A. E., Lang F. The nitroso-donor S-nitroso-cysteine regulates IsK expressed in Xenopus oocytes via a c-GMP independent mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Feb 6;207(1):195–201. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takumi T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning of a membrane protein that induces a slow voltage-gated potassium current. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1042–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.3194754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


