Abstract
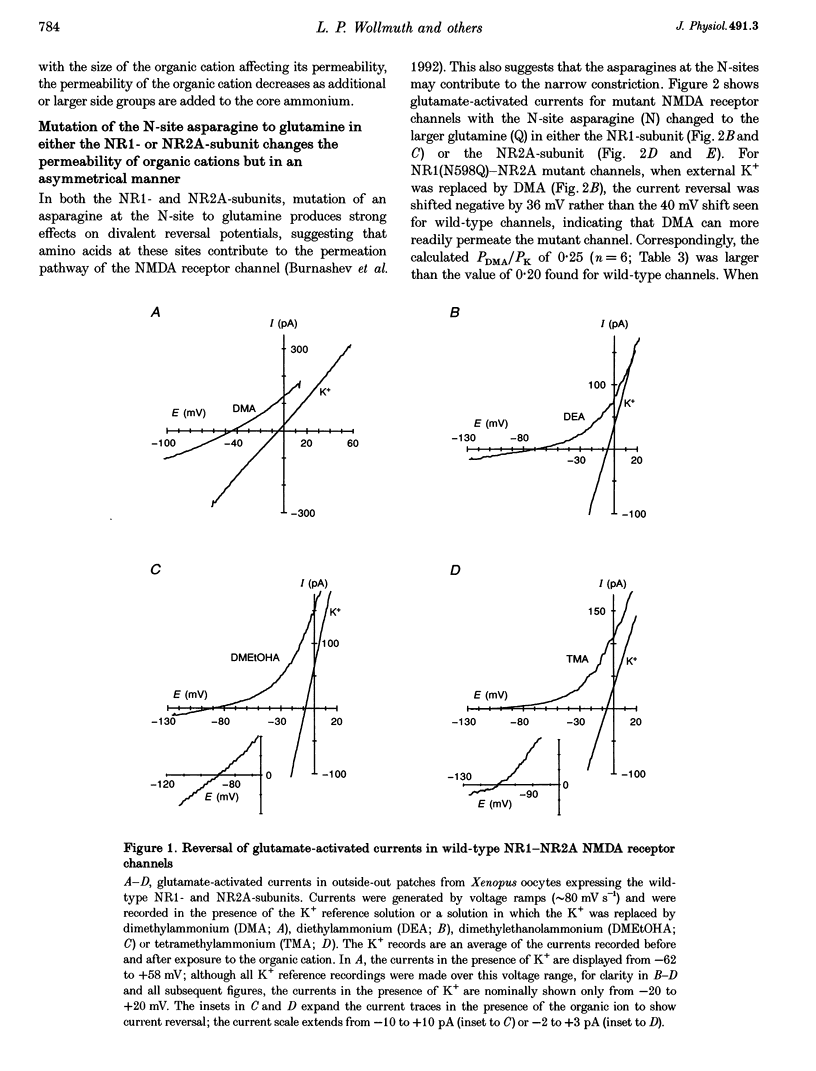
1. The molecular determinants for the narrow constriction of recombinant N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor channels composed of wild-type and mutant NR1- and NR2A-subunits were studied in Xenopus oocytes. 2. The relative permeability of differently sized organic cations was used as an indicator of the size of the narrow constriction. From measured reversal potentials under bi-ionic conditions with K+ as the reference solution, permeability ratios were calculated with the Lewis equation. 3. For wild-type NMDA receptor channels, five organic cations showed clear reversal potentials, with permeability ratios (PX/PK): ammonium, 1.28; methylammonium, 0.48; dimethylammonium (DMA), 0.20; diethylammonium, 0.07; and dimethylethanol-ammonium, 0.02. 4. Mutation of the N-site asparagine (N) to glutamine (Q) at homologous positions in either NR1 (position 598) or NR2A (position 595) increased the permeability of DMA relative to wild-type channels about equally. However, for larger sized organic cations, the NR1(N598Q) mutation had stronger effects on increasing their permeability whereas the NR2A(N595Q) mutation was without effect. These changes in organic cation permeability suggest that the NR1(N598Q) mutation increases the pore size while the NR2A(N595Q) mutation does not. 5. Channels in which the NR1 N-site asparagine was replaced by the smaller glycine (G), NR1(N598G)-NR2A, showed the largest increase in pore size of all sites examined in either subunit. In contrast, in the NR2A-subunit the same N-site substitution to glycine produced only small effects on pore size. 6. For the NR2A-subunit, an asparagine residue (position 596) on the C-terminal side of the N-site, when mutated to larger or smaller sized amino acids, produced large, volume-specific effects on pore size. The mutant channel NR1-NR2A(N596G) had the largest increase in pore size of all sites examined in the NR2A-subunit. In contrast, mutation of the homologous position in the NR1-subunit had no effect on pore size. 7. The cross-sectional diameter of the narrow constriction in wild-type NMDA receptor channels was estimated to be 0.55 nm. The pore sizes of the NR1(N598G)-NR2A and NR1-NR2A(N596G) mutant channels increased to approximately 0.75 and 0.67 nm, respectively. The double mutation, NR1(N598G)-NR2A(596G), increased the pore size to approximately 0.87 nm, essentially the sum of the increase produced by the individual mutations. 8. It is concluded that both the NR1- and NR2A-subunits contribute to the narrow constriction of NMDA receptor channels with asparagines located at non-homologous positions. The major determinants of the narrow constriction in NMDA receptor channels are the NR1 N-site asparagine and an asparagine adjacent to the NR2A N-site.
Full text
PDF




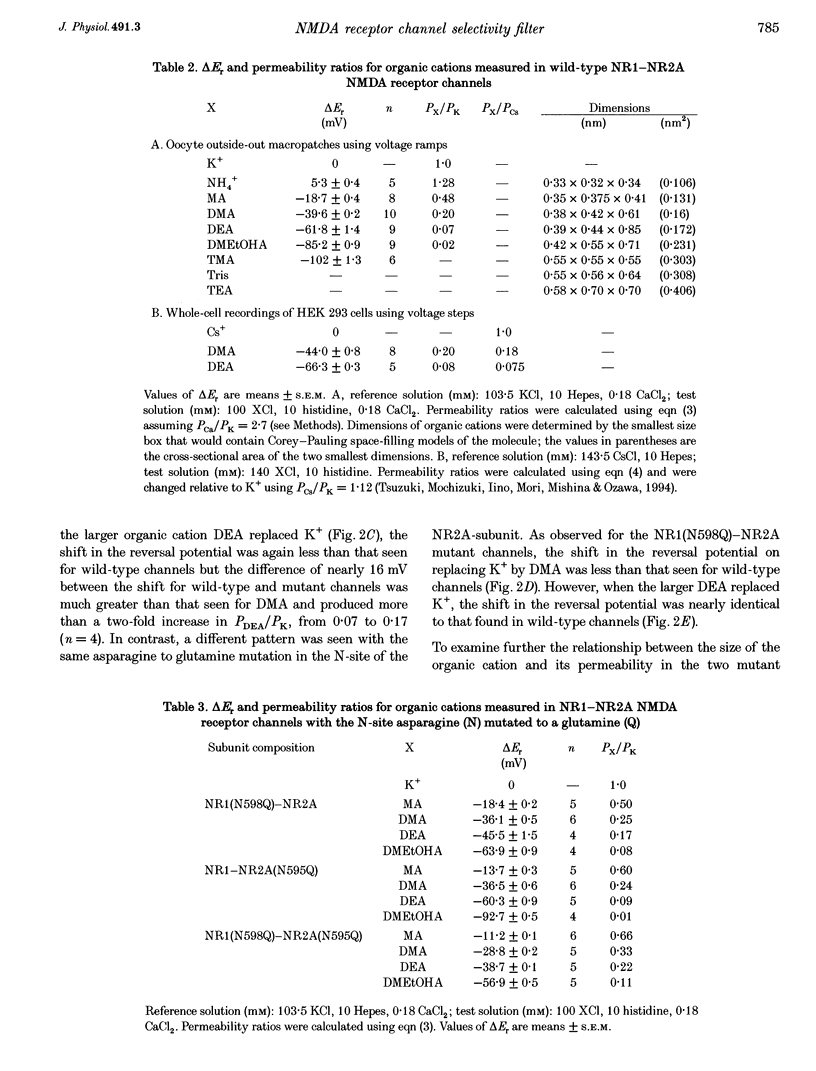
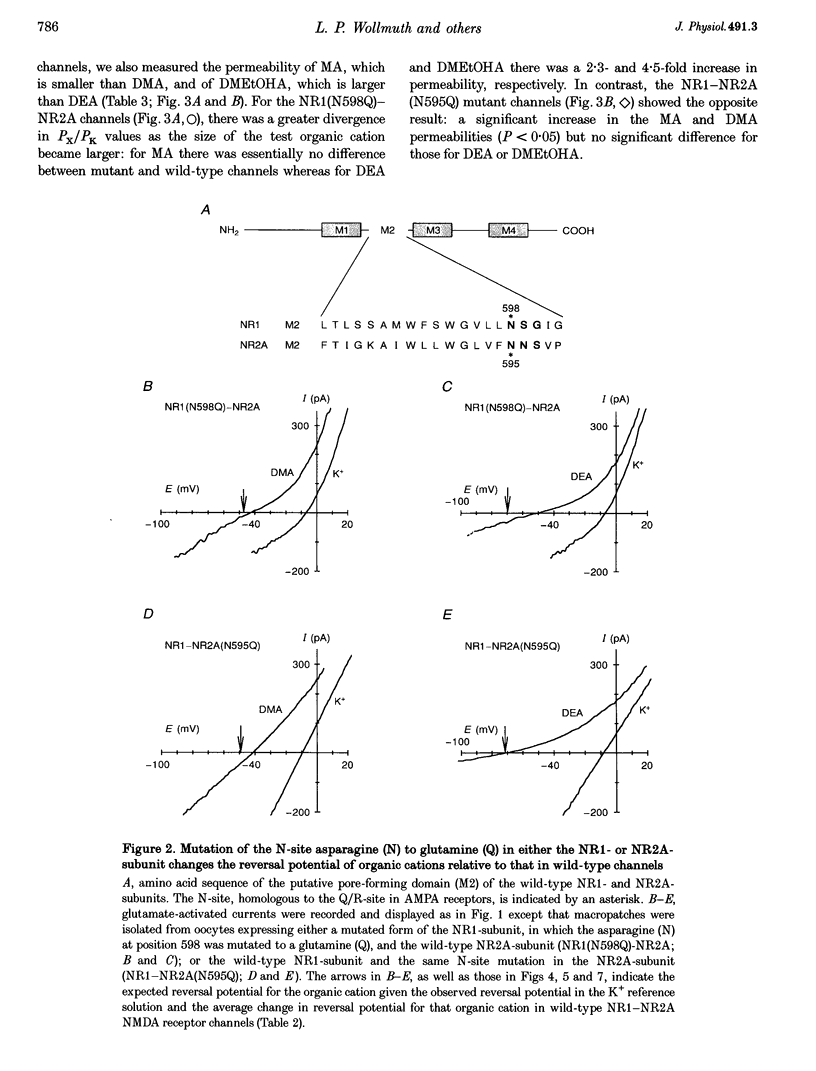
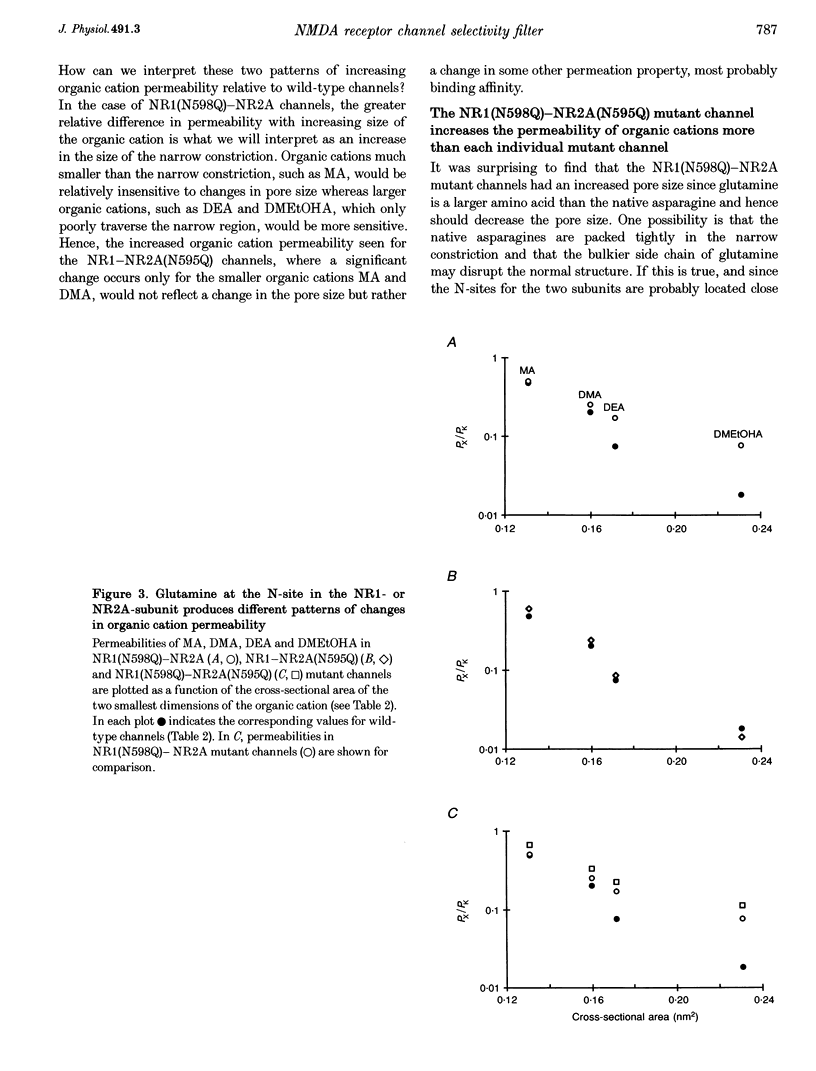
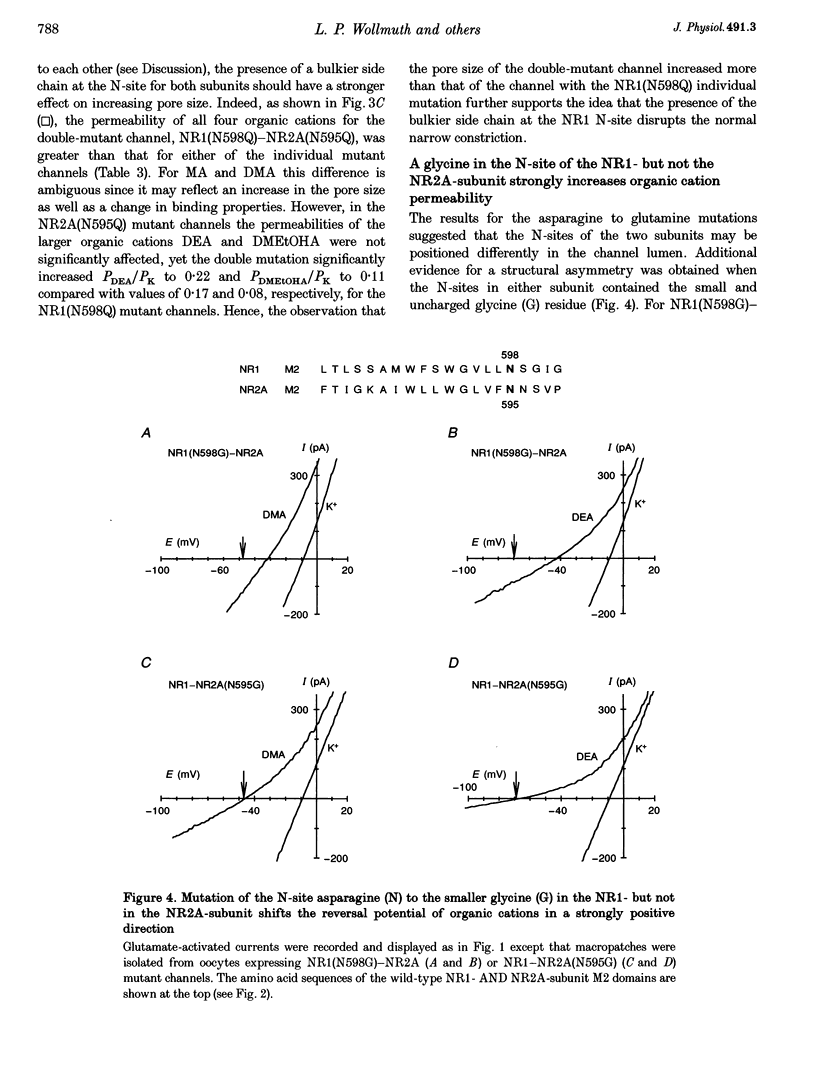





Images in this article
Selected References
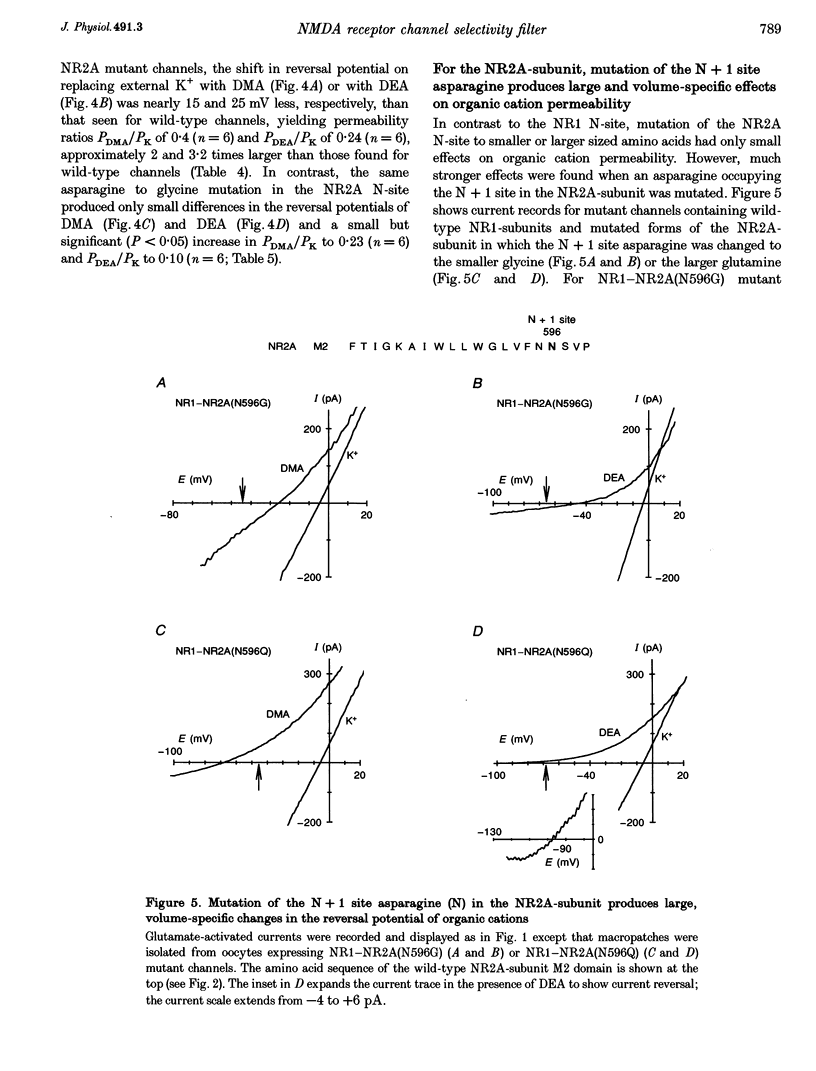
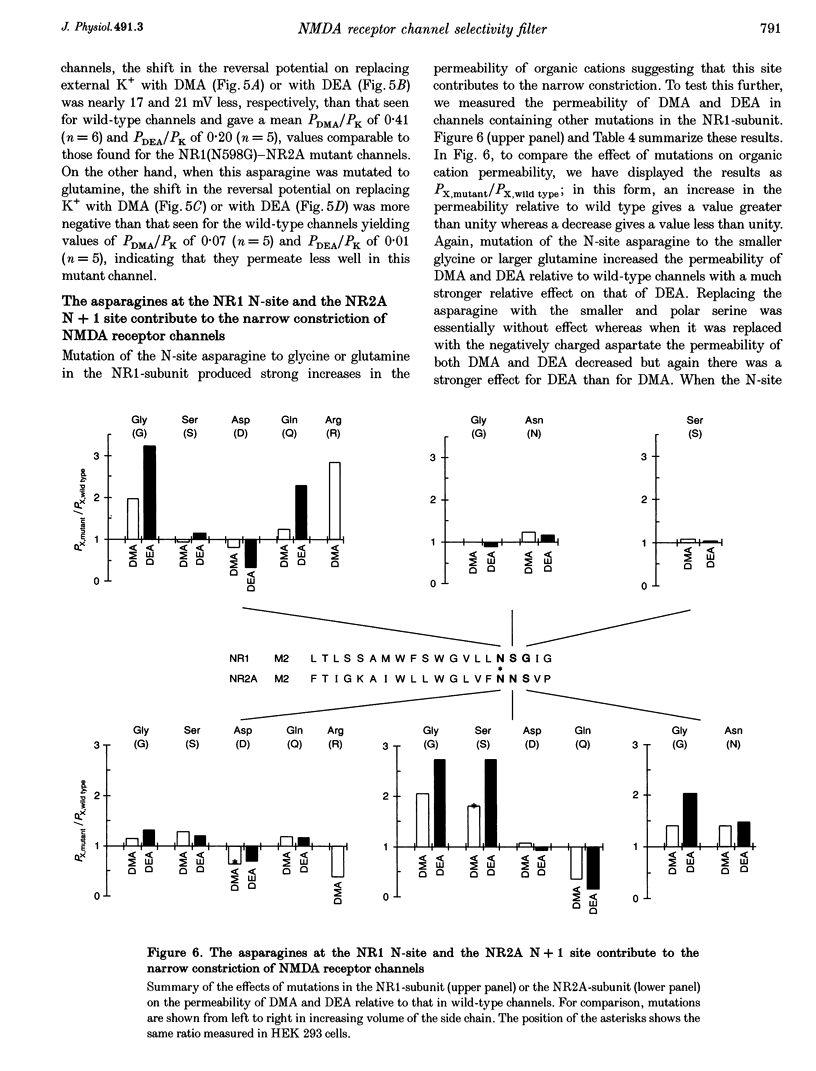
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
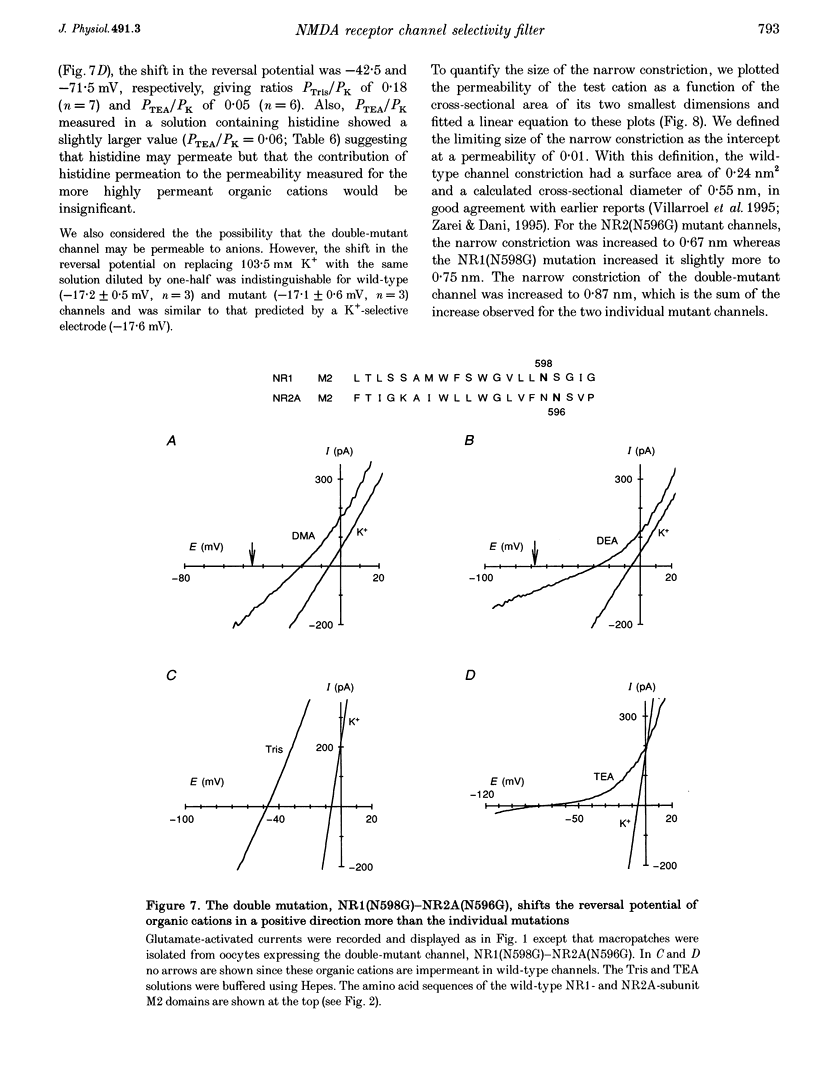
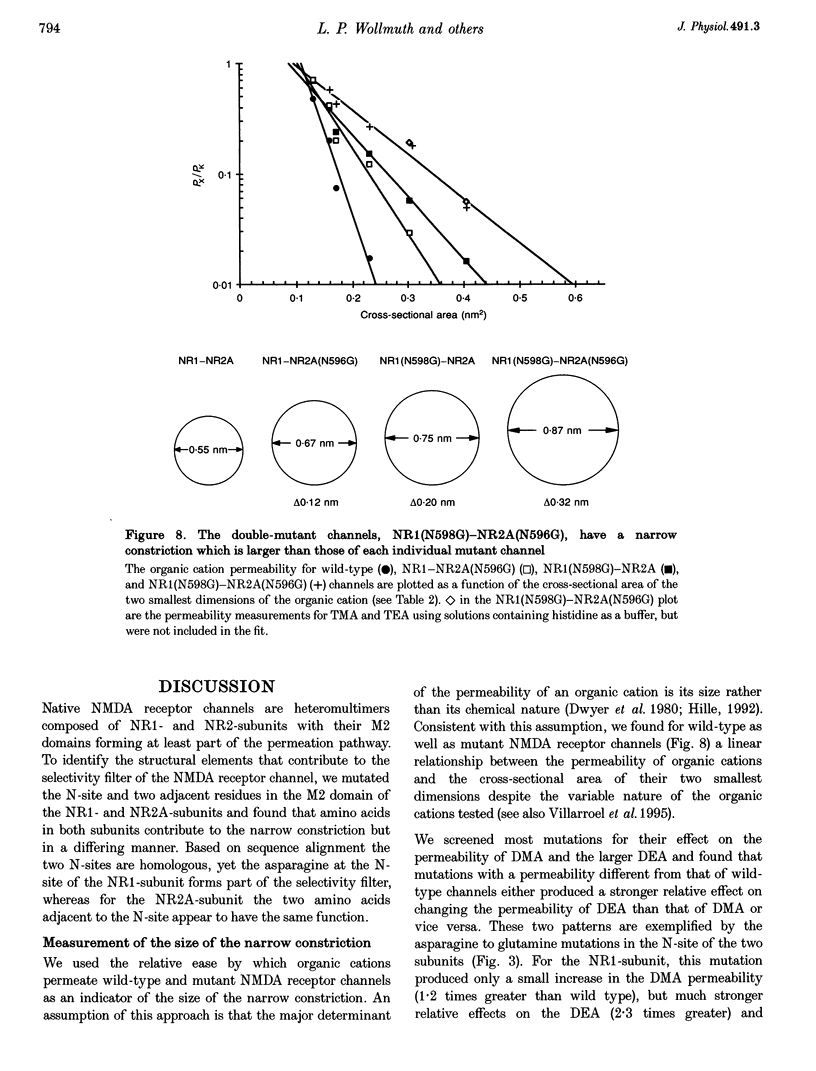
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W. Non-selective conductance in calcium channels of frog muscle: calcium selectivity in a single-file pore. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:585–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. A., Dingledine R. Topology profile for a glutamate receptor: three transmembrane domains and a channel-lining reentrant membrane loop. Neuron. 1995 Feb;14(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Schoepfer R., Monyer H., Ruppersberg J. P., Günther W., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Control by asparagine residues of calcium permeability and magnesium blockade in the NMDA receptor. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1415–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1382314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M., Tu Y., Euskirchen G., Ward W. W., Prasher D. C. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):802–805. doi: 10.1126/science.8303295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Jonas P., Sakmann B. Action of brief pulses of glutamate on AMPA/kainate receptors in patches from different neurones of rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:261–287. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C. W., Monaghan D. T., Ganong A. H. Excitatory amino acid neurotransmission: NMDA receptors and Hebb-type synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:61–80. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer T. M., Adams D. J., Hille B. The permeability of the endplate channel to organic cations in frog muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):469–492. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic G. P., Hollmann M. Molecular neurobiology of glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:507–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:31–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Maron C., Heinemann S. N-glycosylation site tagging suggests a three transmembrane domain topology for the glutamate receptor GluR1. Neuron. 1994 Dec;13(6):1331–1343. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90419-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Rogers S. W., Heinemann S. Cloning by functional expression of a member of the glutamate receptor family. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):643–648. doi: 10.1038/342643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Nagasawa M., Mori H., Araki K., Sakimura K., Watanabe M., Inoue Y., Mishina M. Cloning and expression of the epsilon 4 subunit of the NMDA receptor channel. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 16;313(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81178-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutsuwada T., Kashiwabuchi N., Mori H., Sakimura K., Kushiya E., Araki K., Meguro H., Masaki H., Kumanishi T., Arakawa M. Molecular diversity of the NMDA receptor channel. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):36–41. doi: 10.1038/358036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A. The permeation pathway of neurotransmitter-gated ion channels. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1992;21:267–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.21.060192.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. A. Ion-concentration dependence of the reversal potential and the single channel conductance of ion channels at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:417–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Miller R. J. Excitatory amino acid receptors, second messengers and regulation of intracellular Ca2+ in mammalian neurons. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jun;11(6):254–260. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B., Garthwaite J. Excitatory amino acid neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Sep;11(9):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90184-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Witzemann V., Takahashi T., Mishina M., Numa S., Sakmann B. Patch clamp measurements on Xenopus laevis oocytes: currents through endogenous channels and implanted acetylcholine receptor and sodium channels. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Dec;407(6):577–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00582635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monyer H., Sprengel R., Schoepfer R., Herb A., Higuchi M., Lomeli H., Burnashev N., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Heteromeric NMDA receptors: molecular and functional distinction of subtypes. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1217–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raditsch M., Ruppersberg J. P., Kuner T., Günther W., Schoepfer R., Seeburg P. H., Jahn W., Witzemann V. Subunit-specific block of cloned NMDA receptors by argiotoxin636. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 7;324(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81533-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Cummings J., Roldan L. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Changing subunit composition of heteromeric NMDA receptors during development of rat cortex. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):144–147. doi: 10.1038/368144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara H., Moriyoshi K., Ishii T., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Structures and properties of seven isoforms of the NMDA receptor generated by alternative splicing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):826–832. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91701-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuzuki K., Mochizuki S., Iino M., Mori H., Mishina M., Ozawa S. Ion permeation properties of the cloned mouse epsilon 2/zeta 1 NMDA receptor channel. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Oct;26(1-2):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarroel A., Burnashev N., Sakmann B. Dimensions of the narrow portion of a recombinant NMDA receptor channel. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):866–875. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80263-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wo Z. G., Oswald R. E. Unraveling the modular design of glutamate-gated ion channels. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Apr;18(4):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)93895-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood M. W., VanDongen H. M., VanDongen A. M. Structural conservation of ion conduction pathways in K channels and glutamate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):4882–4886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.4882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarei M. M., Dani J. A. Ionic permeability characteristics of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Feb;103(2):231–248. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarei M. M., Dani J. A. Structural basis for explaining open-channel blockade of the NMDA receptor. J Neurosci. 1995 Feb;15(2):1446–1454. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-02-01446.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



