Abstract
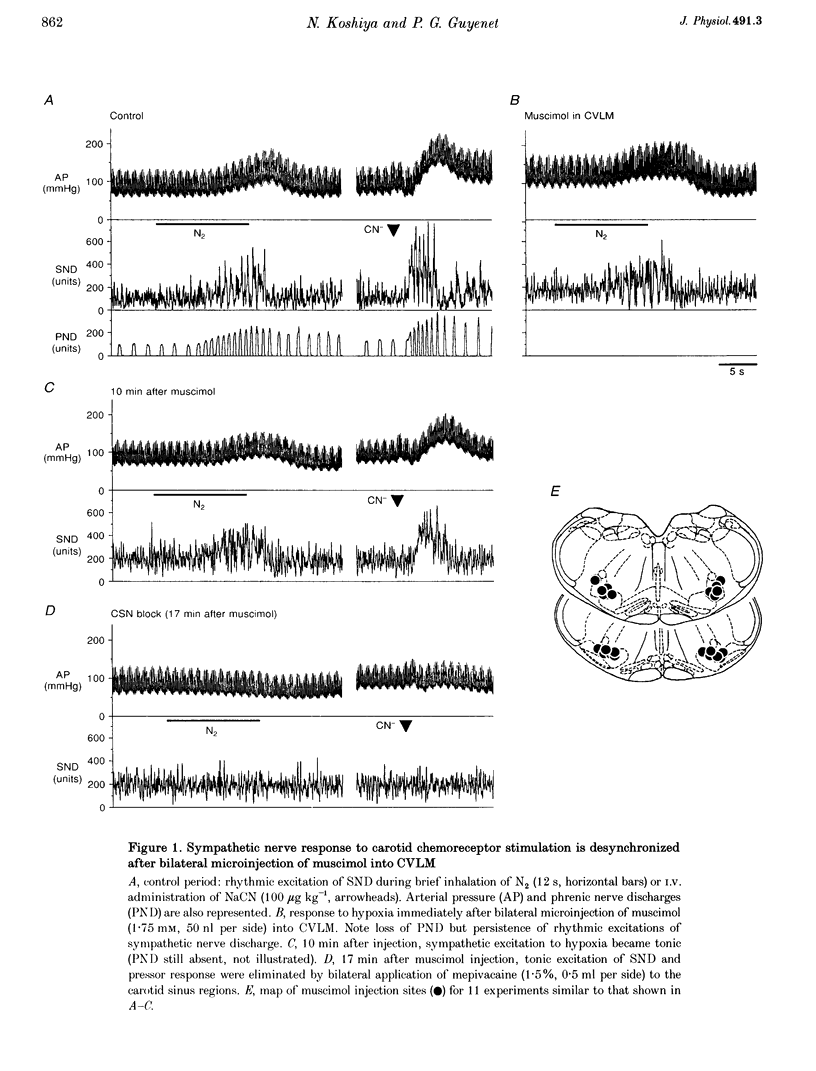
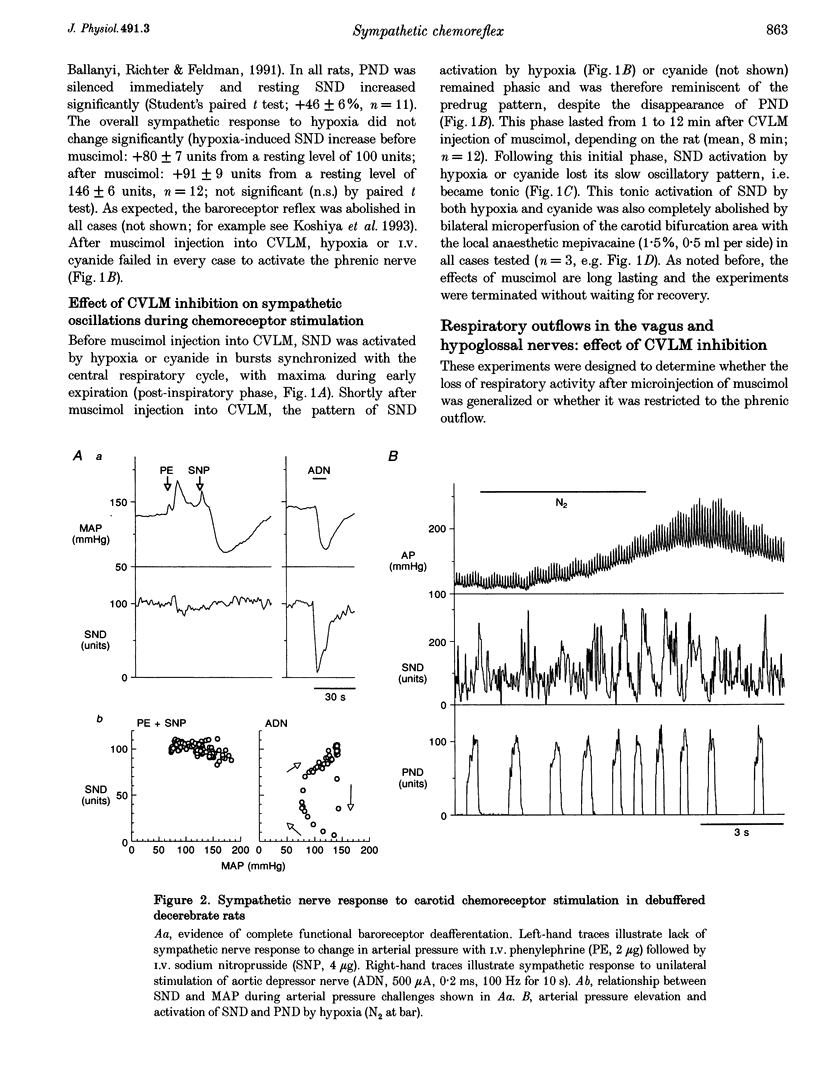
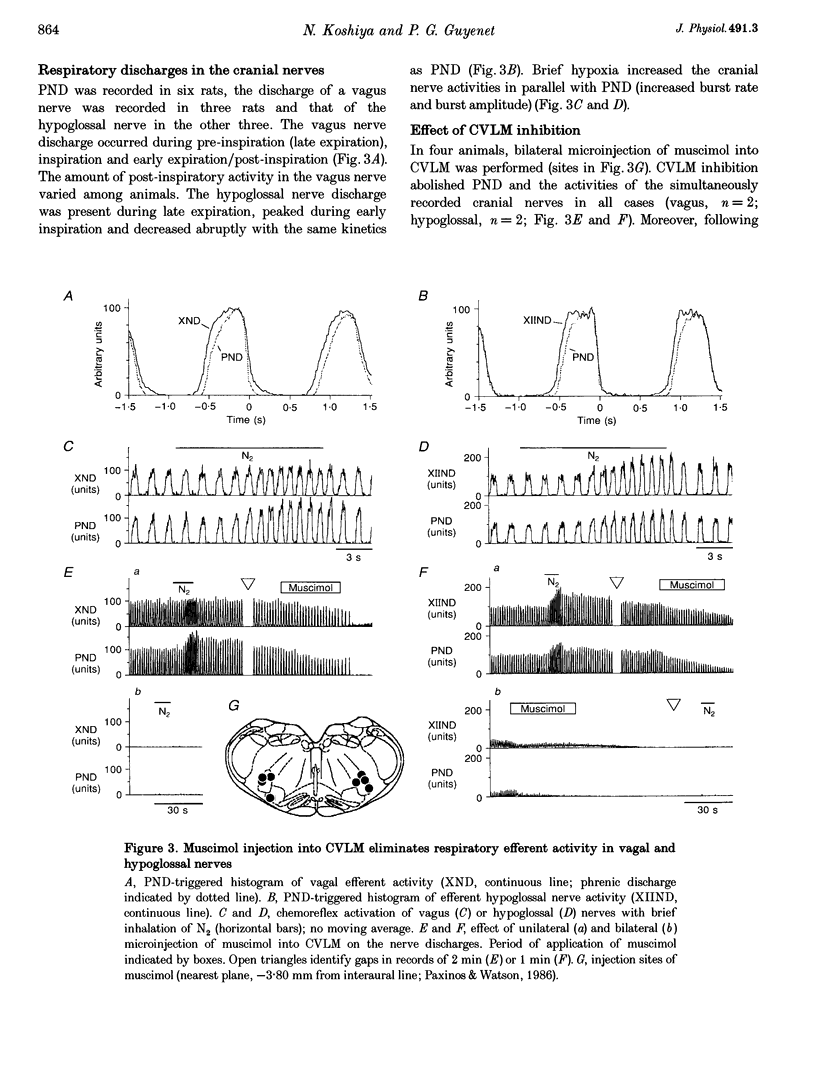
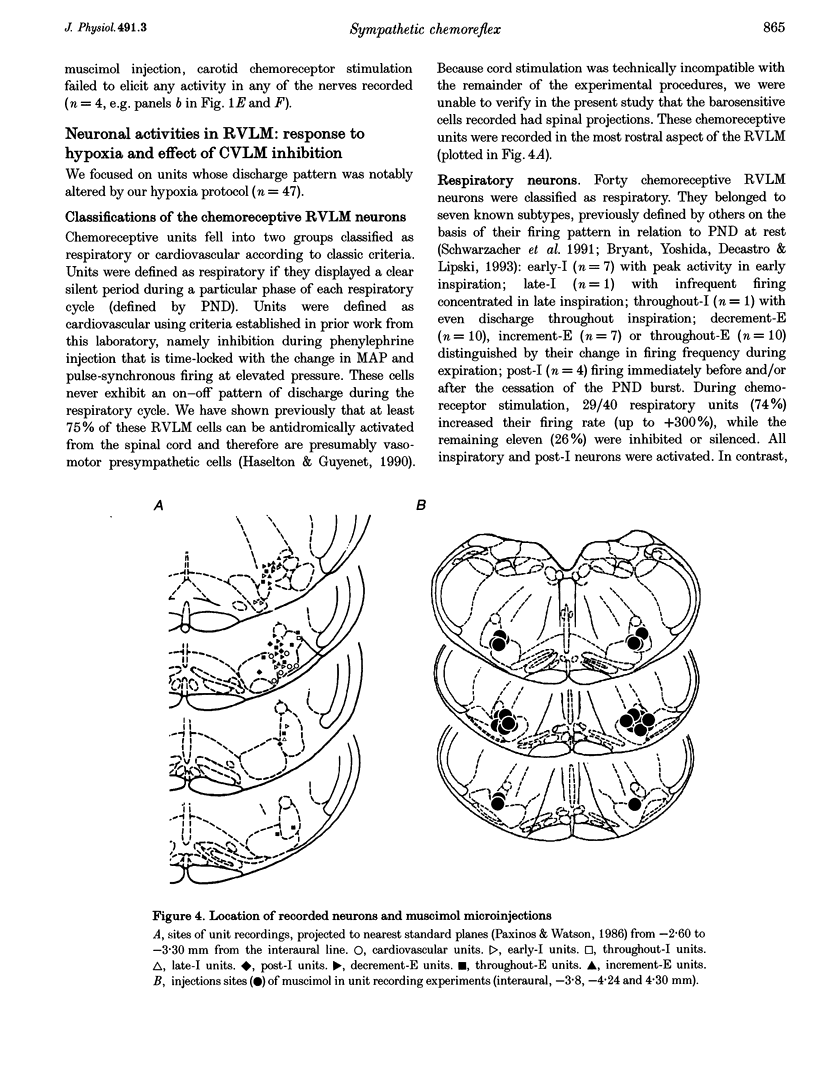
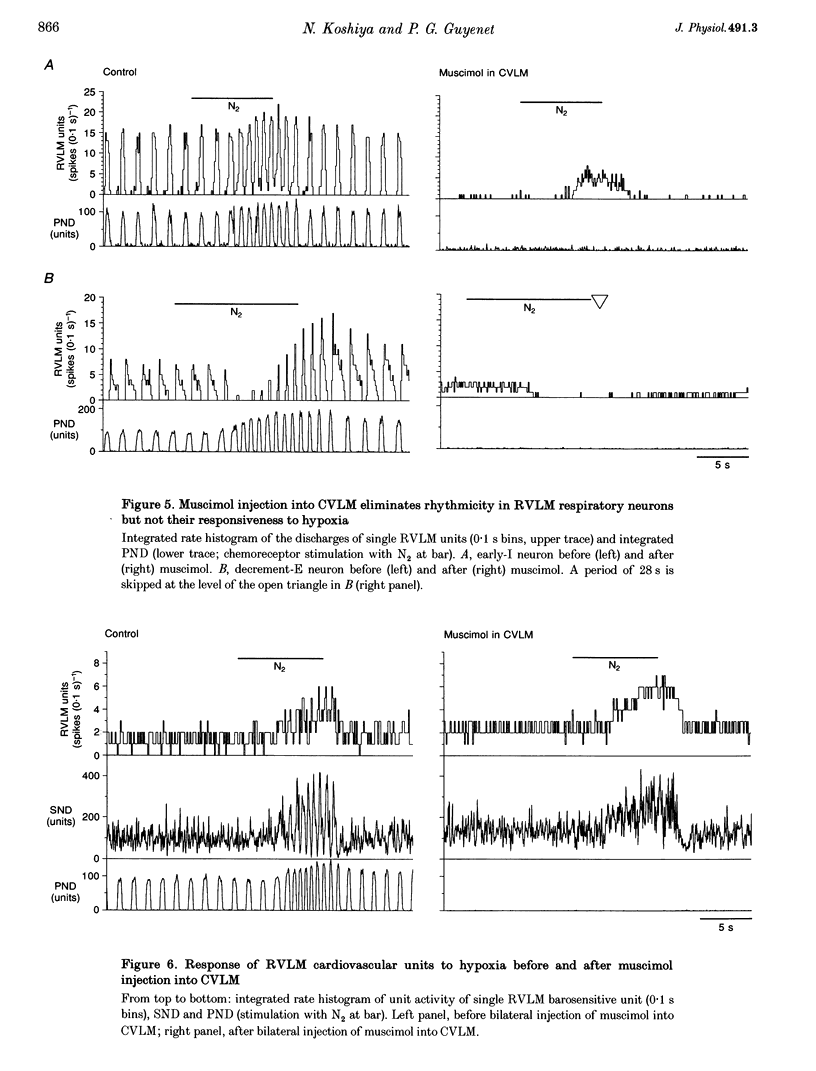
1. We sought to determine whether the increase in sympathetic nerve discharge (SND) caused by carotid chemoreceptor stimulation requires the integrity of ventrolateral medullary structures involved in generating respiratory rhythm and pattern. Experiments were done in urethane-anaesthetized, vagotomized, aortic deafferented, ventilated rats except when indicated (see paragraph 3). 2. Brief hypoxia (N2 for 5-12 s) or I.V. NaCN (50-100 micrograms kg-1) activated SND in bursts synchronized with the phrenic nerve discharge (PND). No effect was produced in chemo-deafferented rats. 3. In unanaesthetized vagotomized decerebrated rats, ligation of the internal carotid arteries preserved peripheral chemoreceptor function but abolished baroreflexes. In this preparation, stimulation of peripheral chemoreceptors (N2 for 2-6 s) also activated SND in bursts synchronized with PND. 4. Bilateral microinjection of the GABAA receptor agonist muscimol into the caudal ventrolateral medulla (CVLM) instantly blocked the sympathetic baroreflex, eliminated PND at rest and during chemoreceptor stimulation but did not change the mean increase in SND produced by chemoreceptor stimulation. Sympathoactivation in response to chemoreceptor stimulation became tonic after 1-13 min and was still totally dependent on the integrity of the carotid sinus nerves. 5. Muscimol injection instantly eliminated the respiratory outflow of the Xth and XIIth cranial nerves, both at rest and during chemoreceptor stimulation. 6. Muscimol eliminated the on-off respiratory pattern of neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM). During chemoreceptor stimulation, these cells became activated or inhibited tonically. 7. Muscimol injection raised the resting discharge rate of vasomotor presympathetic cells in RVLM, blocked their baroreceptor inputs but did not change the magnitude of their excitation by chemoreceptor stimulation. Muscimol injection eliminated their respiratory modulation. 8. In conclusion, the sympathetic response to chemoreceptor stimulation may be due to convergence and integration in RVLM of two processes: respiration-independent excitatory input to RVLM neurons and respiratory patterning of their activities via inputs from the pre-Bötzinger complex.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D. L., Guyenet P. G. Electrophysiological study of cardiovascular neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla in rats. Circ Res. 1985 Mar;56(3):359–369. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant T. H., Yoshida S., de Castro D., Lipski J. Expiratory neurons of the Bötzinger Complex in the rat: a morphological study following intracellular labeling with biocytin. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Sep 8;335(2):267–282. doi: 10.1002/cne.903350210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyenet P. G., Darnall R. A., Riley T. A. Rostral ventrolateral medulla and sympathorespiratory integration in rats. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):R1063–R1074. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.259.5.R1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyenet P. G., Koshiya N. Working model of the sympathetic chemoreflex in rats. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1995 Jan-Feb;17(1-2):167–179. doi: 10.3109/10641969509087063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock M. B. Evidence for direct projections from the nucleus of the solitary tract onto medullary adrenaline cells. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Oct 15;276(3):460–467. doi: 10.1002/cne.902760310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselton J. R., Guyenet P. G. Ascending collaterals of medullary barosensitive neurons and C1 cells in rats. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 2):R1051–R1063. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.258.4.R1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W., Lahiri S., Mokashi A., Sherpa A. K. Relationship between sympathetic and phrenic nerve responses to peripheral chemoreflex in the cat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Dec;25(2-3):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona P. G., Dembowsky K., Czachurski J., Seller H. Chemoreceptor stimulation on sympathetic activity: dependence on respiratory phase. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):R1027–R1033. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.257.5.R1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollai M., Koizumi K. Differential responses in sympathetic outflow evoked by chemoreceptor activation. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 9;138(1):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90791-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshiya N., Guyenet P. G. A5 noradrenergic neurons and the carotid sympathetic chemoreflex. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 2):R519–R526. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.267.2.R519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshiya N., Guyenet P. G. Role of the pons in the carotid sympathetic chemoreflex. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 2):R508–R518. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.267.2.R508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshiya N., Huangfu D., Guyenet P. G. Ventrolateral medulla and sympathetic chemoreflex in the rat. Brain Res. 1993 Apr 23;609(1-2):174–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90871-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumada M., Terui N., Kuwaki T. Arterial baroreceptor reflex: its central and peripheral neural mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;35(5):331–361. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90036-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mifflin S. W. Absence of respiration modulation of carotid sinus nerve inputs to nucleus tractus solitarius neurons receiving arterial chemoreceptor inputs. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1993 Mar;42(3):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(93)90364-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seagard J. L., Hopp F. A., Donegan J. H., Kalbfleisch J. H., Kampine J. P. Halothane and the carotid sinus reflex: evidence for multiple sites of action. Anesthesiology. 1982 Sep;57(3):191–202. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198209000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Ellenberger H. H., Ballanyi K., Richter D. W., Feldman J. L. Pre-Bötzinger complex: a brainstem region that may generate respiratory rhythm in mammals. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):726–729. doi: 10.1126/science.1683005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Reis D. J. NMDA receptor-mediated sympathetic chemoreflex excitation of RVL-spinal vasomotor neurones in rats. J Physiol. 1995 Jan 1;482(Pt 1):53–68. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Young B. S., Hackett J. T., Guyenet P. G. Reticulospinal pacemaker neurons of the rat rostral ventrolateral medulla with putative sympathoexcitatory function: an intracellular study in vitro. Brain Res. 1988 Mar 1;442(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91508-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


