Abstract
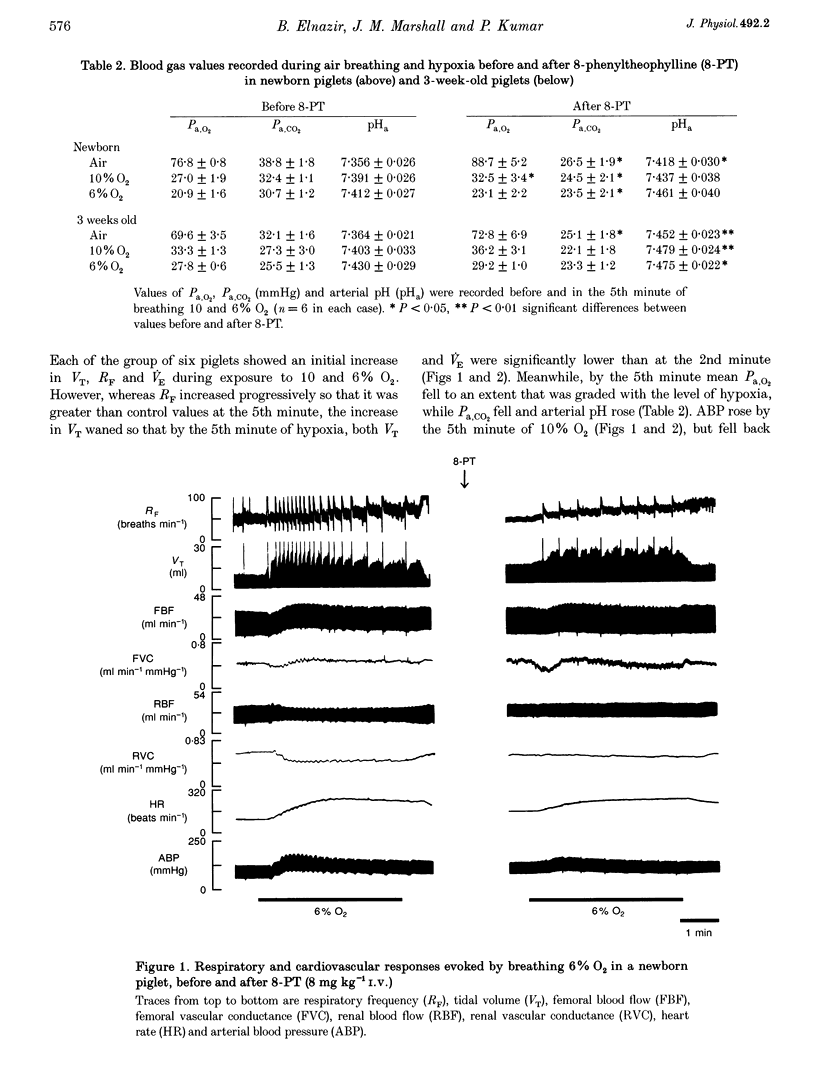
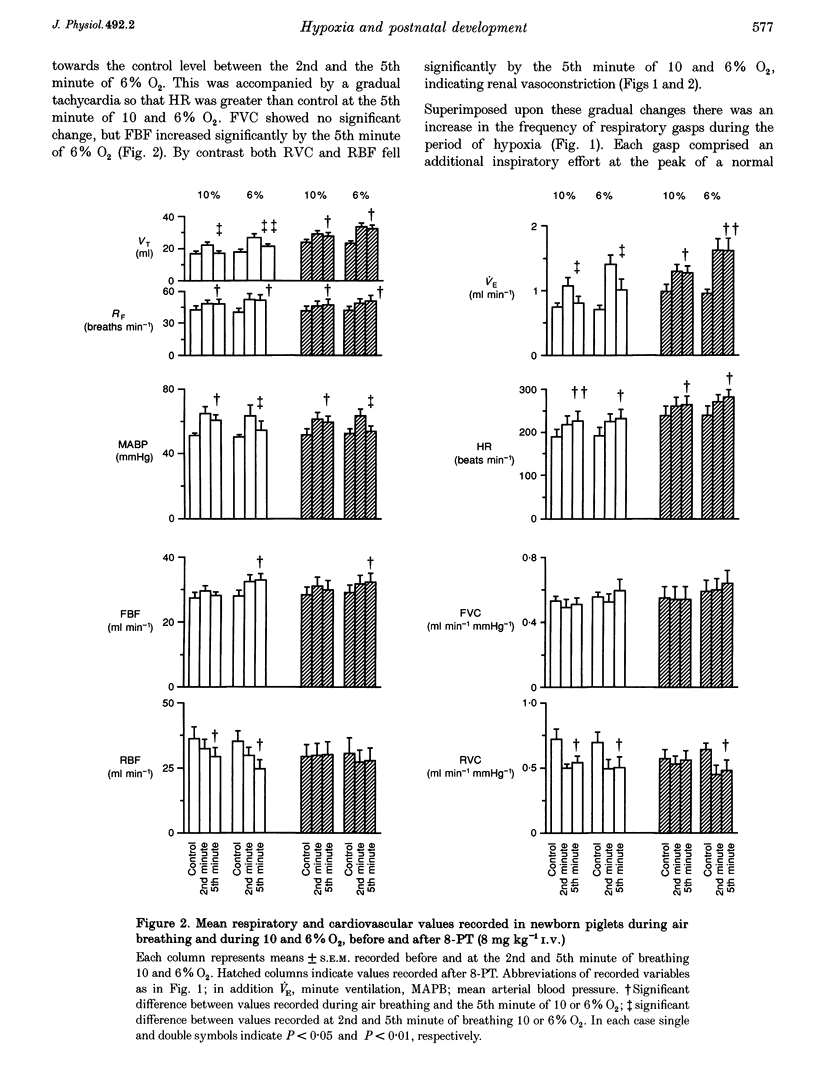
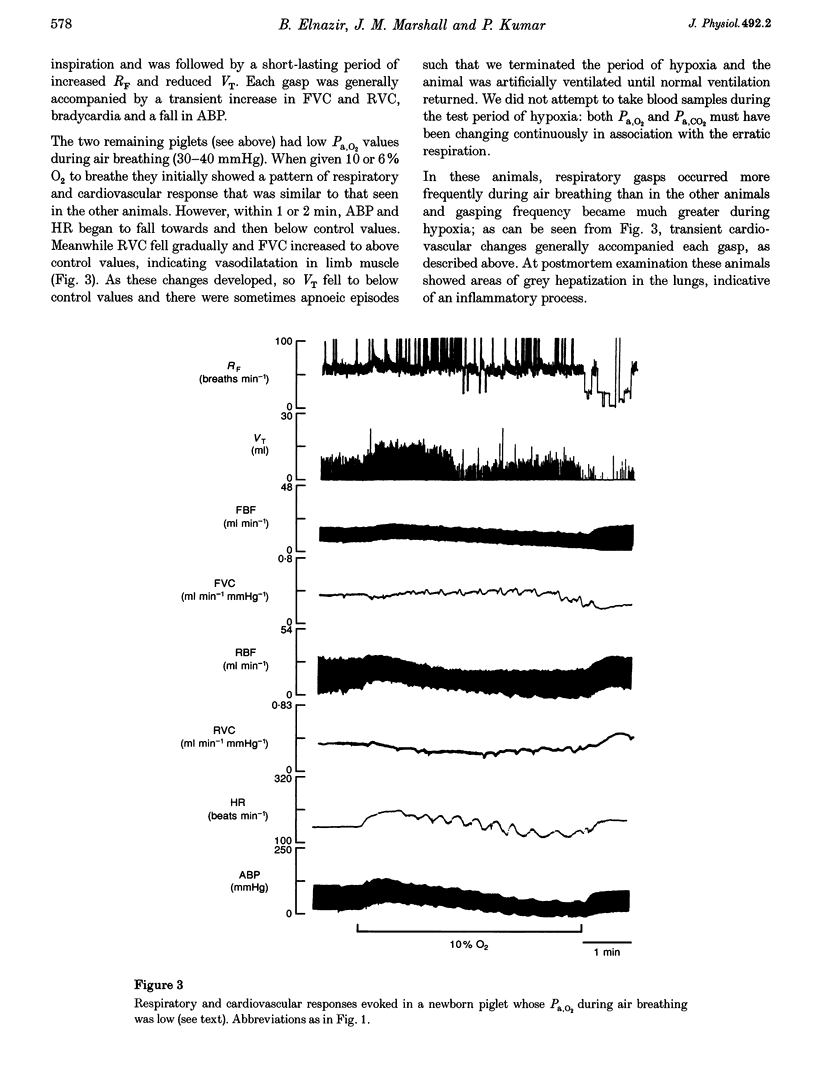
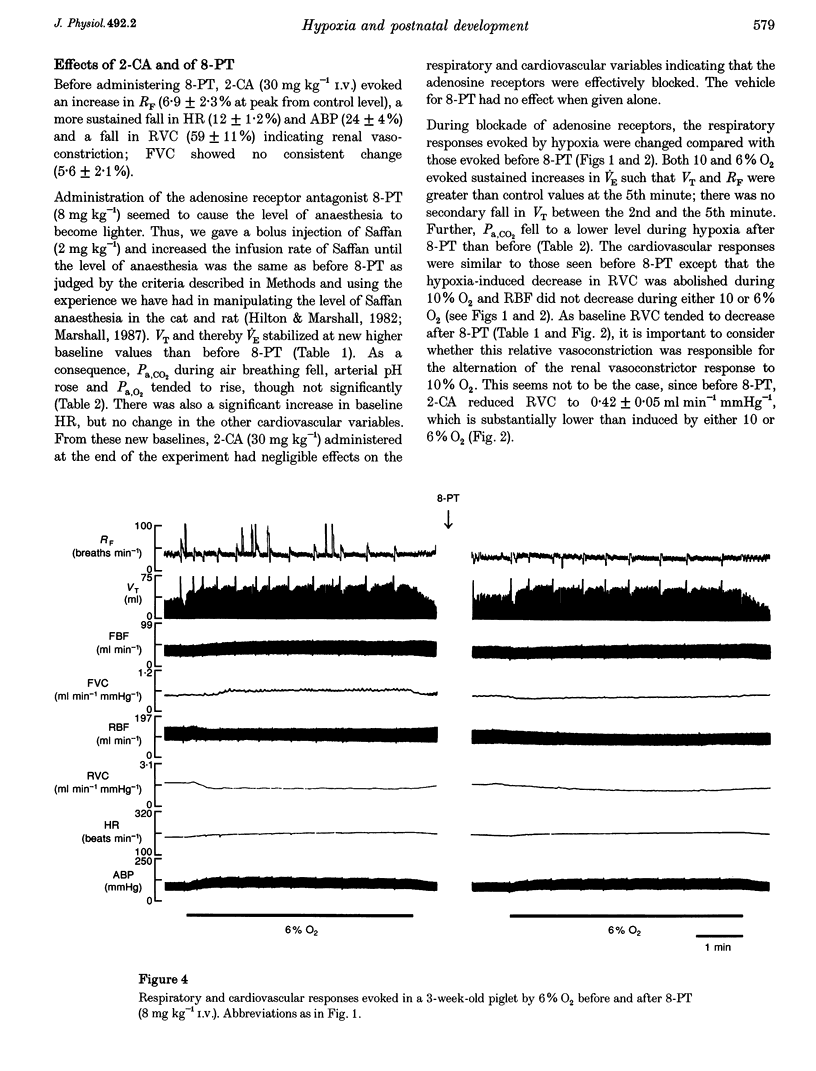
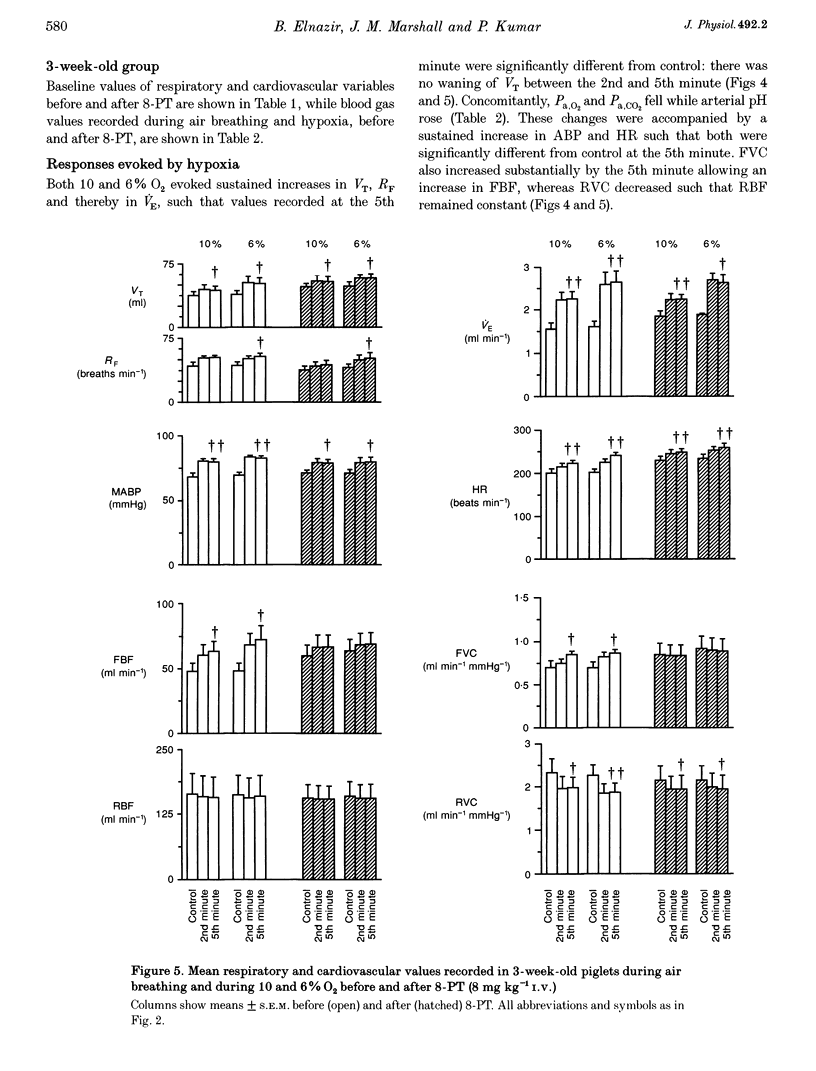
1. In 3-day-old and 3-week-old spontaneously breathing piglets anaesthetized with Saffan, we have studied ventilatory and cardiovascular responses evoked by 5 min periods of hypoxia (breathing 10 and 6% O2). 2. In 3-day-old piglets both 10 and 6% O2 evoked an increase followed by a secondary fall in ventilation, a gradual tachycardia and a renal vasoconstriction, with an increase in femoral blood flow that was attributable to femoral vasodilatation. Arterial blood pressure rose initially but fell towards control values by the 5th minute of hypoxia. 3. The stable adenosine analogue 2-chloroadenosine (2-CA; 30 mg kg(-1) i.v.) evoked bradycardia and renal vasoconstriction, but had no effect on femoral vasculature. These responses were blocked by the adenosine receptor antagonist 8-phenyltheophylline (8-PT; 8 mg kg(-1) i.v.). 8-PT also abolished the secondary fall in ventilation evoked by 10 and 6% O2 and the renal vasoconstriction evoked by 10% O2, but had no effect on the tachycardia, or on the femoral vascular response. 4. By contrast, in 3-week-old piglets both 10 and 6% O2 evoked a sustained increase in ventilation, tachycardia and a rise in arterial pressure with renal vasoconstriction, but no change in renal blood flow and substantial femoral vasodilatation with an increase in femoral blood flow. 2-CA evoked bradycardia and renal vasoconstriction, as in 3-day-old piglets, but also evoked pronounced femoral vasodilatation. 8-PT blocked these responses and the hypoxia-induced femoral vasodilatation, but had no significant effect on other components of the hypoxia-induced response. 5. We propose that there is postnatal development of the ventilatory and cardiovascular responses evoked by systemic hypoxia and of the role of locally released adenosine in these responses: at 3 days, adenosine released within the central nervous system and within the kidney is a major contributor to the secondary fall in ventilation and renal vasoconstriction respectively, whereas at 3 weeks, adenosine makes little contribution to the ventilatory response, or renal vasoconstriction, but is largely responsible for hypoxia-induced vaso-dilatation in skeletal muscle.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buckley N. M., Brazeau P., Gootman P. M. Maturation of circulatory responses to adrenergic stimuli. Fed Proc. 1983 Apr;42(6):1643–1647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnall R. A., Green G., Pinto L., Hart N. Effect of acute hypoxia on respiration and brain stem blood flow in the piglet. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Jan;70(1):251–259. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.70.1.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnall R. A., Jr Aminophylline reduces hypoxic ventilatory depression: possible role of adenosine. Pediatr Res. 1985 Jul;19(7):706–710. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198507000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froldi G., Belardinelli L. Species-dependent effects of adenosine on heart rate and atrioventricular nodal conduction. Mechanism and physiological implications. Circ Res. 1990 Oct;67(4):960–978. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.4.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gootman P. M., Gandhi M. R., Steele A. M., Hundley B. W., Cohen H. L., Eberle L. P., Sica A. L. Respiratory modulation of sympathetic activity in neonatal swine. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 2):R1147–R1154. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.261.5.R1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouyon J. B., Guignard J. P. Theophylline prevents the hypoxemia-induced renal hemodynamic changes in rabbits. Kidney Int. 1988 Jun;33(6):1078–1083. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton S. M., Marshall J. M. The pattern of cardiovascular response to carotid chemoreceptor stimulation in the cat. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:495–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudignon N., Aranda J. V., Varma D. R. Effects of adenosine and its analogues on isolated internal carotid arteries from newborn and adult pigs. Biol Neonate. 1990;58(2):91–97. doi: 10.1159/000243238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudignon N., Farri E., Beharry K., Rex J., Aranda J. V. Influence of adenosine on cerebral blood flow during hypoxic hypoxia in the newborn piglet. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Apr;68(4):1534–1541. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.4.1534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson E. E., Long W. A. Central origin of biphasic breathing pattern during hypoxia in newborns. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Aug;55(2):483–488. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.2.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. M. Analysis of cardiovascular responses evoked following changes in peripheral chemoreceptor activity in the rat. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:393–414. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. M., Metcalfe J. D. Analysis of factors that contribute to cardiovascular changes induced in the cat by graded levels of systemic hypoxia. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:429–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. M., Metcalfe J. D. Analysis of the cardiovascular changes induced in the rat by graded levels of systemic hypoxia. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;407:385–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. M. Peripheral chemoreceptors and cardiovascular regulation. Physiol Rev. 1994 Jul;74(3):543–594. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1994.74.3.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. M., Thomas T., Turner L. A link between adenosine, ATP-sensitive K+ channels, potassium and muscle vasodilatation in the rat in systemic hypoxia. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:1–9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen D. S., Ribeiro J. A. On the specificity and type of receptor involved in carotid body chemoreceptor activation by adenosine in the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct;80(2):347–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mian R., Marshall J. M. The role of adenosine in dilator responses induced in arterioles and venules of rat skeletal muscle by systemic hypoxia. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:499–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milerad J. Effects of theophylline on ventilatory response to hypoxic challenge. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Dec;62(12):1242–1246. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.12.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millhorn D. E., Eldridge F. L., Kiley J. P., Waldrop T. G. Prolonged inhibition of respiration following acute hypoxia in glomectomized cats. Respir Physiol. 1984 Sep;57(3):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(84)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss I. R., Runold M., Dahlin I., Fredholm B. B., Nyberg F., Lagercrantz H. Respiratory and neuroendocrine responses of piglets to hypoxia during postnatal development. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Dec;131(4):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon M., Marshall J. M. The role of adenosine in the respiratory and cardiovascular response to systemic hypoxia in the rat. J Physiol. 1991;440:529–545. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A., Pearson J. D. Cardiovascular purinoceptors. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):761–845. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. L., Schecter W. S., Mellins R. B., Haddad G. G. Effect of acute hypoxia on metabolism and ventilation in awake piglets. Respir Physiol. 1993 Mar;91(2-3):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(93)90108-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runold M., Lagercrantz H., Prabhakar N. R., Fredholm B. B. Role of adenosine in hypoxic ventilatory depression. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Aug;67(2):541–546. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.2.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidi D., Kuipers J. R., Teitel D., Heymann M. A., Rudolph A. M. Developmental changes in oxygenation and circulatory responses to hypoxemia in lambs. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):H674–H682. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.4.H674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smellie F. W., Davis C. W., Daly J. W., Wells J. N. Alkylxanthines: inhibition of adenosine-elicited accumulation of cyclic AMP in brain slices and of brain phosphodiesterase activity. Life Sci. 1979 Jun 25;24(26):2475–2482. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman W. S., Thompson C. I. A proposed role for adenosine in the regulation of renal hemodynamics and renin release. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):F423–F435. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.5.F423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T., Elnazir B. K., Marshall J. M. Differentiation of the peripherally mediated from the centrally mediated influences of adenosine in the rat during systemic hypoxia. Exp Physiol. 1994 Sep;79(5):809–822. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1994.sp003809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T., Marshall J. M. A study on rats of the effects of chronic hypoxia from birth on respiratory and cardiovascular responses evoked by acute hypoxia. J Physiol. 1995 Sep 1;487(Pt 2):513–525. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T., Marshall J. M. Interdependence of respiratory and cardiovascular changes induced by systemic hypoxia in the rat: the roles of adenosine. J Physiol. 1994 Nov 1;480(Pt 3):627–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timms R. J. A study of the amygdaloid defence reaction showing the value of Althesin anaesthesia in studies of the functions of the fore-brain in cats. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Jul;391(1):49–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00580694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verlato G., Borgdorff P. Endogenous adenosine enhances vagal negative chronotropic effect during hypoxia in the anaesthetised rabbit. Cardiovasc Res. 1990 Jul;24(7):532–539. doi: 10.1093/cvr/24.7.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. Adenosine antagonists. Med Res Rev. 1989 Apr-Jun;9(2):219–243. doi: 10.1002/med.2610090205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn H. R., Rubio R., Berne R. M. Brain adenosine concentration during hypoxia in rats. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):H235–H242. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.241.2.H235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H. Signalling via ATP in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Oct;17(10):420–426. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


