Abstract
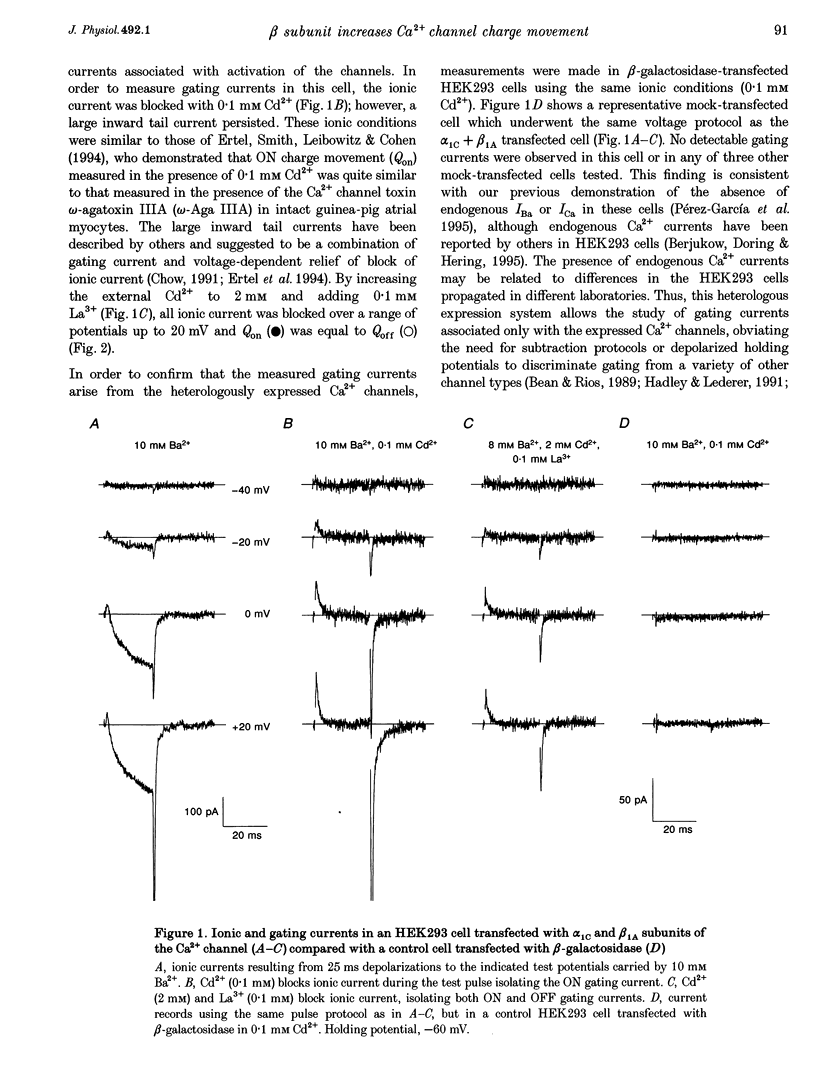
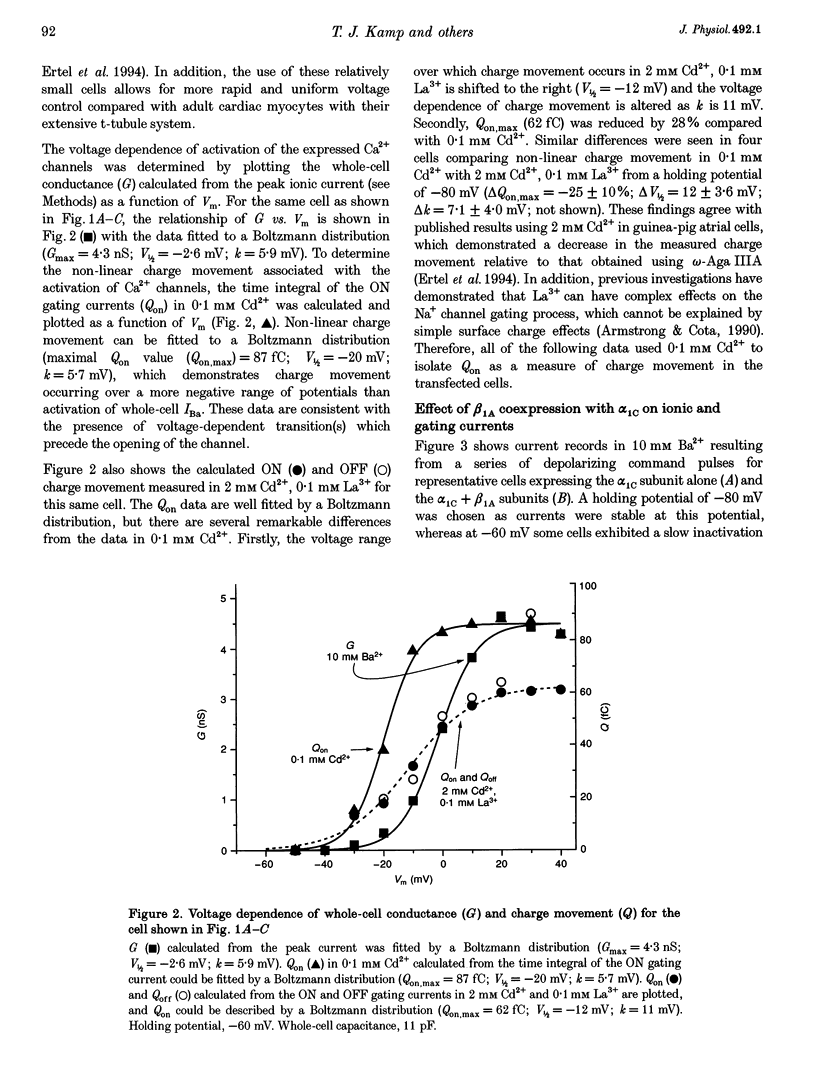
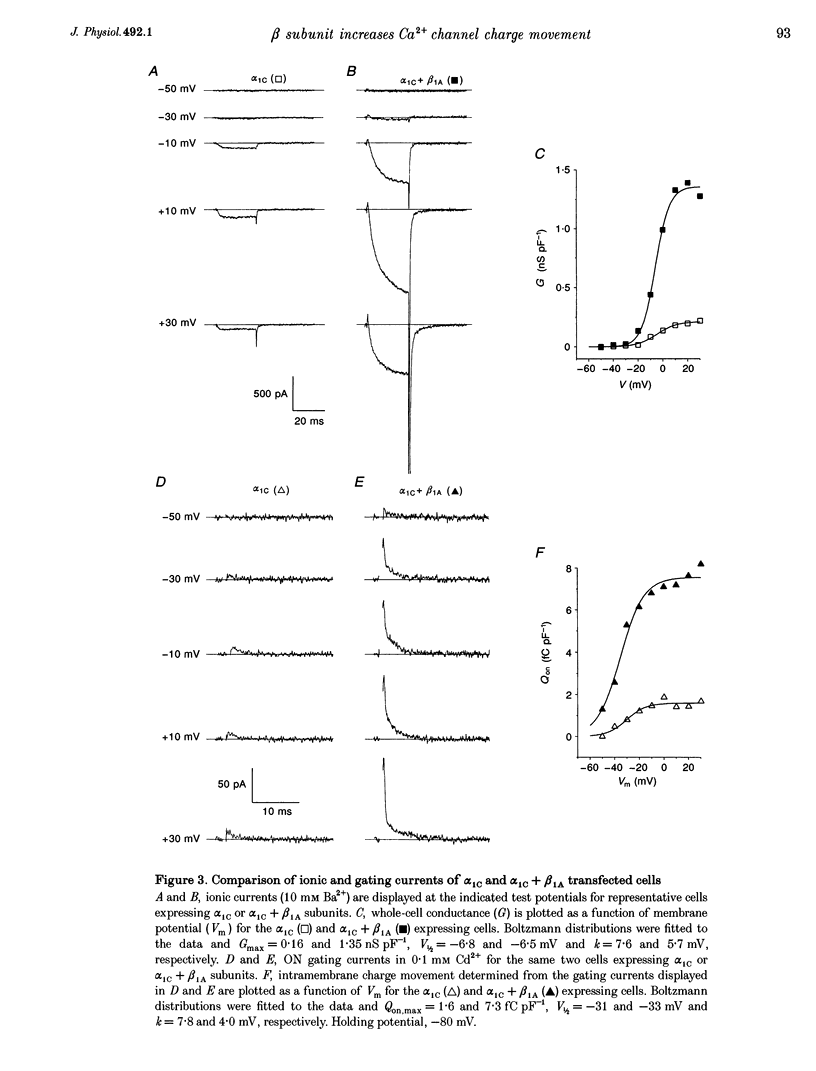
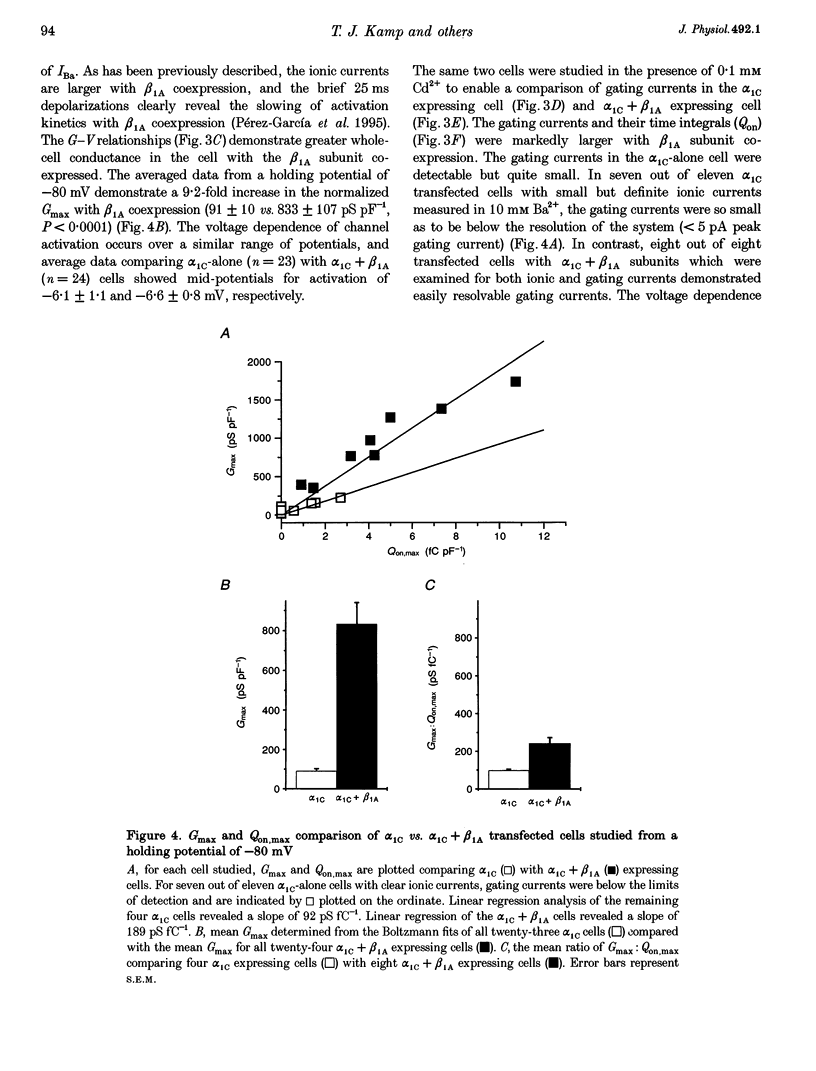
1. Coexpression of the beta subunit with the alpha 1C subunit of the cardiac L-type Ca2+ channel has been shown to increase ionic current. To examine the mechanism of this increase, ionic and gating currents were measured in transiently transfected HEK293 cells. 2. Beta 1A subunit coexpression increased the maximal whole-cell conductance (Gmax) measured in 10 mM Ba2+ from 91 +/- 11 to 833 +/- 107 pS pF-1 without a change in the voltage dependence of activation (V1/2: -6.1 +/- 1.1 and -6.6 +/- 0.9 mV, respectively). 3. Gating currents were smaller in cells expressing only the alpha 1C subunit (only four out of eleven cells exhibited gating currents above the limits of detection, whereas eight out of eight beta 1A coexpressing cells had measurable gating currents). The gating currents were integrated to measure the intramembrane charge movement (Q). The ON charge movement (Qon) could be described by a Boltzmann distribution reaching a maximal value of Qon,max. 4. The mean ratio of Gmax: Qon,max increased from 99 +/- 6 to 243 +/- 30 pS fC-1 with beta 1A coexpression, demonstrating that the beta 1A subunit changes the gating of alpha 1C channels to favour the opening of the channels. However, this 2.5-fold change in the Gmax: Qon,max ratio explains less than half of the 9.2-fold increase in Gmax with beta 1A subunit coexpression. The major effect is due to a 3.7-fold increase in Qon,max, demonstrating that beta 1A subunit coexpression increases the number of functional surface membrane channels.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Cota G. Modification of sodium channel gating by lanthanum. Some effects that cannot be explained by surface charge theory. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Dec;96(6):1129–1140. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.6.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P., Rios E. Nonlinear charge movement in mammalian cardiac ventricular cells. Components from Na and Ca channel gating. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):65–93. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien A. J., Zhao X., Shirokov R. E., Puri T. S., Chang C. F., Sun D., Rios E., Hosey M. M. Roles of a membrane-localized beta subunit in the formation and targeting of functional L-type Ca2+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 15;270(50):30036–30044. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.50.30036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow R. H. Cadmium block of squid calcium currents. Macroscopic data and a kinetic model. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Oct;98(4):751–770. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.4.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertel E. A., Smith M. M., Leibowitz M. D., Cohen C. J. Isolation of myocardial L-type calcium channel gating currents with the spider toxin omega-Aga-IIIA. J Gen Physiol. 1994 May;103(5):731–753. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.5.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadley R. W., Lederer W. J. Properties of L-type calcium channel gating current in isolated guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Aug;98(2):265–285. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hullin R., Singer-Lahat D., Freichel M., Biel M., Dascal N., Hofmann F., Flockerzi V. Calcium channel beta subunit heterogeneity: functional expression of cloned cDNA from heart, aorta and brain. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):885–890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Catterall W. A. Auxiliary subunits of voltage-gated ion channels. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1183–1194. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori Y., Friedrich T., Kim M. S., Mikami A., Nakai J., Ruth P., Bosse E., Hofmann F., Flockerzi V., Furuichi T. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of a brain calcium channel. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):398–402. doi: 10.1038/350398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely A., Wei X., Olcese R., Birnbaumer L., Stefani E. Potentiation by the beta subunit of the ratio of the ionic current to the charge movement in the cardiac calcium channel. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):575–578. doi: 10.1126/science.8211185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuss H. B., Chiamvimonvat N., Pérez-García M. T., Tomaselli G. F., Marbán E. Functional association of the beta 1 subunit with human cardiac (hH1) and rat skeletal muscle (mu 1) sodium channel alpha subunits expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Dec;106(6):1171–1191. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.6.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragnell M., Sakamoto J., Jay S. D., Campbell K. P. Cloning and tissue-specific expression of the brain calcium channel beta-subunit. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 21;291(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81296-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-García M. T., Kamp T. J., Marbán E. Functional properties of cardiac L-type calcium channels transiently expressed in HEK293 cells. Roles of alpha 1 and beta subunits. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Feb;105(2):289–305. doi: 10.1085/jgp.105.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruth P., Röhrkasten A., Biel M., Bosse E., Regulla S., Meyer H. E., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Primary structure of the beta subunit of the DHP-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1115–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.2549640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D., Biel M., Lotan I., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F., Dascal N. The roles of the subunits in the function of the calcium channel. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1553–1557. doi: 10.1126/science.1716787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slish D. F., Engle D. B., Varadi G., Lotan I., Singer D., Dascal N., Schwartz A. Evidence for the existence of a cardiac specific isoform of the alpha 1 subunit of the voltage dependent calcium channel. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):509–514. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80786-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamori M., Mikala G., Schwartz A., Yatani A. Single-channel analysis of a cloned human heart L-type Ca2+ channel alpha 1 subunit and the effects of a cardiac beta subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Nov 15;196(3):1170–1176. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Feldman D. H., McCue A. F., Brenner R., Velicelebi G., Ellis S. B., Harpold M. M. Structure and functional expression of alpha 1, alpha 2, and beta subunits of a novel human neuronal calcium channel subtype. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90109-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. F., Randall A. D., Ellinor P. T., Horne W. A., Sather W. A., Tanabe T., Schwarz T. L., Tsien R. W. Distinctive pharmacology and kinetics of cloned neuronal Ca2+ channels and their possible counterparts in mammalian CNS neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Nov;32(11):1075–1088. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90003-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


