Abstract
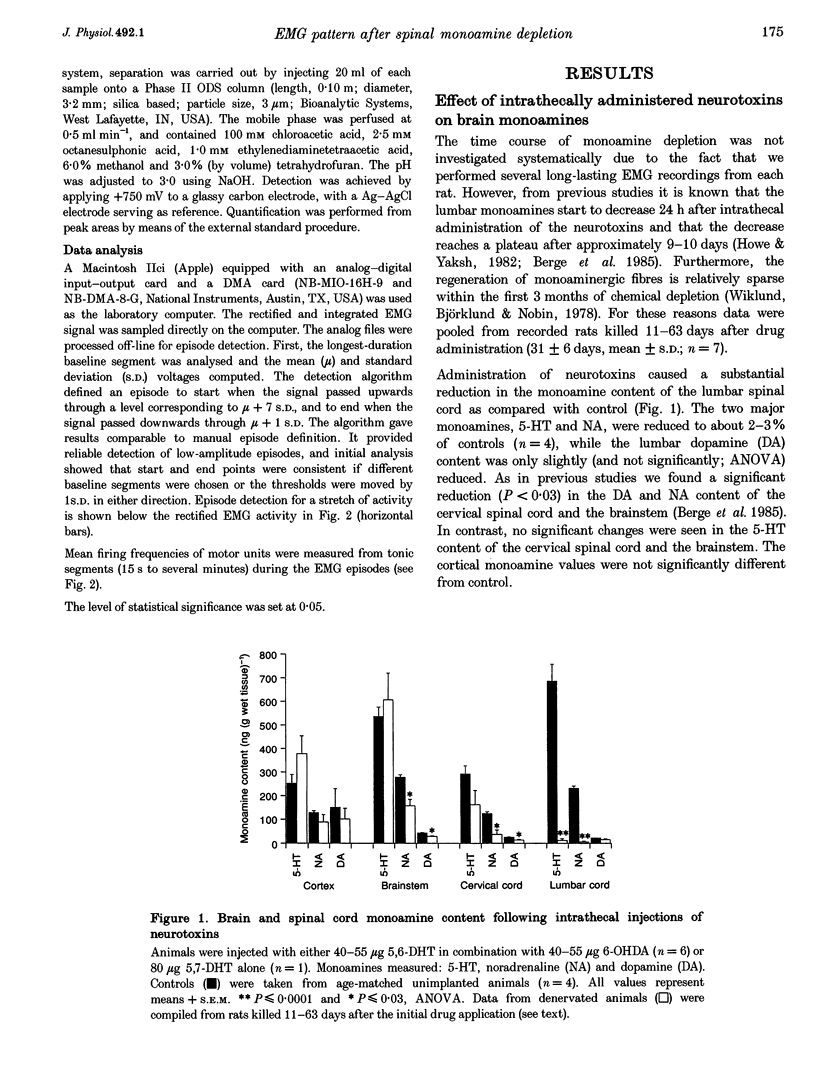
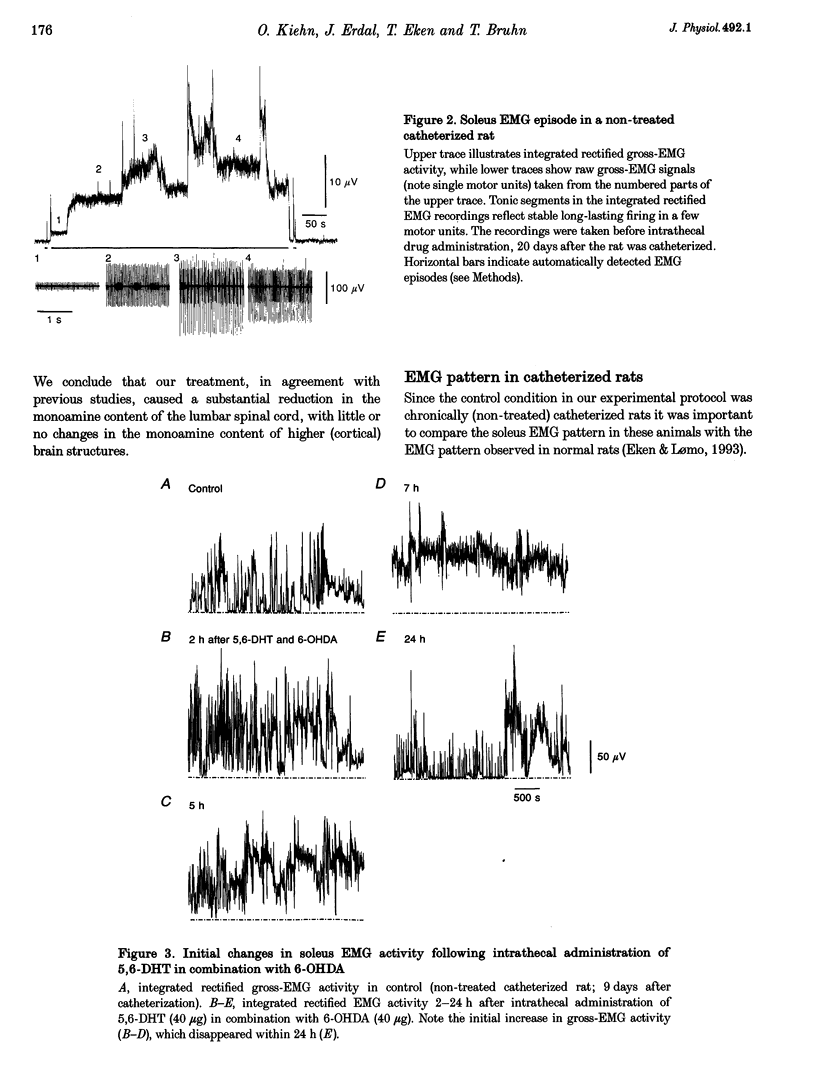
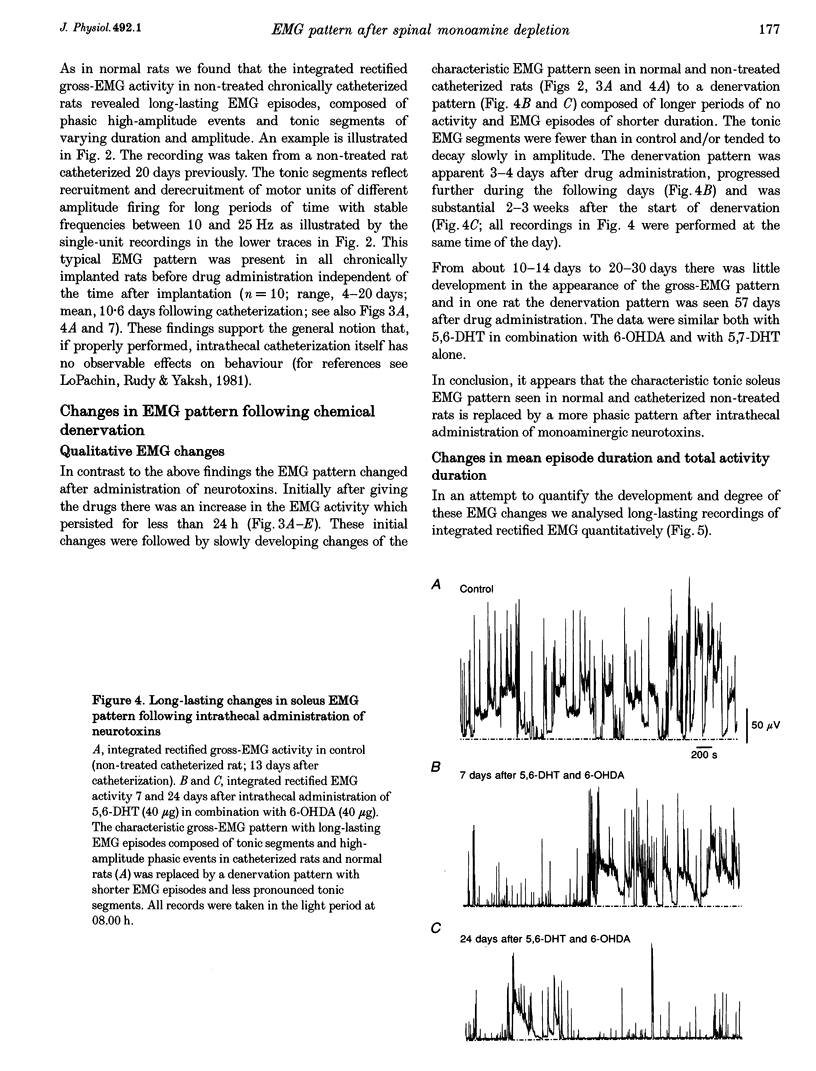
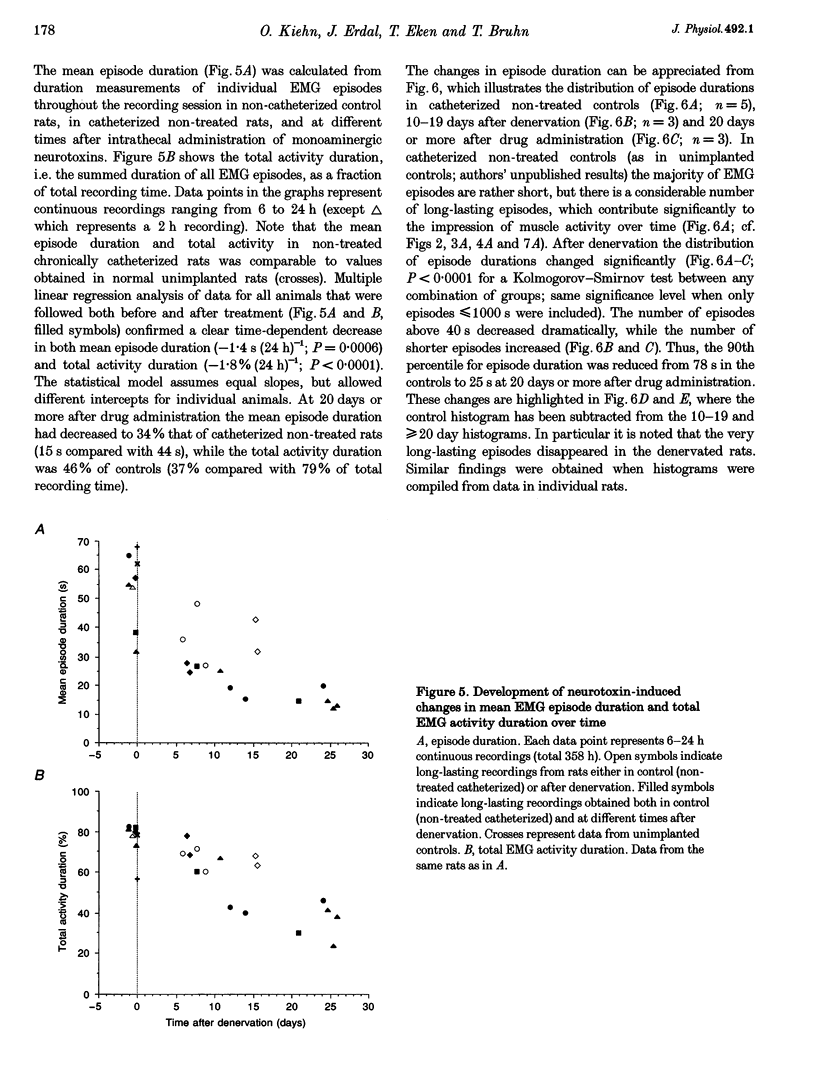
1. To assess the role of descending monoaminergic pathways for motor activity long-lasting EMG recordings were performed from the adult soleus muscle before and after selective depletion of spinal monoamines. 2. Rats were chronically implanted with an intrathecal catheter placed in the lumbar subarachnoid space and gross-EMG recording electrodes in the soleus muscle. EMG recordings were performed in control conditions and at different times after intrathecal administration of either 40-55 micrograms 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine (5,6-DHT) and 40-55 micrograms 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) or 80 micrograms 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine (5,7-DHT) alone. The depletions were evaluated biochemically in brains and spinal cords after recordings. 3. In agreement with previous studies the intrathecal administration of neurotoxins caused a reduction of the noradrenaline (NA) and serotonin (5-HT) content of the lumbar spinal cord to about 2-3% of control, with little or no changes in the monoamine content of the cortex. 4. In non-treated chronically catheterized rats the integrated rectified gross EMG displayed long-lasting EMG episodes composed of phasic high-amplitude events and tonic segments of varying duration and amplitude. 5. After intrathecal administration of neurotoxins the number of long-lasting gross-EMG episodes, the mean episode duration, and the total EMG activity per 24 h, were reduced. These changes were accompanied by a simultaneous increase both in the number of short-lasting EMG episodes and the total number of EMG episodes per 24 h period. The changes were apparent 5-6 days after drug administration and fully developed after 2-3 weeks. 6. No changes in general movement ability were observed, except that the denervated animals had a tendency to a less errect posture. 7. These results indicate that descending monoaminergic pathways are important for the maintained motor output in tonic hindlimb muscles.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
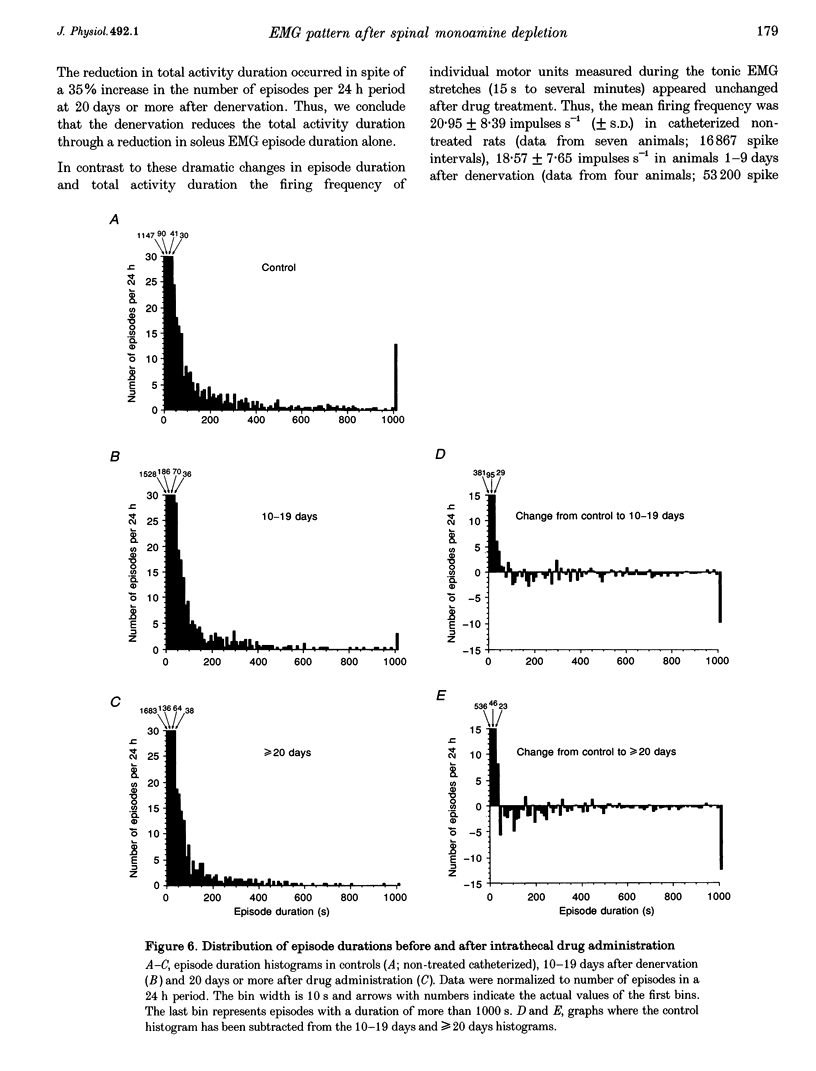
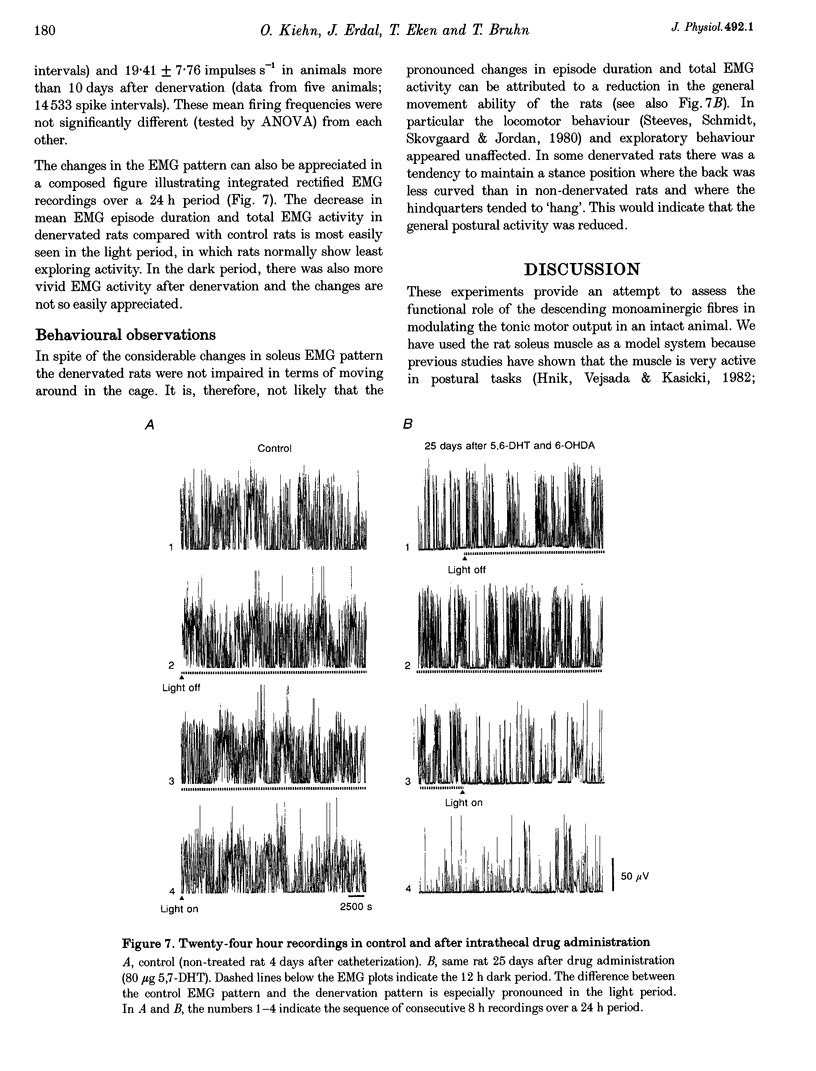
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDEN N. E., JUKES M. G., LUNDBERG A. SPINAL REFLEXES AND MONOAMINE LIBERATION. Nature. 1964 Jun 20;202:1222–1223. doi: 10.1038/2021222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berge O. G., Fasmer O. B., Flatmark T., Hole K. Time course of changes in nociception after 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine lesions of descending 5-HT pathways. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1983 Apr;18(4):637–643. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(83)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berge O. G., Fasmer O. B., Tveiten L., Hole K. Selective neurotoxic lesions of descending serotonergic and noradrenergic pathways in the rat. J Neurochem. 1985 Apr;44(4):1156–1161. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb08738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway B. A., Hultborn H., Kiehn O., Mintz I. Plateau potentials in alpha-motoneurones induced by intravenous injection of L-dopa and clonidine in the spinal cat. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:369–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eken T., Kiehn O. Bistable firing properties of soleus motor units in unrestrained rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989 Jul;136(3):383–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1989.tb08679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert R. F., Emson P. C., Hunt S. P., Bennett G. W., Marsden C. A., Sandberg B. E., Steinbusch H. W., Verhofstad A. A. The effects of monoamine neurotoxins on peptides in the rat spinal cord. Neuroscience. 1982 Jan;7(1):69–87. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Growdon J. H. Changes in motor behavior following the administration of serotonin neurotoxins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 12;305:510–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb31545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig R., Lømo T. Firing patterns of motor units in normal rats. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):164–166. doi: 10.1038/314164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hník P., Vejsada R., Kasicki S. EMG changes in rat hind limb muscles following bilateral deafferentation. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Nov 11;395(3):182–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00584806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holstege J. C., Kuypers H. G. Brainstem projections to spinal motoneurons: an update. Neuroscience. 1987 Dec;23(3):809–821. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J., Hultborn H., Jespersen B., Kiehn O. Bistability of alpha-motoneurones in the decerebrate cat and in the acute spinal cat after intravenous 5-hydroxytryptophan. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:345–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Yaksh T. L. Changes in sensitivity to intrathecal norepinephrine and serotonin after 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine (5,6-DHT) or repeated monoamine administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Feb;220(2):311–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs B. L., Fornal C. A. 5-HT and motor control: a hypothesis. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Sep;16(9):346–352. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn O. Plateau potentials and active integration in the 'final common pathway' for motor behaviour. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90023-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoPachin R. M., Rudy T. A., Yaksh T. L. An improved method for chronic catheterization of the rat spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1981 Sep;27(3):559–561. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(81)90350-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarrete R., Vrbová G. Differential effect of nerve injury at birth on the activity pattern of reinnervated slow and fast muscles of the rat. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:675–685. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobin A., Baumgarten H. G., Björklund A., Lachenmayer L., Stenevi U. Axonal degeneration and regeneration of bulbo-spinal indolamine neurons after 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine treatment. Brain Res. 1973 Jun 29;56:1–24. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90324-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygren L. G., Fuxe K., Jonsson G., Olson L. Functional regeneration of 5-hydroxytryptamine nerve terminals in the rat spinal cord following 5, 6-dihydroxytryptamine induced degeneration. Brain Res. 1974 Oct 4;78(3):377–394. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90922-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygren L. G., Olson L. On spinal noradrenaline receptor supersensitivity: correlation between nerve terminal densities and flexor reflexes various times after intracisternal 6-hydroxydopamine. Brain Res. 1976 Nov 12;116(3):455–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90493-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy R. R., Hutchison D. L., Pierotti D. J., Hodgson J. A., Edgerton V. R. EMG patterns of rat ankle extensors and flexors during treadmill locomotion and swimming. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Jun;70(6):2522–2529. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.70.6.2522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Feldman J. L., Schmidt B. J. Neural mechanisms generating locomotion studied in mammalian brain stem-spinal cord in vitro. FASEB J. 1988 Apr;2(7):2283–2288. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.7.2450802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeves J. D., Schmidt B. J., Skovgaard B. J., Jordan L. M. Effect of noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine depletion on locomotion in the cat. Brain Res. 1980 Mar 10;185(2):349–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay L. E., Bédard P. J., Maheux R., Di Paolo T. Denervation supersensitivity to 5-hydroxytryptamine in the rat spinal cord is not due to the absence of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 18;330(1):174–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanderMaelen C. P., Aghajanian G. K. Intracellular studies showing modulation of facial motoneurone excitability by serotonin. Nature. 1980 Sep 25;287(5780):346–347. doi: 10.1038/287346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund L., Björklund A., Nobin A. Regeneration of serotonin neurons in the rat brain after 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine-induced axotomy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 12;305:370–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb31534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Rudy T. A. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976 Dec;17(6):1031–1036. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(76)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


