Abstract
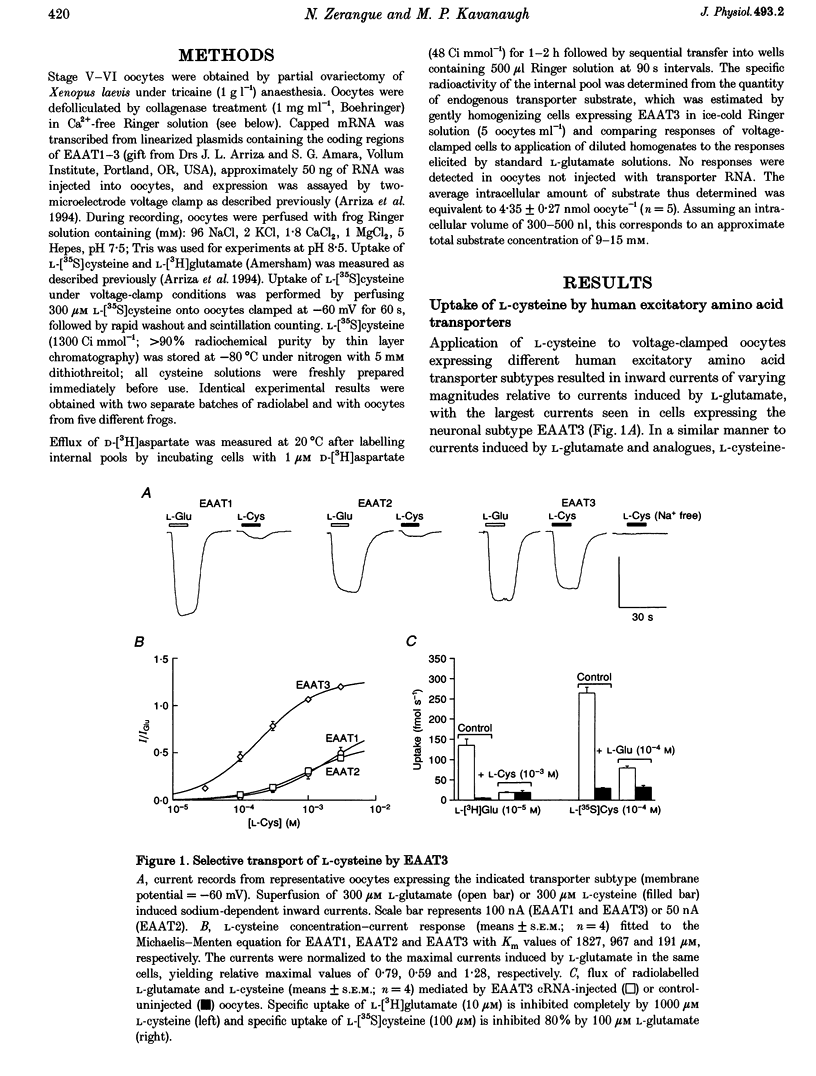
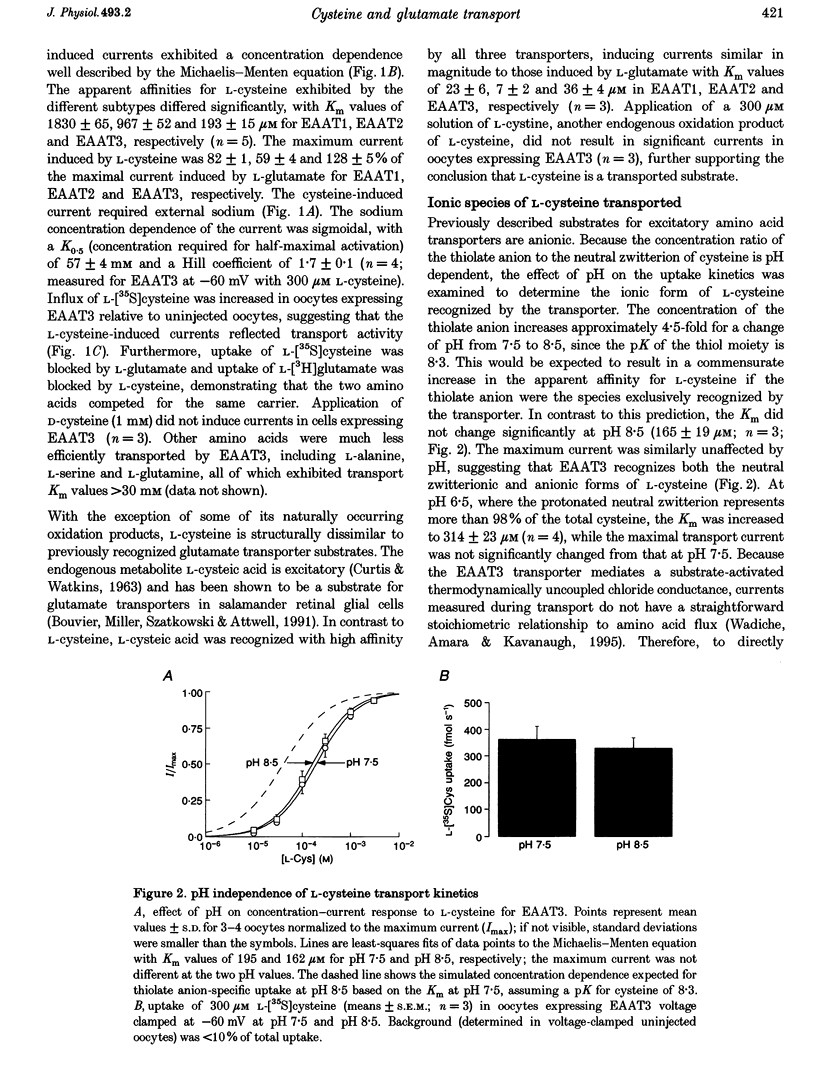
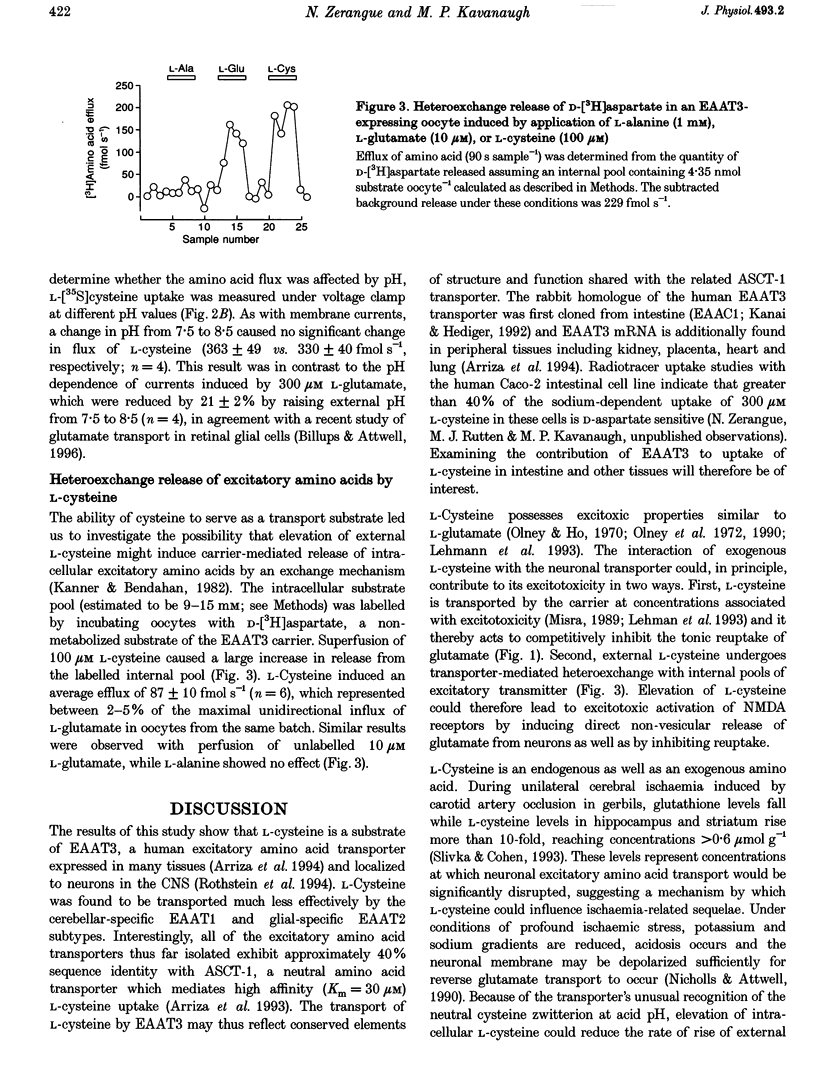
1. The interaction of L-cysteine with three excitatory amino acid transporter subtypes cloned from human brain (EAAT1-3) was examined by measuring transporter-mediated electrical currents and radiolabelled amino acid flux in voltage-clamped Xenopus oocytes expressing the transporters. 2. L-Cysteine was transported by the neuronal subtype EAAT3 (EAAC1) with an affinity constant of 190 microM and a maximal rate of flux similar to that of L-glutamate; the relative efficacies (Vmax/K(m)) of the EAAT1 and EAAT2 subtypes for transporting L-cysteine were 10- to 20-fold lower. 3. Changing the ionization state of L-cysteine by raising the external pH did not significantly change the apparent affinity, transport rate, or magnitude of currents induced by L-cysteine, suggesting that both the neutral zwitterionic and anionic forms of the amino acid are transported with the same net charge stoichiometry. 4. In addition to competing with L-glutamate for uptake by the neuronal carrier, L-cysteine caused transporter-mediated release of transmitter by heteroexchange; both actions would elevate extracellular glutamate concentrations and may thus contribute to the known excitotoxic actions of L-cysteine in the brain. 5. Because the EAAT3 transporter is also expressed in tissues including kidney and intestine, the results suggest the possibility of a heretofore unrecognized mechanism of L-cysteine uptake in peripheral tissues as well as in brain.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouvier M., Miller B. A., Szatkowski M., Attwell D. Electrogenic uptake of sulphur-containing analogues of glutamate and aspartate by Müller cells from the salamander retina. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:441–457. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Szatkowski M., Amato A., Attwell D. The glial cell glutamate uptake carrier countertransports pH-changing anions. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):471–474. doi: 10.1038/360471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., WATKINS J. C. Acidic amino acids with strong excitatory actions on mammalian neurones. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:1–14. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A., Hagberg H., Orwar O., Sandberg M. Cysteine sulphinate and cysteate: mediators of cysteine toxicity in the neonatal rat brain? Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Oct 1;5(10):1398–1412. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra C. H. Is a certain amount of cysteine prerequisite to produce brain damage in neonatal rats? Neurochem Res. 1989 Mar;14(3):253–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00971320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. J., Dean G. E., Aronson P. S., Rudnick G. Hydrogen ion cotransport by the renal brush border glutamate transporter. Biochemistry. 1983 Nov 8;22(23):5459–5463. doi: 10.1021/bi00292a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D., Attwell D. The release and uptake of excitatory amino acids. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Nov;11(11):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90129-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn P. B., Davis A. J., O'Brien P. Carbamate formation and the neurotoxicity of L-alpha amino acids. Science. 1991 Mar 29;251(5001):1619–1620. doi: 10.1126/science.1859531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W., Ho O. L. Brain damage in infant mice following oral intake of glutamate, aspartate or cysteine. Nature. 1970 Aug 8;227(5258):609–611. doi: 10.1038/227609b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W., Ho O. L., Rhee V., Schainker B. Cysteine-induced brain damage in infant and fetal rodents. Brain Res. 1972 Oct 13;45(1):309–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W., Zorumski C., Price M. T., Labruyere J. L-cysteine, a bicarbonate-sensitive endogenous excitotoxin. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):596–599. doi: 10.1126/science.2185543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. D., Martin L., Levey A. I., Dykes-Hoberg M., Jin L., Wu D., Nash N., Kuncl R. W. Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron. 1994 Sep;13(3):713–725. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slivka A., Cohen G. Brain ischemia markedly elevates levels of the neurotoxic amino acid, cysteine. Brain Res. 1993 Apr 9;608(1):33–37. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90770-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple C. S., Bronk J. R., Bailey P. D., Boyd C. A. Substrate-charge dependence of stoichiometry shows membrane potential is the driving force for proton-peptide cotransport in rat renal cortex. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Sep;430(5):825–829. doi: 10.1007/BF00386182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadiche J. I., Amara S. G., Kavanaugh M. P. Ion fluxes associated with excitatory amino acid transport. Neuron. 1995 Sep;15(3):721–728. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


