Abstract
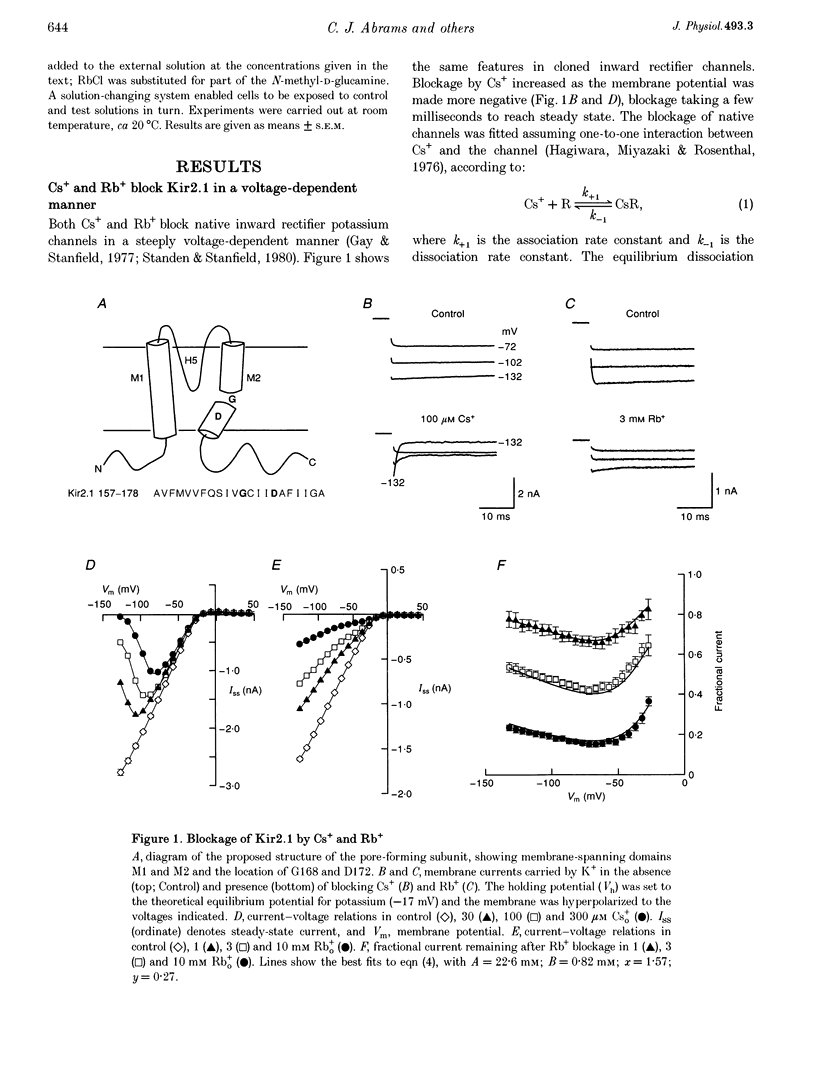
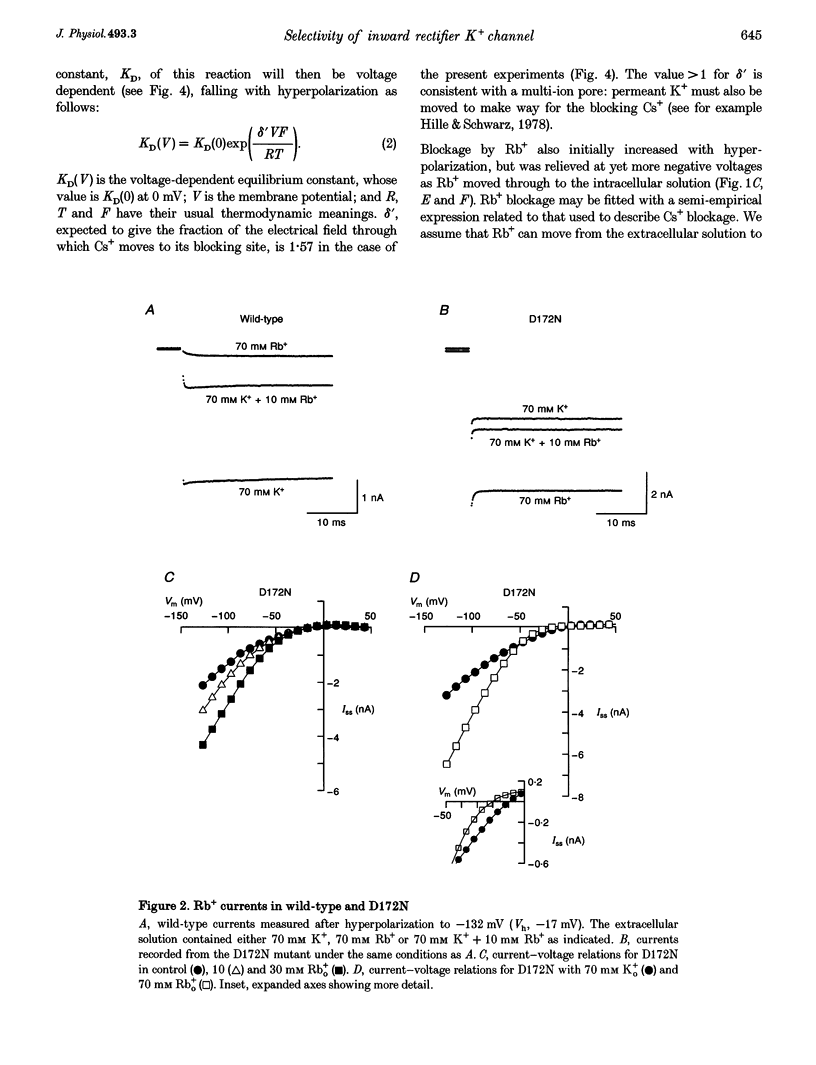
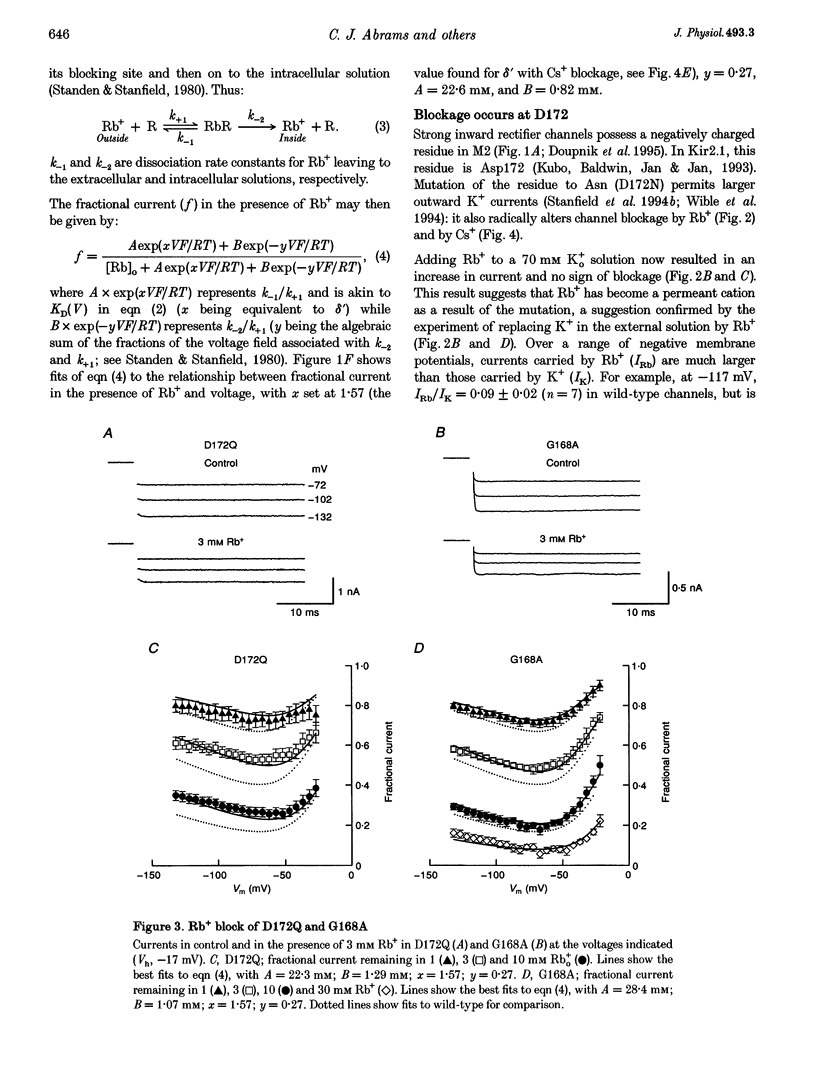
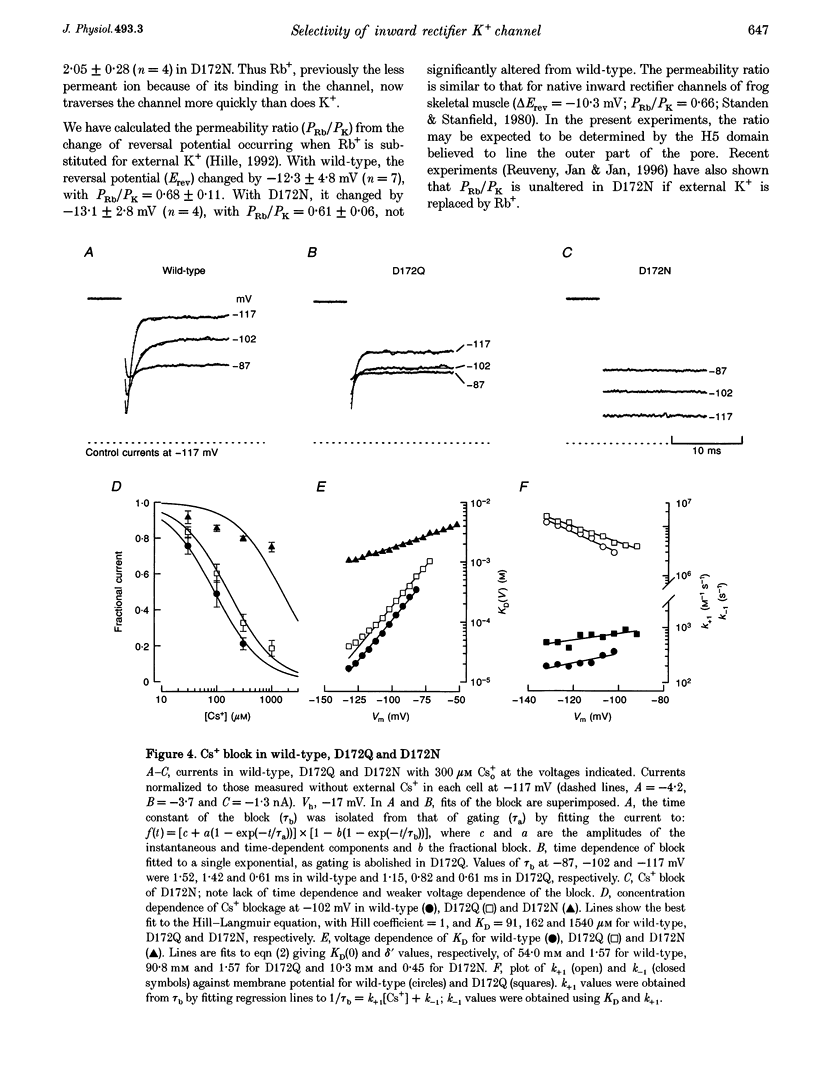
1. The effects of Rb+ and Cs+ as blocking ions were investigated on wild-type and mutant forms of the inward rectifier K+ channel, IRK1 (Kir2.1). 2. In wild-type channels, Rb+ blockage was voltage dependent, increasing and then falling with increasing hyperpolarization. 3. Rb+ blockage was abolished by replacing Asp172 in the M2 domain of the pore-forming subunit by Asn, but was re-established by a change to Gln, narrowing the pore. Blocking affinity was reduced in D172Q, and was also reduced by replacing Gly168 in M2 by Ala. 4. Cs+ blockage was also abolished in D172N but was re-established in D172Q. 5. There appears to be a balance between charge and pore size in determining whether ions block or permeate. A major part of the selectivity of Kir2.1 is associated with Asp172 in the M2 domain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. THE RUBIDIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY OF FROG MUSCLE MEMBRANE. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:134–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupnik C. A., Davidson N., Lester H. A. The inward rectifier potassium channel family. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Jun;5(3):268–277. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakler B., Brändle U., Bond C., Glowatzki E., König C., Adelman J. P., Zenner H. P., Ruppersberg J. P. A structural determinant of differential sensitivity of cloned inward rectifier K+ channels to intracellular spermine. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 19;356(2-3):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ficker E., Taglialatela M., Wible B. A., Henley C. M., Brown A. M. Spermine and spermidine as gating molecules for inward rectifier K+ channels. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1068–1072. doi: 10.1126/science.7973666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay L. A., Stanfield P. R. Cs(+) causes a voltage-dependent block of inward K currents in resting skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):169–170. doi: 10.1038/267169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Rosenthal N. P. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomalous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):621–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Schwarz W. Potassium channels as multi-ion single-file pores. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Oct;72(4):409–442. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Baldwin T. J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):127–133. doi: 10.1038/362127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopatin A. N., Makhina E. N., Nichols C. G. Potassium channel block by cytoplasmic polyamines as the mechanism of intrinsic rectification. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):366–369. doi: 10.1038/372366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Z., MacKinnon R. Probing a potassium channel pore with an engineered protonatable site. Biochemistry. 1995 Oct 10;34(40):13133–13138. doi: 10.1021/bi00040a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuveny E., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Contributions of a negatively charged residue in the hydrophobic domain of the IRK1 inwardly rectifying K+ channel to K(+)-selective permeation. Biophys J. 1996 Feb;70(2):754–761. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79615-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton P. A., Davies N. W., Antoniou M., Grosveld F., Needham M., Hollis M., Brammar W. J., Conley E. C. Regulated expression of K+ channel genes in electrically silent mammalian cells by linkage to beta-globin gene-activation elements. Receptors Channels. 1993;1(1):25–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Rubidium block and rubidium permeability of the inward rectifier of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:415–435. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R., Davies N. W., Shelton P. A., Khan I. A., Brammar W. J., Standen N. B., Conley E. C. The intrinsic gating of inward rectifier K+ channels expressed from the murine IRK1 gene depends on voltage, K+ and Mg2+. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 15;475(1):1–7. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R., Davies N. W., Shelton P. A., Sutcliffe M. J., Khan I. A., Brammar W. J., Conley E. C. A single aspartate residue is involved in both intrinsic gating and blockage by Mg2+ of the inward rectifier, IRK1. J Physiol. 1994 Jul 1;478(Pt 1):1–6. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


