Abstract
Objective
Previous studies have shown that the incidence of peptic ulcer disease (PUD) exhibits seasonal variations. This study aimed to investigate the seasonal variation in PUD incidence in Taiwan, which spans both tropical and subtropical regions, using a nationwide database.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted using real-world claims data from Taiwan, which includes a representative sample of 2 million individuals. Patients hospitalised with a primary diagnosis of PUD between 2001 and 2019 were identified using International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) and International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) codes for gastric ulcers (GUs), duodenal ulcers (DUs) and unspecified peptic ulcers. Descriptive statistics were used to present the seasonal variations in PUD incidence. Patients’ gender, age, PUD type, geographical region and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) usage across the four seasons (spring, summer, fall, winter) were compared using Pearson’s χ2 test.
Results
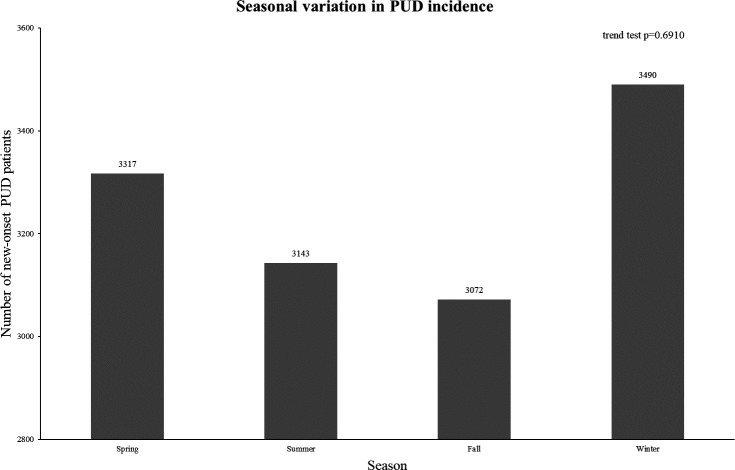
Among the 13 022 patients, new-onset PUD cases varied annually, peaking at 771 cases in 2004 and reaching a low of 614 cases in 2018. PUD incidence was higher in males than in females, and more common in elderly individuals aged ≥65 (59.5%). GU had the highest prevalence (56.1%), followed by DU (36.3%) and unspecified ulcers (7.7%). PUD incidence peaked in winter (26.8%), followed by spring (25.1%), fall (24.2%) and summer (23.9%). This seasonal trend was consistent across gender and age groups, with no significant impact on latitude, NSAID usage or PUD type.
Conclusion
Across the tropical and subtropical regions of Taiwan, seasonal variation in PUD incidence is observed with the highest rates occurring in winter, regardless of age or sex. However, NSAID usage tends to obscure this trend. The seasonal variation in DU incidence showed no significant differences between north and south Taiwan, suggesting that factors other than temperature may affect DU incidence compared with their effect on GU incidence.
Keywords: GASTRIC AND DUODENAL ULCERS, EPIDEMIOLOGY, ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
The incidence of peptic ulcer disease (PUD) exhibits seasonal variations in high-latitude countries; however, seasonal variations in the regions of tropical and subtropical are poorly understood.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
Across the tropical and subtropical regions of Taiwan, seasonal variation in PUD incidence was observed with the highest rates occurring in winter, but this finding was not statistically significant.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
Our results provide a reference for health management agencies to plan preventive health education programmes for PUD and effectively use medical personnel and facilities.
Introduction
Seasonal variations in various medical conditions have been well established in the literature. For instance, cardiovascular diseases,1 stroke,2 cardiac arrest,3 pulmonary disorders4 5 and sepsis6 commonly peak during winter. Understanding seasonal variations in diseases can help explain the nature of illnesses and aid in predicting demands for hospital resources. This knowledge is valuable for policy-makers in planning the appropriate allocation of medical resources and ensuring the presence of backup personnel during peak periods.7 8
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD), a major public health disease affecting millions of individuals worldwide annually,9 10 exhibits seasonal variations.811,15 A higher incidence of PUD during cold or winter seasons has been previously reported.8 12 14 15 The mechanism underlying may be related to the thinner mucosa of the gastric antrum during cold weather and the decreased level of heat shock protein 70.14 However, several studies have reported contradictory results. A nationwide cohort study conducted in the USA by Kanotra et al showed a peak for PUD incidence during the spring and a trough in fall,11 whereas another large-scale study in Italy reported three peak periods (autumn, winter and spring) for the incidence of PUD.16 Therefore, the existing conclusions regarding the seasonal variability in PUD incidence remain inconclusive. Moreover, most of these studies were conducted in Western or Northeast Asian countries with distinct seasonal climatic changes. Research on PUD incidence in Southeast Asian and tropical countries is limited.
To address this gap, we aimed to conduct a nationwide population study to investigate the seasonal variation in PUD incidence in Taiwan, a country that spans both tropical and subtropical regions. Additionally, we further analysed factors, such as age, sex, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) usage and latitudinal differences, to explore their association with seasonal variability in PUD incidence. Our goal was to obtain comprehensive data to assist in planning medical resource allocation, thereby achieving better patient care.
Methods
Data source
The data for this study were obtained from the Health and Welfare Data Science Centre (HWDC) of the Ministry of Health and Welfare in Taiwan, using the longitudinal National Health Insurance Research Database (LHID2005). LHID2005 is a random sample of two million individuals from 2005, and it reflects the demographic characteristics of Taiwan according to the distribution of gender, age and region.17 18 Therefore, the population distribution in LHID2005 accurately reflects the demographic characteristics of Taiwan, where the western region is significantly more populated than the eastern region.19 Additionally, LHID2005 included the detailed medical and prescription records from 2001 to 2019. The accuracy of the diagnosis codes in the National Health Insurance Research Database has been evaluated in several validation studies, demonstrating the reliability of this claims database.17 To protect personal information, the HWDC effectively manages deidentified patient data by linking the relative dataset. This study adhered to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology statement20 (online supplemental material).
Selection of patients
This study focused on PUD incidence in Taiwan, with specific attention paid to gastric ulcers (GUs), duodenal ulcers (DUs) and unspecified peptic ulcers, as classified by ICD-9-CM codes 531–534 and the corresponding ICD-10-CM codes K25–K28. Additionally, the study included data on NSAID usage, identified by the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) code M01A*. Patients with PUD were classified into three groups according to the use of the medication. Non-users were those who did not use NSAIDs in the 6 months before the diagnosis. Non-long-term users were patients who used NSAIDs at least once in the 6 months prior but did not meet the criteria for long-term use. Long-term users were those who used NSAIDs continuously for 14 days or accumulated 28 days of use within 3 months before the diagnosis.
Initially, 44 967 patients hospitalised for PUD between 2001 and 2019 were included. After excluding patients aged less than 20 years (n=465), 44 502 adult patients were included in the study. Patients whose first diagnosis code was PUD were selected from this group, resulting in a final sample size of 13 022.
Measurements
The incidence of PUD refers to the number of new cases diagnosed within a specific period. In this study, the incidence was defined as the number of patients who were first hospitalised with a diagnosis of PUD between 2001 and 2019. To reflect the overall burden of the disease, PUD prevalence was defined as the total number of existing cases of PUD at a given point in time or over a specified period.
Additionally, Taiwan is located between 21°45' and 25°56' north latitude, spanning both tropical and subtropical regions, with seasonal changes ranging from cool to hot, and a consistently humid climate throughout the year. The Central Weather Bureau defines spring as March–May, summer as June–August, fall as September–November and winter as December–February. The seasonal variation in average temperatures across Taiwan forms a symmetrical distribution. The lowest temperatures occur in late January to early February, with an average of around 18°C, followed by a gradual rise, reaching a peak in July with an average temperature of approximately 33°C. There is a notable difference in sunshine hours between northern and southern Taiwan. For instance, in 2019, Taipei in the north had an average sunshine duration percentage of 29.2%, while Kaohsiung in the south had 52.4%. Humidity levels, however, were similar, with Taipei at 76% and Kaohsiung at 75%.21 This geographical and climatic information is intended to provide relevant context for understanding the potential influence of seasonal changes on PUD incidence. Seasonal variations in PUD incidence among patients using different types of NSAIDs and those suffering from different PUD types were observed. Considering the association between area and temperature, PUD incidence in different areas of Taiwan was measured throughout the study.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to summarise baseline characteristics, including age, sex, PUD type, area, NSAID use and season, with frequency distributions. Temporal trends were assessed according to the annual prevalence and incidence rates, and seasonal variations were analysed by comparing the number of cases across the four seasons. Trends in annual prevalence and incidence rates were estimated using a linear trend test. To identify significant patterns, we used Pearson’s χ2 test and estimated the differences among PUD incidence in the four seasons throughout the study. All statistical analyses were performed by using SAS statistical software V.9.4 (SAS Institute), and statistical significance was set as a p value of less than 0.05.
Results
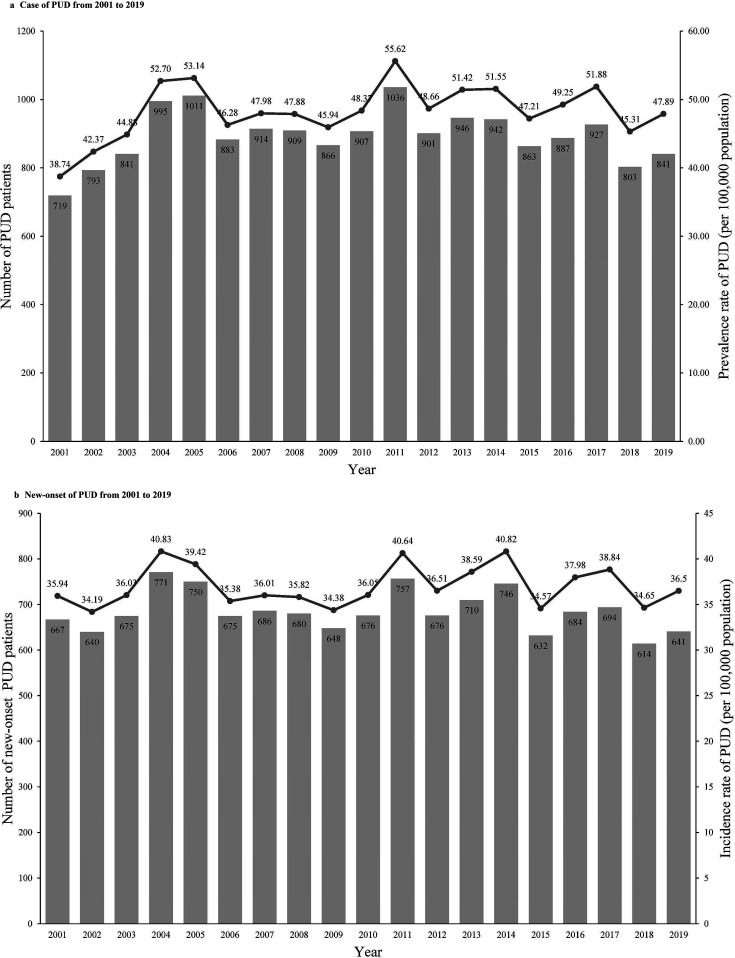
Figure 1 shows the annual trends of PUD prevalence and incidence from 2001 to 2019. PUD prevalence during this period ranged from 719 cases in 2001 to 1036 cases (the peak of PUD prevalence) in 2011, with annual fluctuations. Similarly, the trend of new-onset PUD showed annual variations, ranging from a peak of 771 cases in 2004 to a minimum of 614 cases in 2018. However, these two trends were not statistically significant.
Figure 1. The annual PUD prevalence and incidence from 2001 to 2019. PUD, peptic ulcer disease.
Table 1 presents the baseline information for the overall and seasonal variations. The number of peptic ulcers was higher in males than in females. Additionally, the incidence was higher in the elderly (age ≥65) compared with younger individuals. Among the different types of peptic ulcers, the proportion was highest for GUs, followed by DUs and unspecified peptic ulcers. More than half of the individuals had used NSAIDs within 6 months before developing peptic ulcers. Additionally, the currently observed seasonal distribution of PUD was highest in winter, followed by spring, summer and autumn (figure 2).
Table 1. The overall and subgroup of selected variables among PUD patients in different seasons.
| Overall | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | P value | |
| Overall | 13 022 | 3317 (25.47) | 3143 (24.14) | 3072 (23.59) | 3490 (26.8) | |
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 8392 (64.44) | 2146 (25.57) | 2035 (24.25) | 1959 (23.34) | 2252 (26.84) | 0.8391 |
| Female | 4630 (35.56) | 1171 (25.29) | 1108 (23.93) | 1113 (24.04) | 1238 (26.74) | |
| Age | ||||||
| <65 | 5273 (40.49) | 1342 (25.45) | 1299 (24.63) | 1250 (23.71) | 1382 (26.21) | 0.5473 |
| ≥65 | 7749 (59.51) | 1975 (25.49) | 1844 (23.8) | 1822 (23.51) | 2108 (27.2) | |
| PUD type | ||||||
| GU | 7306 (56.11) | 1822 (24.94) | 1814 (24.83) | 1750 (23.95) | 1920 (26.28) | 0.0816 |
| DU | 4720 (36.25) | 1256 (26.61) | 1090 (23.09) | 1078 (22.84) | 1296 (27.46) | |
| Others | 996 (7.65) | 239(24) | 239(24) | 244 (24.5) | 274 (27.51) | |
| Area | ||||||
| North | 4953 (38.04) | 1269 (25.62) | 1175 (23.72) | 1159 (23.4) | 1350 (27.26) | 0.6972 |
| Central | 3244 (24.91) | 825 (25.43) | 791 (24.38) | 792 (24.41) | 836 (25.77) | |
| South | 4292 (32.96) | 1086 (25.3) | 1056 (24.6) | 1010 (23.53) | 1140 (26.56) | |
| East | 472 (3.62) | 121 (25.64) | 107 (22.67) | 99 (20.97) | 145 (30.72) | |
| Others | 61 (0.47) | 16 (26.23) | 14 (22.95) | 12 (19.67) | 19 (31.15) | |
| NSAIDs use | ||||||
| Non-NSAIDs users | 4065 (31.22) | 1049 (25.81) | 941 (23.15) | 909 (22.36) | 1166 (28.68) | 0.0194 |
| NSAIDs users (non-long term) | 5111 (39.25) | 1304 (25.51) | 1239 (24.24) | 1242 (24.3) | 1326 (25.94) | |
| NSAIDs users (long term) | 3846 (29.53) | 964 (25.07) | 963 (25.04) | 921 (23.95) | 998 (25.95) |
DUduodenal ulcerGUgastric ulcerNSAIDsnon-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugsPUDpeptic ulcer disease
Figure 2. The seasonal variation in PUD incidence. PUD, peptic ulcer disease.
Table 2 presents the number of new patients with peptic ulcers across all seasons in the NSAID-use group and across different subgroups, including sex, age, PUD type and area. Among non-NSAID users, the seasonal trend for PUD incidence was highest in winter, followed by spring. However, NSAID use exhibited different seasonal variations. Long-term NSAID users presented higher rates of PUD incidence during winter among males (25.96%), females (25.93%), the elderly (age ≥65) (26.11%), those suffering from DUs (27.78%) and those residing in north (26.75%) and central (25.67%) Taiwan.
Table 2. The new PUD cases in different seasons among various subgroups (gender and age Groups) based on the usage of NSAIDs.
| Non-NSAIDs users | NSAIDs users (non-long term) | NSAIDs users (long term) | ||||||||||
| Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | |
| Gender | ||||||||||||
| Male | 719 (24.9) | 683 (23.65) | 650 (22.51) | 836 (28.95) | 885 (26.23) | 807 (23.92) | 819 (24.27) | 863 (25.58) | 542 (25.45) | 545 (25.59) | 490(23) | 553 (25.96) |
| Female | 330 (28.04) | 258 (21.92) | 259 (22.01) | 330 (28.04) | 419 (24.12) | 432 (24.87) | 423 (24.35) | 463 (26.66) | 422 (24.59) | 418 (24.36) | 431 (25.12) | 445 (25.93) |
| Age | ||||||||||||
| <65 | 501 (26.01) | 459 (23.83) | 444 (23.05) | 522 (27.1) | 605 (25.99) | 573 (24.61) | 550 (23.63) | 600 (25.77) | 236 (23.16) | 267 (26.2) | 256 (25.12) | 260 (25.52) |
| ≥65 | 548 (25.62) | 482 (22.53) | 465 (21.74) | 644 (30.11) | 699 (25.12) | 666 (23.93) | 692 (24.87) | 726 (26.09) | 728 (25.75) | 696 (24.62) | 665 (23.52) | 738 (26.11) |
| PUD type | ||||||||||||
| GU | 532 (24.72) | 508 (23.61) | 485 (22.54) | 627 (29.14) | 726 (25.41) | 702 (24.57) | 711 (24.89) | 718 (25.13) | 564 (24.55) | 604 (26.3) | 554 (24.12) | 575 (25.03) |
| DU | 436 (27.82) | 343 (21.89) | 352 (22.46) | 436 (27.82) | 485 (25.87) | 455 (24.27) | 430 (22.93) | 505 (26.93) | 335 (26.21) | 292 (22.85) | 296 (23.16) | 355 (27.78) |
| Others | 81 (23.41) | 90 (26.01) | 72 (20.81) | 103 (29.77) | 93 (24.54) | 82 (21.64) | 101 (26.65) | 103 (27.18) | 65 (23.99) | 67 (24.72) | 71 (26.2) | 68 (25.09) |
| Area | ||||||||||||
| North | 418 (25.66) | 373 (22.9) | 361 (22.16) | 477 (29.28) | 470 (25.54) | 437 (23.75) | 457 (24.84) | 476 (25.87) | 381 (25.67) | 365 (24.6) | 341 (22.98) | 397 (26.75) |
| Central | 255 (25.97) | 227 (23.12) | 224 (22.81) | 276 (28.11) | 332 (25.7) | 319 (24.69) | 330 (25.54) | 311 (24.07) | 238 (24.54) | 245 (25.26) | 238 (24.54) | 249 (25.67) |
| South | 334 (25.93) | 302 (23.45) | 293 (22.75) | 359 (27.87) | 462 (25.62) | 445 (24.68) | 418 (23.18) | 478 (26.51) | 290 (24.15) | 309 (25.73) | 299 (24.9) | 303 (25.23) |
| East | 36 (24.66) | 37 (25.34) | 28 (19.18) | 45 (30.82) | 36 (23.53) | 28 (18.3) | 31 (20.26) | 58 (37.91) | 49 (28.32) | 42 (24.28) | 40 (23.12) | 42 (24.28) |
| Others | 6 (30) | 2 (10) | 3 (15) | 9 (45) | 4 (17.39) | 10 (43.48) | 6 (26.09) | 3 (13.04) | 6 (33.33) | 2 (11.11) | 3 (16.67) | 7 (38.89) |
DUduodenal ulcerGUgastric ulcerNSAIDsnon-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugsPUDpeptic ulcer disease
Table 3 presents the categorised data by PUD type and shows the number of new PUD cases across different subgroups (sex and age) by season. In these subgroups, patients in the GU and DU subgroups presented higher rates of PUD in winter, particularly among patients older than 65 years (27.98%).
Table 3. Incidence and number of new occurrences in different seasons among various subgroups (gender and age groups) by different PUD types.
| GU | DU | Others | ||||||||||
| Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | |
| Gender | ||||||||||||
| Male | 1105 (24.8) | 1108 (24.87) | 1072 (24.06) | 1170 (26.26) | 877 (27.03) | 753 (23.2) | 729 (22.47) | 886 (27.3) | 164 (23.7) | 174 (25.14) | 158 (22.83) | 196 (28.32) |
| Female | 717 (25.15) | 706 (24.76) | 678 (23.78) | 750 (26.31) | 379 (25.69) | 337 (22.85) | 349 (23.66) | 410 (27.8) | 75 (24.67) | 65 (21.38) | 86 (28.29) | 78 (25.66) |
| Age | ||||||||||||
| <65 | 691 (24.47) | 709 (25.11) | 700 (24.79) | 724 (25.64) | 546 (27.06) | 491 (24.33) | 441 (21.85) | 540 (26.76) | 105 (24.36) | 99 (22.97) | 109 (25.29) | 118 (27.38) |
| ≥65 | 1131 (25.23) | 1105 (24.65) | 1050 (23.43) | 1196 (26.68) | 710 (26.28) | 599 (22.17) | 637 (23.58) | 756 (27.98) | 134 (23.72) | 140 (24.78) | 135 (23.89) | 156 (27.61) |
| Area | ||||||||||||
| North | 684 (24.64) | 690 (24.86) | 639 (23.02) | 763 (27.49) | 483 (26.98) | 388 (21.68) | 420 (23.46) | 499 (27.88) | 102 (26.36) | 97 (25.06) | 100 (25.84) | 88 (22.74) |
| Central | 449 (25.31) | 441 (24.86) | 442 (24.92) | 442 (24.92) | 322 (26.29) | 283 (23.1) | 294(24) | 326 (26.61) | 54 (22.04) | 67 (27.35) | 56 (22.86) | 68 (27.76) |
| South | 609 (24.93) | 603 (24.68) | 606 (24.81) | 625 (25.58) | 405 (26.15) | 386 (24.92) | 329 (21.24) | 429 (27.7) | 72 (24.08) | 66 (22.07) | 75 (25.08) | 86 (28.76) |
| East | 70 (25.45) | 72 (26.18) | 53 (19.27) | 80 (29.09) | 41 (28.87) | 28 (19.72) | 33 (23.24) | 40 (28.17) | 10 (18.18) | 7 (12.73) | 13 (23.64) | 25 (45.45) |
| Others | 10 (26.32) | 8 (21.05) | 10 (26.32) | 10 (26.32) | 5 (35.71) | 5 (35.71) | 2 (14.29) | 2 (14.29) | 1 (10.00) | 2 (20.00) | 0 (0.00) | 7 (70.00) |
DUduodenal ulcerGUgastric ulcePUDpeptic ulcer disease
Discussion
Studies on the seasonal variability in PUD incidence have primarily been conducted in Western and Northern Asian countries with distinct seasons. Many studies have suggested a peak incidence during winter; however, their results are inconclusive. Ours is the first large, real-world database study on the seasonal variability of PUD incidence conducted in Taiwan, which spans both tropical and subtropical zones. This study provides clinically important reference data to assist in planning the appropriate allocation of medical resources to address their availability during peak seasons. The findings indicated that males and elderly individuals (age ≥65) exhibited a higher incidence of peptic ulcers. The frequency of peptic ulcer occurrences and the number of new cases peaked during winter. These results were consistent across all age and sex groups, with no significant effect of differences in latitude, NSAID usage or PUD type. However, subtle differences were observed when analysed further, which are discussed in detail below.
Demographics
According to a previous study, the global prevalence of PUD decreased from 143.4 per 100 000 population in 1990 to 99.4 in 2019. Countries with low to middle Socio-Demographic Index (SDI) experienced a more significant decline, while the trend in countries with high SDI remained relatively stable.22 In the current study, the prevalence of PUD in Taiwan was 38.74 per 100 000 population in 2001 and 47.89 in 2019, which is similar to the trends observed in other high SDI countries. Consistent with previous studies, the present results indicated a higher incidence of ulcers in males than in females.23 24 This was attributed to the significantly higher smoking rates among males in Taiwan,25 the higher global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection among males,25 26 and sex-related differences in gastroduodenal mucosal defence mechanisms.27 28 Additionally, PUD incidence was higher in older adults than in younger ones. Both the incidence of PUD and the frequency of hospitalisations due to PUD-related complications are increasing in elderly populations.23 29 This trend may be associated with several factors such as a higher rate of H. pylori infection among older individuals,30 an increased use of aspirin and other NSAIDs by older individuals owing to specific medical conditions,31 and a weakening of gastric and duodenal mucosal defence mechanisms in this age group. Gastric and duodenal mucosal defence mechanisms include reduced bicarbonate secretion,32 lower prostaglandin concentrations in the stomach and duodenum and altered prostaglandin responses of the mucosa to injuries.33
Our results showed that the frequency of hospitalisation due to peptic ulcers in Taiwan did not significantly change from 2001 to 2019. Recent studies using the Global Burden of Disease database have shown that the incidence and mortality rates of PUD have remained stable over the past decade. A noticeable decrease observed once attributed to the use of proton pump inhibitors as well as to the treatment for H. pylori infection was no longer apparent. This stability may be related to a shift in primary risk factors for peptic ulcers from H. pylori infection to NSAID use, along with the ageing of the global population.10 22
Seasonal variations in PUD incidence and related determinants
Taiwan has an insular climate, with the Tropic of Cancer passing through Chiayi County, the northernmost part of southern Taiwan, placing most of southern Taiwan in the tropical zone. Furthermore, temperatures remain high throughout the year, with moderate seasonal temperature variance of about 8°C. In contrast, central and northern Taiwan has a subtropical climate, characterised by more distinct seasonal changes, with temperature differences between winter and summer around 12°C.
The present findings indicated that DU, GU and other types of PUD exhibited the highest prevalence and incidence in winter, followed by spring, with more pronounced seasonal variation observed for DU. Similarly, Tsai et al conducted a cross-sectional study in Taiwan and found a higher incidence of symptomatic DU during colder months, from November to March.34 Xirasagar et al adjusted for meteorological factors and found an inverse correlation between the rates of hospitalisation for DU and temperature in Taiwan.35 However, the present study revealed that seasonal variations in DU incidence between northern and southern Taiwan were similar, suggesting that temperature may not be the sole affecting factor. Additionally, smoking may contribute to the seasonal prevalence of DUs during winter. Historically, smoking has been considered a primary causative factor for PUD.36 37 Smokers in Taiwan tend to smoke more during the winter and rainy seasons,35 with smoking rates significantly higher among men than women, mirroring the significantly higher incidence of DU among males observed in the present study. Seasonal variation in light exposure, which induces annual rhythms of melatonin, might also be a critical factor triggering DU, in addition to stress induced by harsh winter conditions.35 38
In contrast, the seasonal variations in GU incidence were more pronounced in northern and southern Taiwan. This discrepancy may be associated with the more distinct four-season climate and colder winters in the north. Cold weather and rapid temperature fluctuations can trigger an acute stress reaction, leading to the increased secretion of epinephrine, norepinephrine and endothelin, causing vasoconstriction in the gastrointestinal mucosa, reduced blood flow and damage to protective barriers due to insufficient oxygen. These factors increase gastric acid levels and accelerate PUD development.39 40
Seasonal differences in PUD incidence were most consistent among non-NSAID users, possibly because NSAID usage itself is a major risk factor for PUD, thereby obscuring seasonal variations. A study from Spain showed that DU bleeding was most frequent in autumn and winter; however, this trend was not observed in NSAID users.41 Similarly, a study from Greece found that the seasonal distribution of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding was only evident in patients who did not use NSAIDs.42 The present results revealed that the peak of PUD prevalence in short-term NSAID users occurred during winter and spring. This may be related to the seasonal peaks of respiratory illnesses43 44 and other diseases, such as osteoarthritis and rheumatic arthritis,45 46 which are more prevalent in colder seasons. The increased likelihood of short-term NSAID use during these periods could affect the seasonal variation in PUD incidence. Although the overall incidence of PUD remained the highest in winter, the differences across seasons were minimal, and the results varied considerably among the subgroups. This inconsistency may be attributed to the strong effect of prolonged NSAID use on PUD incidence, which could overshadow any seasonal variation.
Strengths and limitations
The primary strength of this study is the use of a nationwide population-based database that provides representative data to investigate seasonal variations in PUD incidence. Another strength is its location in Taiwan, which spans tropical and subtropical regions. The present subgroup analyses based on latitude helped us gain a deeper understanding of the seasonal variability in PUD incidence across regions with different climates.
Nevertheless, the study has several limitations. First, the LHID2005 lacks comprehensive clinical information, making it impossible to assess and adjust for risk factors for PUD such as smoking, alcohol consumption, caffeine intake, H. pylori infection, gastric bypass surgery and stress.47 Second, we did not adjust for individual meteorological factors such as atmospheric pressure, humidity, sunshine duration and rainfall, which may affect the seasonal variability in PUD incidence.35 Third, some acute conditions related to seasonal changes, such as arthritis and acute respiratory illnesses, can lead to the short-term use of NSAIDs, thereby potentially affecting PUD incidence and seasonal variations in its incidence, and ultimately affecting the present results. Additionally, the exact season and dates of NSAID use as well as medication adherence among these patients could not be obtained from the LHID2005. Furthermore, the possibility of misclassification bias exists within this administrative claims data, which may affect the accuracy of the diagnosis codes used to identify diseases in this study. However, due to the large sample size and standardised coding practices in Taiwan’s healthcare insurance system, the potential impact of this bias could be limited.
Across the tropical and subtropical regions of Taiwan, a significant seasonal variation in PUD incidence is observed, with the highest rates occurring in winter, regardless of age or sex. However, NSAID usage tends to obscure this trend. The seasonal variation in DU incidence showed no significant differences between north and south Taiwan, suggesting that factors other than temperature may affect DU incidence compared with their effect on GU incidence.
Conclusion
The current results provide a reference for medical institutions to plan health education programmes for preventing PUD. For example, encouraging the reduction of NSAID use and smoking during the winter months while adjusting the allocation of medical resources according to seasonal variations. Nevertheless, future large-scale prospective studies with comprehensive and precise clinical information on patients with PUD and adjustments for meteorological factors are warranted.
supplementary material
Acknowledgements
We thank the Health Data Science Centre of National Cheng Kung University Hospital for providing administrative and technical support.
The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Funding: This study was supported partly from Chi Mei Medical Center (Grant No. 111CM-KMU-08) for the author S-FW and YK.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Patient consent for publication: Not applicable.
Data availability free text: The data sources are obtained from the Taiwan Nation Health Insurance Database. The data are available with permission from the Taiwan Health and Welfare Data Science Centre (https://dep.mohw.gov.tw/DOS/cp-5119-59201-113.html, accessed on 5 July 2024). Restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under licence for this study.
Ethics approval: This study was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki and has been approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Chi Mei Hospital (IRB permit number: 11306-010). The requirement for informed consent was waived as deidentified data were used.
Contributor Information
Yi-Chen Lai, Email: johnnyliyijin@gmail.com.
Yu-Han Chen, Email: smallquai@gmail.com.
Chien-An Chen, Email: anan731030@gmail.com.
Chung-Han Ho, Email: ho.c.hank@gmail.com.
Yu-Cih Wu, Email: cih830927@gmail.com.
Jhi-Joung Wang, Email: 400002@mail.chimei.org.tw.
Shih-Feng Weng, Email: sfweng@kmu.edu.tw.
Yuan Kao, Email: vincentkao6703@gmail.com.
Data availability statement
Data may be obtained from a third party and are not publicly available.
References
- 1.Stewart S, Keates AK, Redfern A, et al. Seasonal variations in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017;14:654–64. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fujii T, Arima H, Takashima N, et al. Seasonal Variation in Incidence of Stroke in a General Population of 1.4 Million Japanese: The Shiga Stroke Registry. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022;51:75–81. doi: 10.1159/000518370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.El Sibai RH, Bachir RH, El Sayed MJ. Seasonal variation in incidence and outcomes of out of hospital cardiac arrest: A retrospective national observational study in the United States. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021;100:e25643. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ho ATN, Shmelev A, Charbek E. Trends and seasonal variation of hospitalization and mortality of interstitial lung disease in the United States from 2006 to 2016. Respir Res. 2020;21:152. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01421-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Donaldson GC, Wedzicha JA. The causes and consequences of seasonal variation in COPD exacerbations. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014;9:1101–10. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S54475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Danai PA, Sinha S, Moss M, et al. Seasonal variation in the epidemiology of sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:410–5. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000253405.17038.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zangbar B, Rhee P, Pandit V, et al. Seasonal Variation in Emergency General Surgery. Ann Surg. 2016;263:76–81. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yoon JY, Cha JM, Kim HI, et al. Seasonal variation of peptic ulcer disease, peptic ulcer bleeding, and acute pancreatitis: A nationwide population-based study using a common data model. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021;100:e25820. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Abbasi-Kangevari M, Ahmadi N, Fattahi N, et al. Quality of care of peptic ulcer disease worldwide: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 1990-2019. PLoS One. 2022;17:e0271284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xie X, Ren K, Zhou Z, et al. The global, regional and national burden of peptic ulcer disease from 1990 to 2019: a population-based study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:58. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02130-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kanotra R, Ahmed M, Patel N, et al. Seasonal Variations and Trends in Hospitalization for Peptic Ulcer Disease in the United States: A 12-Year Analysis of the Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Cureus. 2016;8:e854. doi: 10.7759/cureus.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hui W, Lam S. Monthly variation in frequency of active duodenal ulcer and maximal acid output. J of Gastro and Hepatol. 1988;3:457–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1988.tb01401.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tzagournis M. SEASONAL AND MONTHLY INCIDENCE OF PEPTIC ULCER. JAMA. 1965;193:972–5. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03090110110039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yuan X-G, Xie C, Chen J, et al. Seasonal changes in gastric mucosal factors associated with peptic ulcer bleeding. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9:125–30. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lam SK. Differences in peptic ulcer between East and West. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;14:41–52. doi: 10.1053/bega.1999.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Manfredini R, De Giorgio R, Smolensky MH, et al. Seasonal pattern of peptic ulcer hospitalizations: analysis of the hospital discharge data of the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010;10:37. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hsieh C-Y, Su C-C, Shao S-C, et al. Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database: past and future. Clin Epidemiol. 2019;11:349–58. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S196293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lin L-Y, Warren-Gash C, Smeeth L, et al. Data resource profile: the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) Epidemiol Health. 2018;40:e2018062. doi: 10.4178/epih.e2018062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Department of Household Registration, Ministry of the Interior, R.O.C. (Taiwan) Statistics. [09-Oct-2024]. https://www.ris.gov.tw/app/en/3910 Available. Accessed.
- 20.von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, et al. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61:344–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2007.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Central Weather Administration Research publications and annual reports. [09-Oct-2024];2024 https://www.cwa.gov.tw/V8/E/D/publication.html?key=12 Available. accessed.
- 22.Ren J, Jin X, Li J, et al. The global burden of peptic ulcer disease in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Int J Epidemiol. 2022;51:1666–76. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyac033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cai S, García Rodríguez LA, Massó-González EL, et al. Uncomplicated peptic ulcer in the UK: trends from 1997 to 2005. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;30:1039–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.04131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Feinstein LB, Holman RC, Yorita Christensen KL, et al. Trends in hospitalizations for peptic ulcer disease, United States, 1998-2005. Emerg Infect Dis . 2010;16:1410–8. doi: 10.3201/eid1609.091126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chiang CY, Chang HY. A population study on the time trend of cigarette smoking, cessation, and exposure to secondhand smoking from 2001 to 2013 in Taiwan. Popul Health Metr. 2016;14:38. doi: 10.1186/s12963-016-0109-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.de Martel C, Parsonnet J. Helicobacter pylori infection and gender: a meta-analysis of population-based prevalence surveys. Dig Dis Sci. 2006;51:2292–301. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-9210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.El-Tawil A. Gender and the Pathogenesis of Gastrointestinal Diseases: The Role of Steroid Sex Hormones in the Development. J Steroids Horm Sci . 2013;02 doi: 10.4172/2157-7536.1000e101. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Liu ES, Wong BC, Cho CH. Influence of gender difference and gastritis on gastric ulcer formation in rats. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;16:740–7. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2001.02506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Walt R, Katschinski B, Logan R, et al. Rising frequency of ulcer perforation in elderly people in the United Kingdom. Lancet. 1986;1:489–92. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92940-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Graham DY, Adam E, Reddy GT, et al. Seroepidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection in India. Comparison of developing and developed countries. Dig Dis Sci. 1991;36:1084–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01297451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Khaghan N, Holt PR. Peptic disease in elderly patients. Can J Gastroenterol. 2000;14:922–8. doi: 10.1155/2000/697943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Feldman M, Cryer B. Effects of age on gastric alkaline and nonparietal fluid secretion in humans. Gerontology. 1998;44:222–7. doi: 10.1159/000022014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee M, Feldman M. Age-related reductions in gastric mucosal prostaglandin levels increase susceptibility to aspirin-induced injury in rats. Gastroenterology. 1994;107:1746–50. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90816-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tsai CJ, Lin CY. Seasonal changes in symptomatic duodenal ulcer activity in Taiwan: a comparison between subjects with and without haemorrhage. J Intern Med. 1998;244:405–10. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.1998.00383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Xirasagar S, Lin HC, Chen CS. Role of meteorological factors in duodenal ulcer seasonality: a nation-wide, population-based study. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22:1439–46. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0288-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li LF, Chan RLY, Lu L, et al. Cigarette smoking and gastrointestinal diseases: the causal relationship and underlying molecular mechanisms (review) Int J Mol Med. 2014;34:372–80. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Maity P, Biswas K, Roy S, et al. Smoking and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal ulcer--recent mechanistic update. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;253:329–38. doi: 10.1023/a:1026040723669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Malinovskaya N, Komarov FI, Rapoport SI, et al. Melatonin production in patients with duodenal ulcer. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2001;22:109–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fares A. Global patterns of seasonal variation in gastrointestinal diseases. J Postgrad Med. 2013;59:203–7. doi: 10.4103/0022-3859.118039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Liu D, Gao A, Tang G, et al. Study of the relationship between the onset of peptic ulcers and meteorological factors. Chin Med J (Engl) 2003;116:1940–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tenías Burillo JM, Llorente Melero MJ, Zaragoza Marcet A. Epidemiologic aspects on nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding in a mediterranean region: incidence and sociogeographic and temporal fluctuations. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2001;93:96–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Thomopoulos KC, Katsakoulis EC, Margaritis VG, et al. Seasonality in the prevalence of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1997;25:576–9. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199712000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lin Y-K, Chang C-K, Chang S-C, et al. Temperature, nitrogen dioxide, circulating respiratory viruses and acute upper respiratory infections among children in Taipei, Taiwan: a population-based study. Environ Res. 2013;120:109–18. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2012.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Su C-P, Tsou T-P, Chen C-H, et al. Seasonal influenza prevention and control in Taiwan-Strategies revisited. J Formos Med Assoc. 2019;118:657–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2018.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mori H, Sawada T, Nishiyama S, et al. Influence of seasonal changes on disease activity and distribution of affected joints in rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20:30. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2418-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Timmermans EJ, Schaap LA, Herbolsheimer F, et al. The Influence of Weather Conditions on Joint Pain in Older People with Osteoarthritis: Results from the European Project on OSteoArthritis. J Rheumatol. 2015;42:1885–92. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.141594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sverdén E, Agréus L, Dunn JM, et al. Peptic ulcer disease. BMJ. 2019;367:l5495. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l5495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Data may be obtained from a third party and are not publicly available.