Abstract
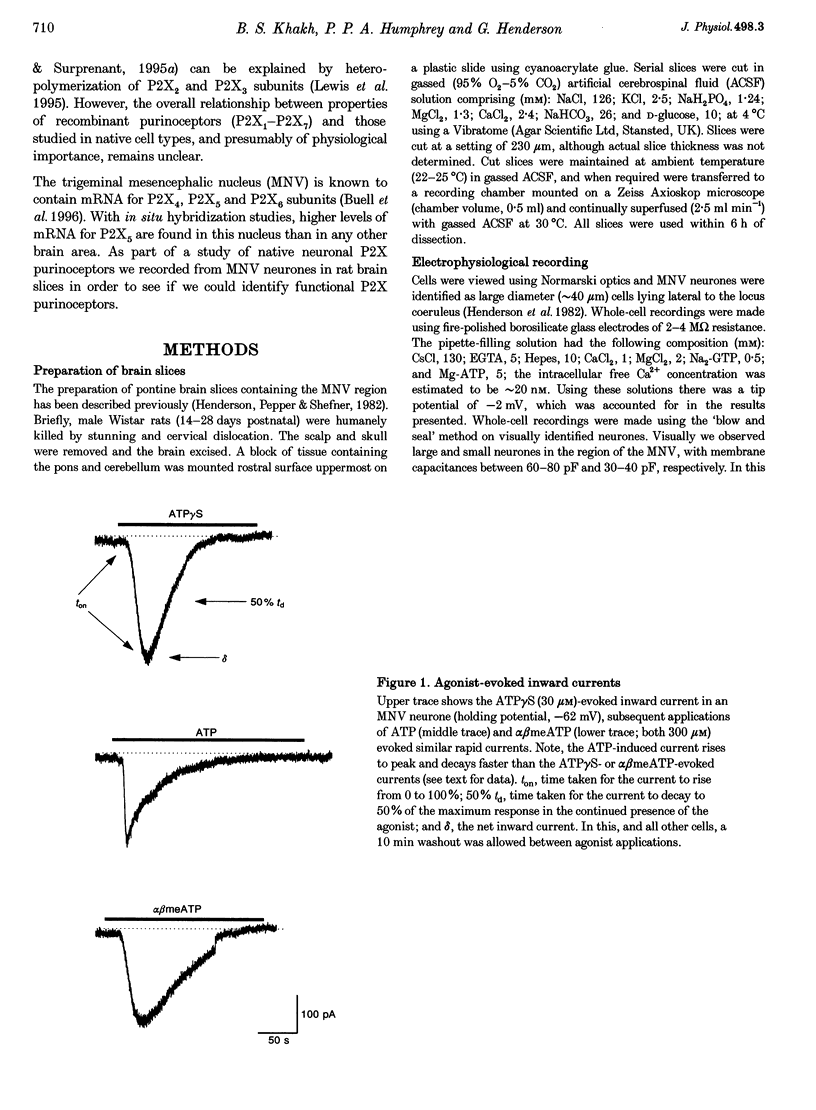
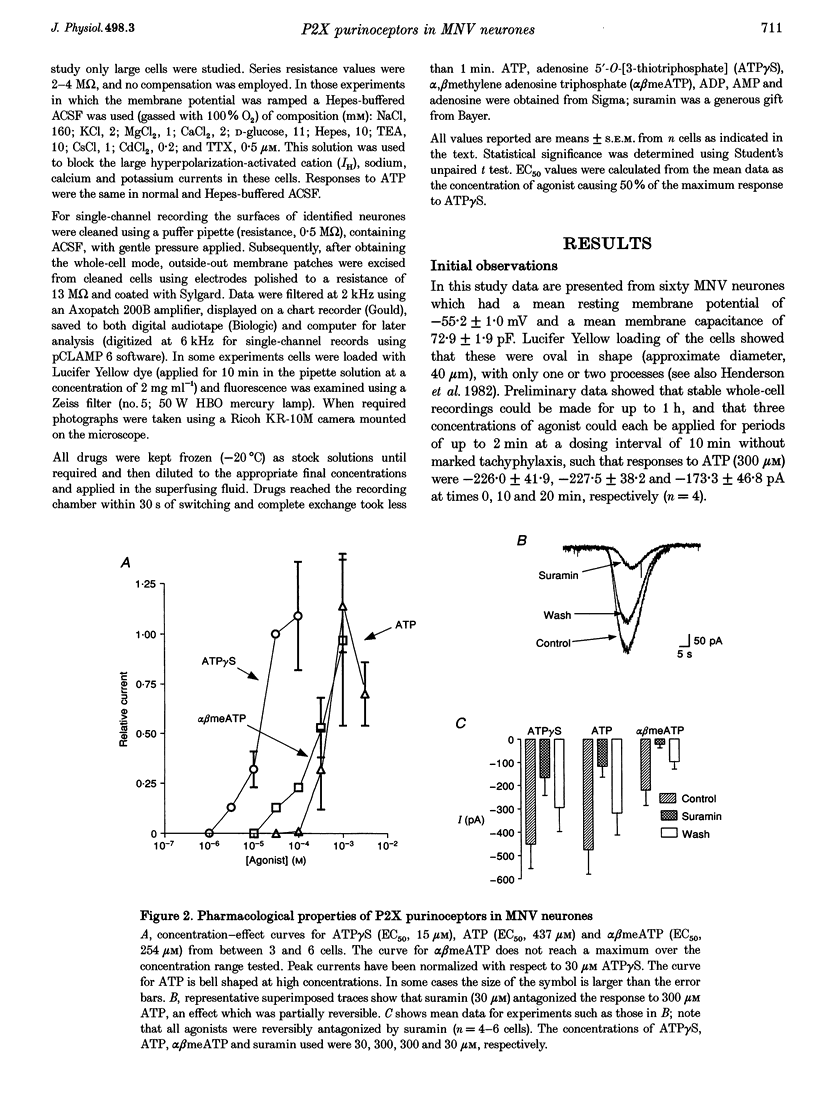
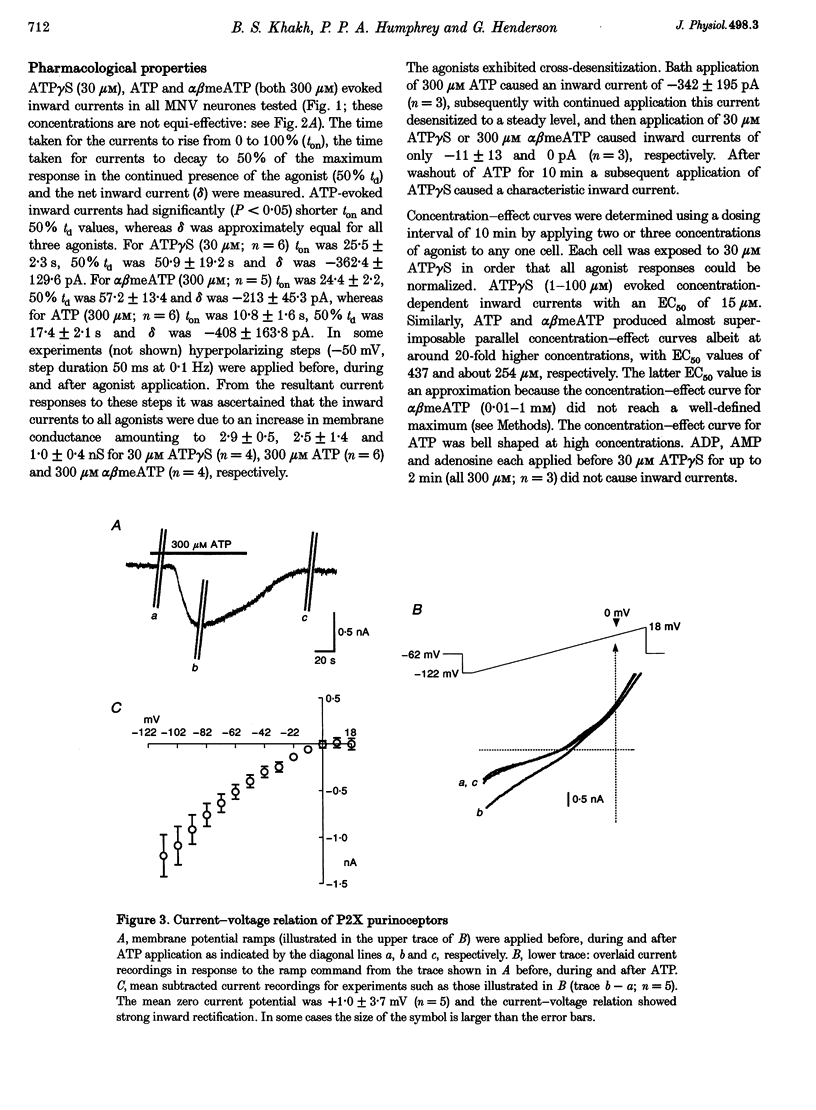
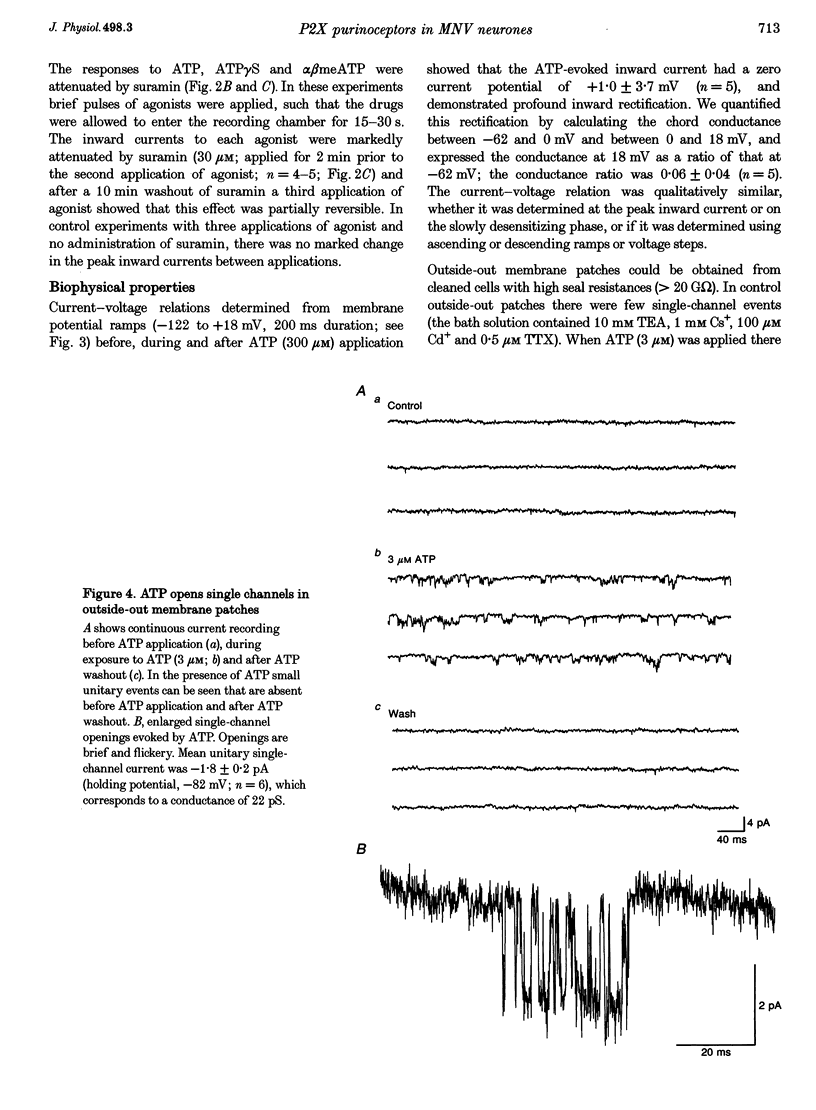
1. We have investigated whether receptors for ATP exist on neurones of the trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus (MNV) of the rat using whole-cell and outside-out patch-clamp recording in coronal brainstem slices. 2. With whole-cell recording, the batch application of ATP, adenosine 5'-O-[3-thiotriphosphate] (ATP gamma S) and alpha,beta methylene adenosine triphosphate (alpha beta meATP) caused concentration-dependent inward currents in all cells tested (holding potential, -62 mV), with EC50 values of 437, 15 and 254 microM, respectively. All three agonist-evoked currents developed rapidly (rise time, approximately 10-25 s), desensitized slowly (over approximately 20-50 s), cross-desensitized with each other, were associated with an increase in membrane conductance and were attenuated by the application of suramin (30 microM). 3. The inward current evoked by ATP decreased as the membrane potential was made less negative and had a zero current potential of +1.0 +/- 3.7 mV. The current-voltage relationship showed marked inward rectification. 4. Brief flickery single-channel openings could be resolved in response to ATP (3 microM) in outside-out membrane patches. Unitary current at -82 mV was -1.81 +/- 0.2 pA, which corresponds to a unitary conductance of 22 pS. 5. We conclude that proprioceptive MNV neurones contain ATP-gated cation channels. Such P2X purinoceptors may be involved in the processing of proprioceptive information, thus suggesting a potentially important physiological role of ATP.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P., Friel D. D. ATP-activated channels in excitable cells. Ion Channels. 1990;2:169–203. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7305-0_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bo X., Zhang Y., Nassar M., Burnstock G., Schoepfer R. A P2X purinoceptor cDNA conferring a novel pharmacological profile. FEBS Lett. 1995 Nov 13;375(1-2):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01203-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake A. J., Wagenbach M. J., Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):519–523. doi: 10.1038/371519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell G., Lewis C., Collo G., North R. A., Surprenant A. An antagonist-insensitive P2X receptor expressed in epithelia and brain. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 2;15(1):55–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. A unifying purinergic hypothesis for the initiation of pain. Lancet. 1996 Jun 8;347(9015):1604–1605. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)91082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Akopian A. N., Sivilotti L., Colquhoun D., Burnstock G., Wood J. N. A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):428–431. doi: 10.1038/377428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collo G., North R. A., Kawashima E., Merlo-Pich E., Neidhart S., Surprenant A., Buell G. Cloning OF P2X5 and P2X6 receptors and the distribution and properties of an extended family of ATP-gated ion channels. J Neurosci. 1996 Apr 15;16(8):2495–2507. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-08-02495.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Lewis C., Buell G., Valera S., North R. A., Surprenant A. Pharmacological characterization of heterologously expressed ATP-gated cation channels (P2x purinoceptors). Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;48(2):178–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J. Single channel properties of ATP-gated cation channels (P2X receptors) heterologously expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Neurosci Lett. 1996 Jul 19;212(3):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(96)12804-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Pepper C. M., Shefner S. A. Electrophysiological properties of neurons contained in the locus coeruleus and mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal nerve in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1982;45(1-2):29–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00235760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakh B. S., Humphrey P. P., Surprenant A. Electrophysiological properties of P2X-purinoceptors in rat superior cervical, nodose and guinea-pig coeliac neurones. J Physiol. 1995 Apr 15;484(Pt 2):385–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khakh B. S., Surprenant A., Humphrey P. P. A study on P2X purinoceptors mediating the electrophysiological and contractile effects of purine nucleotides in rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(1):177–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C., Neidhart S., Holy C., North R. A., Buell G., Surprenant A. Coexpression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits can account for ATP-gated currents in sensory neurons. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):432–435. doi: 10.1038/377432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem R. S., Copray J. C., van Willigen J. D. Ultrastructure of the rat mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus. Acta Anat (Basel) 1991;140(2):112–119. doi: 10.1159/000147045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Lundström K., Buell G. N., Surprenant A., Valera S., Humphrey P. P. A comparison of the binding characteristics of recombinant P2X1 and P2X2 purinoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Aug;118(7):1806–1812. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., Buell G., North R. A. P2X receptors bring new structure to ligand-gated ion channels. Trends Neurosci. 1995 May;18(5):224–229. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)93907-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., Rassendren F., Kawashima E., North R. A., Buell G. The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7). Science. 1996 May 3;272(5262):735–738. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5262.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera S., Hussy N., Evans R. J., Adami N., North R. A., Surprenant A., Buell G. A new class of ligand-gated ion channel defined by P2x receptor for extracellular ATP. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):516–519. doi: 10.1038/371516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


