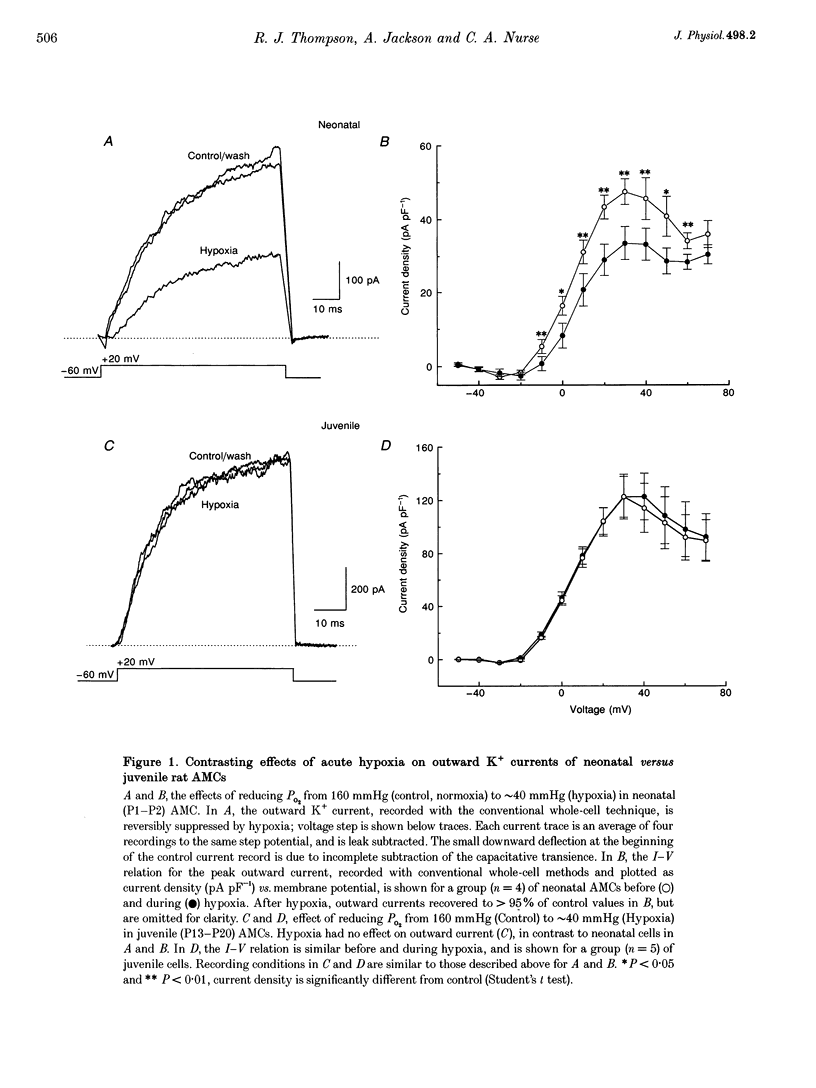
Abstract
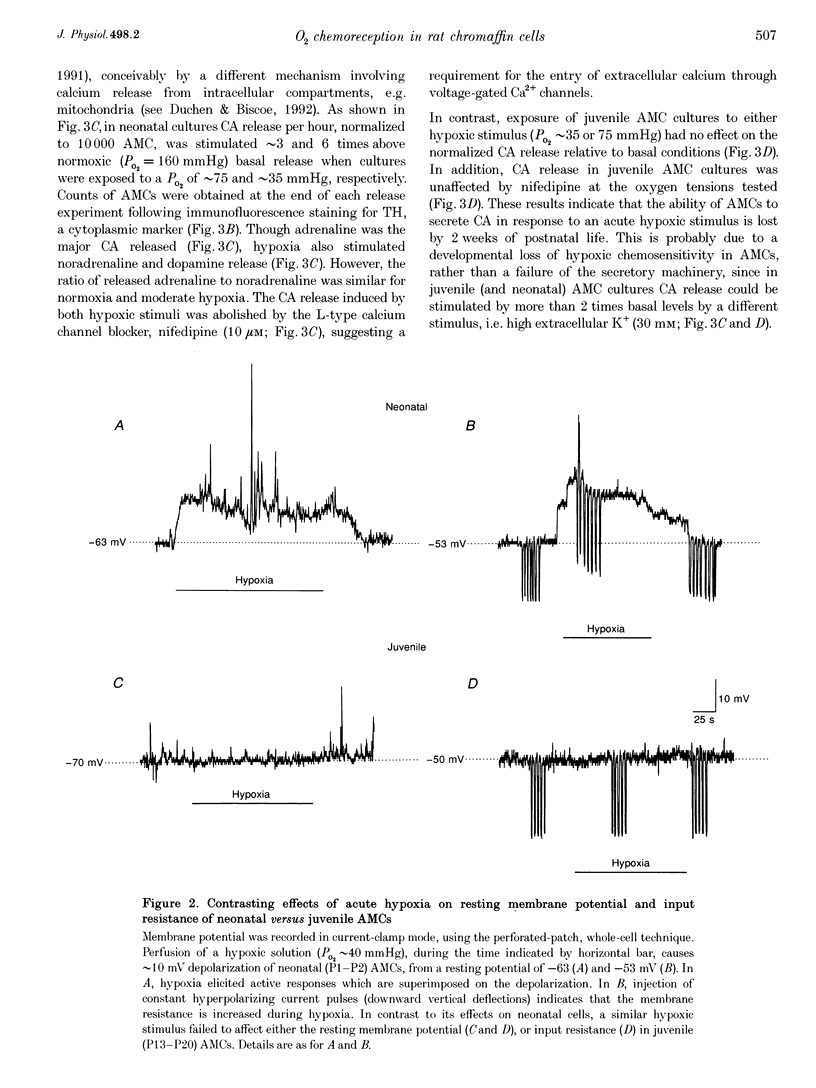
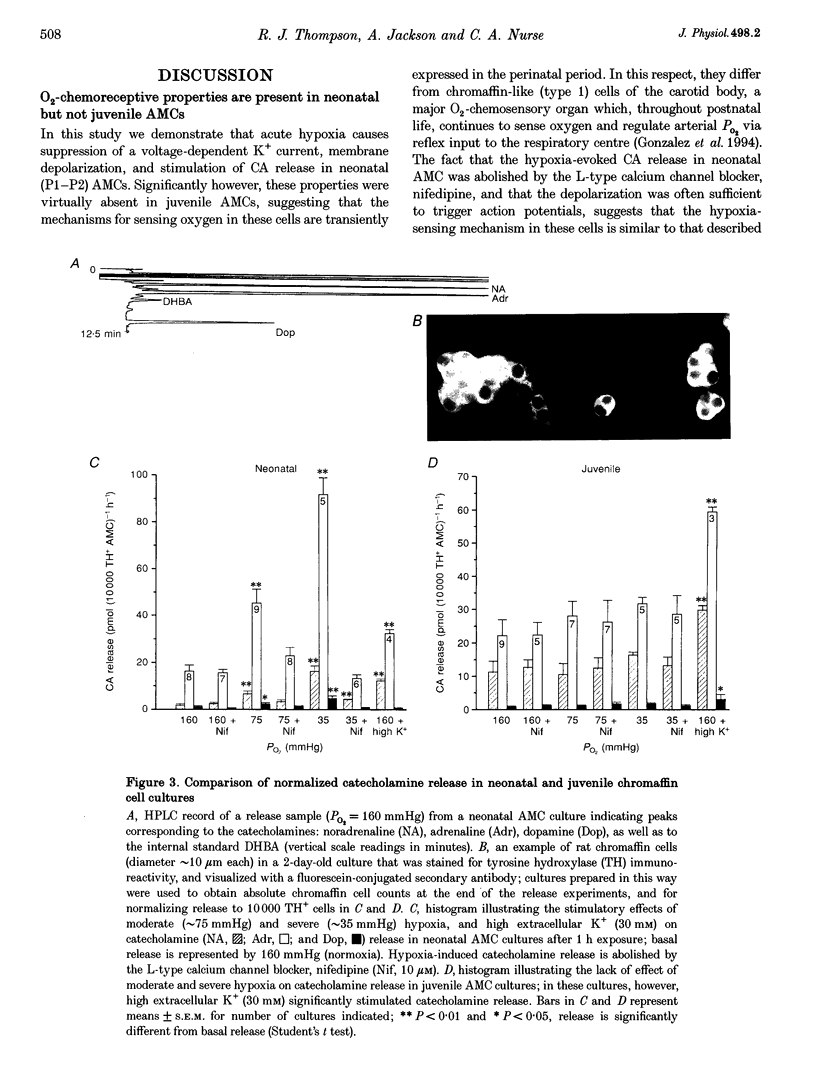
1. We investigated whether adrenomedullary chromaffin cells (AMCs) derived from neonatal (postnatal day (P) 1-P2) and juvenile (P13-P20) rats, and maintained in short-term culture (1-3 days), express O2-chemoreceptive properties. 2. In whole-cell recordings, the majority (approximately 70%; n = 47) of neonatal AMCs were sensitive to hypoxia. Under voltage clamp, acute hypoxia (PO2 approximately 40 mmHg) suppressed voltage-dependent K+ current by 25.1 +/- 3.4% (mean +/- S.E.M.; n = 22); under current clamp, acute hypoxia caused a membrane depolarization of 14.1 +/- 1.3 mV (n = 13) from a resting potential of -54.8 +/- 2.8 mV (n = 13), and this was often sufficient to trigger action potentials. 3. Exposure of neonatal AMC cultures to a moderate (PO2 approximately 75 mmHg) or severe (PO2 approximately 35 mmHg) hypoxia for 1 h caused a dose-dependent stimulation (approximately 3 or 6 times normoxia, respectively) of catecholamine (CA) release, mainly adrenaline, determined by HPLC. This induced CA release was abolished by the L-type calcium channel blocker, nifedipine (10 microM). 4. In contrast to the above results in neonates, hypoxia had no significant effects on voltage-dependent K+ current, membrane potential, or CA release in juvenile AMCs. 5. We conclude that rat adrenal chromaffin cells possess a developmentally regulated O2-sensing mechanism, similar to carotid body type I cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buckler K. J., Vaughan-Jones R. D. Effects of hypoxia on membrane potential and intracellular calcium in rat neonatal carotid body type I cells. J Physiol. 1994 May 1;476(3):423–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung C. Y. Fetal adrenal medulla catecholamine response to hypoxia-direct and neural components. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 2):R1340–R1346. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.258.6.R1340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpiano M. A., Hescheler J. Evidence for a PO2-sensitive K+ channel in the type-I cell of the rabbit carotid body. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80623-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Landis S. C., Patterson P. H. Environmental influences in the development of neural crest derivatives: glucocorticoids, growth factors, and chromaffin cell plasticity. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2119–2142. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dry K. L., Phillips J. H., Dart A. M. Catecholamine release from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells during anoxia or metabolic inhibition. Circ Res. 1991 Aug;69(2):466–474. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.2.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen M. R., Biscoe T. J. Relative mitochondrial membrane potential and [Ca2+]i in type I cells isolated from the rabbit carotid body. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:33–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganfornina M. D., López-Barneo J. Potassium channel types in arterial chemoreceptor cells and their selective modulation by oxygen. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Sep;100(3):401–426. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.3.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C., Almaraz L., Obeso A., Rigual R. Carotid body chemoreceptors: from natural stimuli to sensory discharges. Physiol Rev. 1994 Oct;74(4):829–898. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1994.74.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagercrantz H., Slotkin T. A. The "stress" of being born. Sci Am. 1986 Apr;254(4):100–107. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0486-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Barneo J., López-López J. R., Ureña J., González C. Chemotransduction in the carotid body: K+ current modulated by PO2 in type I chemoreceptor cells. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):580–582. doi: 10.1126/science.2456613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montoro R. J., Ureña J., Fernández-Chacón R., Alvarez de Toledo G., López-Barneo J. Oxygen sensing by ion channels and chemotransduction in single glomus cells. J Gen Physiol. 1996 Jan;107(1):133–143. doi: 10.1085/jgp.107.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely A., Lingle C. J. Two components of calcium-activated potassium current in rat adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992;453:97–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse C. A. Carbonic anhydrase and neuronal enzymes in cultured glomus cells of the carotid body of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1990 Jul;261(1):65–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00329439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peers C. Hypoxic suppression of K+ currents in type I carotid body cells: selective effect on the Ca2(+)-activated K+ current. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Nov 13;119(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90846-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler F. J., Slotkin T. A. Adrenomedullary function in the neonatal rat: responses to acute hypoxia. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler F. J., Slotkin T. A. Ontogeny of adrenomedullary responses to hypoxia and hypoglycemia: role of splanchnic innervation. Brain Res Bull. 1986 Jan;16(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(86)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotkin T. A., Seidler F. J. Adrenomedullary catecholamine release in the fetus and newborn: secretory mechanisms and their role in stress and survival. J Dev Physiol. 1988 Feb;10(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stea A., Nurse C. A. Whole-cell and perforated-patch recordings from O2-sensitive rat carotid body cells grown in short- and long-term culture. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Mar;418(1-2):93–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00370457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt C. N., Wright C., Bee D., Peers C. O2-sensitive K+ currents in carotid body chemoreceptor cells from normoxic and chronically hypoxic rats and their roles in hypoxic chemotransduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 3;92(1):295–299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.1.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngson C., Nurse C., Yeger H., Cutz E. Oxygen sensing in airway chemoreceptors. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):153–155. doi: 10.1038/365153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]