Abstract
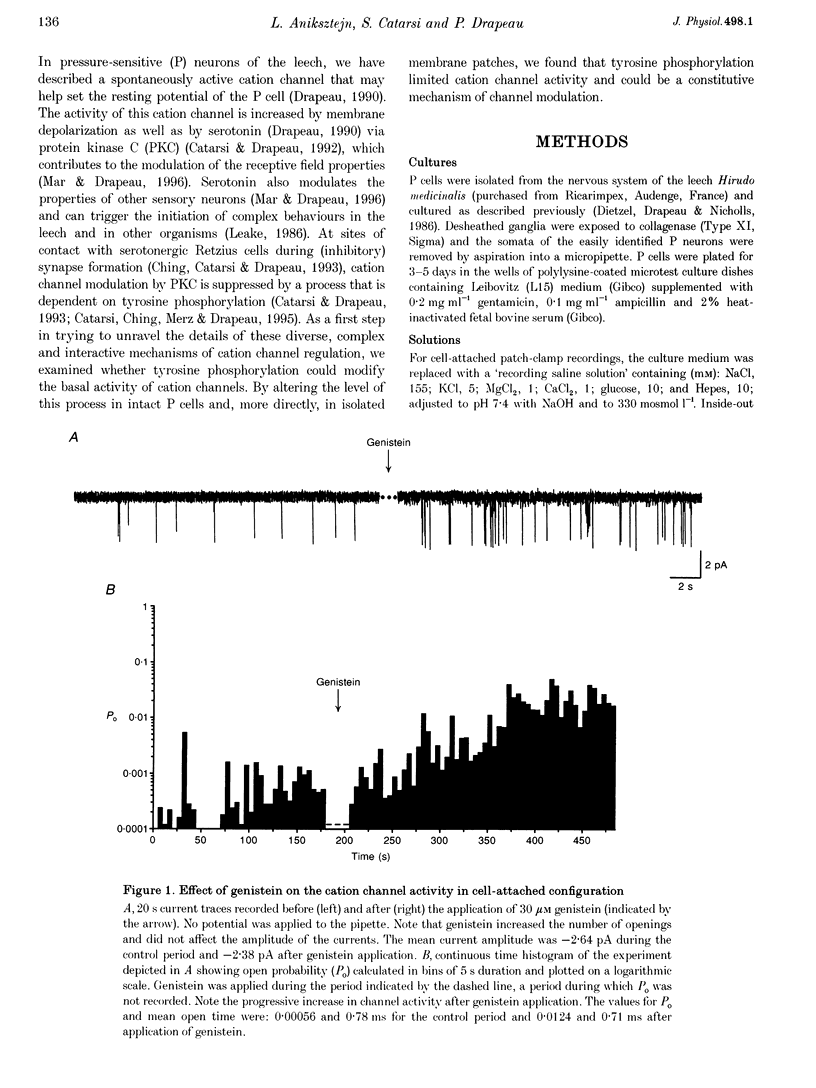
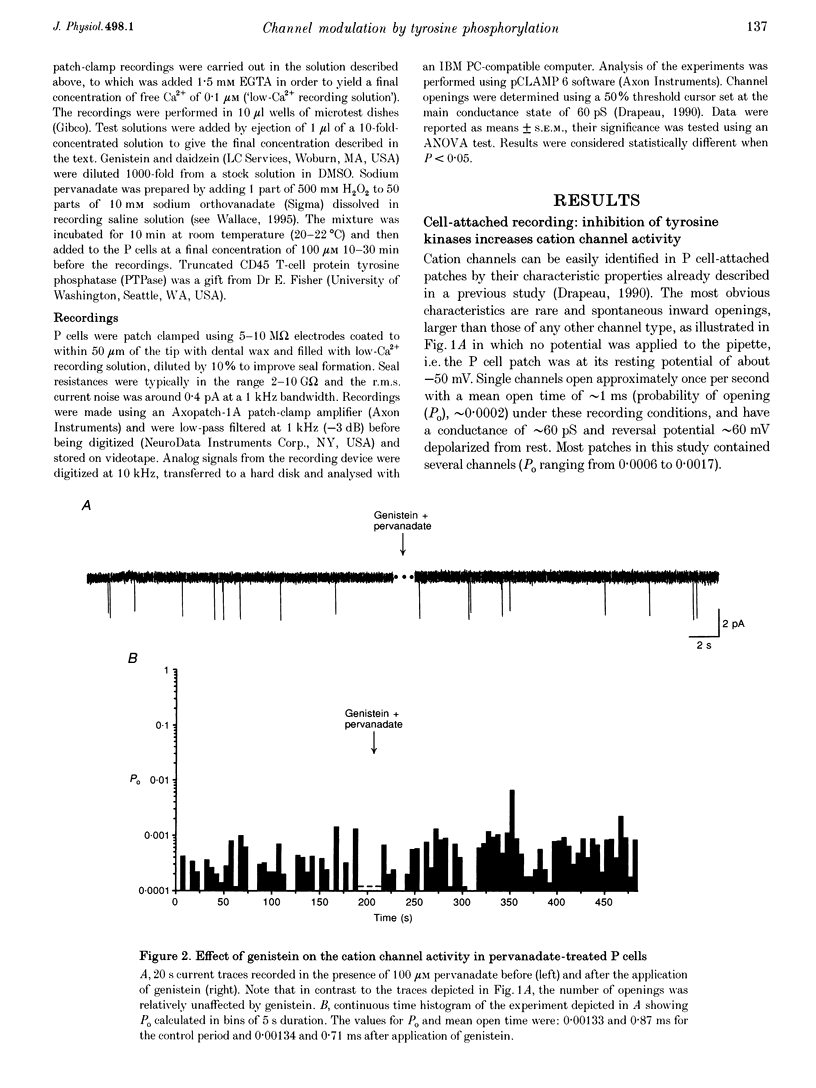
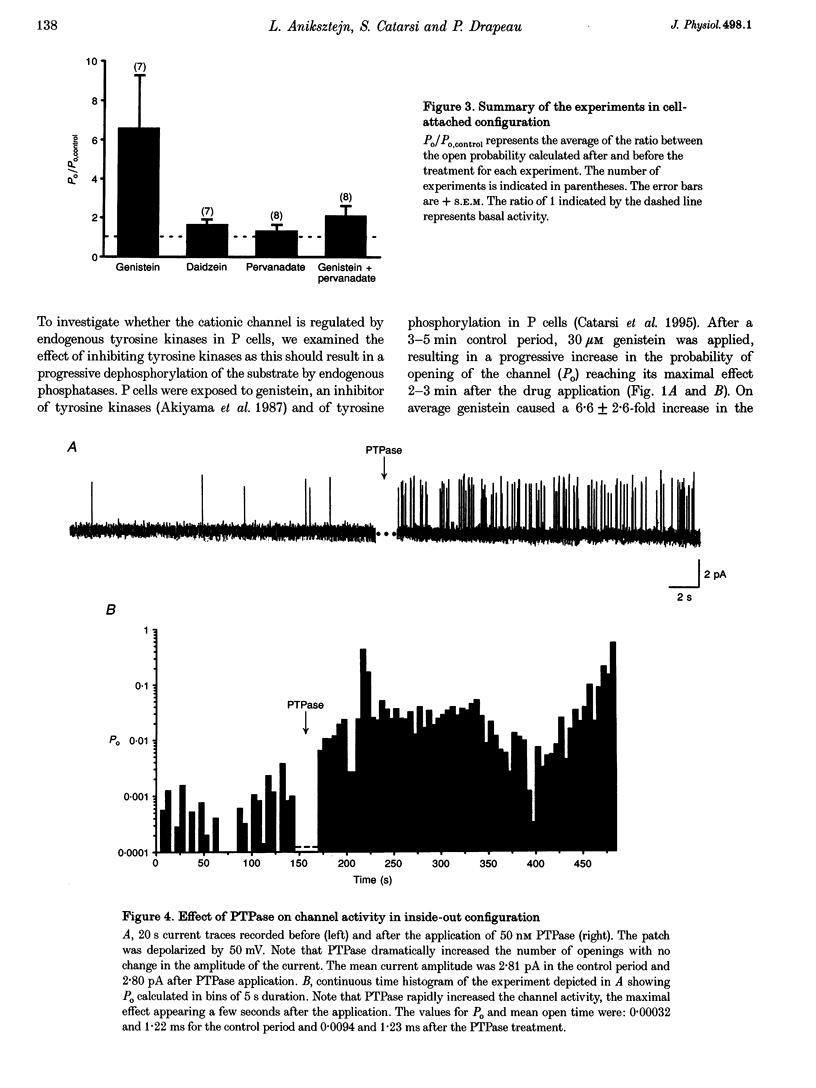
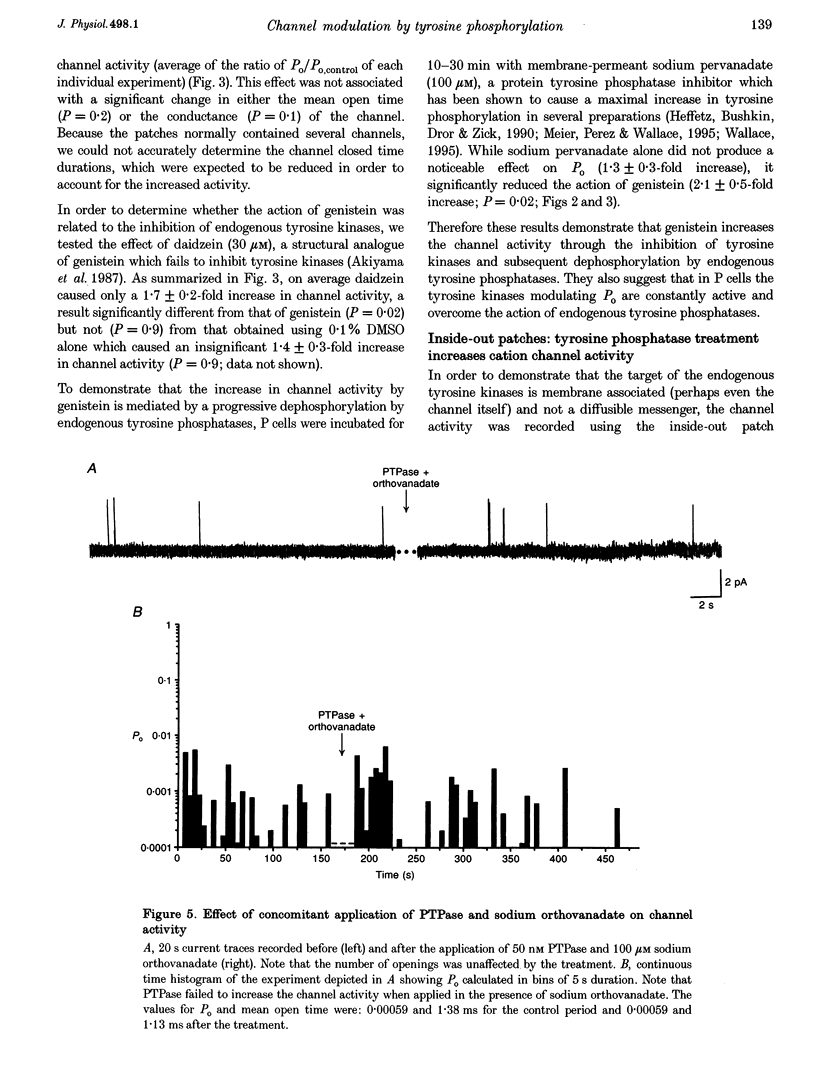
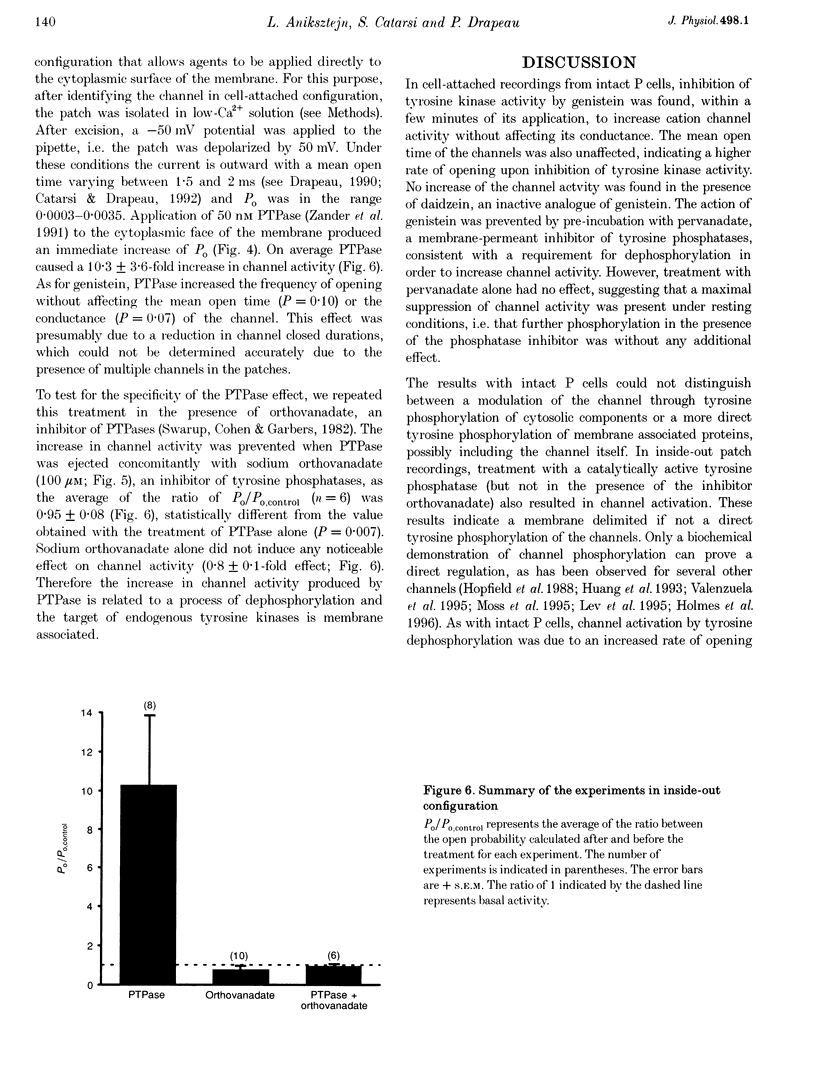
1. We have examined the effects of tyrosine phosphorylation on a spontaneously active cation channel that also participates in the modulation of pressure-sensitive (P) neurons in the leech. Cation channel activity in cell-attached or isolated, inside-out membrane patches from P cells in culture was monitored before and after treatments that altered the level of tyrosine phosphorylation. 2. In cell-attached recordings from intact P cells, bath application of genistein, an inhibitor of tyrosine kinases, resulted in a 6.6 +/- 2.6-fold increase in channel activity with no change in the mean open time or amplitude. Daidzein, an inactive form of genistein, was without effect. Addition of pervanadate, a membrane-permeant inhibitor of tyrosine phosphatases, had no effect on its own and blocked the effect of subsequent addition of genistein. 3. In inside-out P cell membrane patch recordings, exposure to a catalytically active fragment of a tyrosine phosphatase resulted in a 10.3 +/- 3.6-fold increase in channel activity with no change in the mean open time or amplitude. Orthovanadate had no effect on channel activity and, when added with the phosphatase, prevented the increase in activity. 4. Our results demonstrate that the basal activity of cation channels is increased by tyrosine dephosphorylation, suggesting a constitutive modulation of channel activity under resting conditions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Cotton P. C., Queral A. E., Barrett J. N., Nonner D., Keane R. W. Neurones express high levels of a structurally modified, activated form of pp60c-src. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):554–557. doi: 10.1038/316554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll M., Chalfie M. The mec-4 gene is a member of a family of Caenorhabditis elegans genes that can mutate to induce neuronal degeneration. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):588–593. doi: 10.1038/349588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E. H., Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: a diverse family of intracellular and transmembrane enzymes. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):401–406. doi: 10.1126/science.1650499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I., Rubin G. M. Making a difference: the role of cell-cell interactions in establishing separate identities for equivalent cells. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90470-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley M. R. Proto-oncogenes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1988 May;1(3):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffetz D., Bushkin I., Dror R., Zick Y. The insulinomimetic agents H2O2 and vanadate stimulate protein tyrosine phosphorylation in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2896–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes T. C., Fadool D. A., Levitan I. B. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the Kv1.3 potassium channel. J Neurosci. 1996 Mar 1;16(5):1581–1590. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-05-01581.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. F., Tank D. W., Greengard P., Huganir R. L. Functional modulation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by tyrosine phosphorylation. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):677–680. doi: 10.1038/336677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon I. S., Apperson M. L., Kennedy M. B. The major tyrosine-phosphorylated protein in the postsynaptic density fraction is N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3954–3958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss S. J., Gorrie G. H., Amato A., Smart T. G. Modulation of GABAA receptors by tyrosine phosphorylation. Nature. 1995 Sep 28;377(6547):344–348. doi: 10.1038/377344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Armass S., Merz D. C., Drapeau P. Distinct receptors, second messengers and conductances underlying the dual responses to serotonin in an identified leech neurone. J Exp Biol. 1991 Jan;155:531–547. doi: 10.1242/jeb.155.1.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A. Channel regulation. Ion channel control by tyrosine phosphorylation. Curr Biol. 1994 Mar 1;4(3):242–245. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela C. F., Machu T. K., McKernan R. M., Whiting P., VanRenterghem B. B., McManaman J. L., Brozowski S. J., Smith G. B., Olsen R. W., Harris R. A. Tyrosine kinase phosphorylation of GABAA receptors. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1995 Jul;31(1-2):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00048-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. G. Regulation of the interaction of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors with the cytoskeleton by agrin-activated protein tyrosine kinase. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1121–1129. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. T., Salter M. W. Regulation of NMDA receptors by tyrosine kinases and phosphatases. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):233–235. doi: 10.1038/369233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. F., Kaczmarek L. K. Mode-switching of a voltage-gated cation channel is mediated by a protein kinase A-regulated tyrosine phosphatase. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):433–438. doi: 10.1038/366433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zander N. F., Lorenzen J. A., Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Daum G., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Purification and characterization of a human recombinant T-cell protein-tyrosine-phosphatase from a baculovirus expression system. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6964–6970. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


