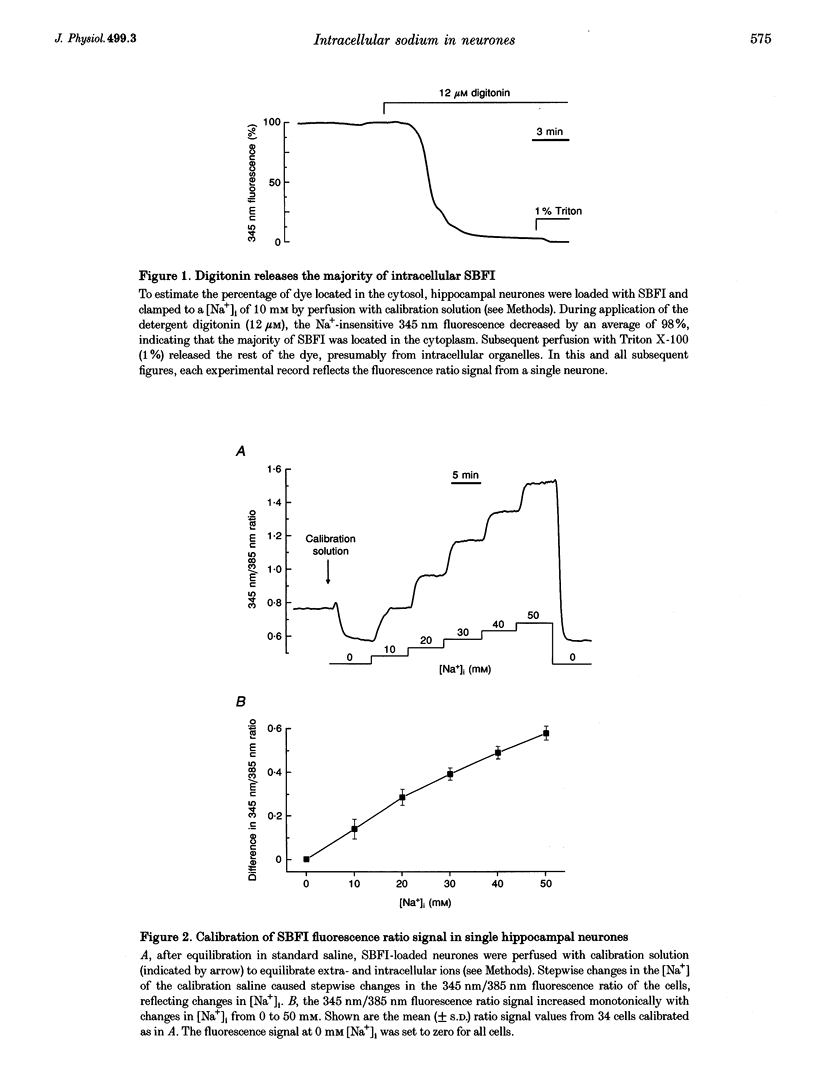
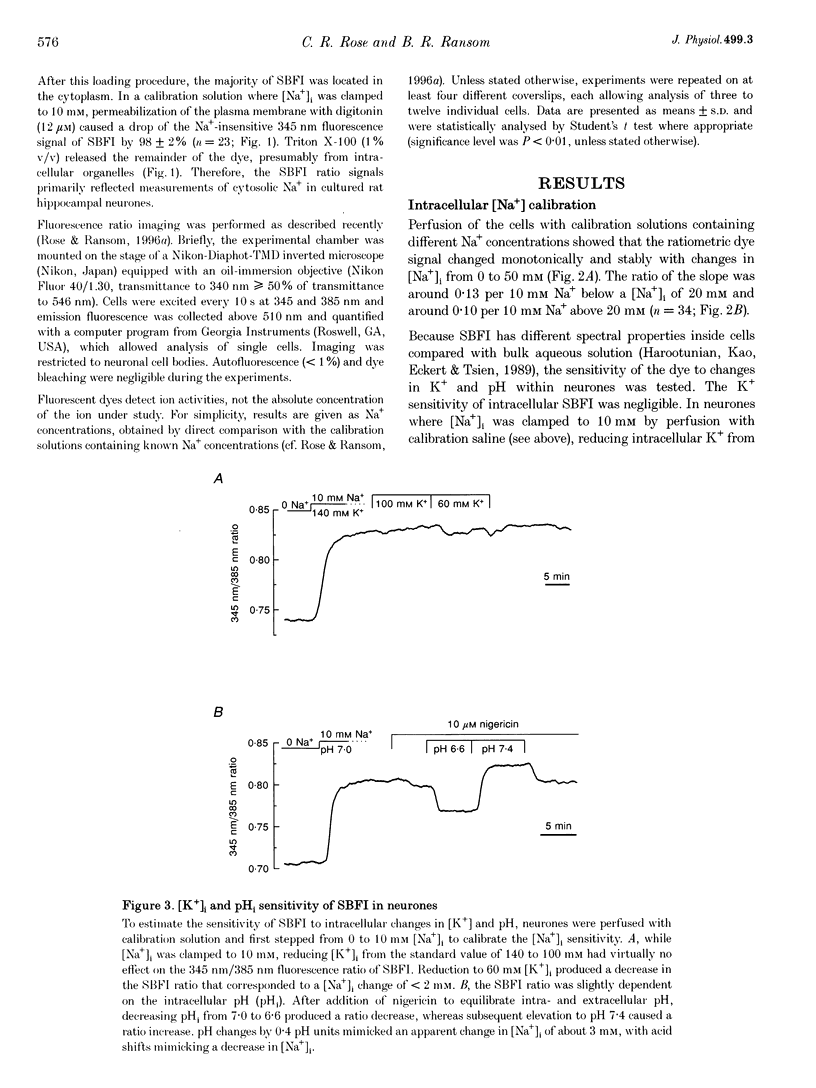
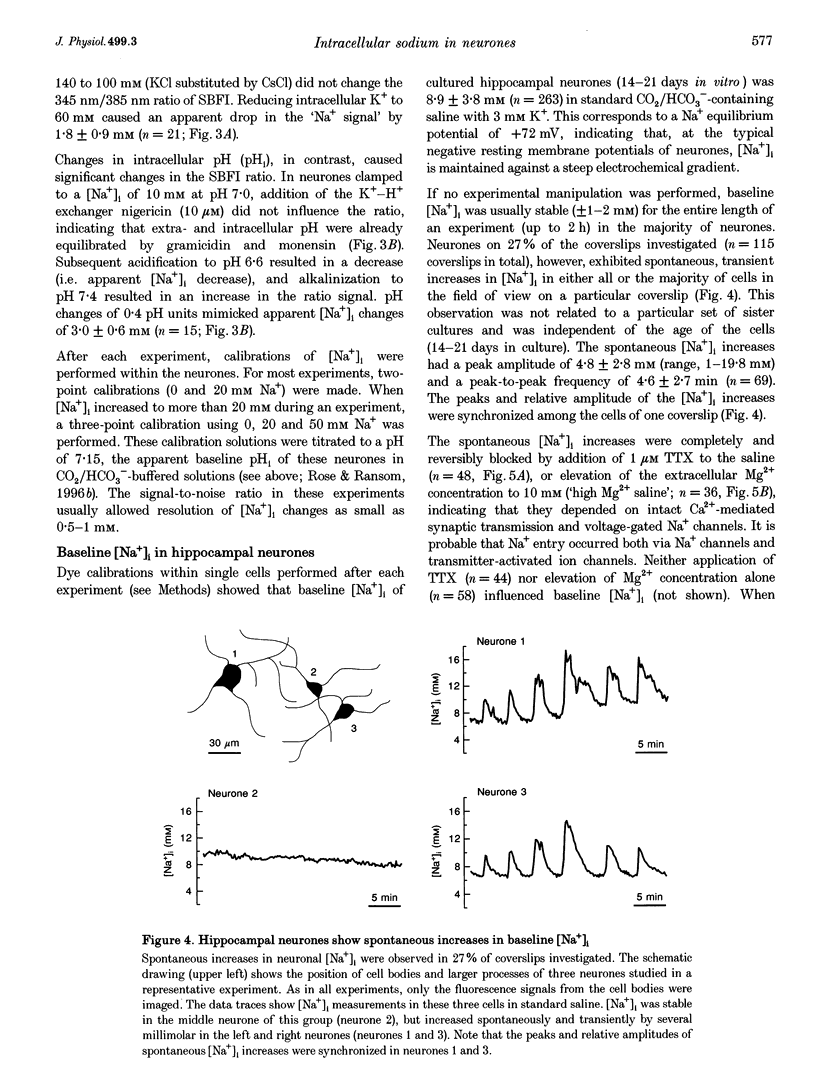
Abstract
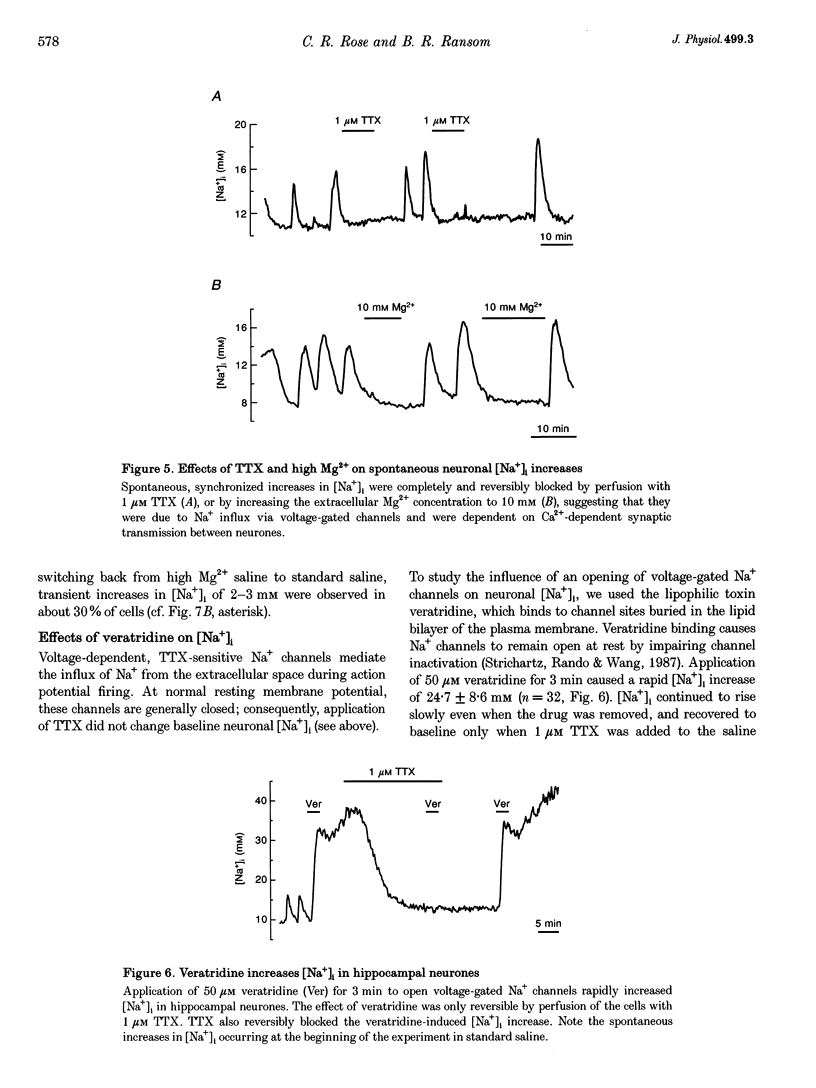
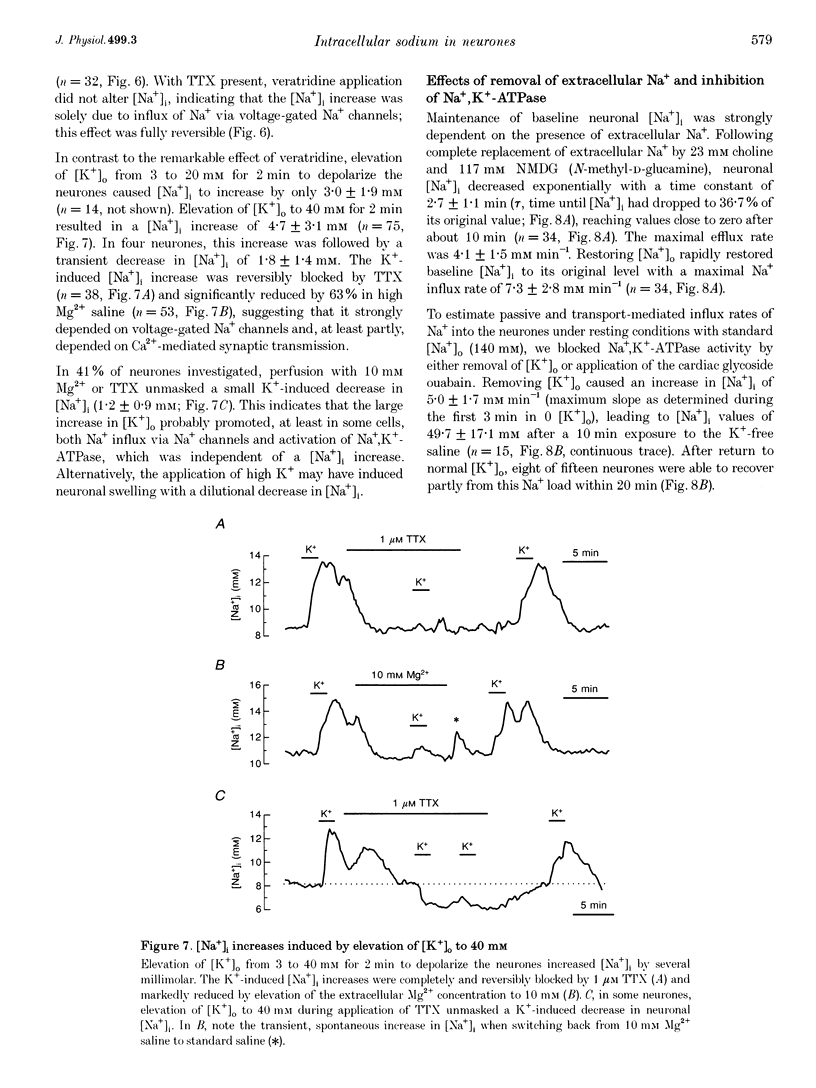
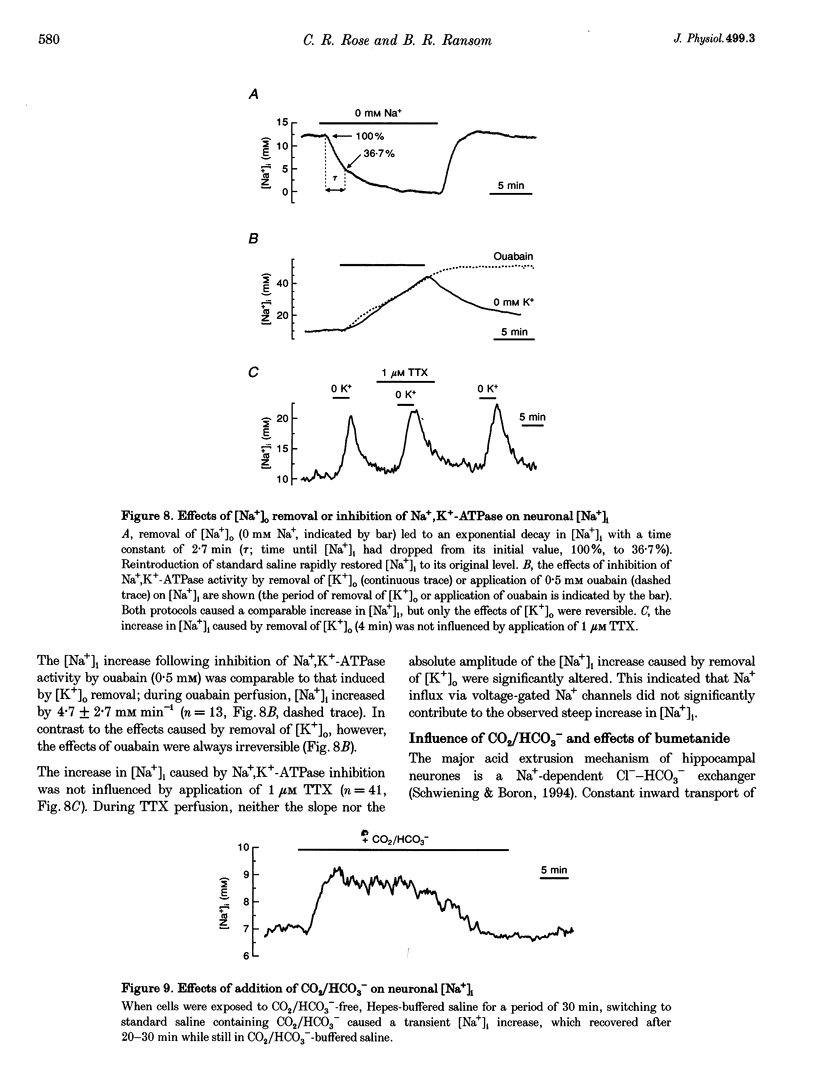
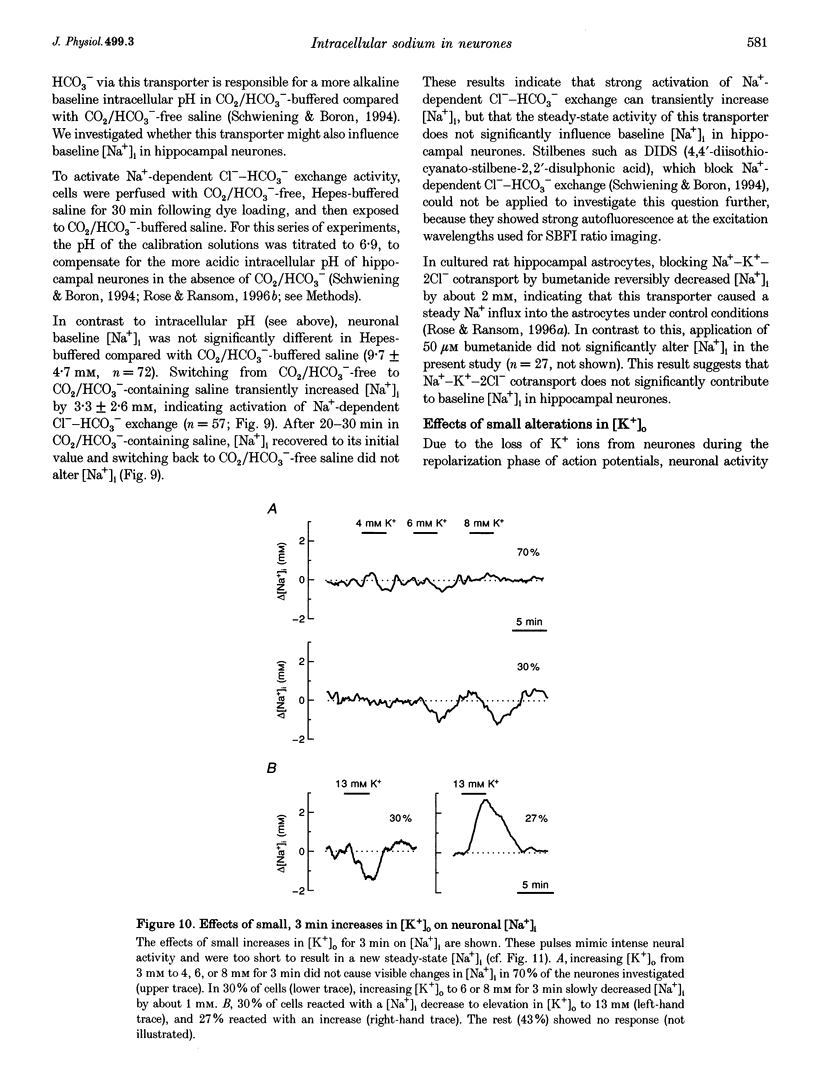
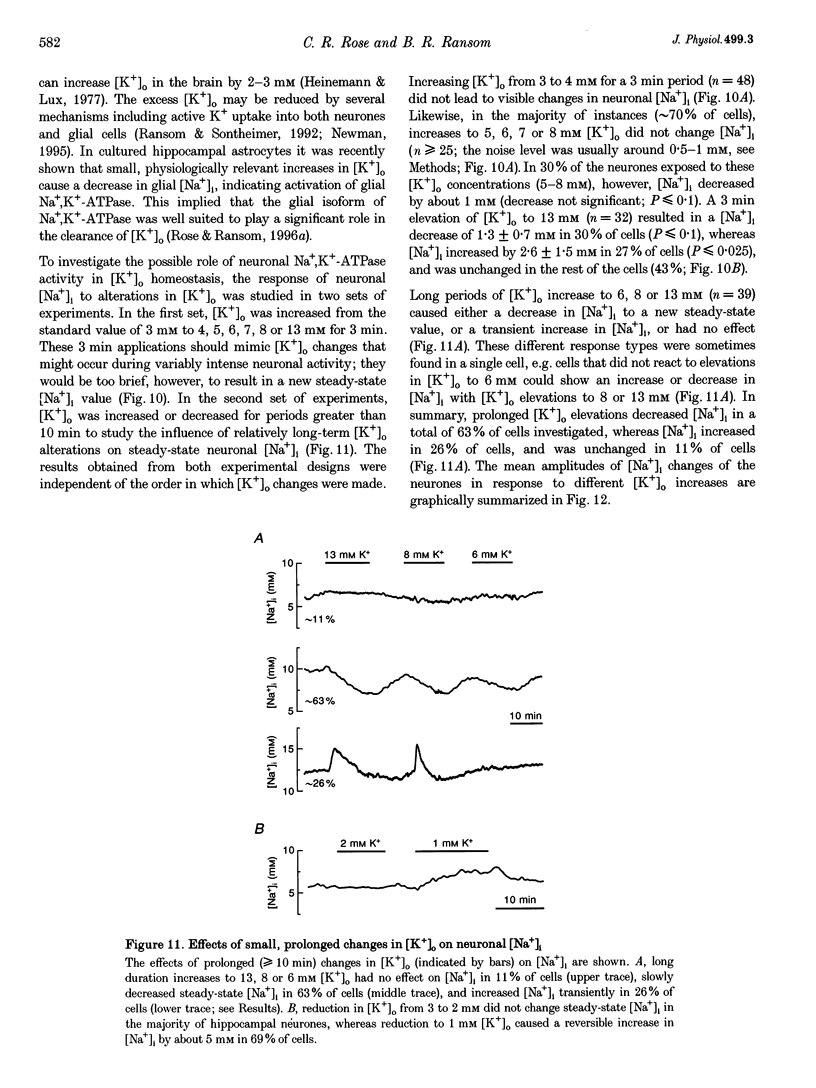
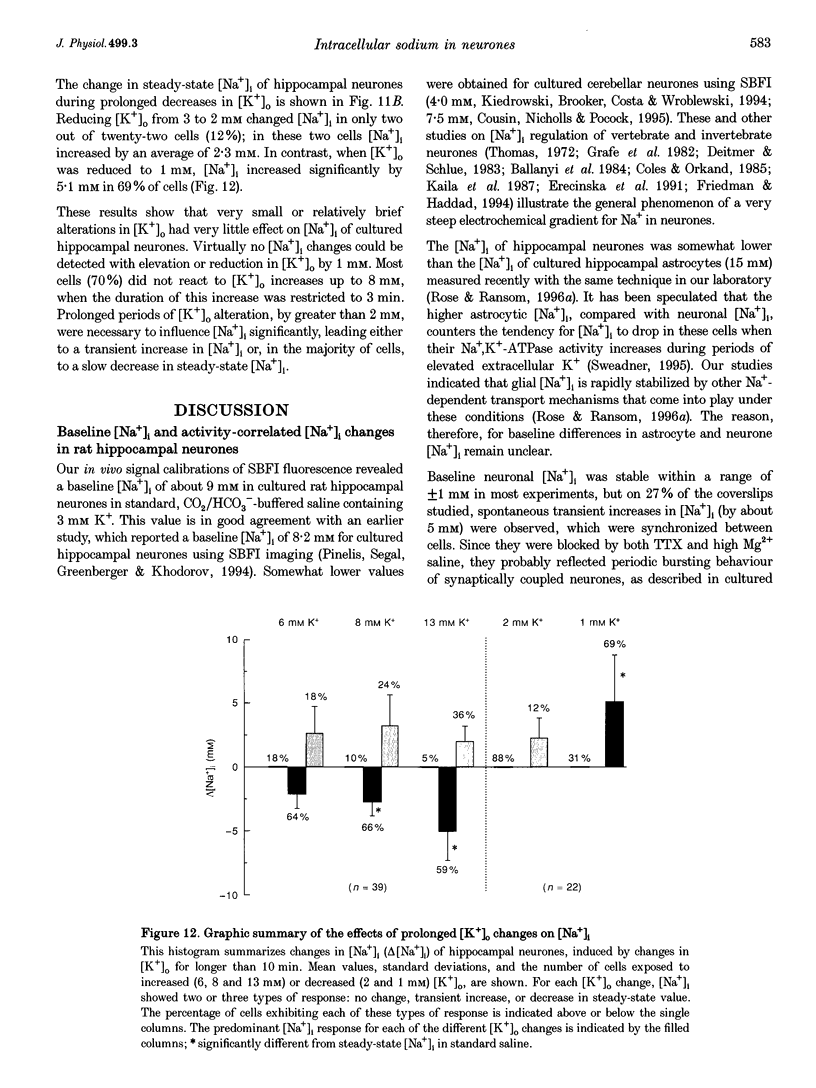
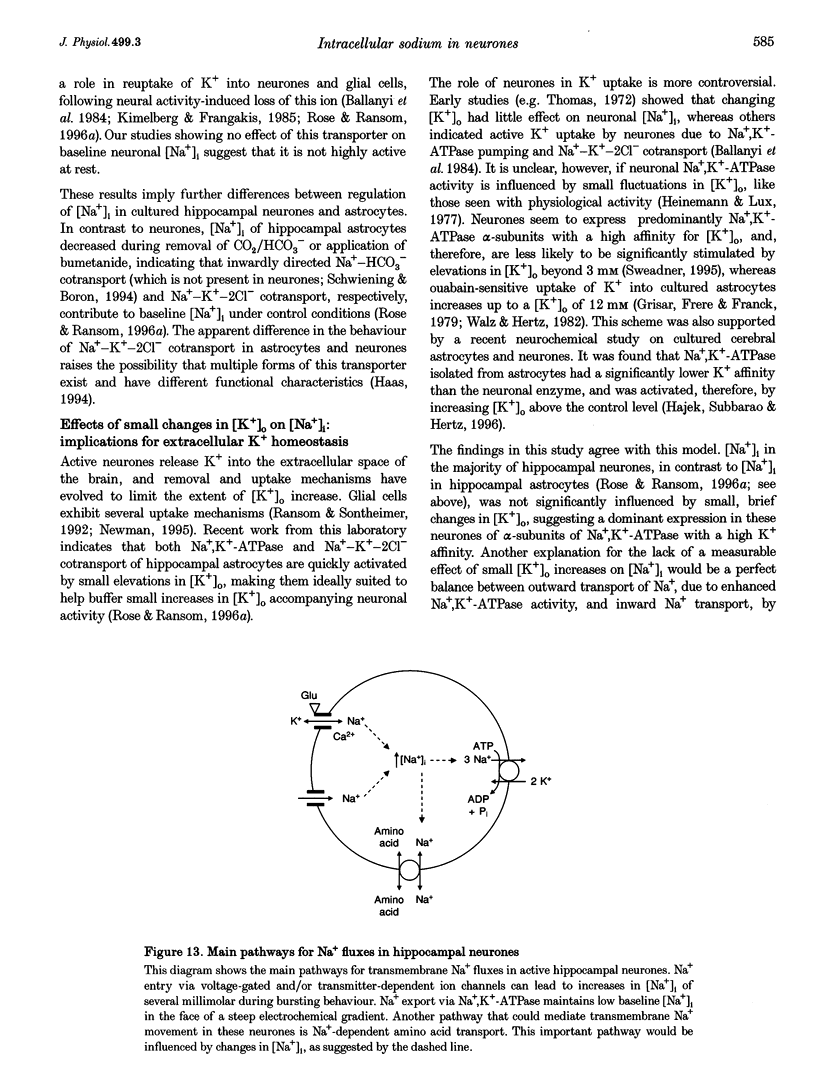
1. We studied regulation of intracellular Na+ concentration ([Na+]i) in cultured rat hippocampal neurones using fluorescence ratio imaging of the Na+ indicator dye SBFI (sodium-binding benzofuran isophthalate). 2. In standard CO2/HCO3(-)-buffered saline with 3 mM K+, neurones had a baseline [Na+]i of 8.9 +/- 3.8 mM (mean +/- S.D.). Spontaneous, transient [Na+]i increases of 5 mM were observed in neurones on 27% of the coverslips studied. These [Na+]i increases were often synchronized among nearby neurones and were blocked reversibly by 1 microM tetrodotoxin (TTX) or by saline containing 10 mM Mg2+, suggesting that they were caused by periodic bursting activity of synaptically coupled cells. Opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels by application of 50 microM veratridine caused a TTX-sensitive [Na+]i increase of 25 mM. 3. Removing extracellular Na+ caused an exponential decline in [Na+]i to values close to zero within 10 min. Inhibition of Na+,K(+)-ATPase by removal of extracellular K+ or ouabain application evoked a [Na+]i increase of 5 mM min-1. Baseline [Na+]i was similar in the presence or absence of CO2/HCO3-; switching from CO2/HCO3(-)-free to CO2/HCO3(-)-buffered saline, however, increased [Na+]i transiently by 3 mM, indicating activation of Na(+)-dependent Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange. Inhibition of Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl- cotransport by bumetanide had no effect on [Na+]i. 4. Brief, small changes in extracellular K+ concentration ([K+]o) influenced neuronal [Na+]i only weakly. Virtually no change in [Na+]i was observed with elevation or reduction of [K+]o by 1 mM. Only 30% of cells reacted to 3 min [K+]o elevations of up to 5 mM. In contrast, long [K+]o alterations (> or = 10 min) to 6 mM or greater slowly changed steady-state [Na+]i in the majority of cells. 5. Our results indicate several differences between [Na+]i regulation in cultured hippocampal neurones and astrocytes. Baseline [Na+]i is lower in neurones compared with astrocytes and is mainly determined by Na+,K(+)-ATPase, whereas Na(+)-dependent Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange, Na(+)-HCO3- cotransport or Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl- cotransport do not play a significant role. In contrast to glial cells, [Na+]i of neurones changes only weakly with small alterations in bath [K+]o, suggesting that activity-induced [K+]o changes in the brain might not significantly influence neuronal Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballanyi K., Grafe P., Reddy M. M., ten Bruggencate G. Different types of potassium transport linked to carbachol and gamma-aminobutyric acid actions in rat sympathetic neurons. Neuroscience. 1984 Jul;12(3):917–927. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Calcium transport and buffering in neurons. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):438–443. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesler M. The regulation and modulation of pH in the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;34(5):401–427. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90034-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles J. A., Orkand R. K. Changes in sodium activity during light stimulation in photoreceptors, glia and extracellular space in drone retina. J Physiol. 1985 May;362:415–435. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousin M. A., Nicholls D. G., Pocock J. M. Modulation of ion gradients and glutamate release in cultured cerebellar granule cells by ouabain. J Neurochem. 1995 May;64(5):2097–2104. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64052097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Schlue W. R. Intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ in leech Retzius neurones during inhibition of the Na+-K+ pump. Pflugers Arch. 1983 May;397(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00584357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erecińska M., Dagani F., Nelson D., Deas J., Silver I. A. Relations between intracellular ions and energy metabolism: a study with monensin in synaptosomes, neurons, and C6 glioma cells. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2410–2421. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02410.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. E., Haddad G. G. Anoxia induces an increase in intracellular sodium in rat central neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1994 Nov 14;663(2):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimm H., Ficker E., Heinemann U. Electrophysiological properties of neurones in cultures from postnatal rat dentate gyrus. Exp Brain Res. 1996;107(3):367–381. doi: 10.1007/BF00230419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafe P., Rimpel J., Reddy M. M., ten Bruggencate G. Changes of intracellular sodium and potassium ion concentrations in frog spinal motoneurons induced by repetitive synaptic stimulation. Neuroscience. 1982;7(12):3213–3220. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisar T., Frere J. M., Franck G. Effect of K+ ions on kinetic properties of the (Na+, K+)-ATPase (EC 3.6.1.3) of bulk isolated glial cells, perikarya and synaptosomes from rabbit brain cortex. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 6;165(1):87–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Active transport of cations in giant axons from Sepia and Loligo. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):28–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. The Na-K-Cl cotransporters. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 1):C869–C885. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.4.C869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harootunian A. T., Kao J. P., Eckert B. K., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescence ratio imaging of cytosolic free Na+ in individual fibroblasts and lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19458–19467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Lux H. D. Ceiling of stimulus induced rises in extracellular potassium concentration in the cerebral cortex of cat. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 21;120(2):231–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90903-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe D. B., Johnston D., Lasser-Ross N., Lisman J. E., Miyakawa H., Ross W. N. The spread of Na+ spikes determines the pattern of dendritic Ca2+ entry into hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):244–246. doi: 10.1038/357244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaila K., Rydqvist B., Swerup C., Voipio J. Stimulation-induced changes in the intracellular sodium activity of the crayfish stretch receptor. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Feb 10;74(1):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamioka H., Maeda E., Jimbo Y., Robinson H. P., Kawana A. Spontaneous periodic synchronized bursting during formation of mature patterns of connections in cortical cultures. Neurosci Lett. 1996 Mar 15;206(2-3):109–112. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(96)12448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiedrowski L., Brooker G., Costa E., Wroblewski J. T. Glutamate impairs neuronal calcium extrusion while reducing sodium gradient. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Frangakis M. V. Furosemide- and bumetanide-sensitive ion transport and volume control in primary astrocyte cultures from rat brain. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 30;361(1-2):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasser-Ross N., Ross W. N. Imaging voltage and synaptically activated sodium transients in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Jan 22;247(1318):35–39. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minta A., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescent indicators for cytosolic sodium. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19449–19457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D., Attwell D. The release and uptake of excitatory amino acids. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Nov;11(11):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90129-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Barker J. L., Nelson P. G. Two mechanisms for poststimulus hyperpolarisations in cultured mammalian neurones. Nature. 1975 Jul 31;256(5516):424–425. doi: 10.1038/256424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Sontheimer H. The neurophysiology of glial cells. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1992 Apr;9(2):224–251. doi: 10.1097/00004691-199204010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausche G., Igelmund P., Heinemann U. Effects of changes in extracellular potassium, magnesium and calcium concentration on synaptic transmission in area CA1 and the dentate gyrus of rat hippocampal slices. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Feb;415(5):588–593. doi: 10.1007/BF02583510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose C. R., Ransom B. R. Mechanisms of H+ and Na+ changes induced by glutamate, kainate, and D-aspartate in rat hippocampal astrocytes. J Neurosci. 1996 Sep 1;16(17):5393–5404. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-17-05393.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger A. R., Cowan W. M., Swanson L. W. The time of origin of neurons in Ammon's horn and the associated retrohippocampal fields. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1978 Aug 18;154(2):153–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00304660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwiening C. J., Boron W. F. Regulation of intracellular pH in pyramidal neurones from the rat hippocampus by Na(+)-dependent Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 15;475(1):59–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strichartz G., Rando T., Wang G. K. An integrated view of the molecular toxinology of sodium channel gating in excitable cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:237–267. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Intracellular sodium activity and the sodium pump in snail neurones. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(1):55–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. The role of bicarbonate, chloride and sodium ions in the regulation of intracellular pH in snail neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):317–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz W., Hertz L. Ouabain-sensitive and ouabain-resistant net uptake of potassium into astrocytes and neurons in primary cultures. J Neurochem. 1982 Jul;39(1):70–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb04702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. O., Chernjavsky A., Smith S. J., Shatz C. J. Early functional neural networks in the developing retina. Nature. 1995 Apr 20;374(6524):716–718. doi: 10.1038/374716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]