Abstract
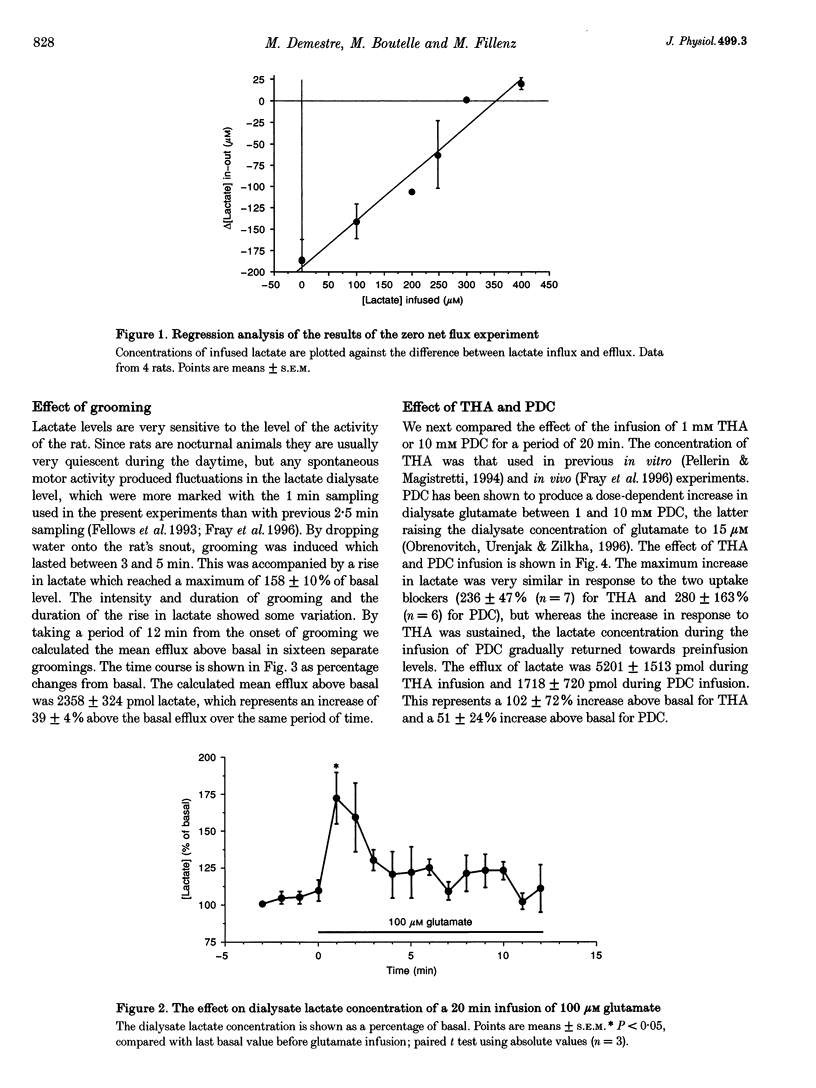
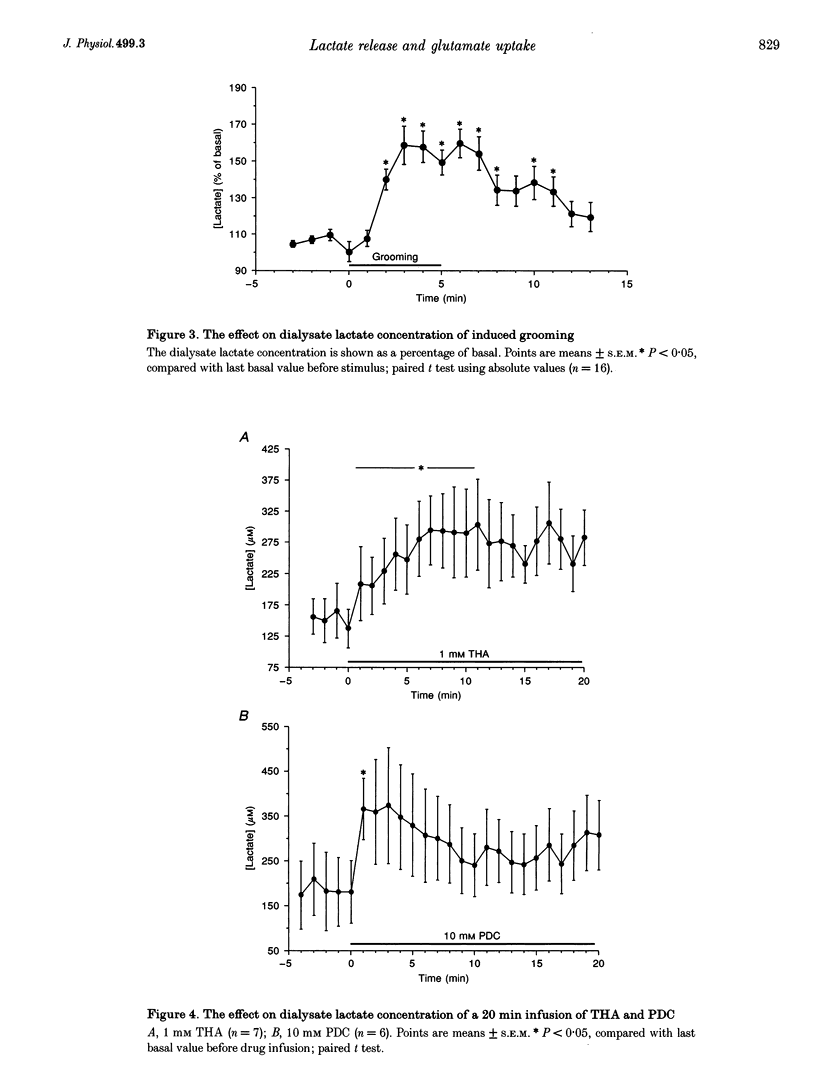
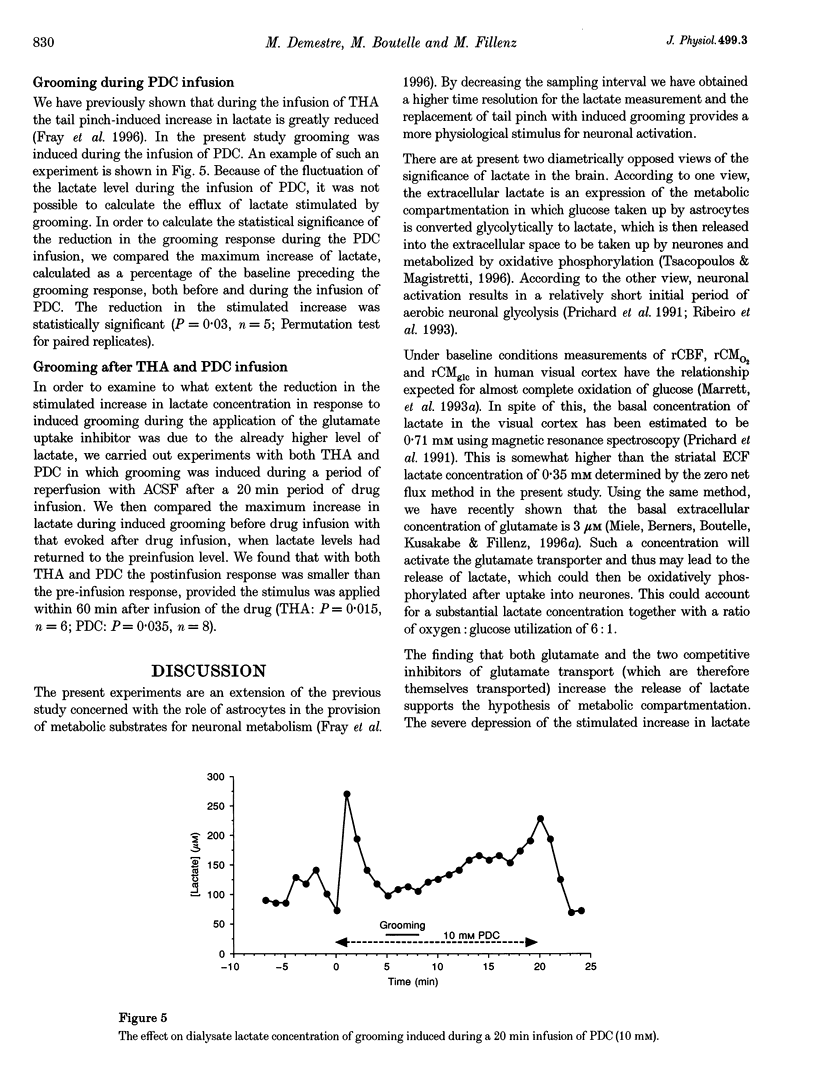
1. Physiological stimulation of neuronal activity induces an increase in extracellular lactate. Experiments were designed to determine the role of the reuptake of neuronally released glutamate in lactate delivery to the extracellular compartment. 2. In vivo microdialysis was used in freely moving rats. The lactate concentration in striatal dialysate was assayed using an enzyme-based on-line assay at 1 min intervals. Drugs were given locally through the dialysis probe. 3. The extracellular concentration of lactate, determined using the zero net flux method, was 346 +/- 21 microM. 4. Induced grooming caused a maximal increase in lactate concentration in striatal dialysate of 58 +/- 10%. 5. Administration of 100 microM glutamate caused a transient increase in dialysate lactate concentration of 72 +/- 17%. 6. A 20 min infusion of the glutamate uptake blockers beta-D,L-threohydroxyaspartate (THA) or pirrolidine-2-4-dicarboxylate (PDC) produced an increase in basal lactate, which was sustained in response to THA and transient in response to PDC. 7. Grooming induced during the infusion of PDC produced no significant increase in lactate. 8. Grooming induced after the infusion of the glutamate uptake blockers gave rise to a reduced increase in lactate. 9. These results support the hypothesis that stimulated release of lactate is dependent on the uptake of glutamate.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron J. C., Lebrun-Grandie P., Collard P., Crouzel C., Mestelan G., Bousser M. G. Noninvasive measurement of blood flow, oxygen consumption, and glucose utilization in the same brain regions in man by positron emission tomography: concise communication. J Nucl Med. 1982 May;23(5):391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berners M. O., Boutelle M. G., Fillenz M. On-line measurement of brain glutamate with an enzyme/polymer-coated tubular electrode. Anal Chem. 1994 Jul 1;66(13):2017–2021. doi: 10.1021/ac00085a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutelle M. G., Fellows L. K., Cook C. Enzyme packed bed system for the on-line measurement of glucose, glutamate, and lactate in brain microdialysate. Anal Chem. 1992 Sep 1;64(17):1790–1794. doi: 10.1021/ac00041a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutelle M. G., Fillenz M. Clinical microdialysis: the role of on-line measurement and quantitative microdialysis. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 1996;67:13–20. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6894-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dringen R., Wiesinger H., Hamprecht B. Uptake of L-lactate by cultured rat brain neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Nov 26;163(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellows L. K., Boutelle M. G., Fillenz M. Physiological stimulation increases nonoxidative glucose metabolism in the brain of the freely moving rat. J Neurochem. 1993 Apr;60(4):1258–1263. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray A. E., Forsyth R. J., Boutelle M. G., Fillenz M. The mechanisms controlling physiologically stimulated changes in rat brain glucose and lactate: a microdialysis study. J Physiol. 1996 Oct 1;496(Pt 1):49–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada M., Sawa T., Okuda C., Matsuda T., Tanaka Y. Effects of glucose load on brain extracellular lactate concentration in conscious rats using a microdialysis technique. Horm Metab Res. 1993 Nov;25(11):560–563. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope P. L., Cady E. B., Chu A., Delpy D. T., Gardiner R. M., Reynolds E. O. Brain metabolism and intracellular pH during ischaemia and hypoxia: an in vivo 31P and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance study in the lamb. J Neurochem. 1987 Jul;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb03396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope P. L., Cady E. B., Delpy D. T., Ives N. K., Gardiner R. M., Reynolds E. O. Brain metabolism and intracellular pH during ischaemia: effects of systemic glucose and bicarbonate administration studied by 31P and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo in the lamb. J Neurochem. 1988 May;50(5):1394–1402. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi Y., Benz A. M., Zorumski C. F., Olney J. W. Effects of lactate and pyruvate on glucose deprivation in rat hippocampal slices. Neuroreport. 1994 Jan 31;5(5):617–620. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199401000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS W. T. Glutamic-aspartic transaminase. VI. The reaction with certain beta-substituted aspartic acid analogues. J Biol Chem. 1961 Apr;236:1121–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson I., Sandberg M., Hamberger A. Mass transfer in brain dialysis devices--a new method for the estimation of extracellular amino acids concentration. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Nov-Dec;15(3):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhr W. G., Korf J. Extracellular lactic acid as an indicator of brain metabolism: continuous on-line measurement in conscious, freely moving rats with intrastriatal dialysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988 Feb;8(1):130–137. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1988.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhr W. G., van den Berg C. J., Korf J. In vivo identification and quantitative evaluation of carrier-mediated transport of lactate at the cellular level in the striatum of conscious, freely moving rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988 Dec;8(6):848–856. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1988.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear J. L., Kasliwal R. K. Autoradiographic measurement of cerebral lactate transport rate constants in normal and activated conditions. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 Jul;11(4):576–580. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry J. P., Fillenz M. Evidence for uncoupling of oxygen and glucose utilization during neuronal activation in rat striatum. J Physiol. 1997 Jan 15;498(Pt 2):497–501. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp021875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth P., Jansson P. A., Smith U. A microdialysis method allowing characterization of intercellular water space in humans. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):E228–E231. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.2.E228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna M. C., Tildon J. T., Stevenson J. H., Boatright R., Huang S. Regulation of energy metabolism in synaptic terminals and cultured rat brain astrocytes: differences revealed using aminooxyacetate. Dev Neurosci. 1993;15(3-5):320–329. doi: 10.1159/000111351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna M. C., Tildon J. T., Stevenson J. H., Hopkins I. B. Energy metabolism in cortical synaptic terminals from weanling and mature rat brain: evidence for multiple compartments of tricarboxylic acid cycle activity. Dev Neurosci. 1994;16(5-6):291–300. doi: 10.1159/000112122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miele M., Berners M., Boutelle M. G., Kusakabe H., Fillenz M. The determination of the extracellular concentration of brain glutamate using quantitative microdialysis. Brain Res. 1996 Jan 22;707(1):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)01371-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miele M., Boutelle M. G., Fillenz M. The source of physiologically stimulated glutamate efflux from the striatum of conscious rats. J Physiol. 1996 Dec 15;497(Pt 3):745–751. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison P. F., Bungay P. M., Hsiao J. K., Ball B. A., Mefford I. N., Dedrick R. L. Quantitative microdialysis: analysis of transients and application to pharmacokinetics in brain. J Neurochem. 1991 Jul;57(1):103–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. B., Griffiths P. H. Guidelines on the recognition of pain, distress and discomfort in experimental animals and an hypothesis for assessment. Vet Rec. 1985 Apr 20;116(16):431–436. doi: 10.1136/vr.116.16.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrenovitch T. P., Urenjak J., Zilkha E. Evidence disputing the link between seizure activity and high extracellular glutamate. J Neurochem. 1996 Jun;66(6):2446–2454. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.66062446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Connor J. D., Crawford I. L. Permeability changes in the blood-brain barrier: causes and consequences. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1975 Jan;3(2):159–199. doi: 10.3109/10408447509079857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellerin L., Magistretti P. J. Glutamate uptake into astrocytes stimulates aerobic glycolysis: a mechanism coupling neuronal activity to glucose utilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10625–10629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard J., Rothman D., Novotny E., Petroff O., Kuwabara T., Avison M., Howseman A., Hanstock C., Shulman R. Lactate rise detected by 1H NMR in human visual cortex during physiologic stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5829–5831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr A., West C. A., Rigor B. M. Lactate-supported synaptic function in the rat hippocampal slice preparation. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1326–1328. doi: 10.1126/science.3375817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz R. J., Roland P. E. Vibratory stimulation increases and decreases the regional cerebral blood flow and oxidative metabolism: a positron emission tomography (PET) study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1992 Jul;86(1):60–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1992.tb08055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsacopoulos M., Magistretti P. J. Metabolic coupling between glia and neurons. J Neurosci. 1996 Feb 1;16(3):877–885. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-03-00877.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer P., Damsma G., Fibiger H. C., Timmerman W., de Vries J. B., Westerink B. H. Dopaminergic-cholinergic interactions in the striatum: the critical significance of calcium concentrations in brain microdialysis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;342(5):528–534. doi: 10.1007/BF00169041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


