Abstract
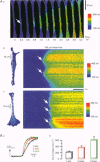
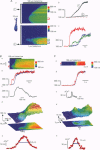
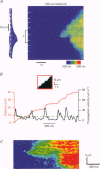
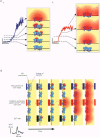
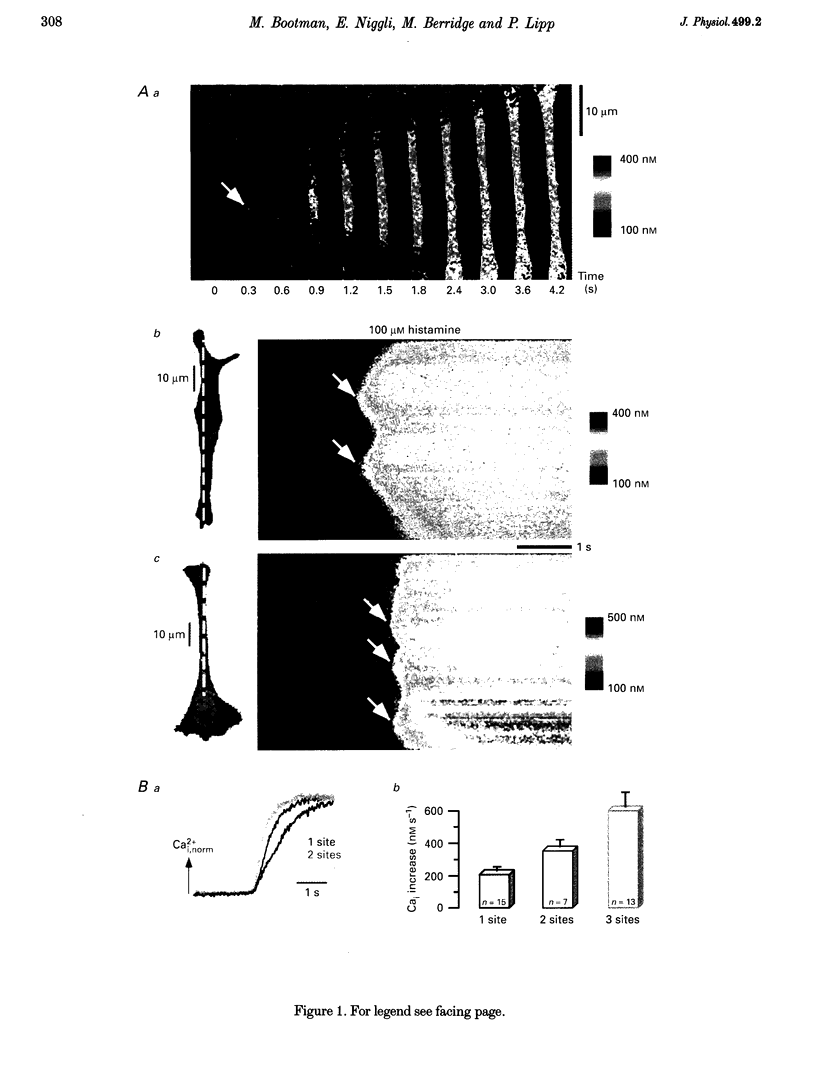
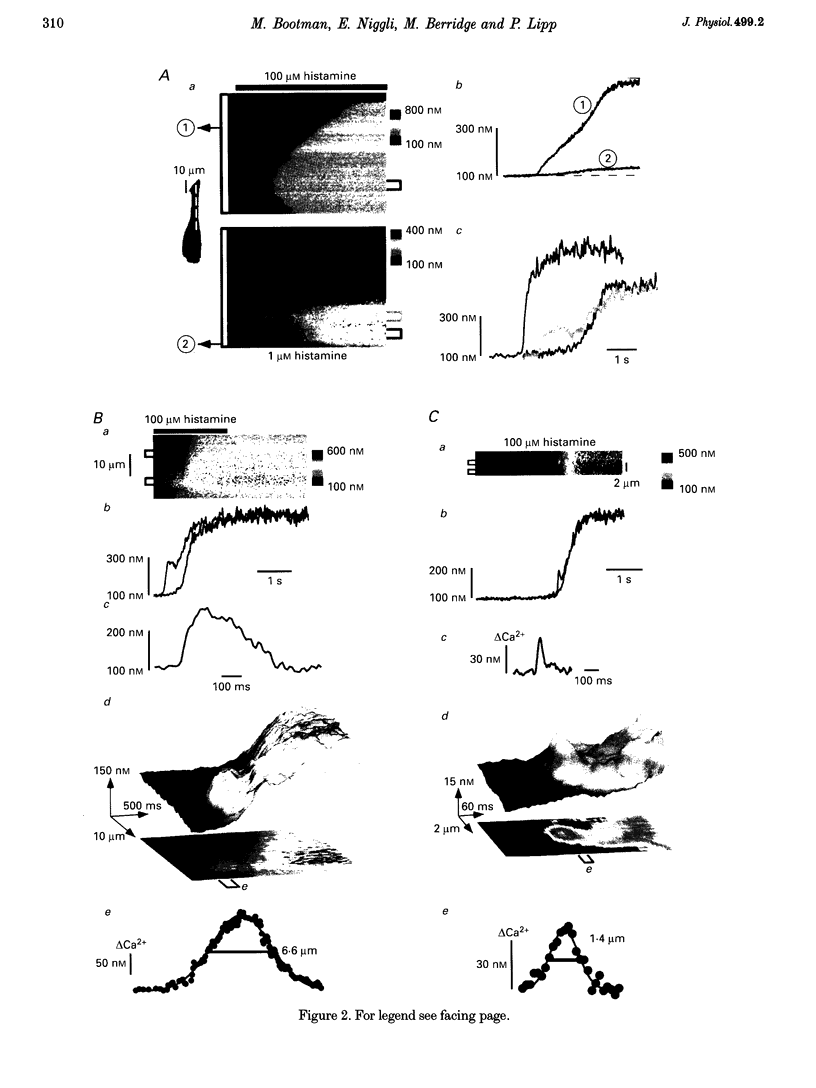
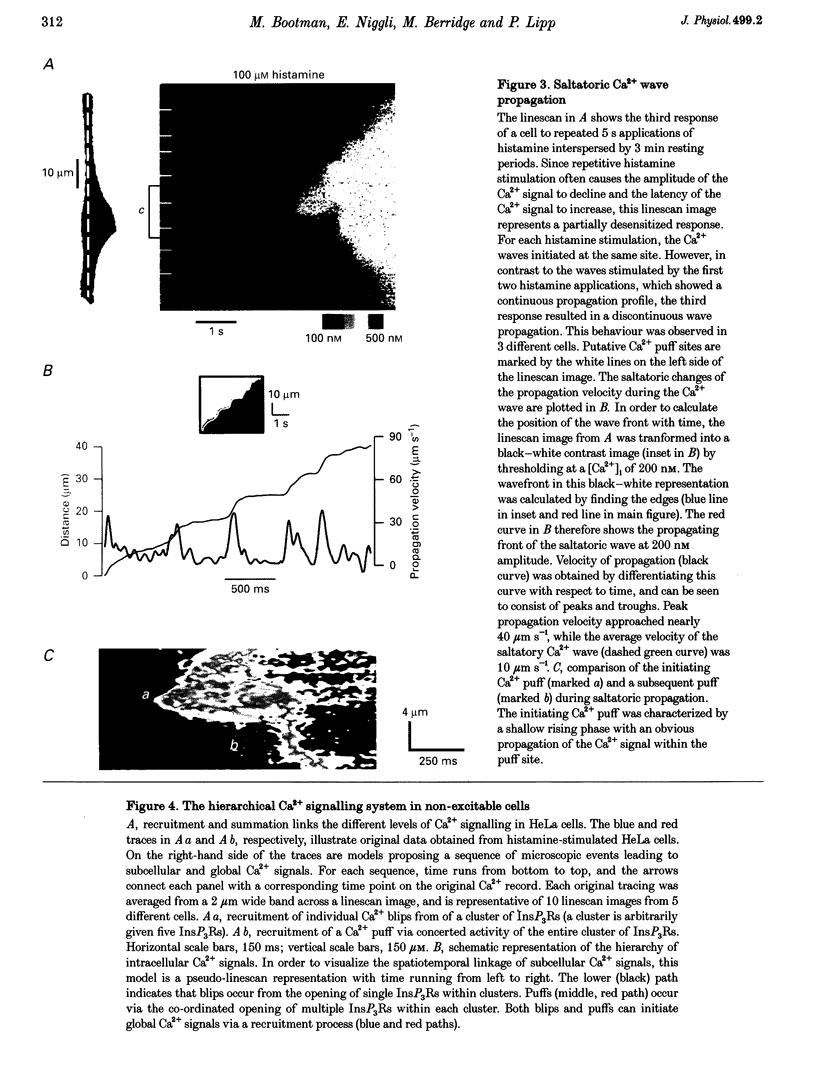
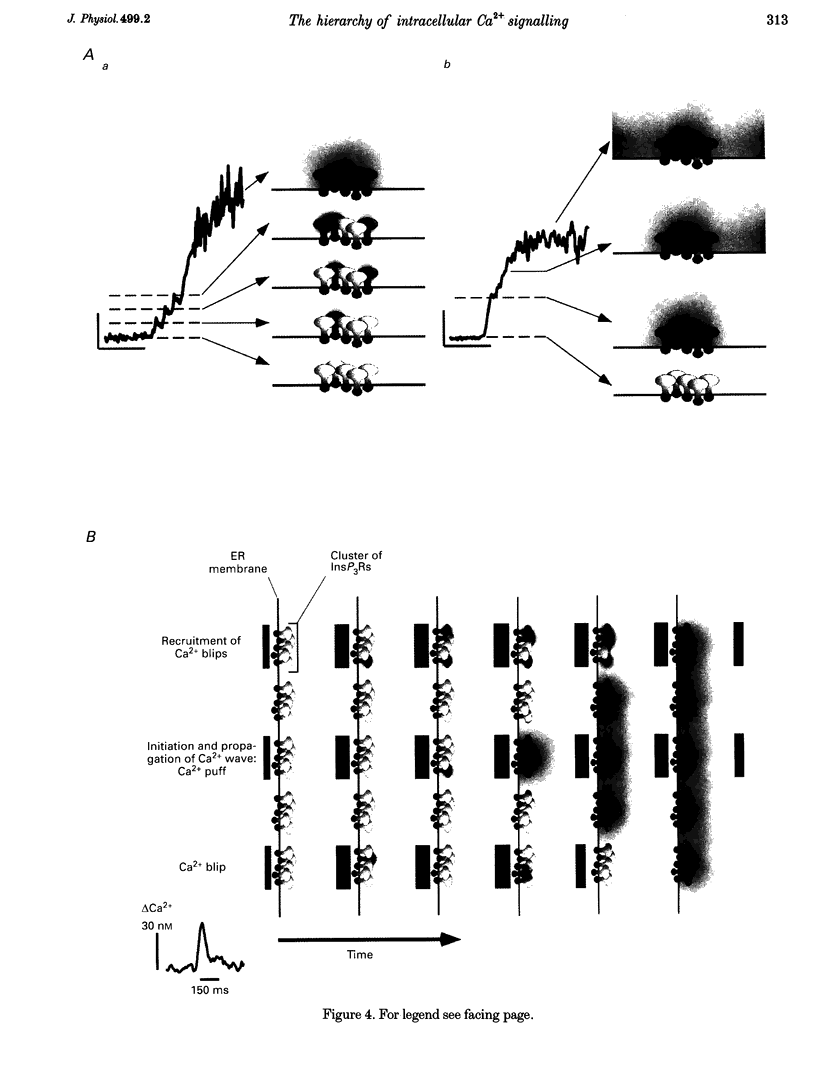
1. Confocal microscopy was used to investigate hormone-induced subcellular Ca2+ release signals from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in a prototype non-excitable cell line (HeLa cells). 2. Histamine application evoked two types of elementary Ca2+ signals: (i) Ca2+ blips arising from single ER Ca2+ release channels (amplitude, 30 nM; lateral spreading, 1.3 microns); (ii) Ca2+ puffs resulting from the concerted activation of several Ca2+ blips (amplitude, 170 nM; spreading, 4 microns). 3. Ca2+ waves in the HeLa cells arose from a variable number of initiation sites, but for individual cells, the number and subcellular location of the initiation sites were constant. The kinetics and amplitude of global Ca2+ signals were directly proportional to the number of initiation sites recruited. 4. Reduction of the feedback inherent in intracellular Ca2+ release caused saltatoric Ca2+ waves, revealing the two principal steps underlying wave propagation: diffusion and regeneration. Threshold stimulation evoked abortive Ca2+ waves, caused by the limited recruitment of Ca2+ puffs. 5. The hierarchy of Ca2+ signalling events, from fundamental levels (blips) to intermediate levels (puffs) to Ca2+ waves, is a prototype for Ca2+ signal transduction for non-excitable cells, and is also analogous to the Ca2+ quarks, Ca2+ sparks and Ca2+ waves in cardiac muscle cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Ehrlich B. E. The inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptor. J Membr Biol. 1995 Jun;145(3):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00232713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootman M. D., Berridge M. J. Subcellular Ca2+ signals underlying waves and graded responses in HeLa cells. Curr Biol. 1996 Jul 1;6(7):855–865. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00609-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootman M. D., Berridge M. J. The elemental principles of calcium signaling. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):675–678. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootman M. D., Cheek T. R., Moreton R. B., Bennett D. L., Berridge M. J. Smoothly graded Ca2+ release from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ stores. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24783–24791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Lederer W. J., Cannell M. B. Calcium sparks: elementary events underlying excitation-contraction coupling in heart muscle. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):740–744. doi: 10.1126/science.8235594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Cheng H., Santana L. F., Jiang Y. H., Lederer W. J., Schneider M. F. Two mechanisms of quantized calcium release in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1996 Feb 1;379(6564):455–458. doi: 10.1038/379455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp P., Niggli E. Modulation of Ca2+ release in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Insight from subcellular release patterns revealed by confocal microscopy. Circ Res. 1994 May;74(5):979–990. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.5.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp P., Niggli E. Submicroscopic calcium signals as fundamental events of excitation--contraction coupling in guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. J Physiol. 1996 Apr 1;492(Pt 1):31–38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-López J. R., Shacklock P. S., Balke C. W., Wier W. G. Local calcium transients triggered by single L-type calcium channel currents in cardiac cells. Science. 1995 May 19;268(5213):1042–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.7754383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Cheng H., Rubart M., Santana L. F., Bonev A. D., Knot H. J., Lederer W. J. Relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by calcium sparks. Science. 1995 Oct 27;270(5236):633–637. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5236.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli E., Lipp P. Subcellular features of calcium signalling in heart muscle: what do we learn? Cardiovasc Res. 1995 Apr;29(4):441–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Yao Y. Ca2+ transients associated with openings of inositol trisphosphate-gated channels in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1996 Mar 15;491(Pt 3):663–668. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Yao Y. Regenerative release of calcium from functionally discrete subcellular stores by inositol trisphosphate. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Dec 23;246(1317):269–274. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parys J. B., Missiaen L., Smedt H. D., Sienaert I., Casteels R. Mechanisms responsible for quantal Ca2+ release from inositol trisphosphate-sensitive calcium stores. Pflugers Arch. 1996 Jul;432(3):359–367. doi: 10.1007/s004240050145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Petersen C. C., Kasai H. Calcium and hormone action. Annu Rev Physiol. 1994;56:297–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.56.030194.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehno-Bittel L., Lückhoff A., Clapham D. E. Calcium release from the nucleus by InsP3 receptor channels. Neuron. 1995 Jan;14(1):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90250-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugorka A., Ríos E., Blatter L. A. Imaging elementary events of calcium release in skeletal muscle cells. Science. 1995 Sep 22;269(5231):1723–1726. doi: 10.1126/science.7569901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Y., Choi J., Parker I. Quantal puffs of intracellular Ca2+ evoked by inositol trisphosphate in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1995 Feb 1;482(Pt 3):533–553. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Neher E. Mobile and immobile calcium buffers in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1993 Sep;469:245–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]