Abstract
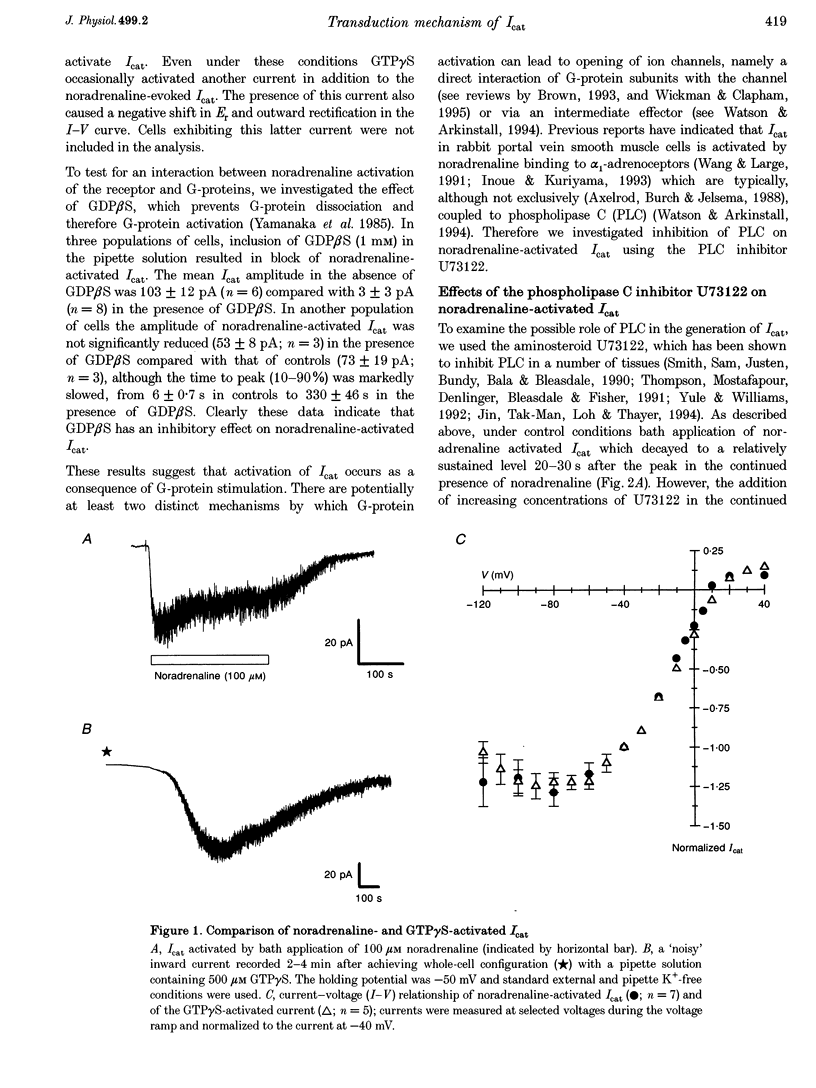
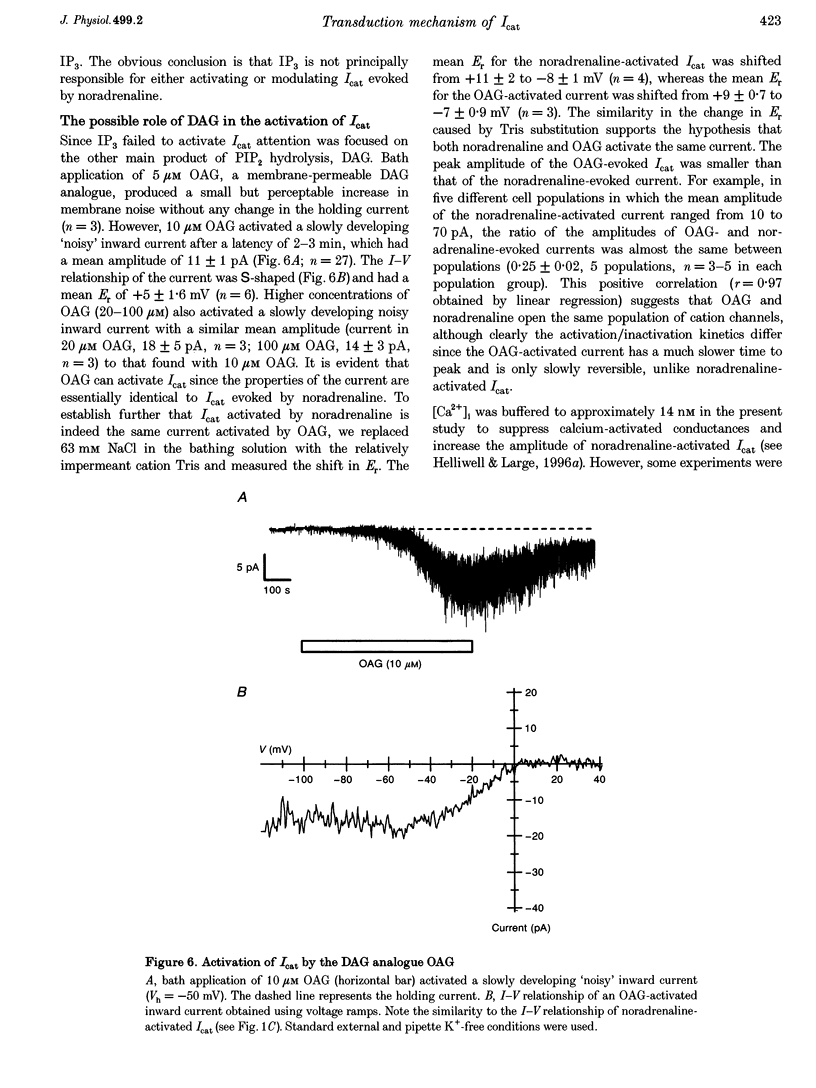
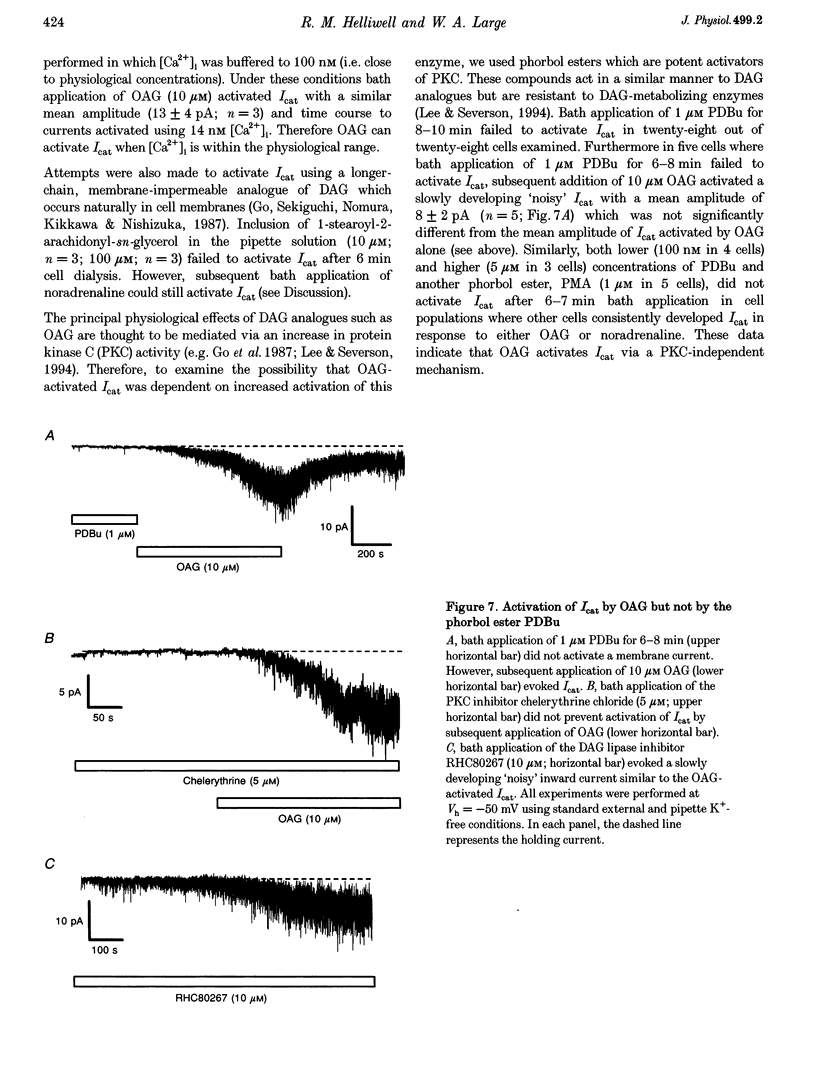
1. The transduction mechanisms involved in the activation and modulation of the noradrenaline-activated cation current (Icat) were investigated with whole-cell patch clamp techniques in rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells. 2. Intracellular application of guanosine 5-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) (GTP gamma S, 500 microM) evoked a 'noisy' inward current at -50 mV with a similar current-voltage relationship and reversal potential to the current evoked by bath application of noradrenaline (100 microM). Guanosine 5-O-(2-thiodiphosphate) (GDP beta S, 1 mM) markedly inhibited noradrenaline-activated Icat. 3. The phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitor U73122 inhibited the amplitude of the noradrenaline-activated Icat in a concentration- and time-dependent manner and the IC50 was about 180 nM. U73122 had similar effects on the cation current evoked by GTP gamma S. 4. Intracellular application of myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3, 100 microM) from the patch pipette did not activate any membrane current in cells where intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) was buffered to 14 nM, but subsequent addition of noradrenaline evoked Icat. 5. Bath application of the 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol (DAG) analogue 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol (OAG, 10 microM) activated Icat, whereas the phorbol ester phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (PDBu, 0.1-5 microM) failed to activate Icat, in every cell examined. Icat activated by OAG after bath application of PDBu was not significantly different from OAG-activated Icat in the absence of PDBu. The DAG lipase inhibitor RHC80267 (10 microM) activated Icat in some cells, whereas the DAG kinase inhibitor R59949 (10 microM) never activated Icat. 6. Bath application of the protein kinase C inhibitor chelerythrine (1-10 microM) had no effect on either OAG-or noradrenaline-activated Icat. 7. It is concluded that noradrenaline activates Icat via a G-protein coupled to PLC and that the resulting DAG product plays a central role in the activation of cation channels via a protein kinase C-independent mechanism.
Full text
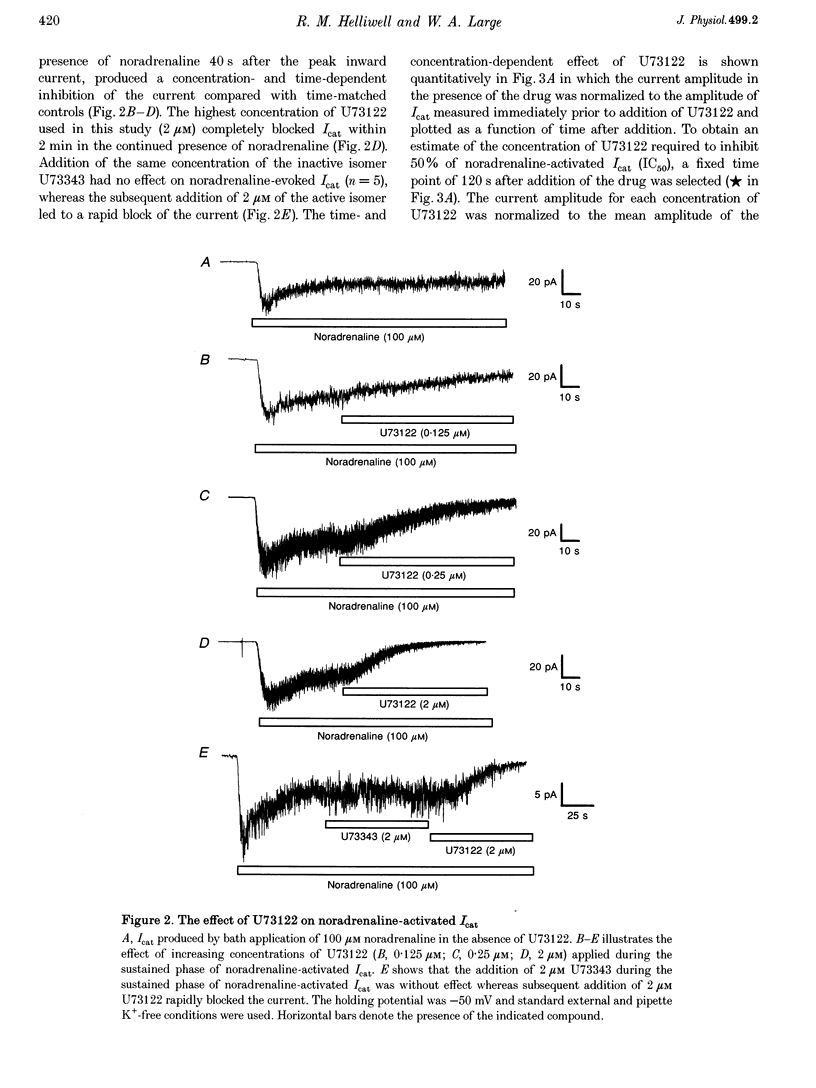
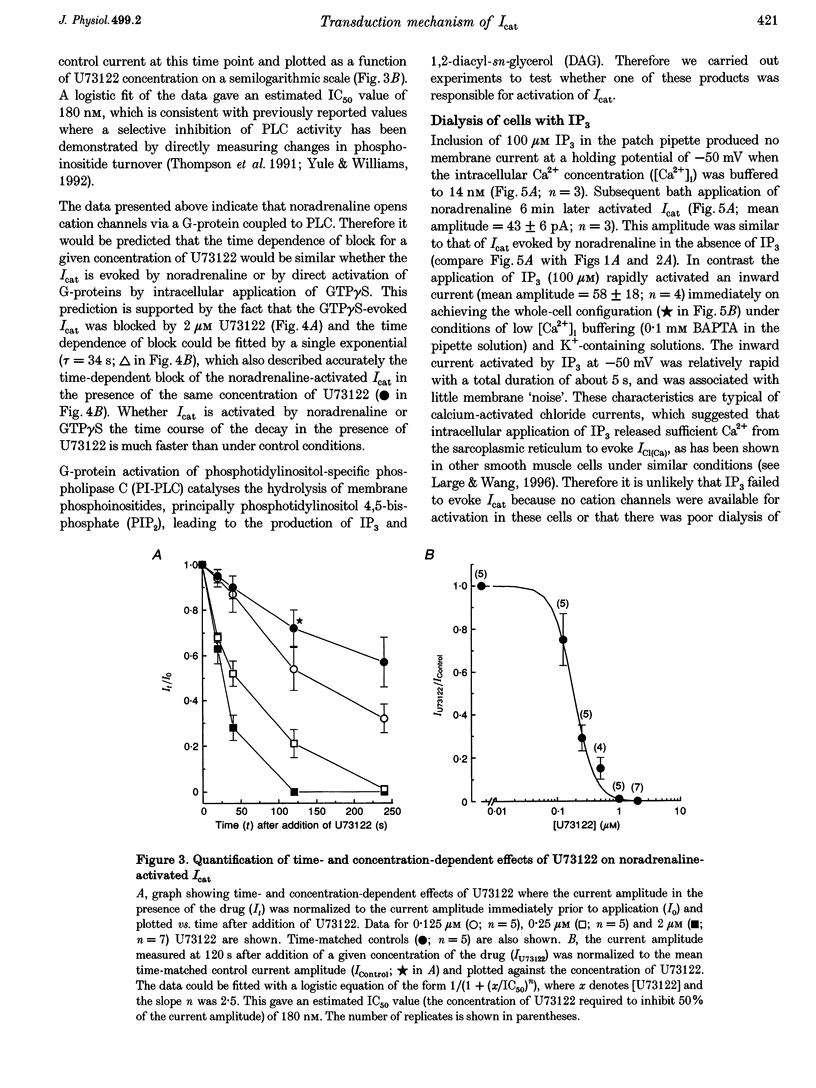
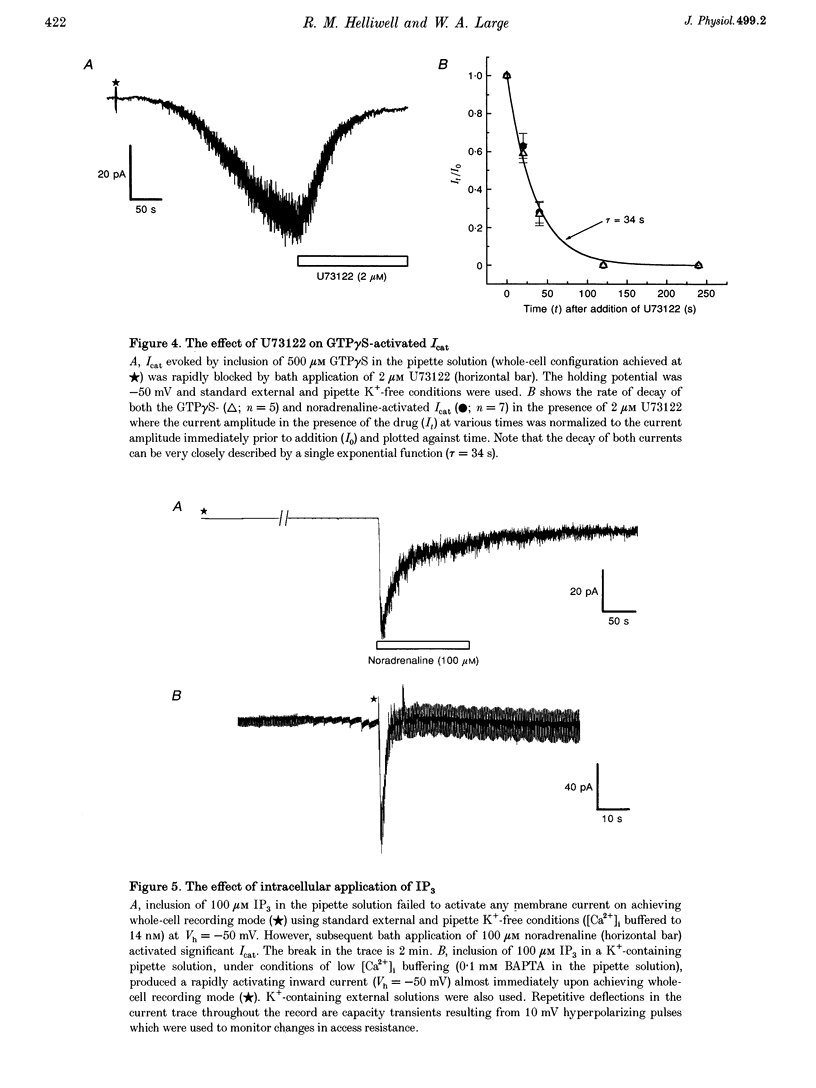
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J., Burch R. M., Jelsema C. L. Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase A2 via GTP-binding proteins: arachidonic acid and its metabolites as second messengers. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Mar;11(3):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasdale J. E., Thakur N. R., Gremban R. S., Bundy G. L., Fitzpatrick F. A., Smith R. J., Bunting S. Selective inhibition of receptor-coupled phospholipase C-dependent processes in human platelets and polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):756–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bross T. E., Prescott S. M., Majerus P. W. RHC 80267 does not inhibit the diglyceride lipase pathway in intact platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 14;116(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M. Membrane-delimited cell signaling complexes: direct ion channel regulation by G proteins. J Membr Biol. 1993 Jan;131(2):93–104. doi: 10.1007/BF02791318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne N. G., Large W. A. Membrane ionic mechanisms activated by noradrenaline in cells isolated from the rabbit portal vein. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:557–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang M., Severson D. L. Inhibition of diacylglycerol metabolism in isolated cardiac myocytes by U-57 908 (RHC 80267), a diacylglycerol lipase inhibitor. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1990 Sep;22(9):1009–1016. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(90)91040-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go M., Sekiguchi K., Nomura H., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Further studies on the specificity of diacylglycerol for protein kinase C activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):598–605. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu H., Trajkovic S., LaBelle E. F. Norepinephrine-induced phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by phospholipases D and C in rat tail artery. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):C1376–C1383. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.6.C1376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helliwell R. M., Large W. A. Dual effect of external Ca2+ on noradrenaline-activated cation current in rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1996 Apr 1;492(Pt 1):75–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert J. M., Augereau J. M., Gleye J., Maffrand J. P. Chelerythrine is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91544-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Acetylcholine activates nonselective cation channels in guinea pig ileum through a G protein. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1173–C1178. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Kuriyama H. Dual regulation of cation-selective channels by muscarinic and alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in the rabbit portal vein. J Physiol. 1993 Jun;465:427–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin W., Lo T. M., Loh H. H., Thayer S. A. U73122 inhibits phospholipase C-dependent calcium mobilization in neuronal cells. Brain Res. 1994 Apr 11;642(1-2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90927-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. W., Shukla S. D., Geisbuhler B. B. Stimulation of phospholipase D activity and phosphatidic acid production by norepinephrine in rat aorta. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):C609–C616. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.3.C609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Bolton T. B. Role of G-proteins in muscarinic receptor inward and outward currents in rabbit jejunal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:395–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large W. A., Wang Q. Characteristics and physiological role of the Ca(2+)-activated Cl- conductance in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1996 Aug;271(2 Pt 1):C435–C454. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.271.2.C435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. W., Severson D. L. Signal transduction in vascular smooth muscle: diacylglycerol second messengers and PKC action. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 1):C659–C678. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.3.C659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobe K., Ohata H., Momose K. Activation of diacylglycerol kinase by carbachol in guinea pig taenia coli. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Nov 29;48(11):2005–2014. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90499-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Terada K., Yamaguchi K., Inoue R., Okabe K., Kitamura K., Hirata M., Kuriyama H. Effects of inositol phosphates on the membrane activity of smooth muscle cells of the rabbit portal vein. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Sep;412(4):382–389. doi: 10.1007/BF01907556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oike M., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Protein kinase C activates the non-selective cation channel in the rabbit portal vein. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Jul;424(2):159–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00374607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Hee-Cheong M. Diacylglycerol metabolism in isolated aortic smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):C11–C17. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.1.C11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Sam L. M., Justen J. M., Bundy G. L., Bala G. A., Bleasdale J. E. Receptor-coupled signal transduction in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils: effects of a novel inhibitor of phospholipase C-dependent processes on cell responsiveness. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):688–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. K., Mostafapour S. P., Denlinger L. C., Bleasdale J. E., Fisher S. K. The aminosteroid U-73122 inhibits muscarinic receptor sequestration and phosphoinositide hydrolysis in SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells. A role for Gp in receptor compartmentation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23856–23862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Large W. A. Noradrenaline-evoked cation conductance recorded with the nystatin whole-cell method in rabbit portal vein cells. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:21–39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickman K., Clapham D. E. Ion channel regulation by G proteins. Physiol Rev. 1995 Oct;75(4):865–885. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1995.75.4.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Z. L., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. ATP activates cationic currents and modulates the calcium current through GTP-binding protein in rabbit portal vein. J Physiol. 1991;440:143–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka G., Eckstein F., Stryer L. Stereochemistry of the guanyl nucleotide binding site of transducin probed by phosphorothioate analogues of GTP and GDP. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):8094–8101. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yule D. I., Williams J. A. U73122 inhibits Ca2+ oscillations in response to cholecystokinin and carbachol but not to JMV-180 in rat pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13830–13835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zholos A. V., Bolton T. B. G-protein control of voltage dependence as well as gating of muscarinic metabotropic channels in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1994 Jul 15;478(Pt 2):195–202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chaffoy de Courcelles D. The use of diacylglycerol kinase inhibitors for elucidating the roles of protein kinase C. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1990;24:491–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


