Abstract
1. Microfibrils are becoming increasingly recognized as an important component of the extra-cellular matrix. However, almost nothing is known about their mechanical role in the diversity of tissues in which they are found. 2. Microfibrils form the principal structural component in the wall of the abdominal artery of the lobster Homarus americanus. We have used previous estimates of the mechanical properties of these microfibrils, estimates of the fraction of the aorta wall volume occupied by the microfibrils, and their angular distribution as a function of strain in a numerical model that predicts the macroscopic mechanical properties of the whole tissue. 3. Microfibrils alone, when their reorientation and deformation are accounted for, characterize the stress-strain behaviour of the vessel. Evidence of the evolutionary conservation of fibrillin between medusans, echinoderms and vertebrates implies that the mechanical properties of lobster microfibrils may apply to microfibrillar function in other taxa. This will have profound implications on the perceived roles of microfibrils in development, physiology and disease.
Full text
PDF




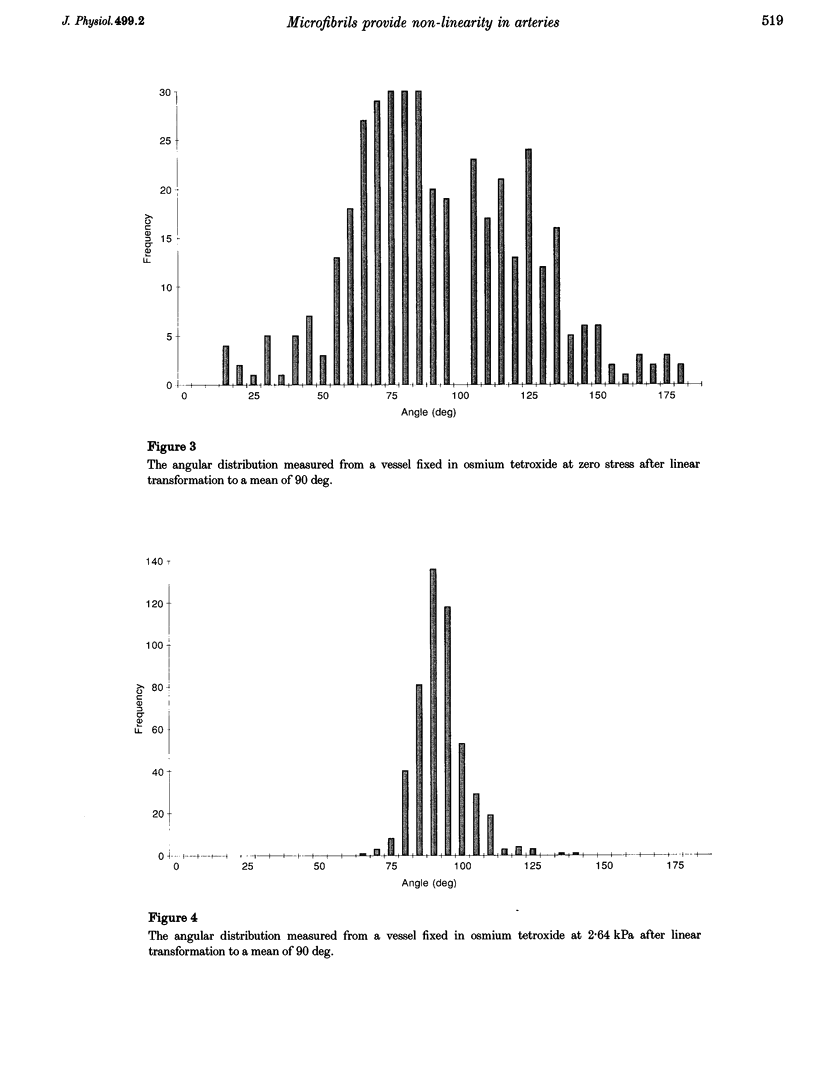
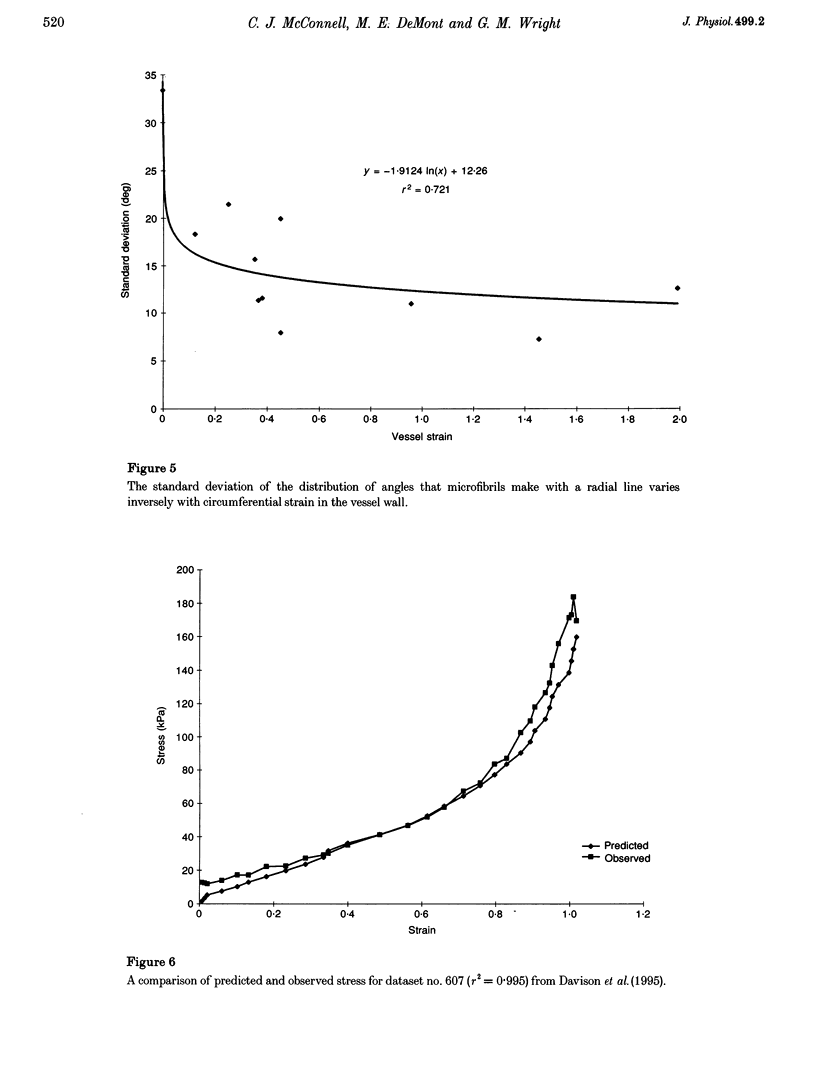
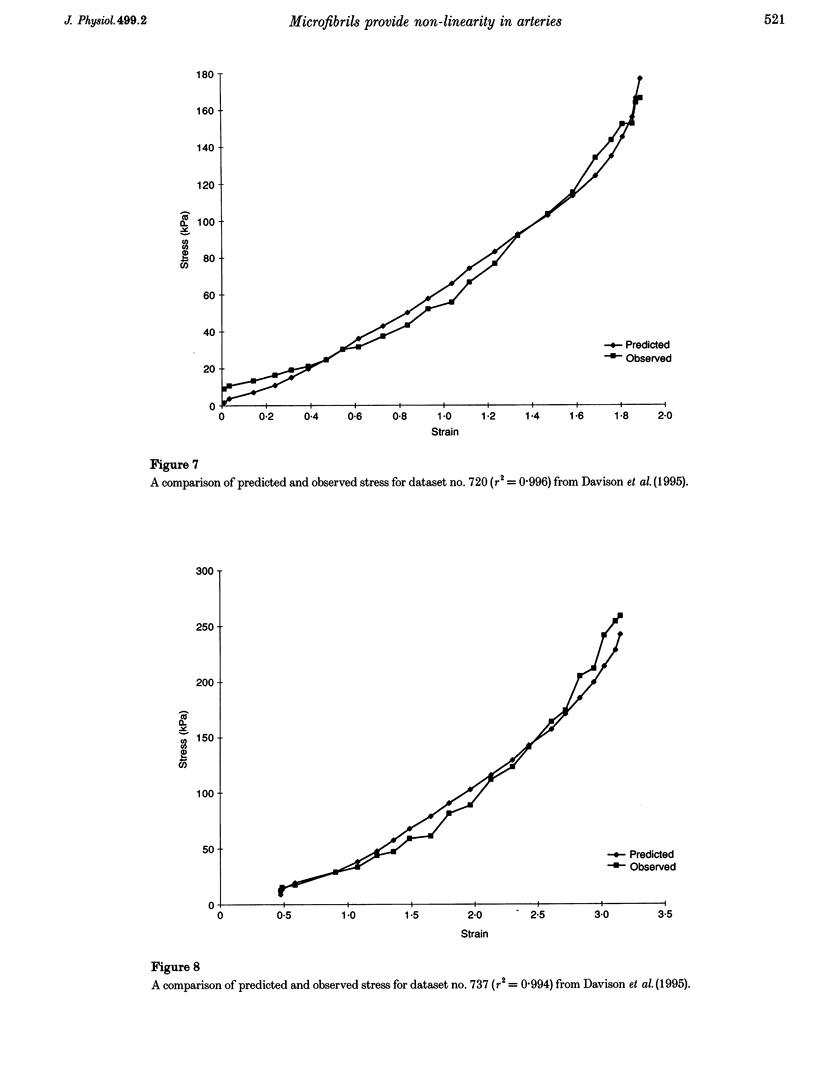





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ault H. K., Hoffman A. H. A composite micromechanical model for connective tissues: Part I--Theory. J Biomech Eng. 1992 Feb;114(1):137–141. doi: 10.1115/1.2895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault H. K., Hoffman A. H. A composite micromechanical model for connective tissues: Part II--Application to rat tail tendon and joint capsule. J Biomech Eng. 1992 Feb;114(1):142–146. doi: 10.1115/1.2895438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergel D. H. The dynamic elastic properties of the arterial wall. J Physiol. 1961 May;156(3):458–469. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison I. G., Wright G. M., DeMont M. E. The structure and physical properties of invertebrate and primitive vertebrate arteries. J Exp Biol. 1995 Oct;198(Pt 10):2185–2196. doi: 10.1242/jeb.198.10.2185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Menashe V., Weleber R. G., Koler R. D., Bigley R. H., Lovrien E., Zonana J., Hollister D. W. Cosegregation of elastin-associated microfibrillar abnormalities with the Marfan phenotype in families. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):652–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Raghunath M., Cisler J., Bevins C. L., DePaepe A., Di Rocco M., Gregoritch J., Imaizumi K., Kaplan P., Kuroki Y. Abnormal morphology of fibrillin microfibrils in fibroblast cultures from patients with neonatal Marfan syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jun;146(6):1414–1421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister D. W., Godfrey M., Sakai L. Y., Pyeritz R. E. Immunohistologic abnormalities of the microfibrillar-fiber system in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 19;323(3):152–159. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007193230303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudetz A. G. Incremental elastic modulus for orthotropic incompressible arteries. J Biomech. 1979;12(9):651–655. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(79)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene D. R., Maddox B. K., Kuo H. J., Sakai L. Y., Glanville R. W. Extraction of extendable beaded structures and their identification as fibrillin-containing extracellular matrix microfibrils. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Apr;39(4):441–449. doi: 10.1177/39.4.2005373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielty C. M., Cummings C., Whittaker S. P., Shuttleworth C. A., Grant M. E. Isolation and ultrastructural analysis of microfibrillar structures from foetal bovine elastic tissues. Relative abundance and supramolecular architecture of type VI collagen assemblies and fibrillin. J Cell Sci. 1991 Aug;99(Pt 4):797–807. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.4.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malak T. M., Bell S. C. Distribution of fibrillin-containing microfibrils and elastin in human fetal membranes: a novel molecular basis for membrane elasticity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994 Jul;171(1):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(94)90469-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell C. J., Wright G. M., DeMont M. E. The modulus of elasticity of lobster aorta microfibrils. Experientia. 1996 Sep 15;52(9):918–921. doi: 10.1007/BF01938880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez F., Pereira L., Zhang H., Lee B. The fibrillin-Marfan syndrome connection. Bioessays. 1993 Sep;15(9):589–594. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reber-Müller S., Spissinger T., Schuchert P., Spring J., Schmid V. An extracellular matrix protein of jellyfish homologous to mammalian fibrillins forms different fibrils depending on the life stage of the animal. Dev Biol. 1995 Jun;169(2):662–672. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt D. P., Keene D. R., Corson G. M., Pöschl E., Bächinger H. P., Gambee J. E., Sakai L. Y. Fibrillin-1: organization in microfibrils and structural properties. J Mol Biol. 1996 Apr 26;258(1):104–116. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Engvall E. Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2499–2509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadwick R. E., Gosline J. M. Elastic arteries in invertebrates: mechanics of the octopus aorta. Science. 1981 Aug 14;213(4509):759–761. doi: 10.1126/science.7256277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurmond F, Trotter J. Morphology and biomechanics of the microfibrillar network of sea cucumber dermis. J Exp Biol. 1996;199(Pt 8):1817–1828. doi: 10.1242/jeb.199.8.1817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]