Abstract
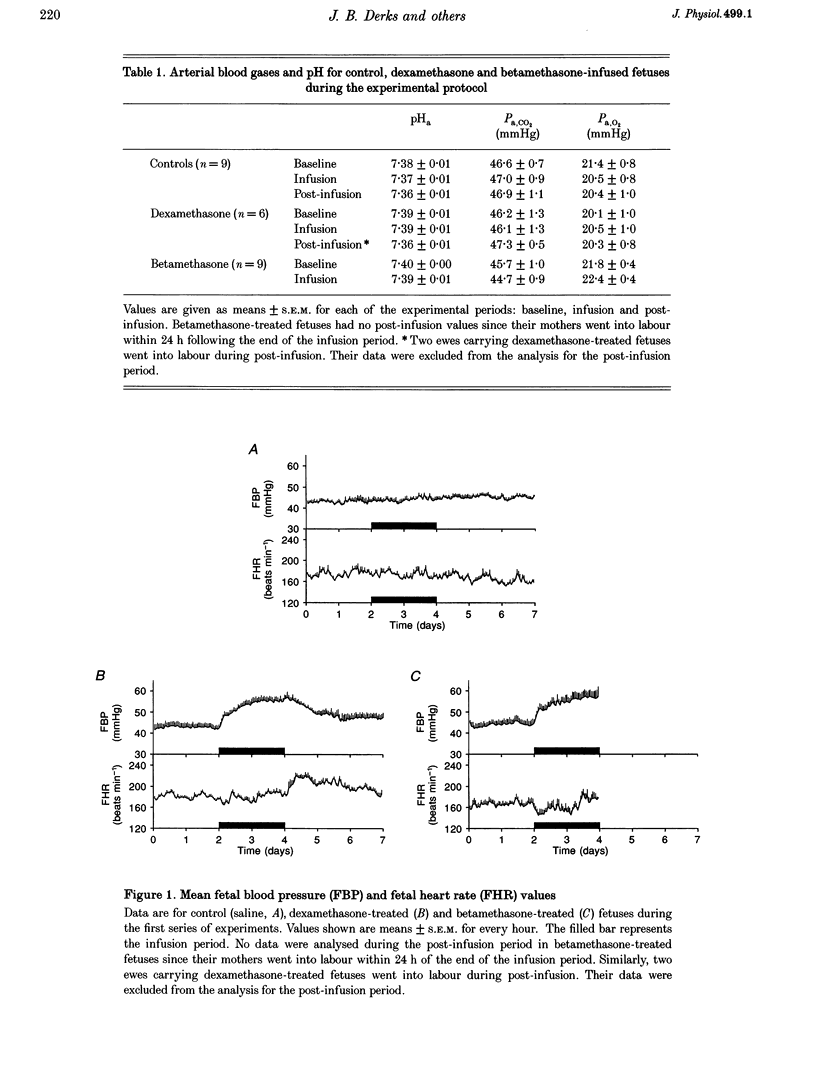
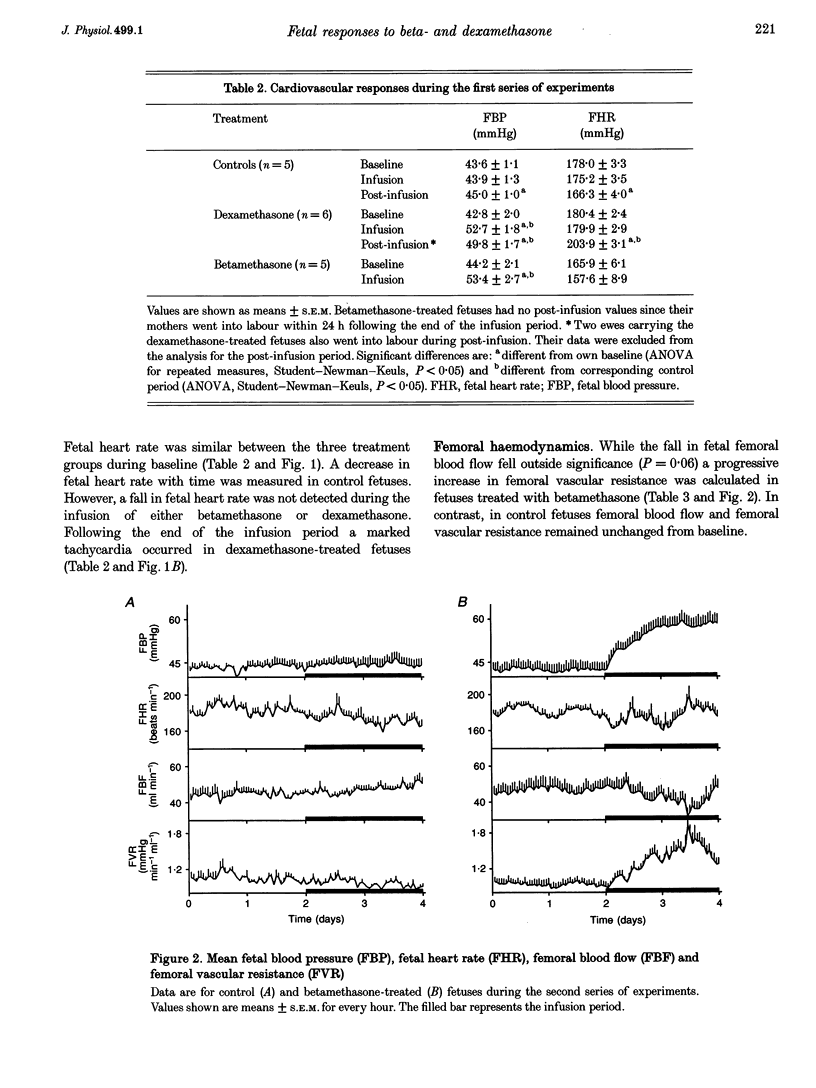
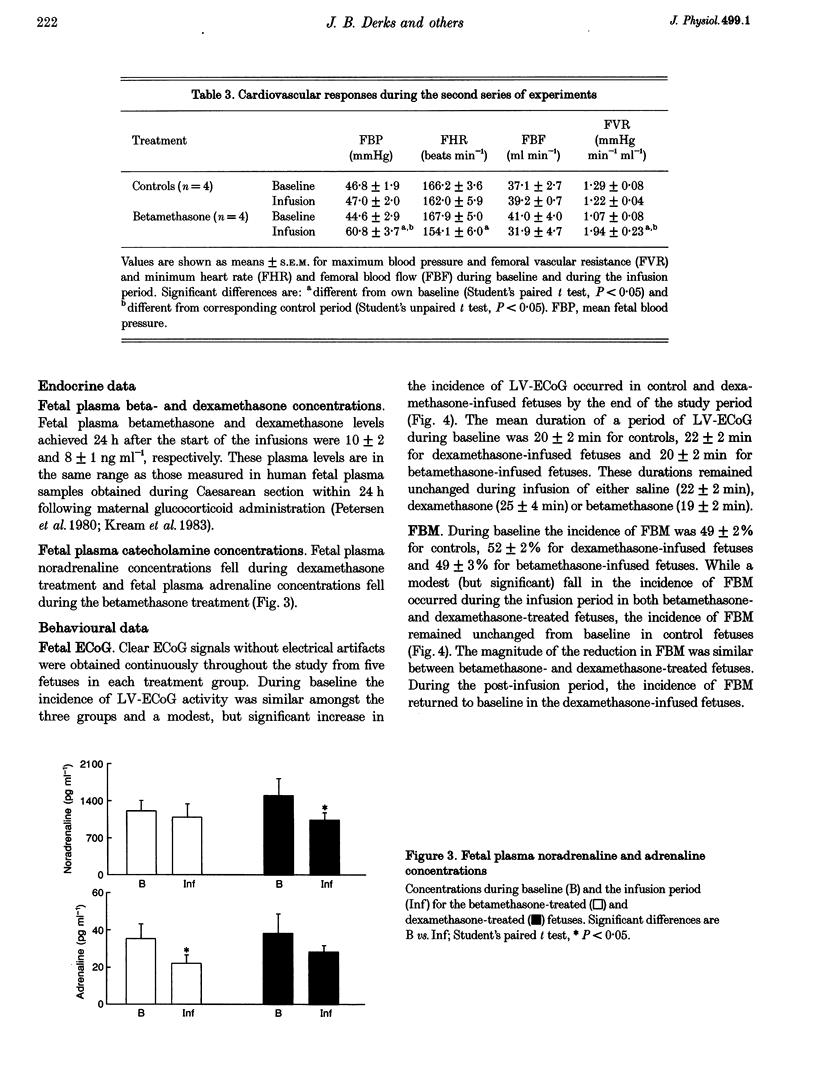
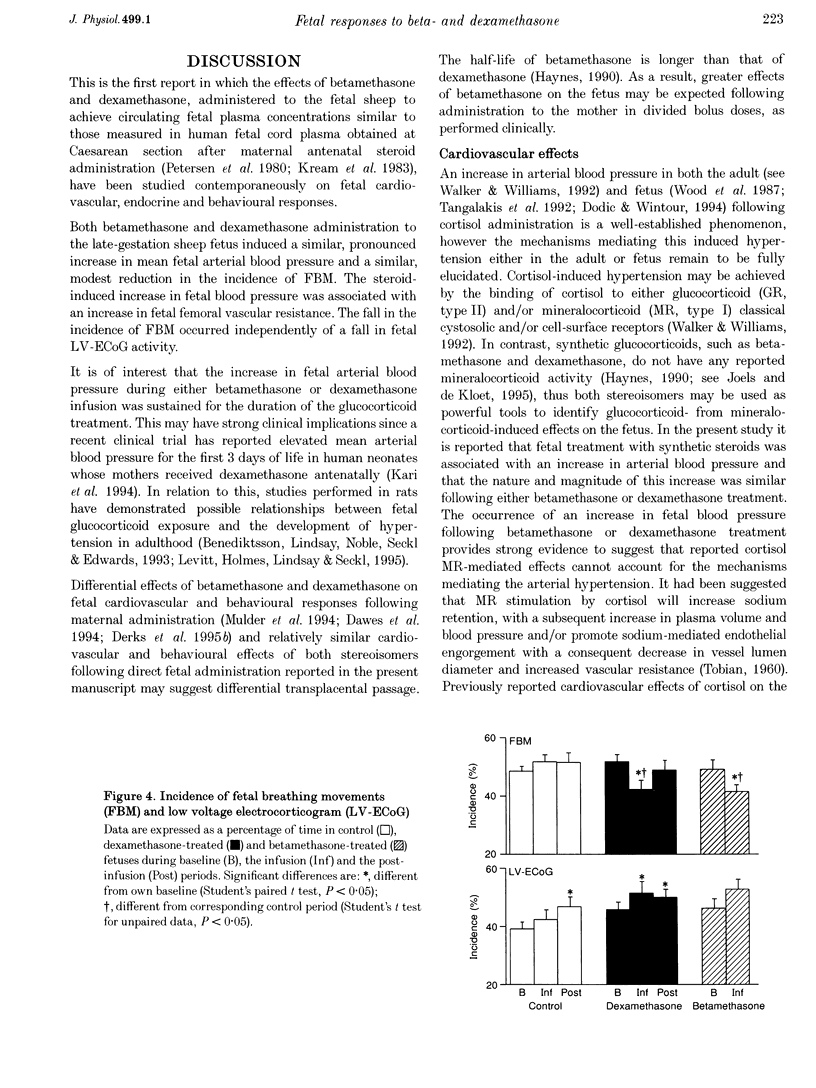
1. Chronically instrumented, late-gestation fetal sheep were prepared to: (1) characterize cardiovascular, endocrine and behavioural effects of fetal treatment with clinical doses of betamethasone and dexamethasone; (2) define specific differences, if any, in the actions of betamethasone and dexamethasone of measured fetal responses; and (3) assess the contribution of changes in peripheral vascular resistance to the glucocorticoid-induced hypertension. 2. Following baseline, either saline (n = 9), betamethasone (n = 9), or dexamethasone (n = 6) was infused for 48 h in fetal sheep commencing at 125 days of gestation. A pronounced increase in fetal blood pressure occurred following both betamethasone and dexamethasone treatment. The nature and magnitude of this increase was similar following treatment with either glucocorticoid. 3. To address possible mechanisms contributing to the glucocorticoid-induced fetal hypertension, fetal plasma catecholamine levels and changes in fetal femoral haemodynamics were assessed following fetal glucocorticoid treatment. A fall in fetal plasma noradrenaline and adrenaline concentrations occurred during betamethasone and dexamethasone treatment. In contrast, a progressive femoral vasoconstriction occurred during betamethasone treatment. 4. A modest fall in the incidence of fetal breathing movements occurred during fetal treatment with either betamethasone or dexamethasone. The magnitude of this reduction was similar with treatment of either glucocorticoid. The fall in fetal breathing during betamethasone and dexamethasone treatment was not associated with a fall in the incidence of fetal low voltage electrocortical activity. 5. Our results indicate that prenatal betamethasone and dexamethasone treatment of late-gestation fetal sheep, in doses similar to those employed clinically, is associated with fetal cardiovascular, endocrine and behavioural effects. Both betamethasone and dexamethasone induce similar increases in fetal blood pressure and similar falls in the incidence of fetal breathing movements. The pronounced betamethasone-induced fetal hypertension is associated with an increase in fetal femoral vascular resistance.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson A. B., Flint A. P., Turnbull A. C. Mechanism of action of glucocorticoids in induction of ovine parturition: effect on placental steroid metabolism. J Endocrinol. 1975 Jul;66(1):61–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod L. Inhibition of prostacyclin production mediates permissive effect of glucocorticoids on vascular tone. Perturbations of this mechanism contribute to pathogenesis of Cushing's syndrome and Addison's disease. Lancet. 1983 Apr 23;1(8330):904–906. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benediktsson R., Lindsay R. S., Noble J., Seckl J. R., Edwards C. R. Glucocorticoid exposure in utero: new model for adult hypertension. Lancet. 1993 Feb 6;341(8841):339–341. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bian X. P., Seidler F. J., Slotkin T. A. Promotional role for glucocorticoids in the development of intracellular signalling: enhanced cardiac and renal adenylate cyclase reactivity to beta-adrenergic and non-adrenergic stimuli after low-dose fetal dexamethasone exposure. J Dev Physiol. 1992 Jun;17(6):289–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challis J. R., Brooks A. N. Maturation and activation of hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal function in fetal sheep. Endocr Rev. 1989 May;10(2):182–204. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-2-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley P., Chalmers I., Keirse M. J. The effects of corticosteroid administration before preterm delivery: an overview of the evidence from controlled trials. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1990 Jan;97(1):11–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1990.tb01711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Serra-Serra V., Moulden M., Redman C. W. Dexamethasone and fetal heart rate variation. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1994 Aug;101(8):675–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1994.tb13183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derks J. B., Mulder E. J., Visser G. H. The effects of maternal betamethasone administration on the fetus. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1995 Jan;102(1):40–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1995.tb09024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodic M., Wintour E. M. Effects of prolonged (48 h) infusion of cortisol on blood pressure, renal function and fetal fluids in the immature ovine foetus. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1994 Dec;21(12):971–980. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1994.tb02659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giussani D. A., Spencer J. A., Moore P. J., Bennet L., Hanson M. A. Afferent and efferent components of the cardiovascular reflex responses to acute hypoxia in term fetal sheep. J Physiol. 1993 Feb;461:431–449. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigh R. M., Jones C. T. Effect of glucocorticoids on alpha 1-adrenergic receptor binding in rat vascular smooth muscle. J Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;5(1):41–48. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0050041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kari M. A., Hallman M., Eronen M., Teramo K., Virtanen M., Koivisto M., Ikonen R. S. Prenatal dexamethasone treatment in conjunction with rescue therapy of human surfactant: a randomized placebo-controlled multicenter study. Pediatrics. 1994 May;93(5):730–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitterman J. A., Liggins G. C., Fewell J. E., Tooley W. H. Inhibition of breathing movements in fetal sheep by prostaglandins. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Mar;54(3):687–692. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.3.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Salter M., Brooks S. L., Moncada S. Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids inhibit the induction by endotoxin of nitric oxide synthase in the lung, liver and aorta of the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1042–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornel L. The role of vascular steroid receptors in the control of vascular contractility and peripheral vascular resistance. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1993 Apr;45(1-3):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(93)90142-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kream J., Mulay S., Fukushima D. K., Solomon S. Determination of plasma dexamethasone in the mother and the newborn after administration of the hormone in a clinical trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jan;56(1):127–133. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggins G. C. Premature delivery of foetal lambs infused with glucocorticoids. J Endocrinol. 1969 Dec;45(4):515–523. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0450515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magyar D. M., Fridshal D., Elsner C. W., Glatz T., Eliot J., Klein A. H., Lowe K. C., Buster J. E., Nathanielsz P. W. Time-trend analysis of plasma cortisol concentrations in the fetal sheep in relation to parturition. Endocrinology. 1980 Jul;107(1):155–159. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. N., Altman D. G., Campbell M. J., Royston P. Analysis of serial measurements in medical research. BMJ. 1990 Jan 27;300(6719):230–235. doi: 10.1136/bmj.300.6719.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder E. J., Derks J. B., Zonneveld M. F., Bruinse H. W., Visser G. H. Transient reduction in fetal activity and heart rate variation after maternal betamethasone administration. Early Hum Dev. 1994 Jan;36(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(94)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanielsz P. W., Bailey A., Poore E. R., Thorburn G. D., Harding R. THe relationship between myometrial activity and sleep state and breathing in fetal sheep throughout the last third of gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Nov 15;138(6):653–659. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson D. M., Lye S. J., Skinner K., Challis J. R. Prostanoid concentrations in maternal/fetal plasma and amniotic fluid and intrauterine tissue prostanoid output in relation to myometrial contractility during the onset of adrenocorticotropin-induced preterm labor in sheep. Endocrinology. 1985 Jan;116(1):389–397. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-1-389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. C., Nation R. L., Ashley J. J., McBride W. G. The placental transfer of betamethasone. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Oct;18(3):245–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00563006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peuler J. D., Johnson G. A. Simultaneous single isotope radioenzymatic assay of plasma norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 1;21(5):625–636. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Suzuki H., Nakazato Y., Shibata H., Inagami T., Saruta T. Increased expression of vascular angiotensin II type 1A receptor gene in glucocorticoid-induced hypertension. J Hypertens. 1994 May;12(5):511–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIAN L. Interrelationship of electrolytes, juxtaglomerular cells and hypertension. Physiol Rev. 1960 Apr;40:280–312. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangalakis K., Lumbers E. R., Moritz K. M., Towstoless M. K., Wintour E. M. Effect of cortisol on blood pressure and vascular reactivity in the ovine fetus. Exp Physiol. 1992 Sep;77(5):709–717. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1992.sp003637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuei S. E., Ashley J. J., Moore R. G., McBride W. G. Quantitation of dexamethasone in biological fluids using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1978 Mar 1;145(2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81341-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. R., Williams B. C. Corticosteroids and vascular tone: mapping the messenger maze. Clin Sci (Lond) 1992 Jun;82(6):597–605. doi: 10.1042/cs0820597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. E., Cheung C. Y., Brace R. A. Fetal heart rate, arterial pressure, and blood volume responses to cortisol infusion. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 2):R904–R909. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.253.6.R904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


