Abstract
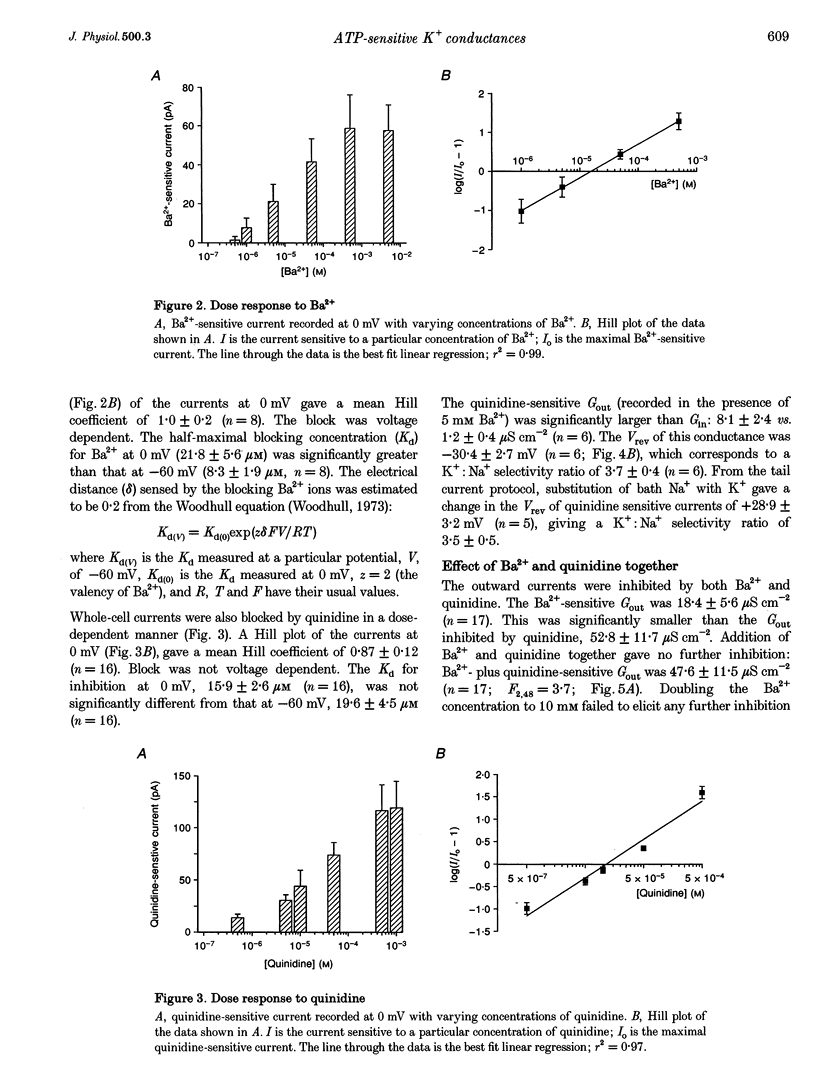
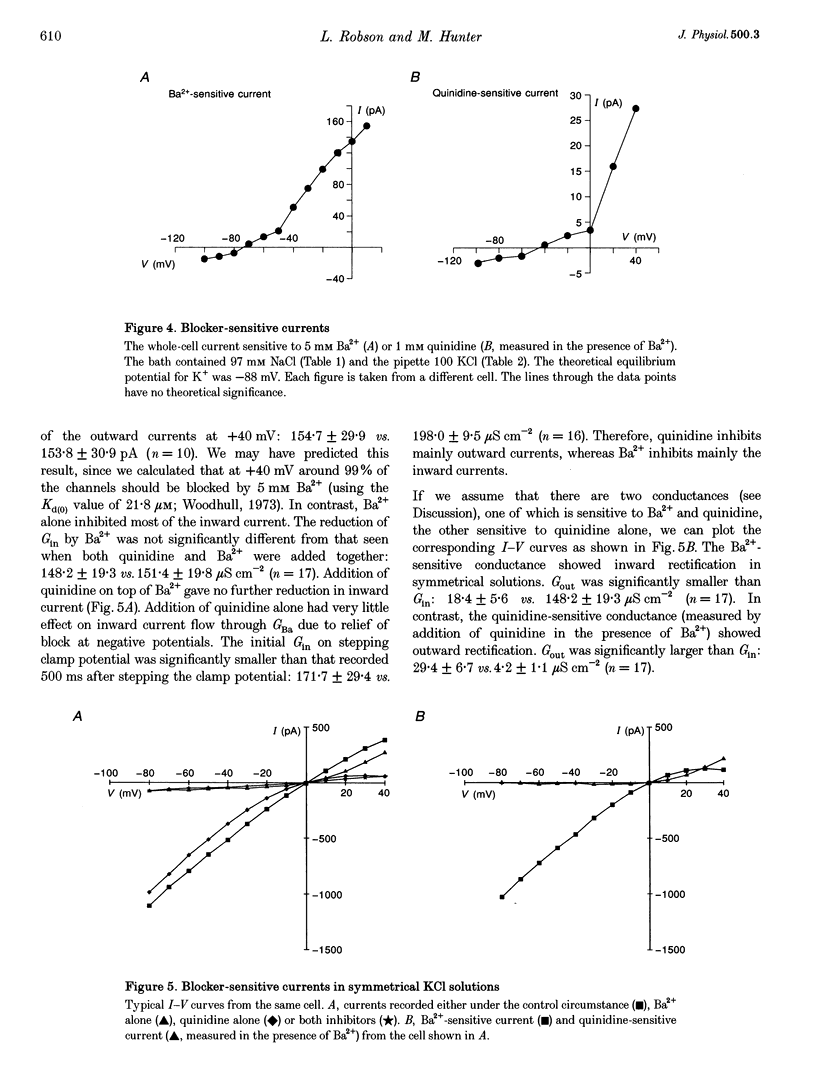
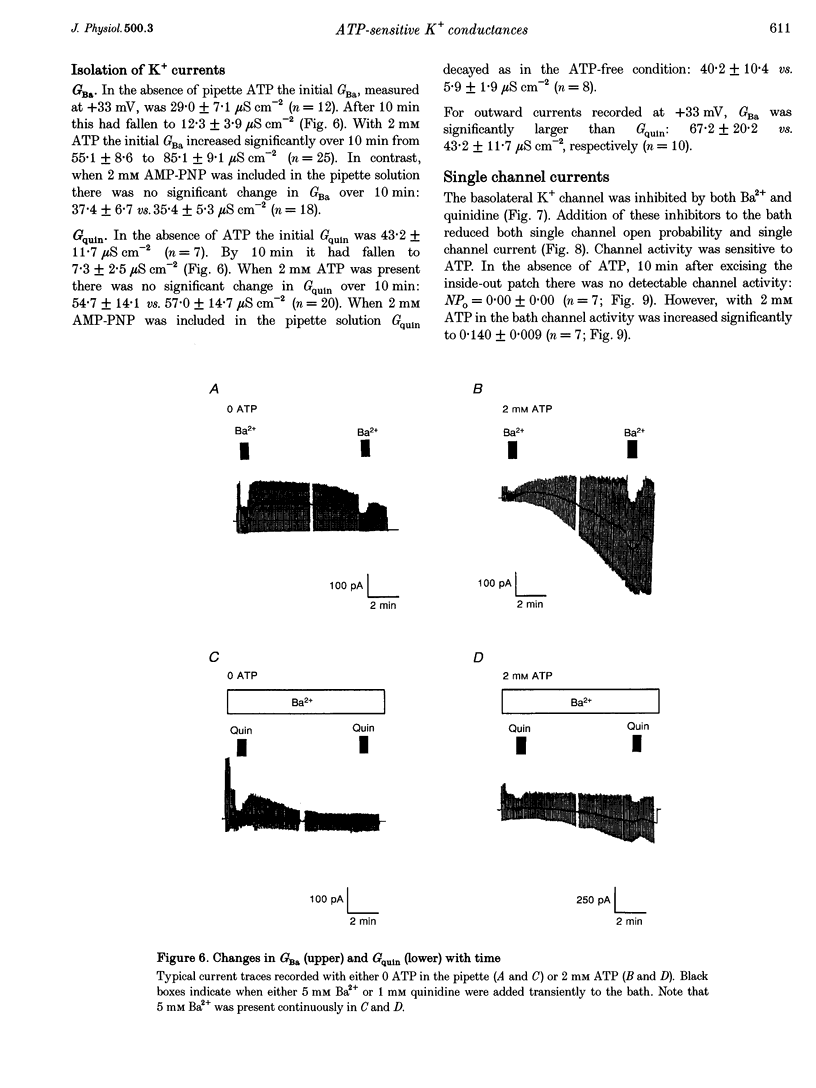
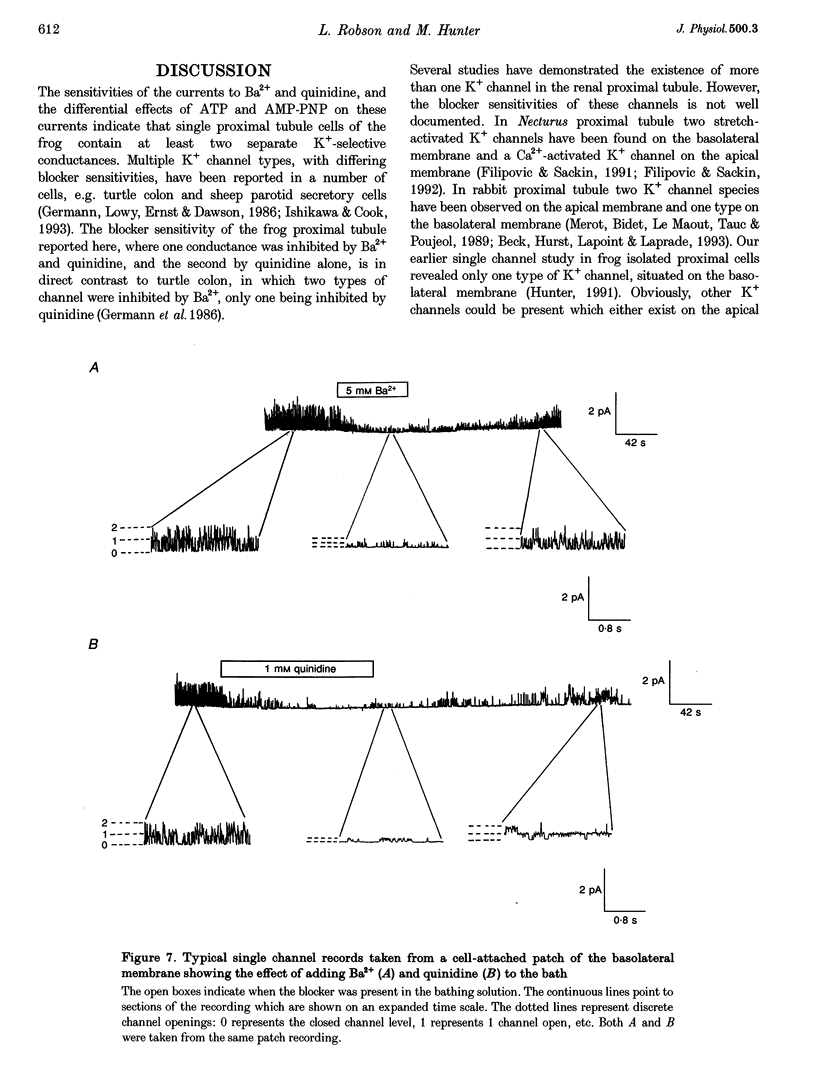
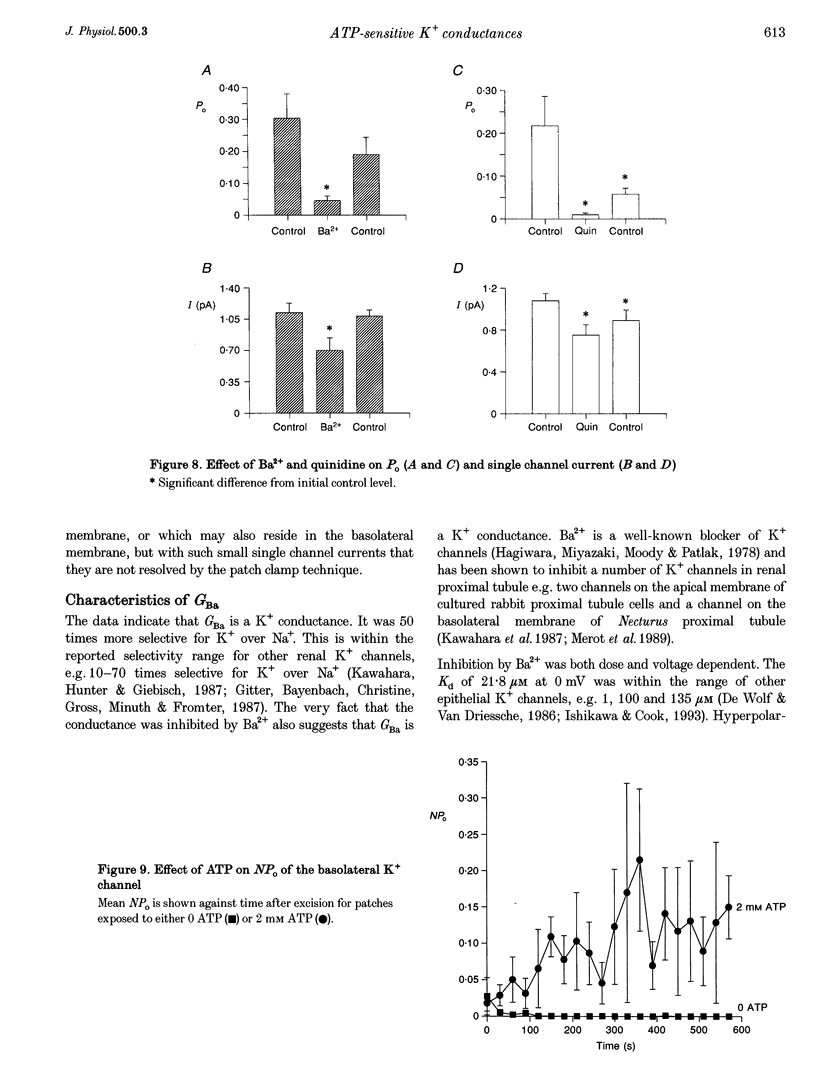
1. The whole-cell and single channel patch clamp techniques were used to identify K(+)-selective conductances in single proximal tubule cells isolated from frog kidney and to examine their ATP sensitivity. Whole-cell currents were inhibited by the K+ channel inhibitors Ba2+ and quinidine in a dose-dependent manner. Addition of Ba2+ alone, quinidine alone, or both inhibitors together revealed two separate conductances, one of which was blocked by both Ba2+ and quinidine (GBa)1, the other being sensitive to quinidine alone (Gquin). 2. With Na(+)-containing Ringer solution in the bath and K(+)-containing Ringer solution in the pipette, both currents were selective for K+ over Na+. The K+ : Na+ selectivity ratio of GBa was around 50:1, while that of Gquin was 4:1. In symmetrical KCl solutions GBa showed inward rectification, while Gquin demonstrated outward rectification. 3. In the absence of pipette ATP, both GBa and Gquin ran down over 10 min. However, when 2 mM ATP was included in the pipette GBa increased, while Gquin remained unchanged. 4. Single channel studies demonstrated that a basolateral K+ channel shared several of the characteristics of GBa. It was inhibited by both Ba2+ and quinidine, underwent run-down in excised patches in the absence of ATP, and was activated by ATP. 5. We conclude that cells of the frog proximal tubule contain at least two distinct K(+)-selective conductances, both of which are regulated by ATP, and which may be involved in pump-leak coupling.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M. Interaction of tetraethylammonium ion derivatives with the potassium channels of giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):413–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Kakei M. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in rat pancreatic beta-cells: modulation by ATP and Mg2+ ions. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:349–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balser J. R., Bennett P. B., Hondeghem L. M., Roden D. M. Suppression of time-dependent outward current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Actions of quinidine and amiodarone. Circ Res. 1991 Aug;69(2):519–529. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.2.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. S., Hurst A. M., Lapointe J. Y., Laprade R. Regulation of basolateral K channels in proximal tubule studied during continuous microperfusion. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 2):F496–F501. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.3.F496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen O., Zeuthen T. Maxi K+ channels in leaky epithelia are regulated by intracellular Ca2+, pH and membrane potential. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Mar;408(3):249–259. doi: 10.1007/BF02181467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wolf I., Van Driessche W. Voltage-dependent Ba2+ block of K+ channels in apical membrane of frog skin. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):C696–C706. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.5.C696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipovic D., Sackin H. A calcium-permeable stretch-activated cation channel in renal proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jan;260(1 Pt 2):F119–F129. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.1.F119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipovic D., Sackin H. Stretch- and volume-activated channels in isolated proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 2):F857–F870. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.5.F857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Díaz J. F. Whole-cell and single channel K+ and Cl- currents in epithelial cells of frog skin. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Jul;98(1):131–161. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germann W. J., Lowy M. E., Ernst S. A., Dawson D. C. Differentiation of two distinct K conductances in the basolateral membrane of turtle colon. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Aug;88(2):237–251. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitter A. H., Beyenbach K. W., Christine C. W., Gross P., Minuth W. W., Frömter E. High-conductance K+ channel in apical membranes of principal cells cultured from rabbit renal cortical collecting duct anlagen. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Mar;408(3):282–290. doi: 10.1007/BF02181471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K., Nichols C. G., Lederer W. J., Lytton J., Vassilev P. M., Kanazirska M. V., Hebert S. C. Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):31–38. doi: 10.1038/362031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson R. L., Schultz S. G. Sodium-coupled glycine uptake by Ehrlich ascites tumor cells results in an increase in cell volume and plasma membrane channel activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):279–283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter M. Potassium-selective channels in the basolateral membrane of single proximal tubule cells of frog kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Mar;418(1-2):26–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00370448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter M. Stretch-activated channels in the basolateral membrane of single proximal cells of frog kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jun;416(4):448–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00370753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A. M., Beck J. S., Laprade R., Lapointe J. Y. Na+ pump inhibition downregulates an ATP-sensitive K+ channel in rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 2):F760–F764. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.4.F760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Cook D. I. Effects of K+ channel blockers on inwardly and outwardly rectifying whole-cell K+ currents in sheep parotid secretory cells. J Membr Biol. 1993 Apr;133(1):29–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00231875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Hunter M., Giebisch G. Potassium channels in Necturus proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):F488–F494. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.3.F488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehl S. J. Quinidine-induced inhibition of the fast transient outward K+ current in rat melanotrophs. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;103(3):1807–1813. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe J. Y., Garneau L., Bell P. D., Cardinal J. Membrane crosstalk in the mammalian proximal tubule during alterations in transepithelial sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F339–F345. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau K. R., Hudson R. L., Schultz S. G. Cell swelling increases a barium-inhibitable potassium conductance in the basolateral membrane of Necturus small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3591–3594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merot J., Bidet M., Le Maout S., Tauc M., Poujeol P. Two types of K+ channels in the apical membrane of rabbit proximal tubule in primary culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 16;978(1):134–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner G., Wang W., Paulmichl M., Oberleithner H., Lang F. Ouabain decreases apparent potassium-conductance in proximal tubules of the amphibian kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1985 May;404(2):131–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00585408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):147–148. doi: 10.1038/305147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Shosaku T., Kubota T., Yamaguchi J., Fukase M., Fujita T., Fujimoto M. Reciprocal effects of Ca2+ and Mg-ATP on the 'run-down' of the K+ channels in opossum kidney cells. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Mar;413(5):562–564. doi: 10.1007/BF00594190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Ciani S., Eddlestone G. T. ATP mediates both activation and inhibition of K(ATP) channel activity via cAMP-dependent protein kinase in insulin-secreting cell lines. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Oct;94(4):693–717. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L., Hunter M. Role of cell volume and protein kinase C in regulation of a Cl- conductance in single proximal tubule cells of Rana temporaria. J Physiol. 1994 Oct 1;480(Pt 1):1–7. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., Mougouris T., Ono S., DuBose T. D., Jr ATP-sensitive K(+)-selective channels of inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 2):F489–F496. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.3.F489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyders J., Knoth K. M., Roberds S. L., Tamkun M. M. Time-, voltage-, and state-dependent block by quinidine of a cloned human cardiac potassium channel. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;41(2):322–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Voltage-dependent ATP-sensitive potassium channels of skeletal muscle membrane. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):736–738. doi: 10.1038/316736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsuta H., Ueda S., Morishima S., Okada Y. Voltage- and time-dependent K+ channel currents in the basolateral membrane of villus enterocytes isolated from guinea pig small intestine. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Mar;103(3):429–446. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]