Abstract
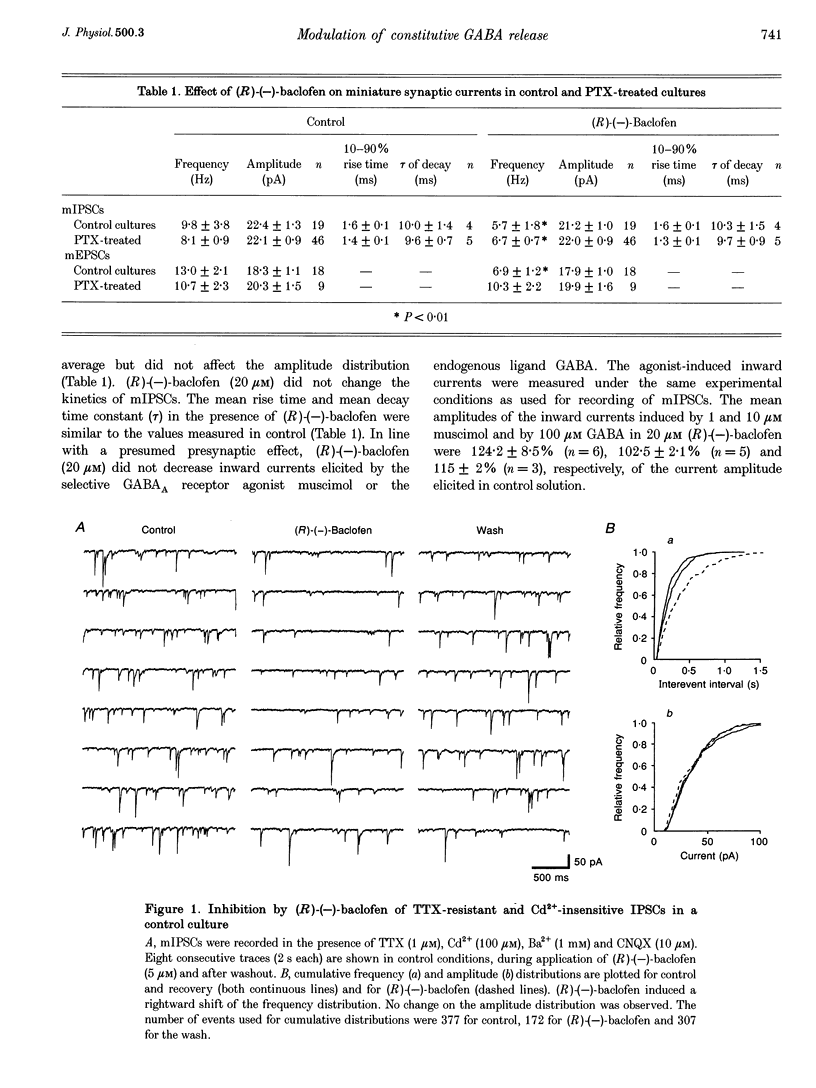
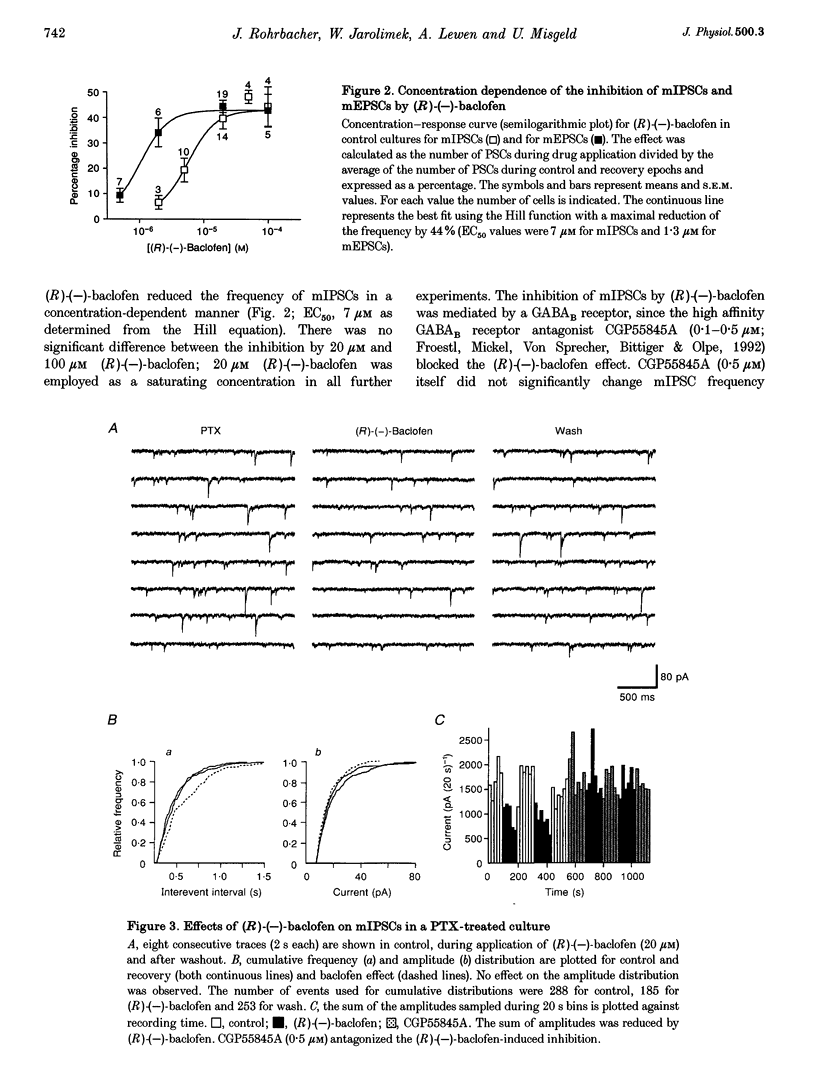
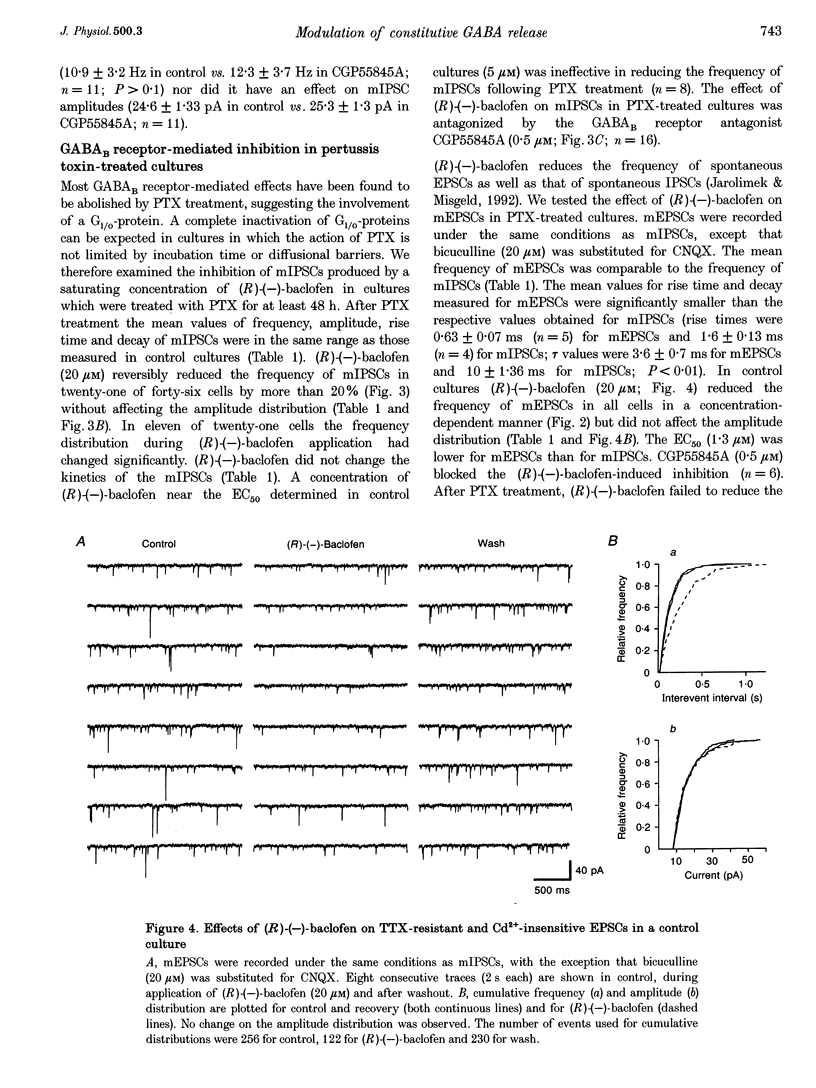
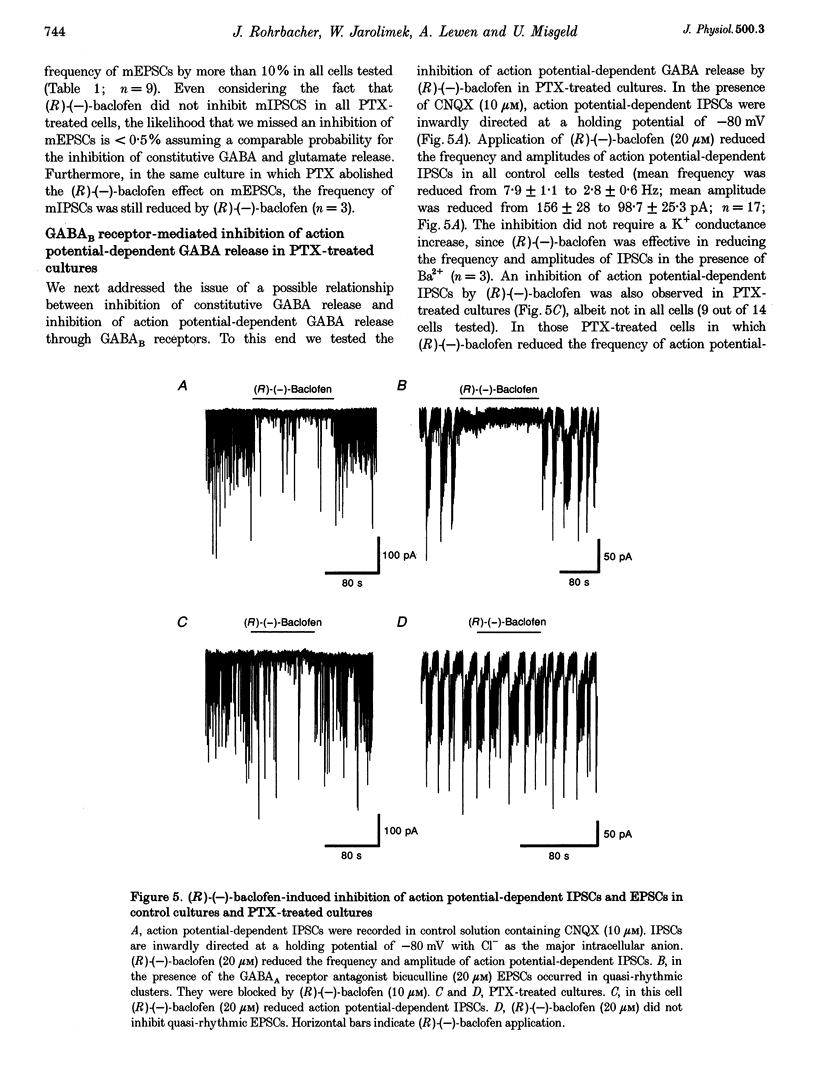
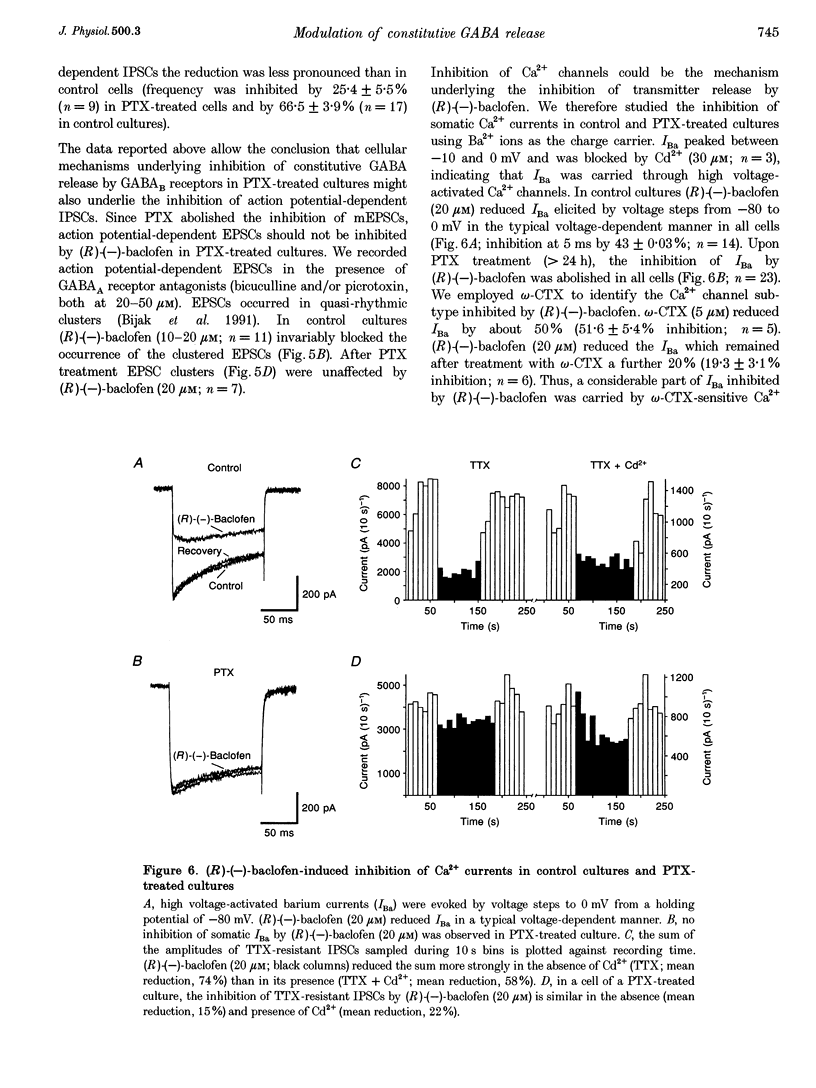
1. Tight-seal, whole-cell recording was used to study GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of spontaneous inhibitory synaptic currents in cultured rat midbrain neurones. 2. Spontaneous miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) were recorded in tetrodotoxin (TTX), Cd2+ and Ba2+. (R)-(-)-baclofen reduced the frequency of mIPSCs through a presynaptic mechanism. The EC50 for this effect was 7 microM. It was antagonized by the GABAB receptor antagonist CGP55845A (0.5 microM). 3. In pertussis toxin (PTX)-treated cultures, some GABAB receptor-mediated reduction of the frequency of mIPSCs persisted. In contrast, PTX treatment totally abolished inhibition of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs). 4. In PTX-treated cultures, a saturating concentration of (R)-(-)-baclofen inhibited action potential-generated IPSCs but no EPSCs. 5. PTX treatment abolished the (R)-(-)-baclofen-mediated inhibition of high voltage-activated somatic Ca2+ currents and of spontaneous IPSCs depending on presynaptic Ca2+ entry. 6. We conclude that cellular mechanisms underlying GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of mIPSCs contribute to auto-inhibition of GABA release.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi A., Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Functionally distinct G proteins selectively couple different receptors to PI hydrolysis in the same cell. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer C., Pilgrim C., Reisert I., Misgeld U. Cells from embryonic rat striatum cocultured with mesencephalic glia express dopaminergic phenotypes. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jul 8;128(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90746-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijak M., Jarolimek W., Misgeld U. Effects of antagonists on quisqualate and nicotinic receptor-mediated currents of midbrain neurones in culture. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):699–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. Kinetics and selectivity of a low-voltage-activated calcium current in chick and rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:547–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Swandulla D. Neuronal calcium channels: kinetics, blockade and modulation. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54(1):31–58. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittman J. S., Regehr W. G. Contributions of calcium-dependent and calcium-independent mechanisms to presynaptic inhibition at a cerebellar synapse. J Neurosci. 1996 Mar 1;16(5):1623–1633. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-05-01623.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doze V. A., Cohen G. A., Madison D. V. Calcium channel involvement in GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of GABA release in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Jul;74(1):43–53. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.74.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Nicoll R. A. Pre- and postsynaptic GABAB receptors in the hippocampus have different pharmacological properties. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):585–591. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L. On the presynaptic action of baclofen at inhibitory synapses between cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:433–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Modulation of ion-channel function by G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Dec;17(12):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarolimek W., Demmelhuber J., Bijak M., Misgeld U. CGP 55845A blocks baclofen, gamma-aminobutyric acid and inhibitory postsynaptic potassium currents in guinea pig CA3 neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1993 May 14;154(1-2):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90164-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarolimek W., Misgeld U. GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of tetrodotoxin-resistant GABA release in rodent hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. J Neurosci. 1997 Feb 1;17(3):1025–1032. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-03-01025.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarolimek W., Misgeld U. On the inhibitory actions of baclofen and gamma-aminobutyric acid in rat ventral midbrain culture. J Physiol. 1992;451:419–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarolimek W., Misgeld U. Reduction of GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition by the non-NMDA receptor antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione in cultured neurons of rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jan 2;121(1-2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90691-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misgeld U., Bijak M., Jarolimek W. A physiological role for GABAB receptors and the effects of baclofen in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1995 Jul;46(4):423–462. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(95)00012-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misgeld U., Müller W., Brunner H. Effects of (-)baclofen on inhibitory neurons in the guinea pig hippocampal slice. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jun;414(2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00580955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan J. F., Jarolimek W., Lewen A., Misgeld U. (-)-Baclofen-induced and constitutively active inwardly rectifying potassium conductances in cultured rat midbrain neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1996 Nov-Dec;433(1-2):49–57. doi: 10.1007/s004240050247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfrieger F. W., Gottmann K., Lux H. D. Kinetics of GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of calcium currents and excitatory synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons in vitro. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potier B., Dutar P. Presynaptic inhibitory effect of baclofen on hippocampal inhibitory synaptic transmission involves a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb 16;231(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrbacher J., Krieglstein K., Honerkamp S., Lewen A., Misgeld U. 5,7-Dihydroxytryptamine uptake discriminates living serotonergic cells from dopaminergic cells in rat midbrain culture. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Oct 27;199(3):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)12060-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanziani M., Capogna M., Gähwiler B. H., Thompson S. M. Presynaptic inhibition of miniature excitatory synaptic currents by baclofen and adenosine in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):919–927. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz K. P., Miller R. J. GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of Ca2+ currents and synaptic transmission in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:669–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Capogna M., Scanziani M. Presynaptic inhibition in the hippocampus. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Jun;16(6):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90160-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Gähwiler B. H. Comparison of the actions of baclofen at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1992;451:329–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich D., Huguenard J. R. GABAB receptor-mediated responses in GABAergic projection neurones of rat nucleus reticularis thalami in vitro. J Physiol. 1996 Jun 15;493(Pt 3):845–854. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. G., Saggau P. GABAB receptor-mediated presynaptic inhibition in guinea-pig hippocampus is caused by reduction of presynaptic Ca2+ influx. J Physiol. 1995 Jun 15;485(Pt 3):649–657. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon K. W., Rothman S. M. The modulation of rat hippocampal synaptic conductances by baclofen and gamma-aminobutyric acid. J Physiol. 1991 Oct;442:377–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


