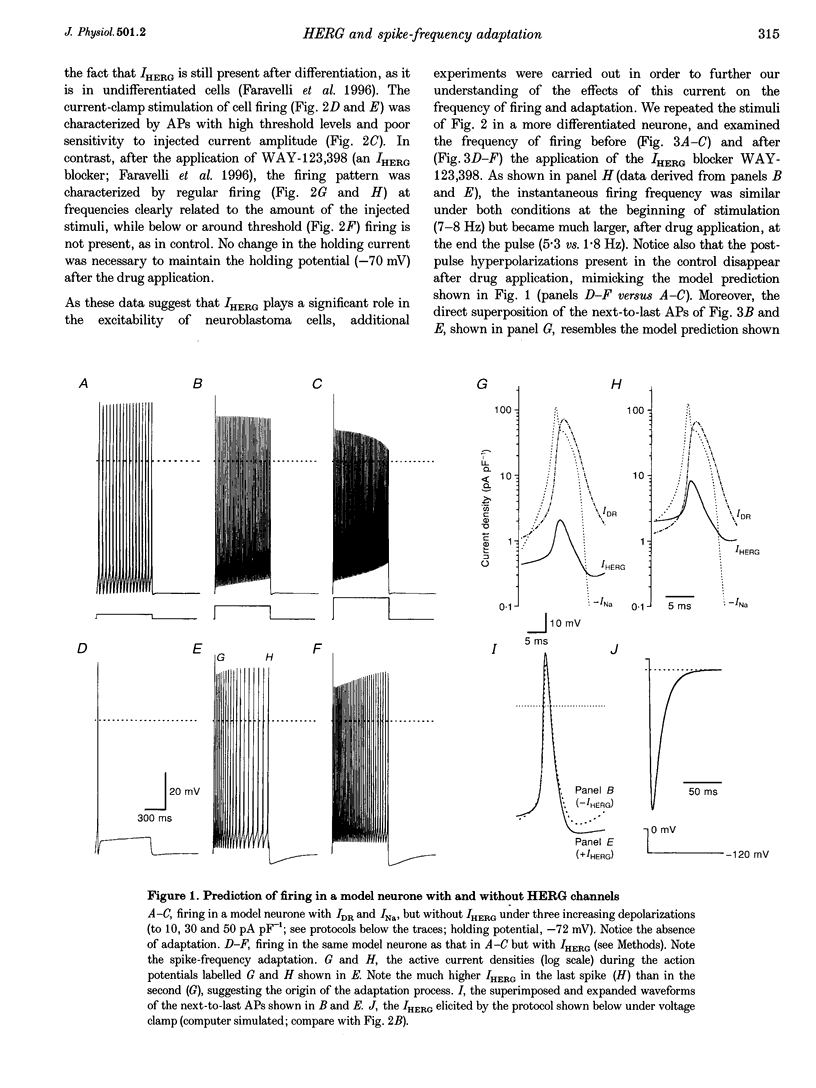
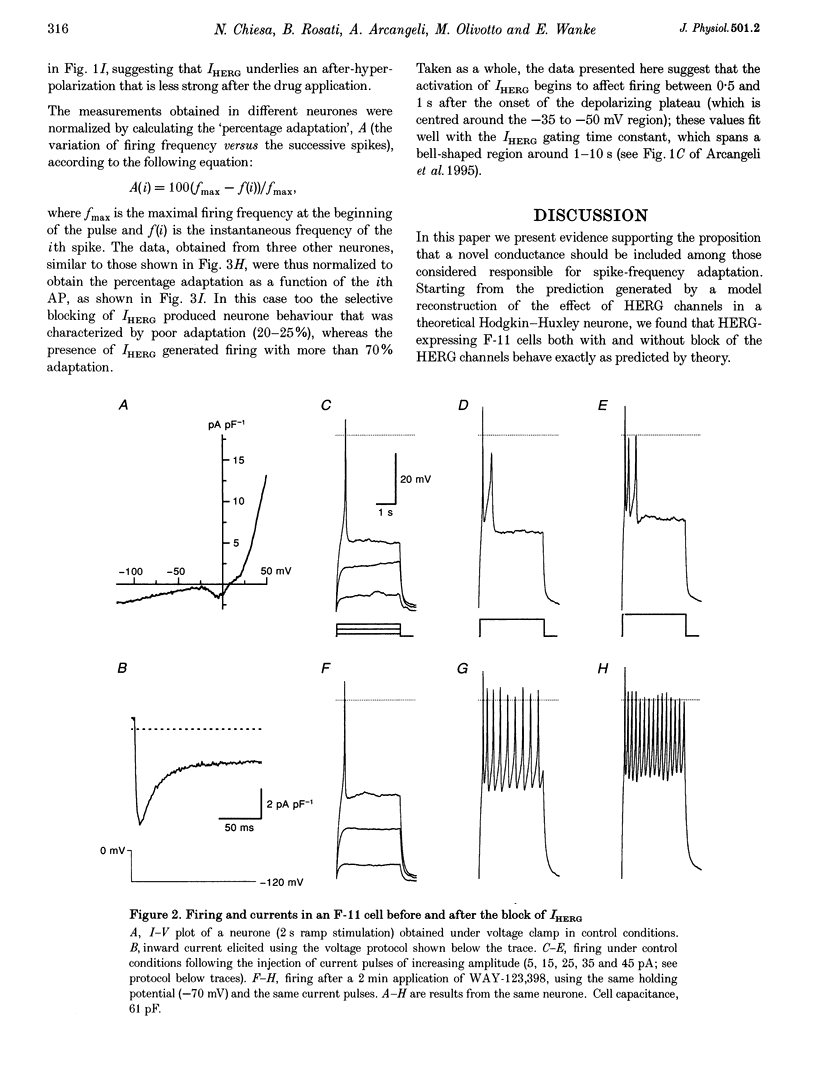
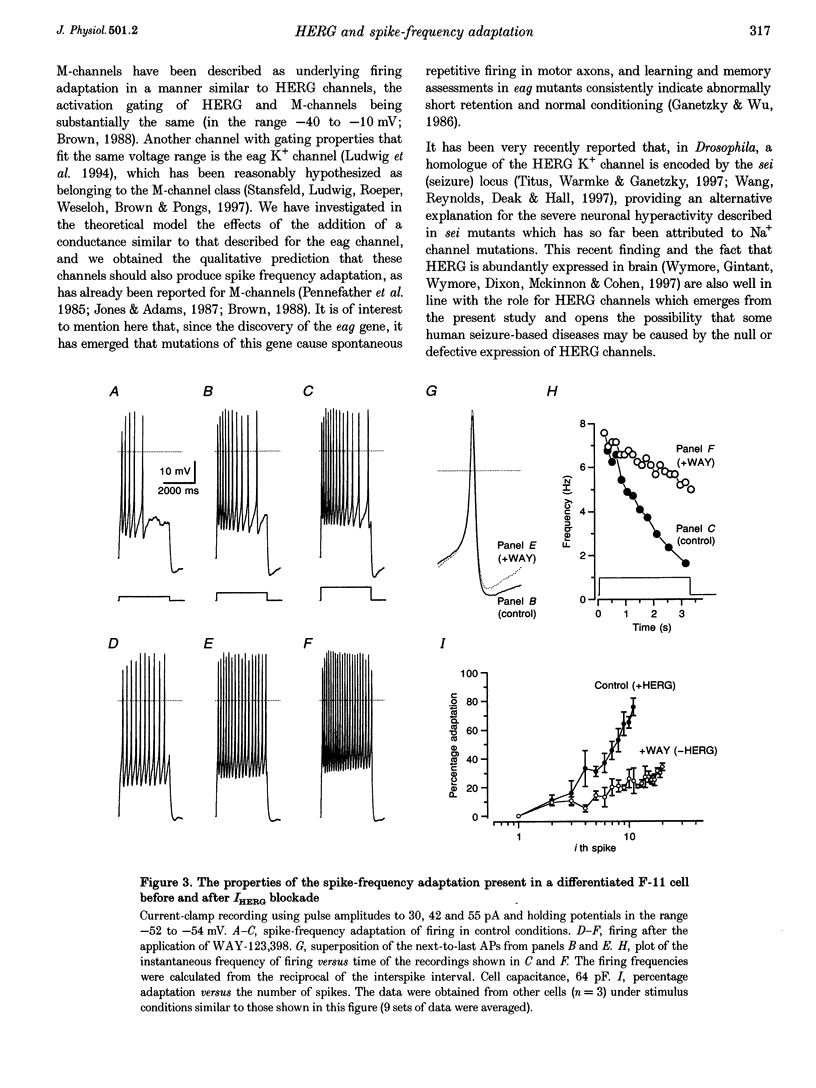
Abstract
1. The regular firing of a Hodgkin-Huxley neurone endowed with fast Na+ and delayed K+ channels can be converted into adapting firing by appending HERG (human eag-related gene) channels. 2. The computer model predictions were verified by studying the firing properties of F-11 DRG neurone x neuroblastoma hybrid cells induced to differentiate by long-term exposure to retinoic acid. These cells, which express HERG currents (IHERG), show clear spike-frequency adaptation of their firing when current clamped with long depolarizations. 3. In agreement with the prediction, the selective blocking of IHERG by class III antiarrhythmic drugs always led to the disappearance of the spike-frequency adaptation, and the conversion of adapting firing to regular firing. 4. It is proposed that, in addition to their role in the repolarization of the heart action potential, HERG channels may sustain a process of spike-frequency adaptation, and hence contribute to the control of burst duration in a way that is similar to that of the K+ currents, IAHP, IC and IM. In addition to the known cardiac arrhythmia syndrome (LQT2), genetic mutations or an altered HERG expression could lead to continuous hyperexcitable states sustained by the inability of nerve or endocrine cells to accommodate to repetitive stimuli. This might help in clarifying the pathogenesis of still undefined idiopathic familial epilepsies.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcangeli A., Becchetti A., Mannini A., Mugnai G., De Filippi P., Tarone G., Del Bene M. R., Barletta E., Wanke E., Olivotto M. Integrin-mediated neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma cells depends on the activation of potassium channels. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1131–1143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcangeli A., Bianchi L., Becchetti A., Faravelli L., Coronnello M., Mini E., Olivotto M., Wanke E. A novel inward-rectifying K+ current with a cell-cycle dependence governs the resting potential of mammalian neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1995 Dec 1;489(Pt 2):455–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp021065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A. M currents. Ion Channels. 1988;1:55–94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7302-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Satin L. S., Hopkins W. F. Pancreatic B cells are bursting, but how? Trends Neurosci. 1991 Sep;14(9):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90033-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran M. E., Splawski I., Timothy K. W., Vincent G. M., Green E. D., Keating M. T. A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faravelli L., Arcangeli A., Olivotto M., Wanke E. A HERG-like K+ channel in rat F-11 DRG cell line: pharmacological identification and biophysical characterization. J Physiol. 1996 Oct 1;496(Pt 1):13–23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganetzky B., Wu C. F. Neurogenetics of membrane excitability in Drosophila. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:13–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J., Terlau H., Wunder F., Brüggemann A., Pardo L. A., Marquardt A., Stühmer W., Pongs O. Functional expression of a rat homologue of the voltage gated either á go-go potassium channel reveals differences in selectivity and activation kinetics between the Drosophila channel and its mammalian counterpart. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 3;13(19):4451–4458. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06767.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magistretti J., Mantegazza M., Guatteo E., Wanke E. Action potentials recorded with patch-clamp amplifiers: are they genuine? Trends Neurosci. 1996 Dec;19(12):530–534. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(96)40004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platika D., Boulos M. H., Baizer L., Fishman M. C. Neuronal traits of clonal cell lines derived by fusion of dorsal root ganglia neurons with neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Jiang C., Curran M. E., Keating M. T. A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinelli W., Moubarak I. F., Parsons R. W., Colatsky T. J. Cellular electrophysiology of WAY-123,398, a new class III antiarrhythmic agent: specificity of IK block and lack of reverse use dependence in cat ventricular myocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 1993 Sep;27(9):1580–1591. doi: 10.1093/cvr/27.9.1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfeld C., Ludwig J., Roeper J., Weseloh R., Brown D., Pongs O. A physiological role for ether-à-go-go K+ channels? Trends Neurosci. 1997 Jan;20(1):13–14. doi: 10.1016/S0166-2236(96)20058-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus S. A., Warmke J. W., Ganetzky B. The Drosophila erg K+ channel polypeptide is encoded by the seizure locus. J Neurosci. 1997 Feb 1;17(3):875–881. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-03-00875.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. J., Reynolds E. R., Déak P., Hall L. M. The seizure locus encodes the Drosophila homolog of the HERG potassium channel. J Neurosci. 1997 Feb 1;17(3):882–890. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-03-00882.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmke J. W., Ganetzky B. A family of potassium channel genes related to eag in Drosophila and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3438–3442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wymore R. S., Gintant G. A., Wymore R. T., Dixon J. E., McKinnon D., Cohen I. S. Tissue and species distribution of mRNA for the IKr-like K+ channel, erg. Circ Res. 1997 Feb;80(2):261–268. doi: 10.1161/01.res.80.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


