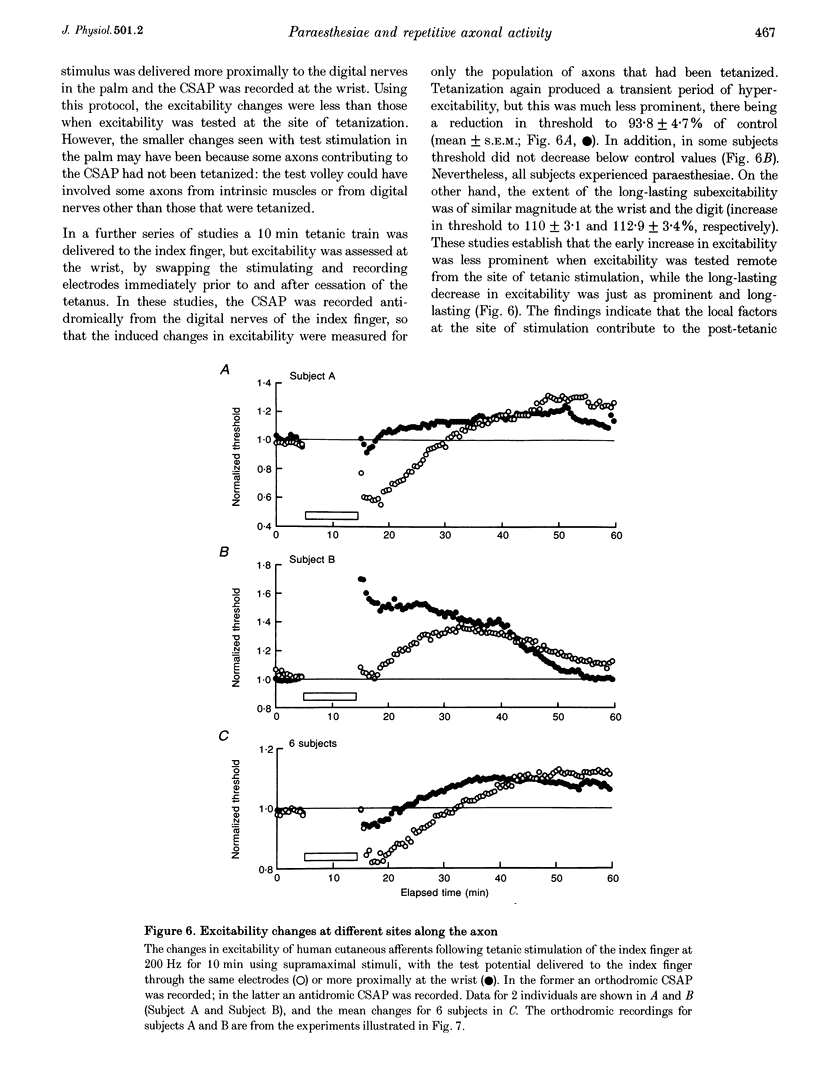
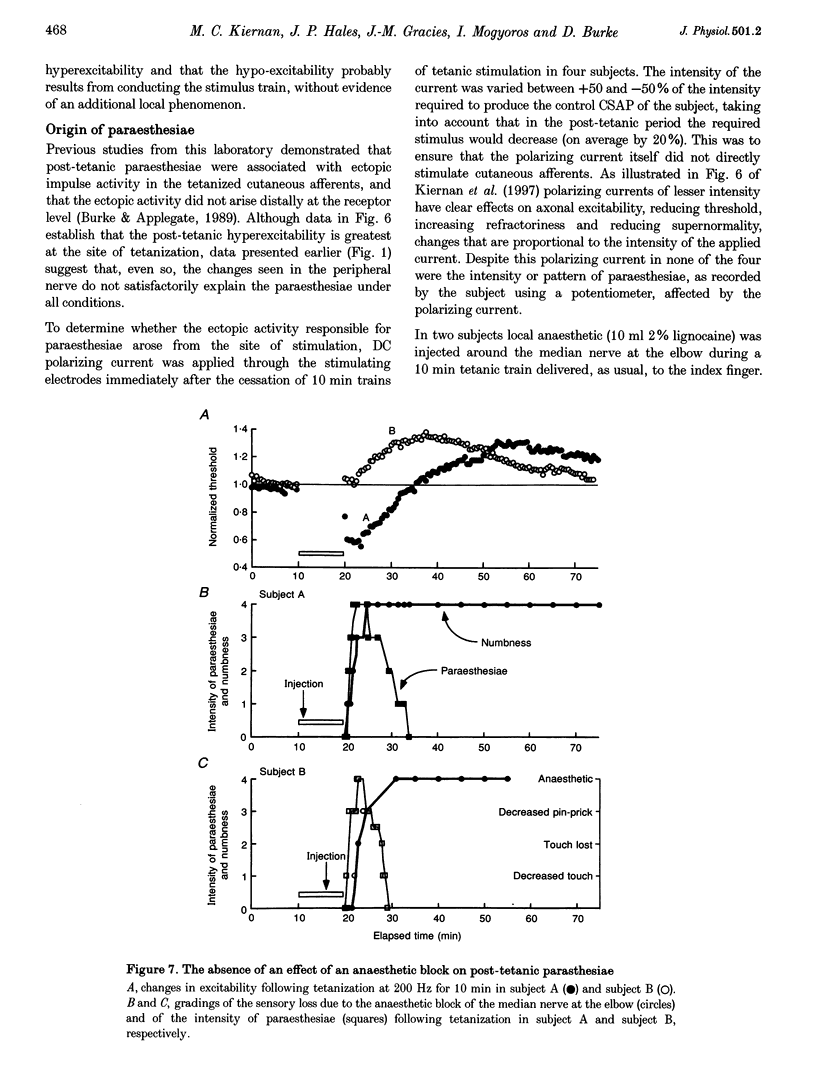
Abstract
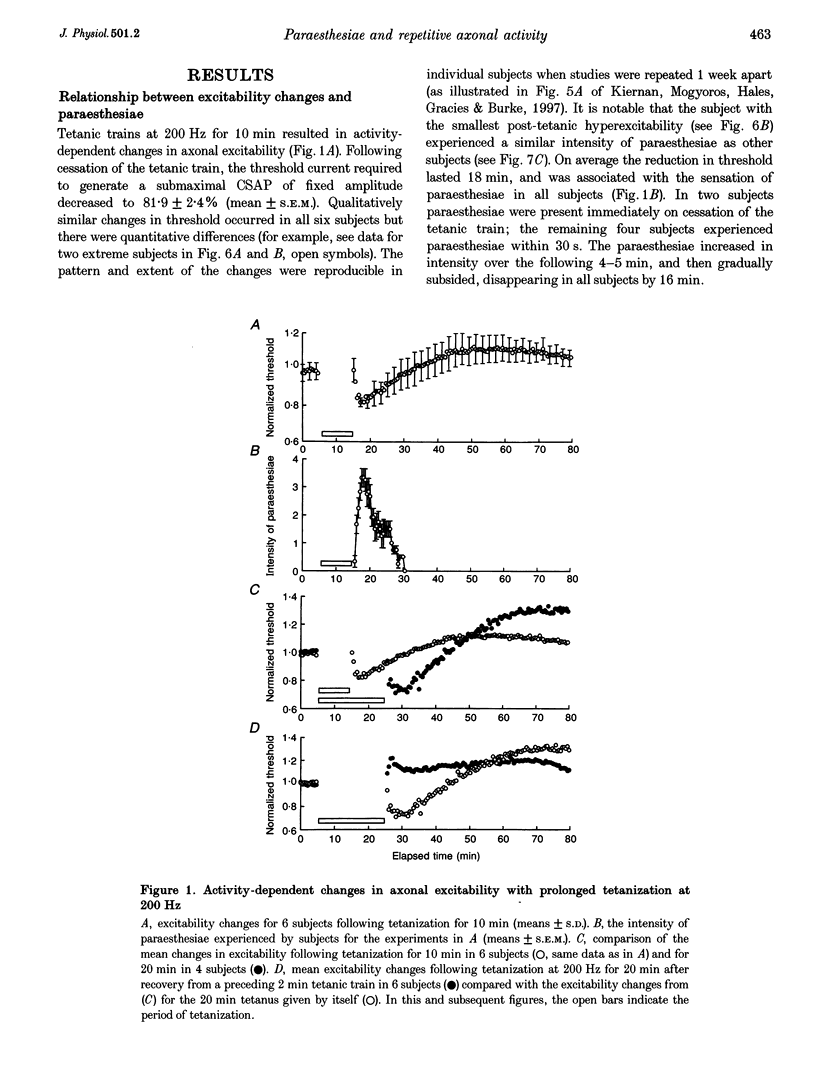
1. The present study has explored the behaviour of human cutaneous afferents following conduction of prolonged trains of impulses at 200 Hz for 10-20 min, correlating the resultant changes in excitability with the perception of paraesthesiae. 2. Tetanization for 10 min resulted in activity-dependent changes in axonal excitability, with an initial period of hyperexcitability, followed by a long-lasting subexcitability. All subjects experienced paraesthesiae soon after cessation of the tetanic train, and these subsided gradually over 16 min. 3. Longer tetanic trains of 20 min duration resulted in greater changes in axonal excitability, but with paraesthesiae of a similar time course. The post-tetanic increase in excitability was abolished when short tetanic trains were delivered > 30 min before long trains, but all subjects still experienced paraesthesiae. 4. Threshold distributions following tetanic stimulation for both 10 and 20 min established that all axons contributing to the sensory volley underwent a uniform pattern of post-tetanic threshold changes. There was no evidence of a bimodal distribution with some axons hyperpolarized and others depolarized, as occurs with motor axons. However, the excitability changes were graded, with axons of lowest threshold undergoing a proportionately greater increase in excitability than axons of higher threshold. 5. The post-tetanic excitability changes were greater at the site of stimulation than elsewhere along the peripheral nerve. However, DC polarizing currents applied at this site failed to alter the sensation of paraesthesiae in the post-tetanic period. Furthermore, local anaesthetic block of the peripheral nerve proximal to the stimulation site failed to suppress the paraesthesiae. 6. The uniform pattern of post-tetanic threshold changes for cutaneous afferents differs from the bimodal distribution seen with post-ischaemic and post-tetanic motor axons. This difference in behaviour may reflect greater inward rectification and greater expression of a non-inactivating threshold conductance in cutaneous afferents. It is suggested that the ectopic activity responsible for paraesthesiae in the post-tetanic period arises from a more central site than the peripheral nerve.
Full text
PDF

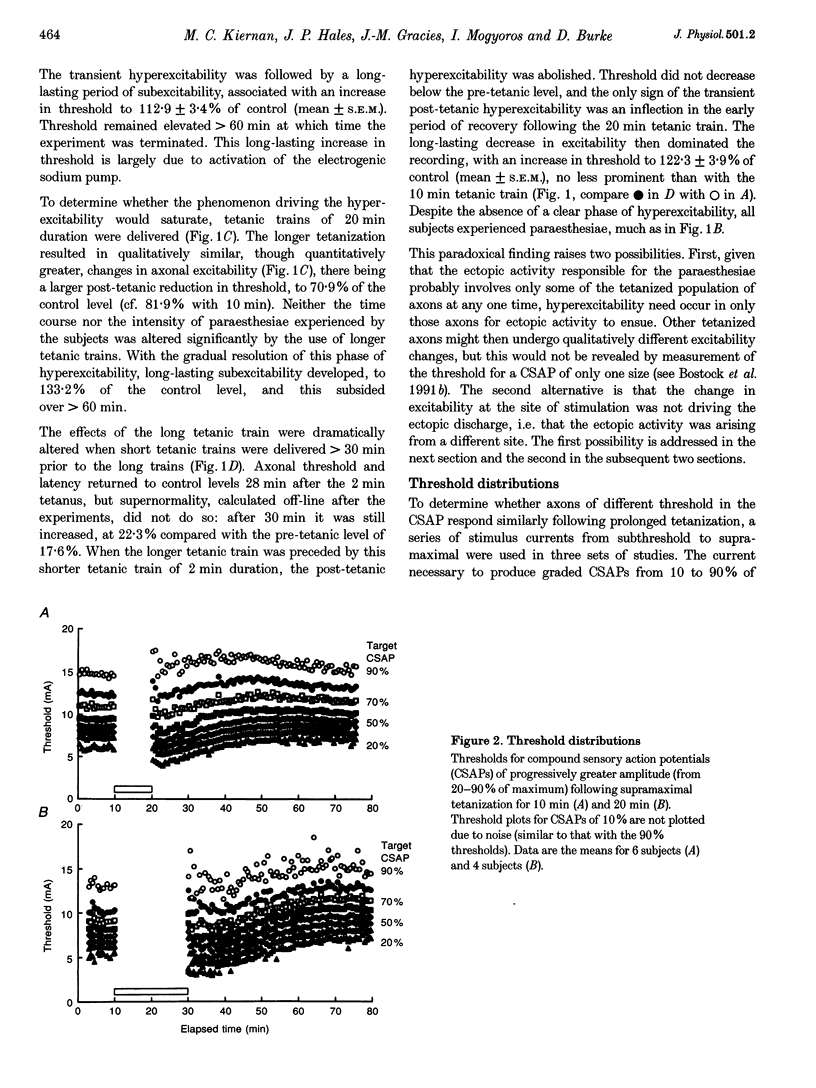
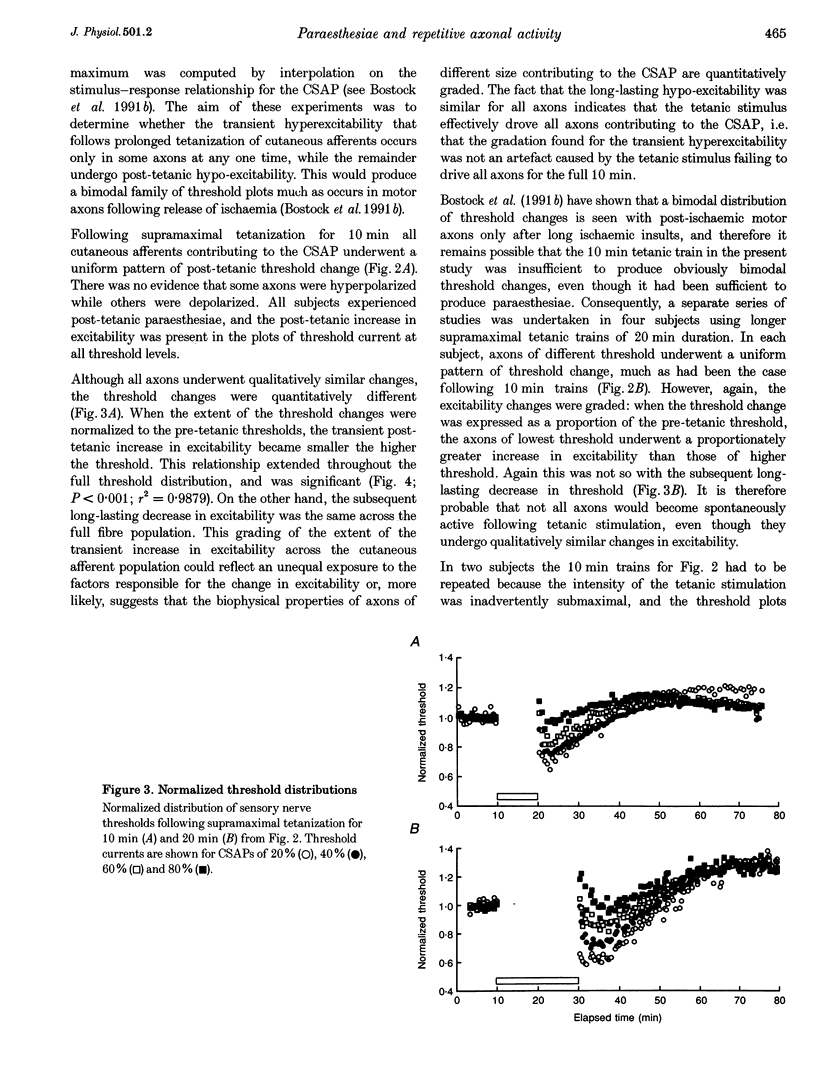
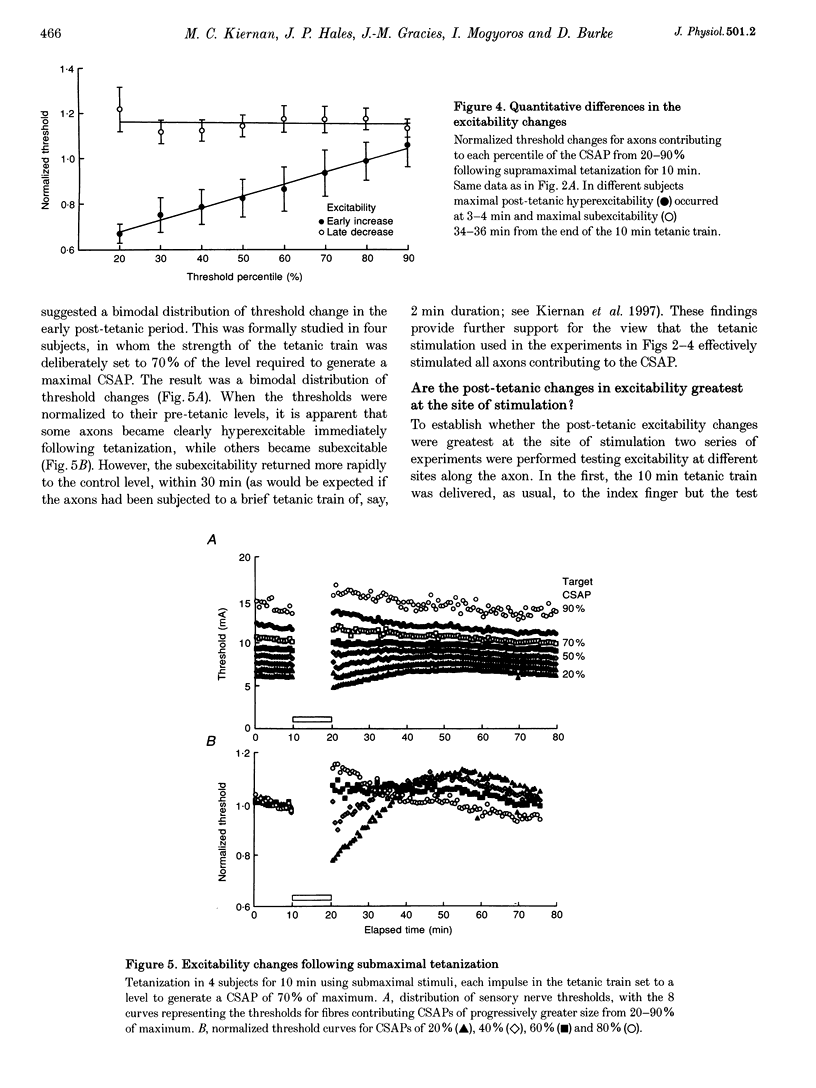



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Applegate C., Burke D. Changes in excitability of human cutaneous afferents following prolonged high-frequency stimulation. Brain. 1989 Feb;112(Pt 1):147–164. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.1.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barrett J. N. Intracellular recording from vertebrate myelinated axons: mechanism of the depolarizing afterpotential. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:117–144. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock H., Baker M., Grafe P., Reid G. Changes in excitability and accommodation of human motor axons following brief periods of ischaemia. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:513–535. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock H., Baker M., Reid G. Changes in excitability of human motor axons underlying post-ischaemic fasciculations: evidence for two stable states. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:537–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock H., Bergmans J. Post-tetanic excitability changes and ectopic discharges in a human motor axon. Brain. 1994 Oct;117(Pt 5):913–928. doi: 10.1093/brain/117.5.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock H., Burke D., Hales J. P. Differences in behaviour of sensory and motor axons following release of ischaemia. Brain. 1994 Apr;117(Pt 2):225–234. doi: 10.1093/brain/117.2.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock H., Grafe P. Activity-dependent excitability changes in normal and demyelinated rat spinal root axons. J Physiol. 1985 Aug;365:239–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock H., Rothwell J. C. Latent addition in motor and sensory fibres of human peripheral nerve. J Physiol. 1997 Jan 1;498(Pt 1):277–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp021857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Applegate C. Paraesthesiae and hypaesthesia following prolonged high-frequency stimulation of cutaneous afferents. Brain. 1989 Aug;112(Pt 4):913–929. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.4.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G., Barrett J. N., Barrett E. F. Activation of internodal potassium conductance in rat myelinated axons. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:177–202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felts P. A., Kapoor R., Smith K. J. A mechanism for ectopic firing in central demyelinated axons. Brain. 1995 Oct;118(Pt 5):1225–1231. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.5.1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon T. R., Kocsis J. D., Waxman S. G. Electrogenic pump (Na+/K(+)-ATPase) activity in rat optic nerve. Neuroscience. 1990;37(3):829–837. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90112-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor R., Smith K. J., Felts P. A., Davies M. Internodal potassium currents can generate ectopic impulses in mammalian myelinated axons. Brain Res. 1993 May 14;611(1):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91790-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan M. C., Mogyoros I., Hales J. P., Gracies J. M., Burke D. Excitability changes in human cutaneous afferents induced by prolonged repetitive axonal activity. J Physiol. 1997 Apr 1;500(Pt 1):255–264. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp022015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., David G., Barrett J. N., Barrett E. F. Posttetanic hyperpolarization produced by electrogenic Na(+)-K+ pump in lizard axons impaled near their motor terminals. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Nov;70(5):1874–1884. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.5.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape H. C. Queer current and pacemaker: the hyperpolarization-activated cation current in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1996;58:299–327. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.58.030196.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE J. M., STRAUB R. W. The hyperpolarization which follows activity in mammalian non-medullated fibres. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):80–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond S. A. Effects of nerve impulses on threshold of frog sciatic nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):273–303. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepfle G. M., Katholi C. R. Posttetanic changes in membrane potential of single medullated nerve fibers. Am J Physiol. 1973 Dec;225(6):1501–1507. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.6.1501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


