Abstract
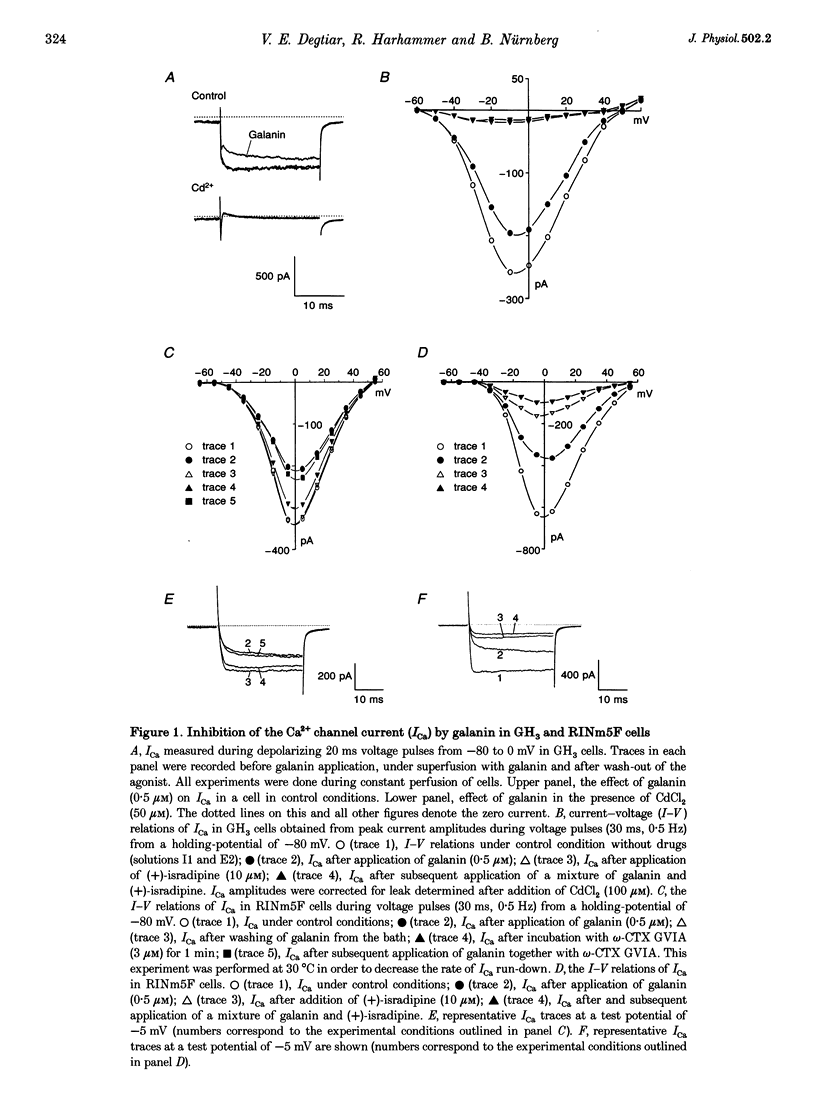
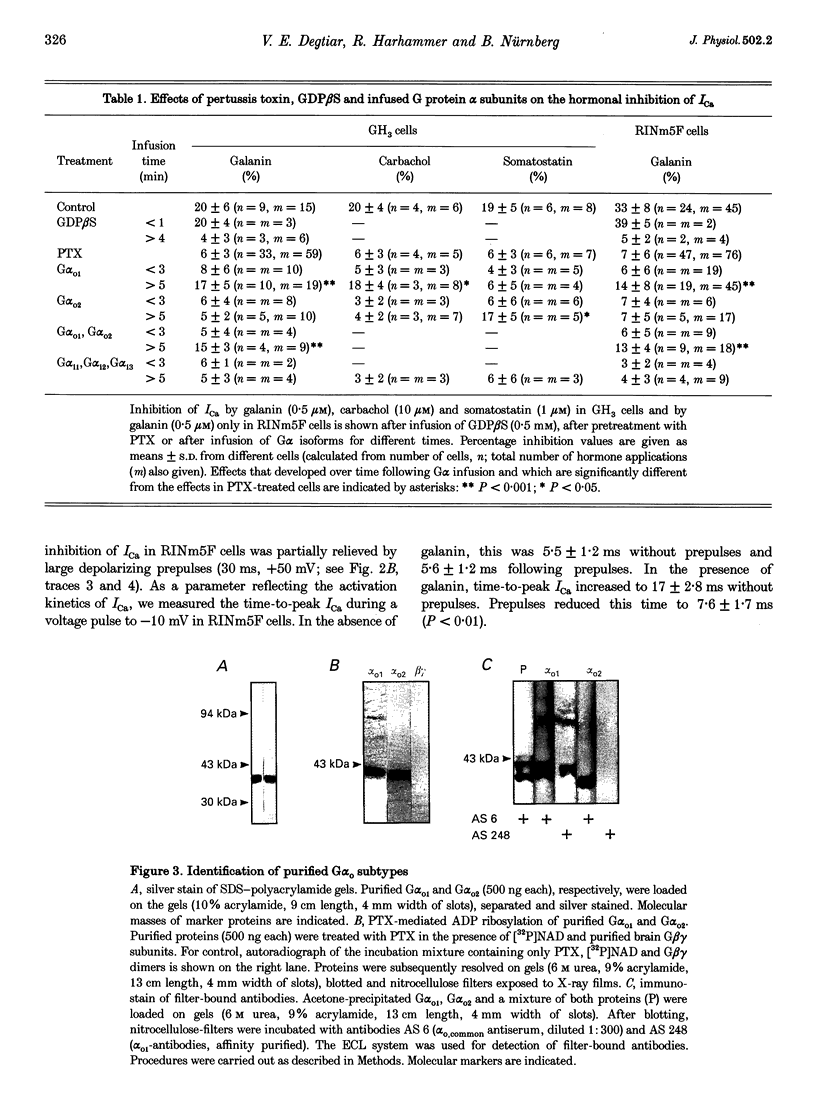
1. The present study examines the hypothesis of G protein subtype selectivity in receptor-induced inhibition of calcium channel currents (ICa) in the insulin-secreting RINm5F and pituitary GH3 rat cell lines. Specificity of receptor coupling to G proteins was studied by infusion of purified G alpha isoforms into cells via a patch pipette. 2. In RINm5F cells, the neuropeptide galanin inhibited dihydropyridine (DHP)- and omega-conotoxin-sensitive components of ICa and slowed down their activation kinetics. In GH3 cells, DHP-sensitive ICa was inhibited by galanin, as well as by somatostatin and carbachol. Agonist-induced ICa inhibition was suppressed by pertussis toxin (PTX) pretreatment of the cells. In PTX-pretreated cells of either cell line, the response to galanin was restored only by the G alpha o1 subunit. Following PTX treatment of GH3 cells, only the G alpha o1 subunit restored carbachol-induced inhibition of ICa, whereas only the G alpha o2 subunit restored somatostatin-induced inhibition of ICa. G(i) subtypes had no effect on ICa inhibition. 3. Both cell lines expressed two distinct immunoreactive Go proteins. Whereas in RINm5F cell membranes Go1 was found to be the predominant isoform, we detected more Go2 than Go1 in GH3 cell membranes. Nevertheless, all agonists stimulated incorporation of the photoreactive GTP analogue [alpha-32P]GTP azidoanilide into both G(o) isoforms. 4. The results indicate that the same Go subtype, i.e. Go1, mediates galanin-induced inhibition of ICa in both cell lines and that the Go subtype specificity of receptor-G protein coupling is confined to intact cells.
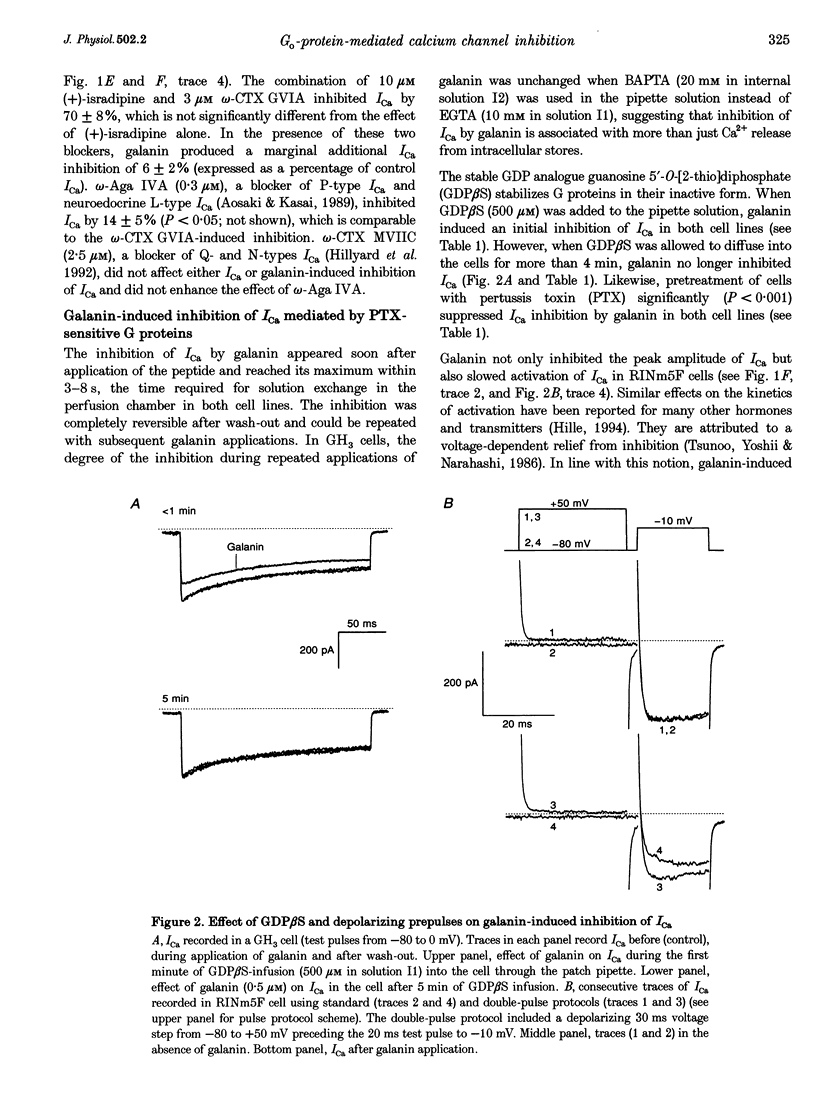
Full text
PDF


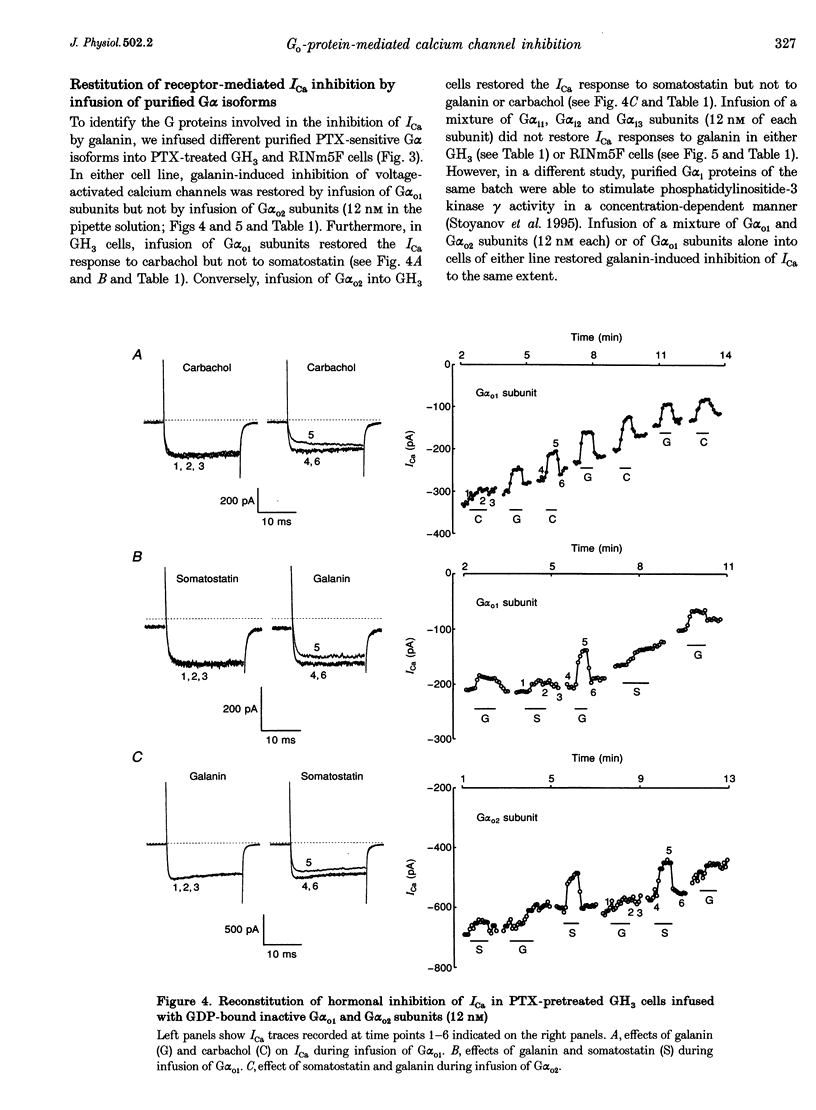




Images in this article
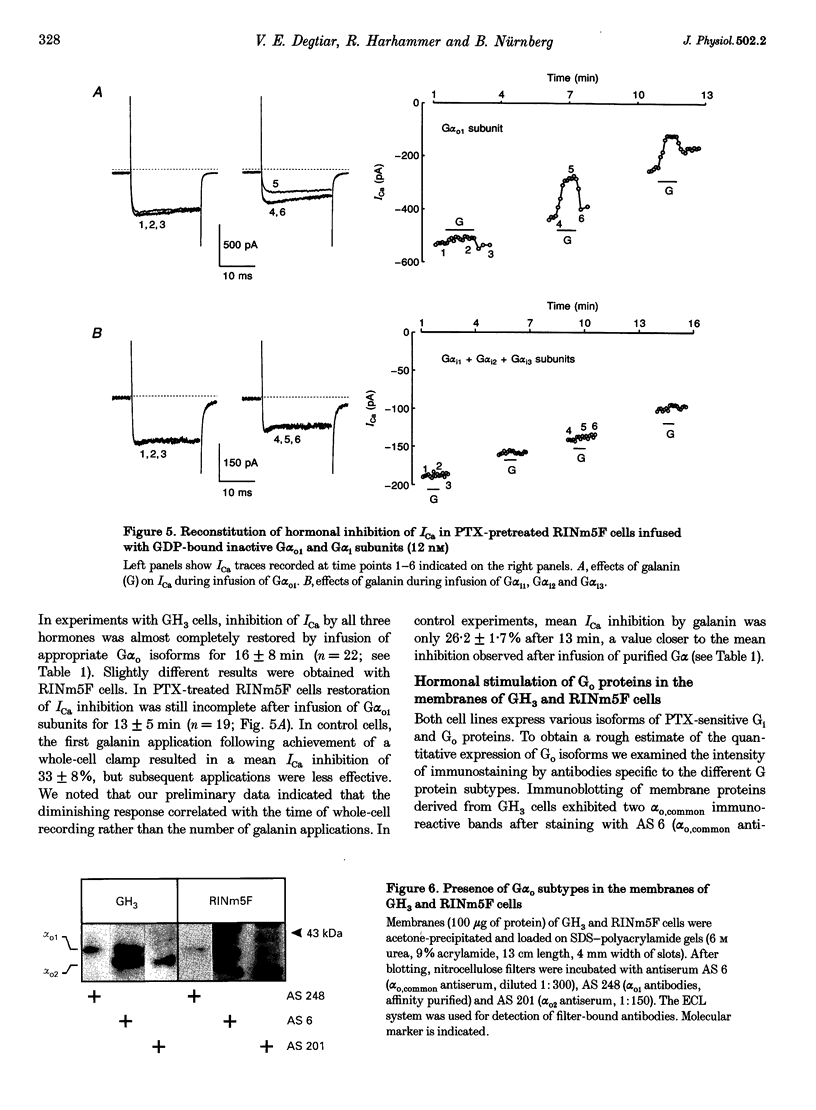
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aicardi G., Pollo A., Sher E., Carbone E. Noradrenergic inhibition and voltage-dependent facilitation of omega-conotoxin-sensitive Ca channels in insulin-secreting RINm5F cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80393-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aosaki T., Kasai H. Characterization of two kinds of high-voltage-activated Ca-channel currents in chick sensory neurons. Differential sensitivity to dihydropyridines and omega-conotoxin GVIA. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jun;414(2):150–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00580957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):153–156. doi: 10.1038/340153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedecs K., Berthold M., Bartfai T. Galanin--10 years with a neuroendocrine peptide. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;27(4):337–349. doi: 10.1016/1357-2725(95)00008-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. E., 3rd, Aguilar-Bryan L., Bryan J., Kunze D. L., Moss L., Nelson D. A., Rajan A. S., Raef H., Xiang H. D., Yaney G. C. Sulfonylurea signal transduction. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1991;47:299–317. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571147-0.50013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell V., Berrow N., Dolphin A. C. GABAB receptor modulation of Ca2+ currents in rat sensory neurones by the G protein G(0): antisense oligonucleotide studies. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:1–11. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Pfeuffer T. Mechanism of cholera toxin action: covalent modification of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W. J., Ying Y. S., Rothberg K. G., Hooper N. M., Turner A. J., Gambliel H. A., De Gunzburg J., Mumby S. M., Gilman A. G., Anderson R. G. Purification and characterization of smooth muscle cell caveolae. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):127–138. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Carty D. J., Birnbaumer L., Iyengar R. Purification of G proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1991;195:177–188. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)95164-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C. The G.L. Brown Prize Lecture. Voltage-dependent calcium channels and their modulation by neurotransmitters and G proteins. Exp Physiol. 1995 Jan;80(1):1–36. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1995.sp003825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawzi A. B., Fay D. S., Murphy E. A., Tamir H., Erdos J. J., Northup J. K. Rhodopsin and the retinal G-protein distinguish among G-protein beta gamma subunit forms. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12194–12200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollasch M., Haller H., Schultz G., Hescheler J. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone induces opposite effects on Ca2+ channel currents in pituitary cells by two pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10262–10266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Strnad J., Eppler C. M. Rat somatostatin receptor type 1 couples to G proteins and inhibition of cyclic AMP accumulation. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):410–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrave P. A., Hamm H. E., Hofmann K. P. Interaction of rhodopsin with the G-protein, transducin. Bioessays. 1993 Jan;15(1):43–50. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlitze S., Garcia D. E., Mackie K., Hille B., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Modulation of Ca2+ channels by G-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1996 Mar 21;380(6571):258–262. doi: 10.1038/380258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Modulation of ion-channel function by G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Dec;17(12):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillyard D. R., Monje V. D., Mintz I. M., Bean B. P., Nadasdi L., Ramachandran J., Miljanich G., Azimi-Zoonooz A., McIntosh J. M., Cruz L. J. A new Conus peptide ligand for mammalian presynaptic Ca2+ channels. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Biel M., Flockerzi V. Molecular basis for Ca2+ channel diversity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:399–418. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homaidan F. R., Sharp G. W., Nowak L. M. Galanin inhibits a dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ current in the RINm5f cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8744–8748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara Y., Yamada Y., Fujii Y., Gonoi T., Yano H., Yasuda K., Inagaki N., Seino Y., Seino S. Molecular diversity and functional characterization of voltage-dependent calcium channels (CACN4) expressed in pancreatic beta-cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Jan;9(1):121–130. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.1.7760845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R. Voltage-dependent modulation of N-type calcium channels by G-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1996 Mar 21;380(6571):255–258. doi: 10.1038/380255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iñiguez-Lluhi J., Kleuss C., Gilman A. G. The importance of G-protein beta lambda subunits. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;3(7):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90122-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalkbrenner F., Degtiar V. E., Schenker M., Brendel S., Zobel A., Heschler J., Wittig B., Schultz G. Subunit composition of G(o) proteins functionally coupling galanin receptors to voltage-gated calcium channels. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 2;14(19):4728–4737. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00154.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalkbrenner F., Dippel E., Wittig B., Schultz G. Specificity of interaction between receptor and G protein: use of antisense techniques to relate G-protein subunits to function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Nov 8;1314(1-2):125–139. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(96)00072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher D. J., Johnson G. L. Transducin inhibition of light-dependent rhodopsin phosphorylation: evidence for beta gamma subunit interaction with rhodopsin. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;34(4):452–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Selectivity in signal transduction determined by gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):832–834. doi: 10.1126/science.8094261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugwitz K. L., Spicher K., Schultz G., Offermanns S. Identification of receptor-activated G proteins: selective immunoprecipitation of photolabeled G-protein alpha subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1994;237:283–294. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(94)37069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. F., Yasuda K., Bell G. I., Reisine T. Gi alpha 3 and G(o) alpha selectively associate with the cloned somatostatin receptor subtype SSTR2. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10721–10727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liévano A., Bolden A., Horn R. Calcium channels in excitable cells: divergent genotypic and phenotypic expression of alpha 1-subunits. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 1):C411–C424. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.2.C411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R. Membrane organization in G-protein mechanisms. FASEB J. 1994 Sep;8(12):939–946. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.12.8088459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nürnberg B., Ahnert-Hilger G. Potential roles of heterotrimeric G proteins of the endomembrane system. FEBS Lett. 1996 Jun 24;389(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00584-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nürnberg B., Gudermann T., Schultz G. Receptors and G proteins as primary components of transmembrane signal transduction. Part 2. G proteins: structure and function. J Mol Med (Berl) 1995 Mar;73(3):123–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00198240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nürnberg B., Spicher K., Harhammer R., Bosserhoff A., Frank R., Hilz H., Schultz G. Purification of a novel G-protein alpha 0-subtype from mammalian brain. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 1;300(Pt 2):387–394. doi: 10.1042/bj3000387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obukhov A. G., Harteneck C., Zobel A., Harhammer R., Kalkbrenner F., Leopoldt D., Lückhoff A., Nürnberg B., Schultz G. Direct activation of trpl cation channels by G alpha11 subunits. EMBO J. 1996 Nov 1;15(21):5833–5838. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Gollasch M., Hescheler J., Spicher K., Schmidt A., Schultz G., Rosenthal W. Inhibition of voltage-dependent Ca2+ currents and activation of pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins via muscarinic receptors in GH3 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):995–1002. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Schultz G. Complex information processing by the transmembrane signaling system involving G proteins. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Oct;350(4):329–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00178947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. J., Cerione R. A. Rhodopsin/transducin interactions. I. Characterization of the binding of the transducin-beta gamma subunit complex to rhodopsin using fluorescence spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17032–17039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollo A., Lovallo M., Biancardi E., Sher E., Socci C., Carbone E. Sensitivity to dihydropyridines, omega-conotoxin and noradrenaline reveals multiple high-voltage-activated Ca2+ channels in rat insulinoma and human pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Jun;423(5-6):462–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00374942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Hescheler J., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Hinsch K. D., Klinz F. J., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Gausepohl H., Frank R. Involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins in the hormonal inhibition of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ currents in an insulin-secreting cell line (RINm5F). J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18025–18033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher E., Biancardi E., Pollo A., Carbone E., Li G., Wollheim C. B., Clementi F. omega-Conotoxin-sensitive, voltage-operated Ca2+ channels in insulin-secreting cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun 17;216(3):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90438-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicher K., Klinz F. J., Rudolph U., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Schultz G., Rosenthal W. Identification of the G-protein alpha-subunit encoded by alpha o2 cDNA as a 39 kDa pertussis toxin substrate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicher K., Nuernberg B., Jäger B., Rosenthal W., Schultz G. Heterogeneity of three electrophoretically distinct Go alpha-subunits in mammalian brain. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 28;307(2):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80770-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C. The purified alpha subunits of Go and Gi from bovine brain require beta gamma for association with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):631–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swandulla D., Carbone E., Lux H. D. Do calcium channel classifications account for neuronal calcium channel diversity? Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):46–51. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90018-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunoo A., Yoshii M., Narahashi T. Block of calcium channels by enkephalin and somatostatin in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9832–9836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verchere C. B., Kwok Y. N., Brown J. C. Stimulus-specific inhibition of insulin release from rat pancreas by both rat and porcine galanin. Life Sci. 1992;51(25):1945–1951. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Feldman D. H., McCue A. F., Brenner R., Velicelebi G., Ellis S. B., Harpold M. M. Structure and functional expression of alpha 1, alpha 2, and beta subunits of a novel human neuronal calcium channel subtype. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90109-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaney G. C., Wheeler M. B., Wei X., Perez-Reyes E., Birnbaumer L., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Moss L. G. Cloning of a novel alpha 1-subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel from the beta-cell. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;6(12):2143–2152. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1337146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]