Abstract
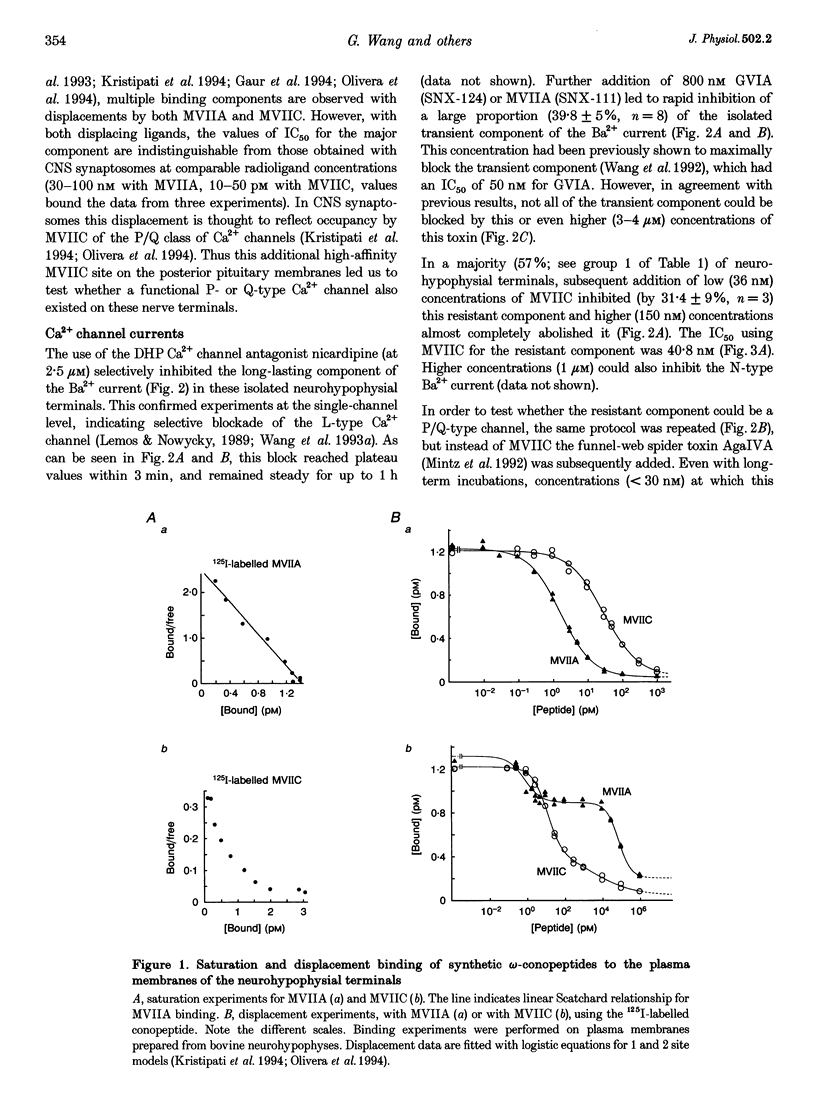
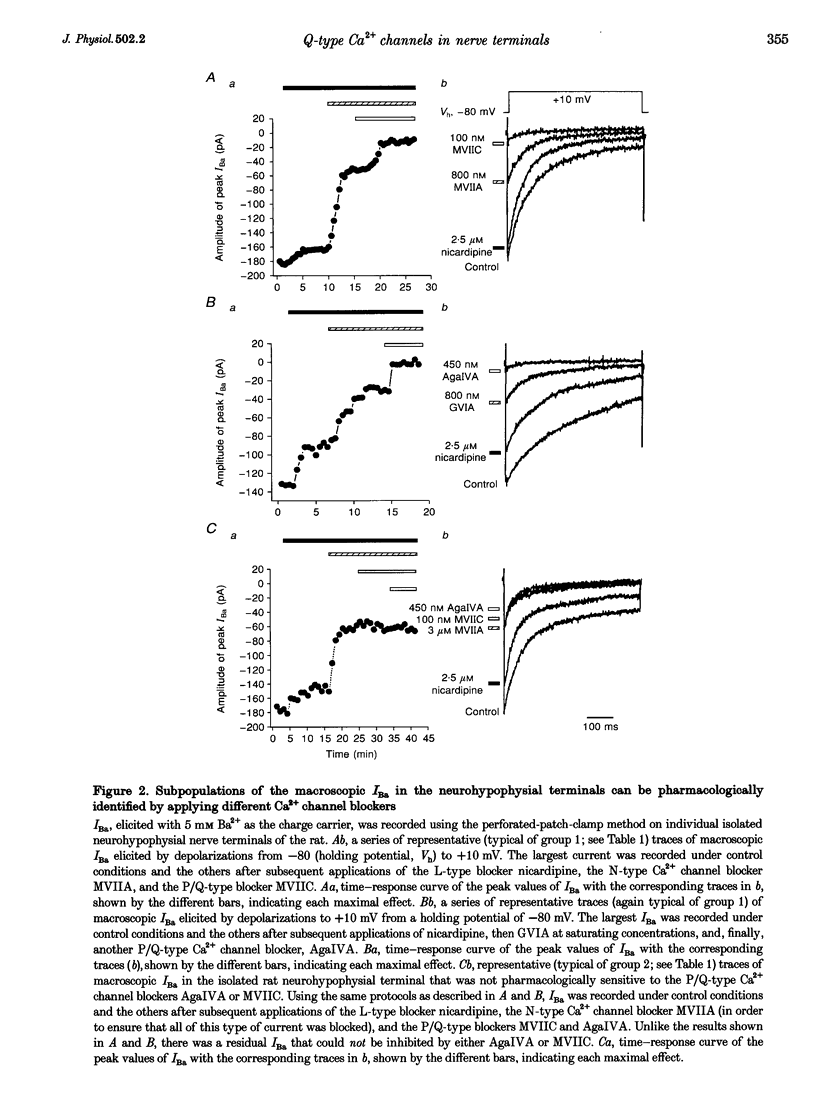
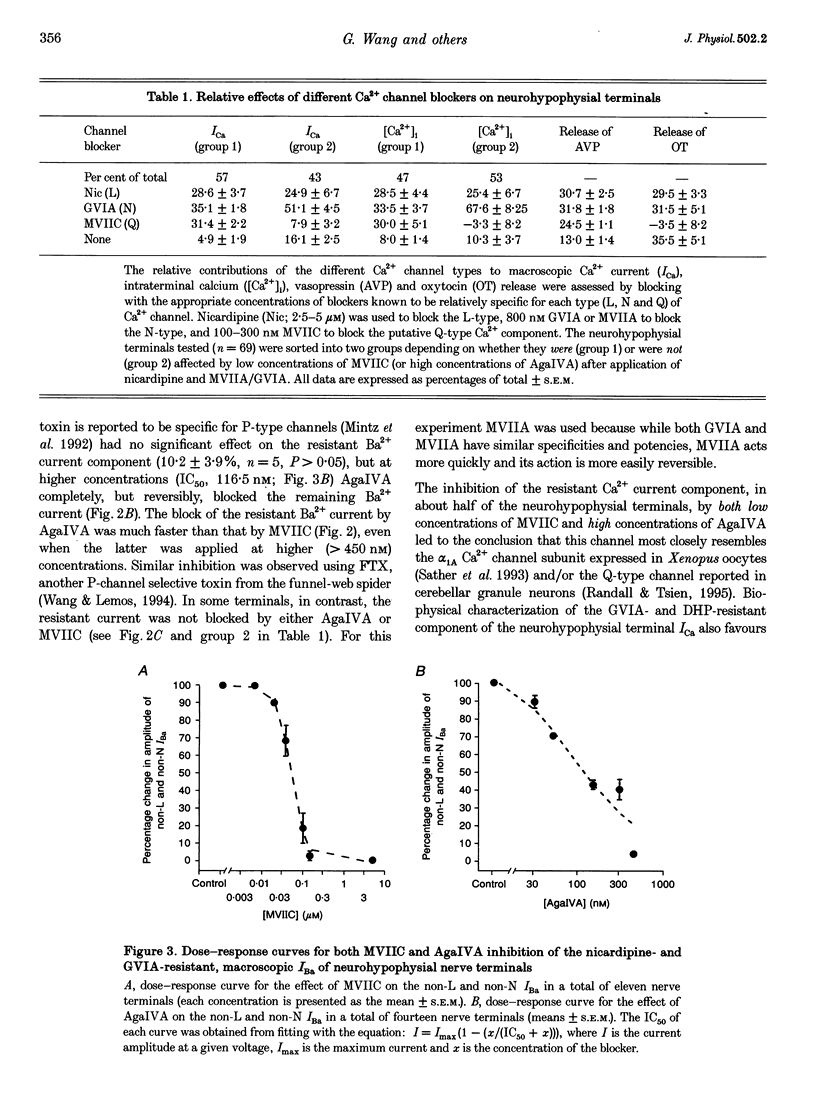
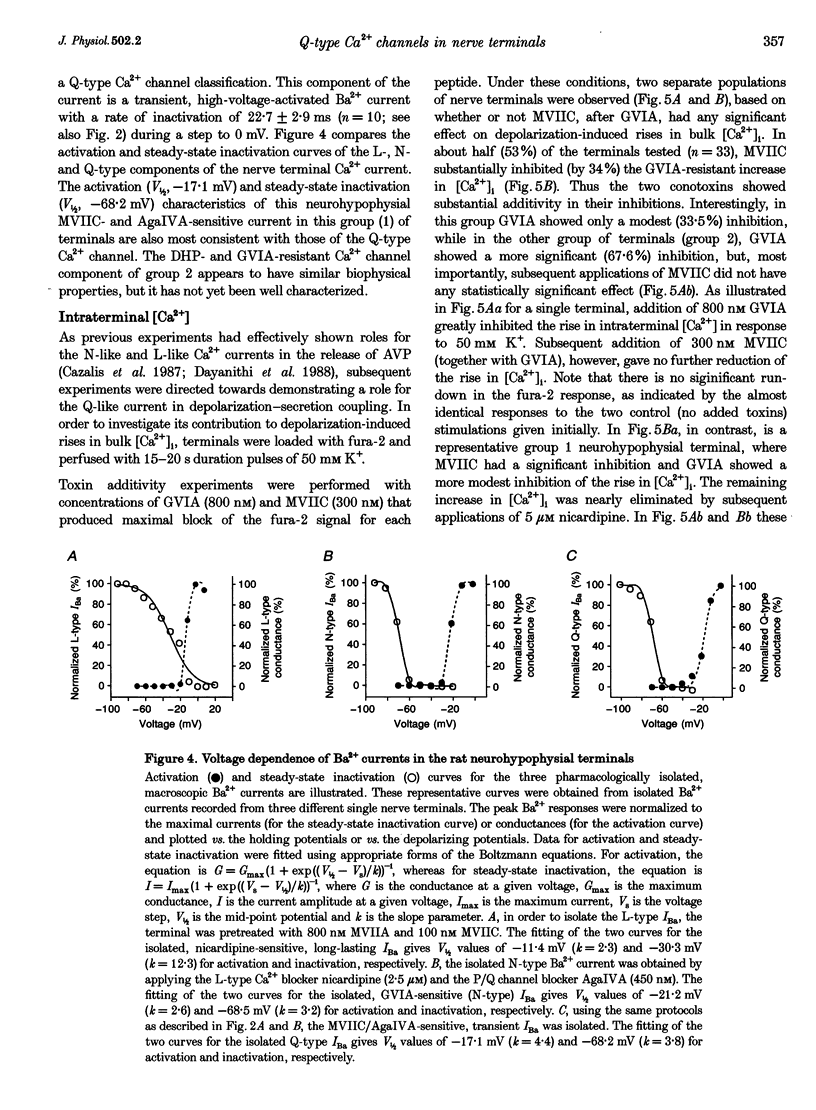
1. The nerve endings of rat neurohypophyses were acutely dissociated and a combination of pharmacological, biophysical and biochemical techniques was used to determine which classes of Ca2+ channels on these central nervous system (CNS) terminals contribute functionally to arginine vasopressin (AVP) and oxytocin (OT) secretion. 2. Purified neurohypophysial plasma membranes not only had a single high-affinity binding site for the N-channel-specific omega-conopeptide MVIIA, but also a distinct high-affinity site for another omega-conopeptide (MVIIC), which affects both N- and P/Q-channels. 3. Neurohypophysial terminals exhibited, besides L- and N-type currents, another component of the Ca2+ current that was only blocked by low concentrations of MVIIC or by high concentrations of omega-AgaIVA, a P/Q-channel-selective spider toxin. 4. This Ca2+ current component had pharmacological and biophysical properties similar to those described for the fast-inactivating form of the P/Q-channel class, suggesting that in the neurohypophysial terminals this current is mediated by a 'Q'-type channel. 5. Pharmacological additivity studies showed that this Q-component contributed to rises in intraterminal Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) in only half of the terminals tested. 6. Furthermore, the non-L- and non-N-component of Ca(2+)-dependent AVP release, but not OT release, was effectively abolished by the same blockers of Q-type current. 7. Thus Q-channels are present on a subset of the neurohypophysial terminals where, in combination with N- and L-channels, they control AVP but not OT peptide neurosecretion.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. E., Myers R. A., Imperial J. S., Olivera B. M. Toxityping rat brain calcium channels with omega-toxins from spider and cone snail venoms. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12566–12570. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazalis M., Dayanithi G., Nordmann J. J. Hormone release from isolated nerve endings of the rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:55–70. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayanithi G., Martin-Moutot N., Barlier S., Colin D. A., Kretz-Zaepfel M., Couraud F., Nordmann J. J. The calcium channel antagonist omega-conotoxin inhibits secretion from peptidergic nerve terminals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):255–262. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K., Luebke J. I., Turner T. J. Exocytotic Ca2+ channels in mammalian central neurons. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Feb;18(2):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinor P. T., Zhang J. F., Randall A. D., Zhou M., Schwarz T. L., Tsien R. W., Horne W. A. Functional expression of a rapidly inactivating neuronal calcium channel. Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):455–458. doi: 10.1038/363455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher T. E., Bourque C. W. Distinct omega-agatoxin-sensitive calcium currents in somata and axon terminals of rat supraoptic neurones. J Physiol. 1995 Dec 1;489(Pt 2):383–388. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp021059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur S., Newcomb R., Rivnay B., Bell J. R., Yamashiro D., Ramachandran J., Miljanich G. P. Calcium channel antagonist peptides define several components of transmitter release in the hippocampus. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Oct;33(10):1211–1219. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(05)80012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillyard D. R., Monje V. D., Mintz I. M., Bean B. P., Nadasdi L., Ramachandran J., Miljanich G., Azimi-Zoonooz A., McIntosh J. M., Cruz L. J. A new Conus peptide ligand for mammalian presynaptic Ca2+ channels. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristipati R., Nádasdi L., Tarczy-Hornoch K., Lau K., Miljanich G. P., Ramachandran J., Bell J. R. Characterization of the binding of omega-conopeptides to different classes of non-L-type neuronal calcium channels. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1994 Jun;5(3):219–228. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1994.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemos J. R., Nowycky M. C. Two types of calcium channels coexist in peptide-releasing vertebrate nerve terminals. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1419–1426. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim N. F., Nowycky M. C., Bookman R. J. Direct measurement of exocytosis and calcium currents in single vertebrate nerve terminals. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):449–451. doi: 10.1038/344449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindau M., Stuenkel E. L., Nordmann J. J. Depolarization, intracellular calcium and exocytosis in single vertebrate nerve endings. Biophys J. 1992 Jan;61(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81812-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Hillman D. E., Cherksey B. Distribution and functional significance of the P-type, voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in the mammalian central nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Sep;15(9):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90053-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miljanich G. P., Ramachandran J. Antagonists of neuronal calcium channels: structure, function, and therapeutic implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1995;35:707–734. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.35.040195.003423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Venema V. J., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Bean B. P., Adams M. E. P-type calcium channels blocked by the spider toxin omega-Aga-IVA. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):827–829. doi: 10.1038/355827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., McIntosh J. M., Cruz L. J., Luque F. A., Gray W. R. Purification and sequence of a presynaptic peptide toxin from Conus geographus venom. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 23;23(22):5087–5090. doi: 10.1021/bi00317a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Miljanich G. P., Ramachandran J., Adams M. E. Calcium channel diversity and neurotransmitter release: the omega-conotoxins and omega-agatoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:823–867. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.004135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J., Cooper K., Gates P., Watsky M. Low access resistance perforated patch recordings using amphotericin B. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 Mar;37(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90017-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall A., Tsien R. W. Pharmacological dissection of multiple types of Ca2+ channel currents in rat cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurosci. 1995 Apr;15(4):2995–3012. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-04-02995.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Chung S., Levitan I. B. A family of calcium-dependent potassium channels from rat brain. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1031–1041. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Measurements of exocytosis from single presynaptic nerve terminals reveal heterogeneous inhibition by Ca(2+)-channel blockers. Neuron. 1995 Apr;14(4):773–779. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather W. A., Tanabe T., Zhang J. F., Mori Y., Adams M. E., Tsien R. W. Distinctive biophysical and pharmacological properties of class A (BI) calcium channel alpha 1 subunits. Neuron. 1993 Aug;11(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90185-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Reiner P. B. Ca2+ channels: diversity of form and function. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Jun;2(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90111-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stea A., Tomlinson W. J., Soong T. W., Bourinet E., Dubel S. J., Vincent S. R., Snutch T. P. Localization and functional properties of a rat brain alpha 1A calcium channel reflect similarities to neuronal Q- and P-type channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10576–10580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Ellinor P. T., Horne W. A. Molecular diversity of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Sep;12(9):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90595-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G., Lemos J. R. Effects of funnel web spider toxin on Ca2+ currents in neurohypophysial terminals. Brain Res. 1994 Nov 14;663(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91266-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Treistman S. N., Lemos J. R. Single channel recordings of Nt- and L-type Ca2+ currents in rat neurohypophysial terminals. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Oct;70(4):1617–1628. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.4.1617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Treistman S. N., Lemos J. R. Two types of high-threshold calcium currents inhibited by omega-conotoxin in nerve terminals of rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:181–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler D. B., Randall A., Tsien R. W. Roles of N-type and Q-type Ca2+ channels in supporting hippocampal synaptic transmission. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):107–111. doi: 10.1126/science.7832825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. F., Randall A. D., Ellinor P. T., Horne W. A., Sather W. A., Tanabe T., Schwarz T. L., Tsien R. W. Distinctive pharmacology and kinetics of cloned neuronal Ca2+ channels and their possible counterparts in mammalian CNS neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Nov;32(11):1075–1088. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90003-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



