Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in Figures 7 and 8 as published. “R300 P.V./TNF alpha” at Figure 6 was mistakenly used again for “F300 P.V./IL-6” at Figure 7; “F100 P.P./TNF alpha” at Figure 6 was mistakenly used again for “F100 P.V./caspase-3” at Figure 8; “FIR300 P.V./IL6” at Figure 7 was mistakenly used gain for “F300 P.V./caspase-3” at Figure 8. The corrected Figure 7 and Figure 8 appear below. The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
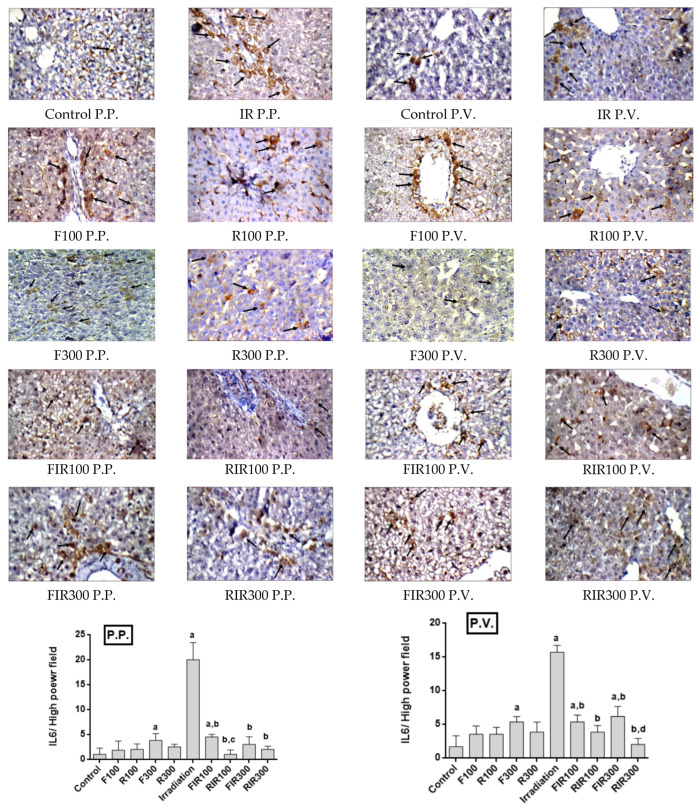
Figure 7.
Immunohistochemical photographs of IL-6 expression in hepatic peri-portal (P.P.) and peri-venular (P.V.) areas in irradiated rats treated with W. filifera and W. robusta leaves ethanolic extract (×400). Sections were taken from livers (P.P. and P.V.) of control rats showing rare expression. Sections taken from livers (P.P. and P.V.) of irradiated rats show extensive cytoplasmic expression (brown color). Sections taken from livers (P.P. and P.V.) of irradiated rats treated with W. filifera or W. robusta show medium to limited expression (brown color). Data conveyed as mean ± SD (n = 6), significance was at p ≤ 0.05 by means of one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer as a post hoc-test. a Significantly different as of control group. b Significantly different as of irradiated group. c Significantly different as of FIR100 group. d Significantly different as of FIR300 group.
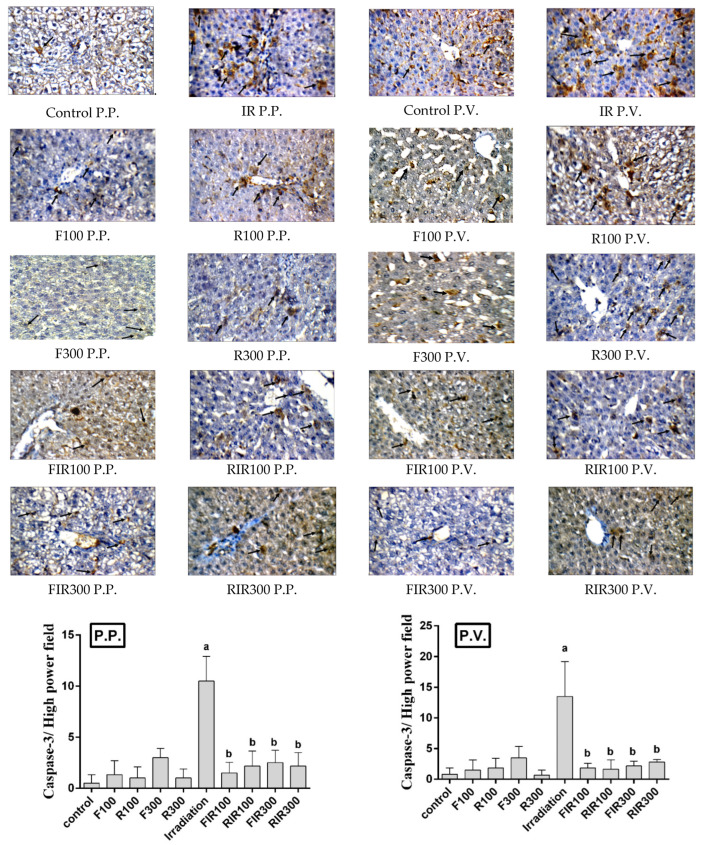
Figure 8.
Immunohistochemical photographs of caspase-3 expression in hepatic peri-portal (P.P.) and peri-venular (P.V.) (black arrows) areas in irradiated rats treated with W. filifera and W. robusta leaves ethanolic extracts (×400). Sections taken from livers (P.P. and P.V.) of control rats showing minimal expression. Sections taken from livers (P.P. and P.V.) of irradiated rats shows extensive cytoplasmic expression (brown color). Sections taken from livers (P.P. and P.V.) of irradiated rats treated with W. filifera or W. robusta showing medium to limited expression (brown color). Data conveyed as mean ± SD (n = 6), significance was at p ≤ 0.05 by means of one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer as a post hoc-test. a Significantly different as of control group. b Significantly different as of irradiated group.
Footnotes
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
Reference
- 1.Selim N.M., El-Hawary S.S., El Zalabani S.M., Shamma R.N., Mahdy N.E.S., Sherif N.H., Fahmy H.A., Mekkawy M.H., Yasri A., Sobeh M. Impact of Washingtonia robusta Leaves on Gamma Irradiation-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats and Correlation with STING Pathway and Phenolic Composition. Pharmaceuticals. 2020;13:320. doi: 10.3390/ph13100320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]