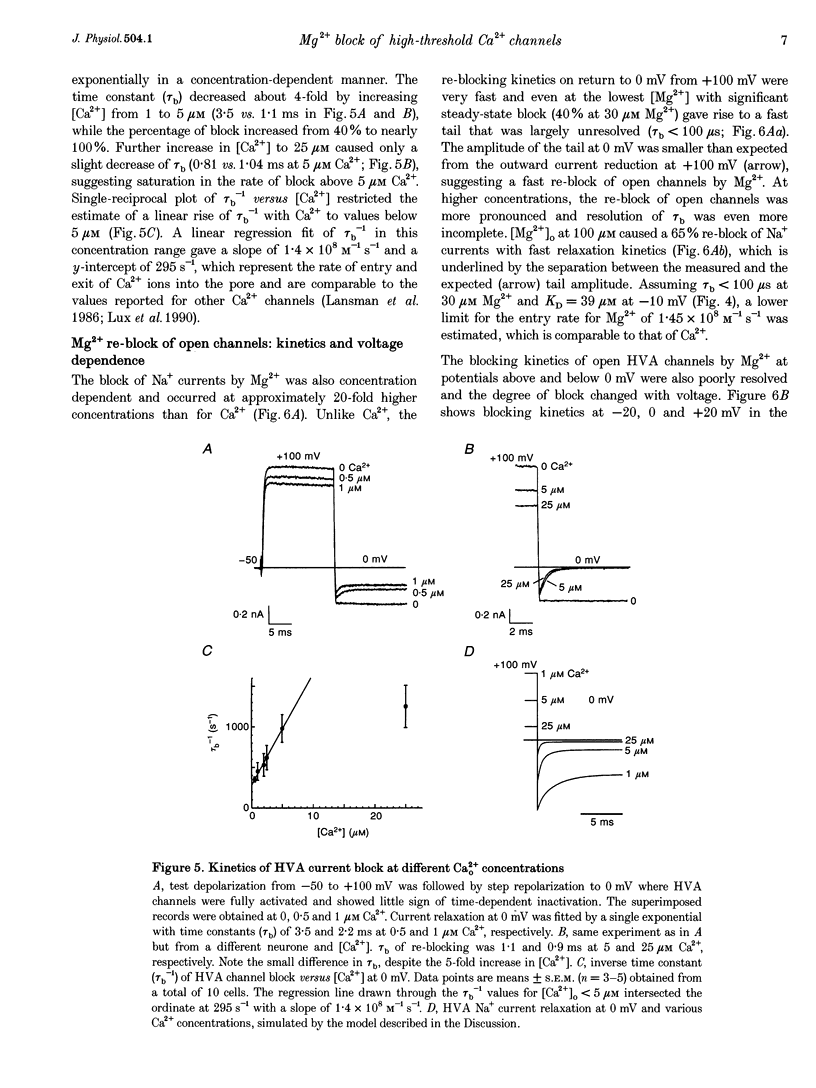
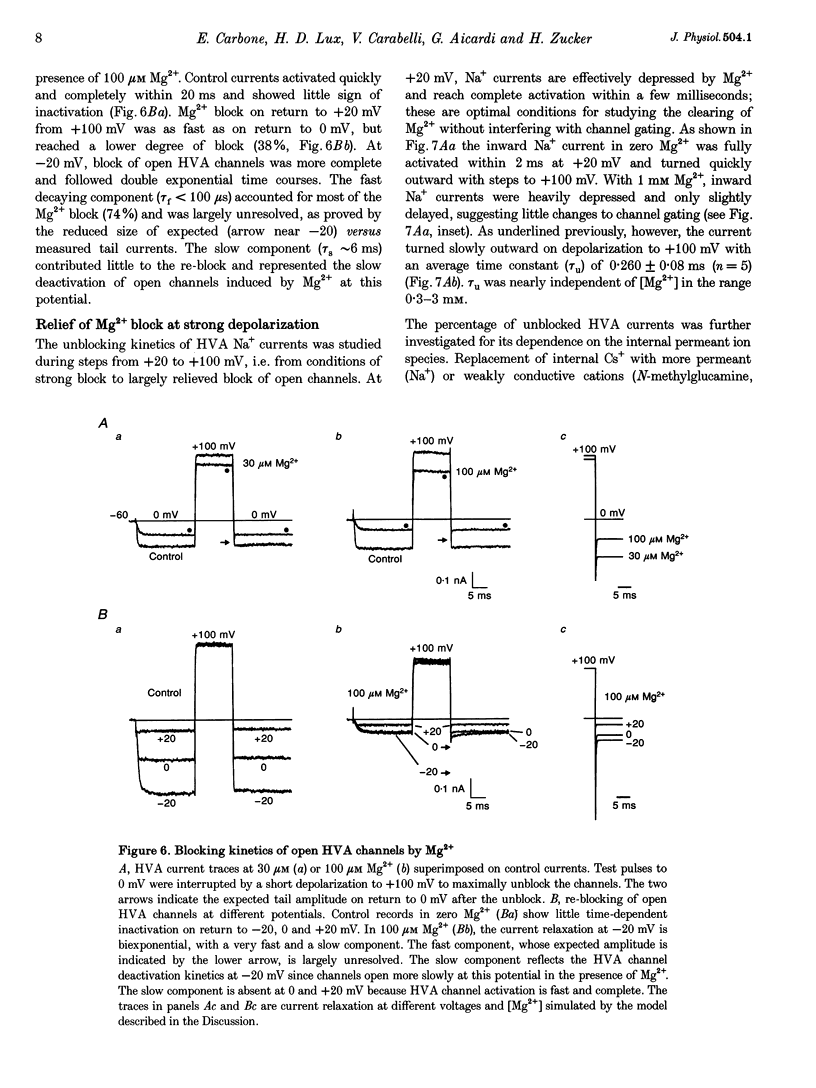
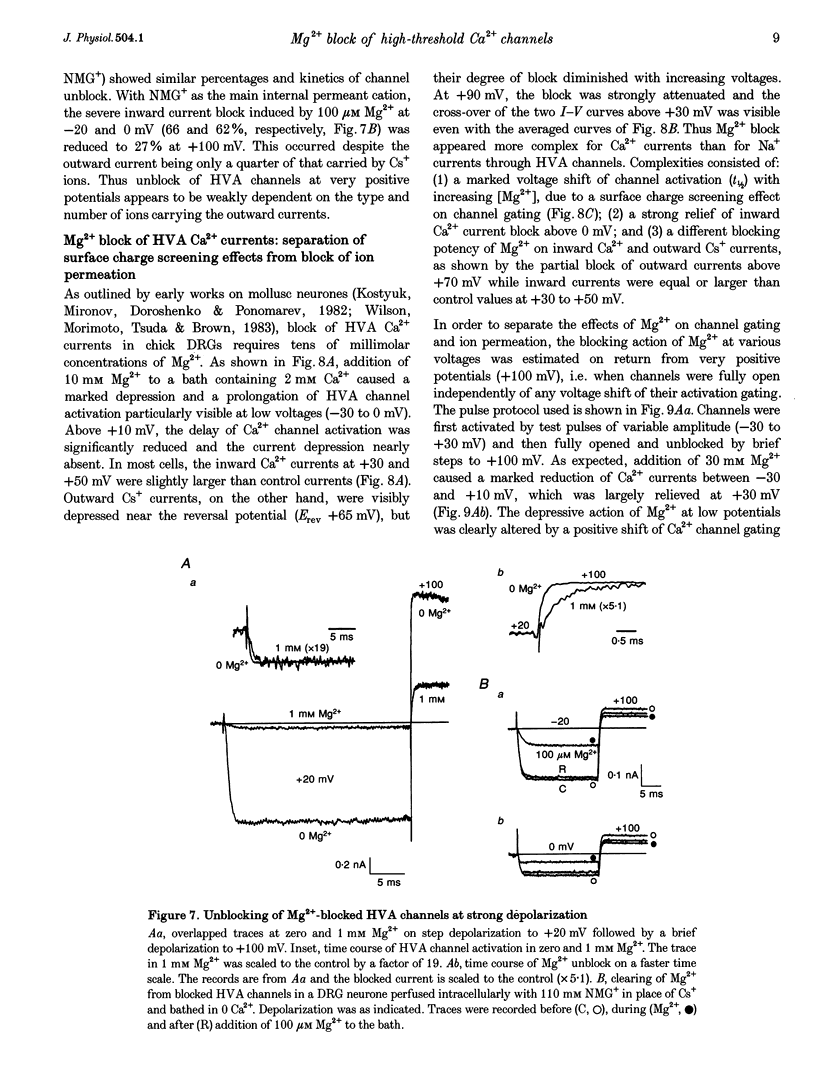
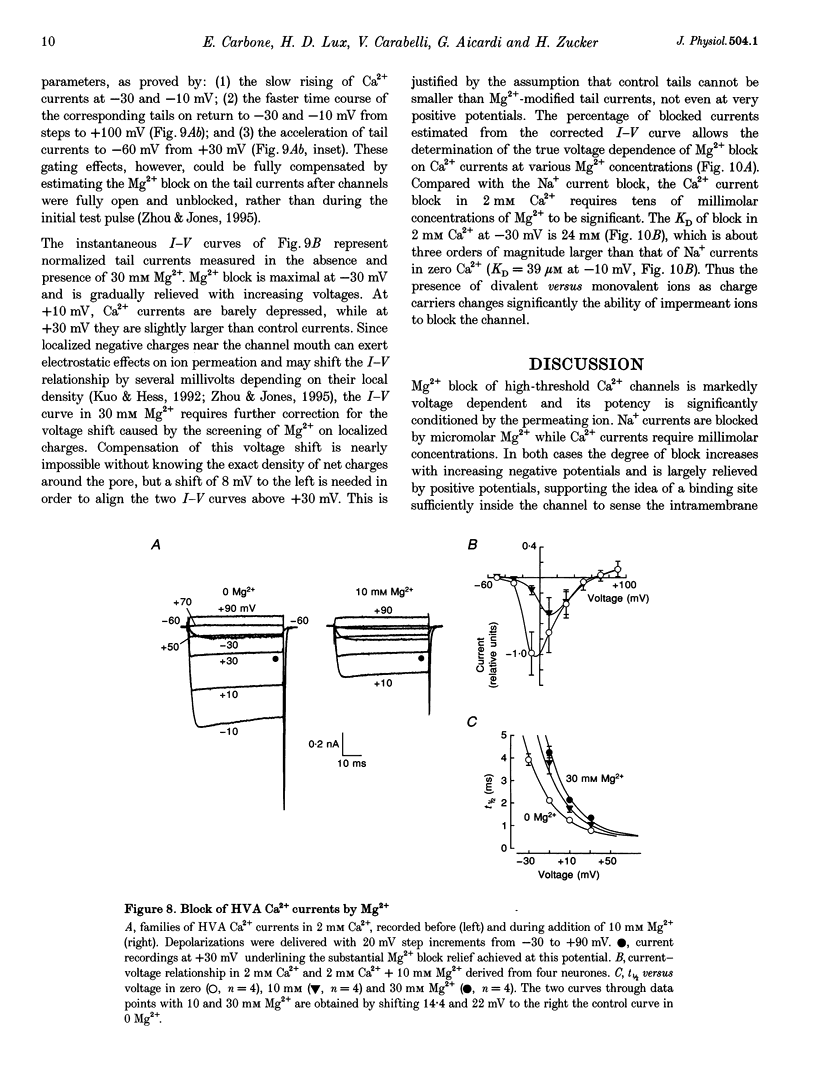
Abstract
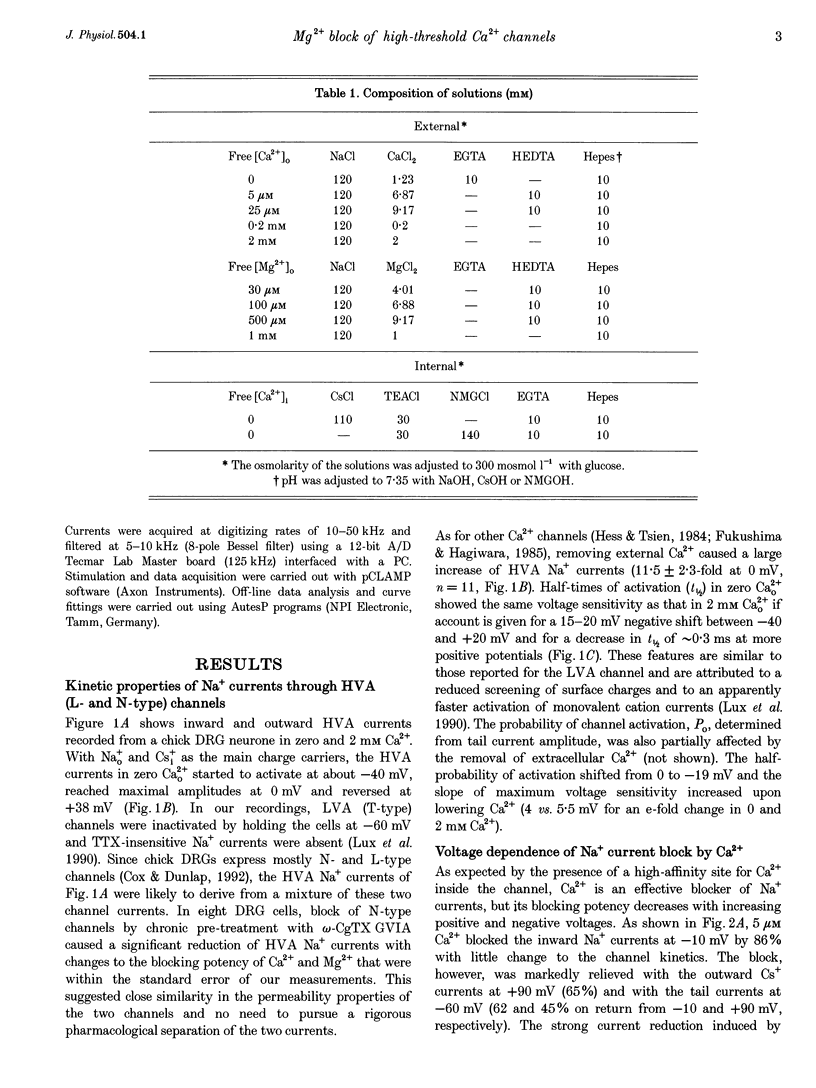
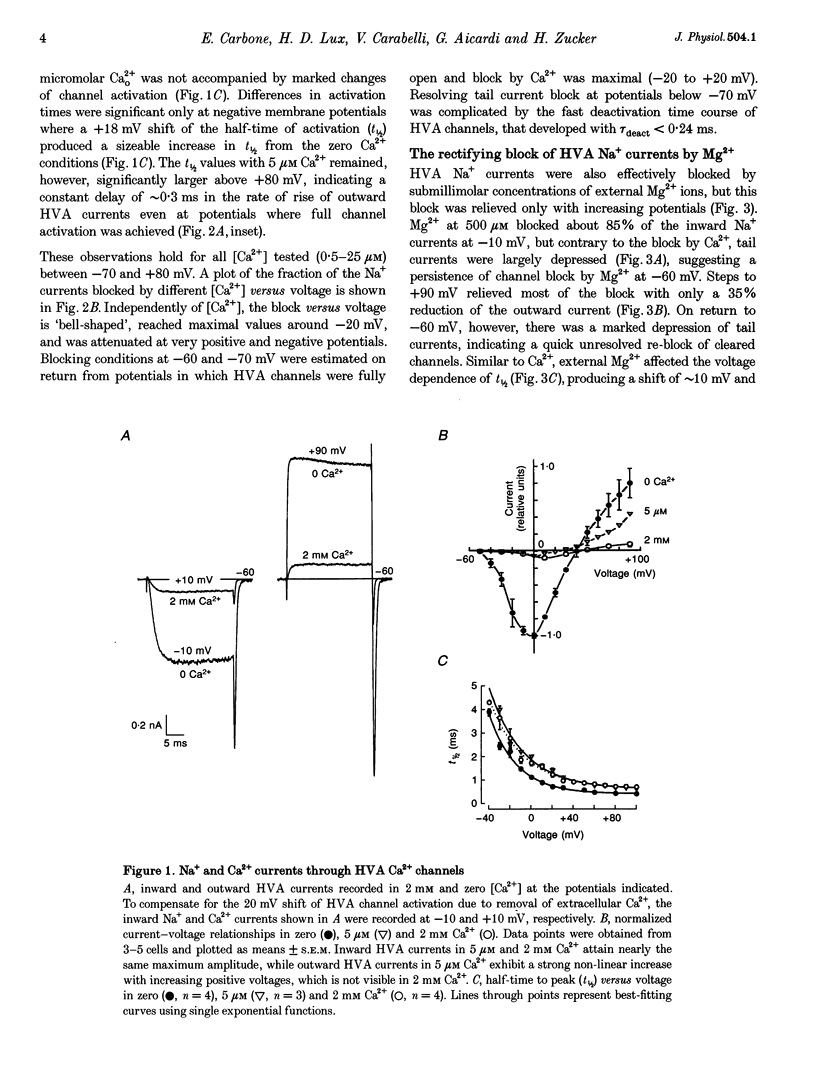
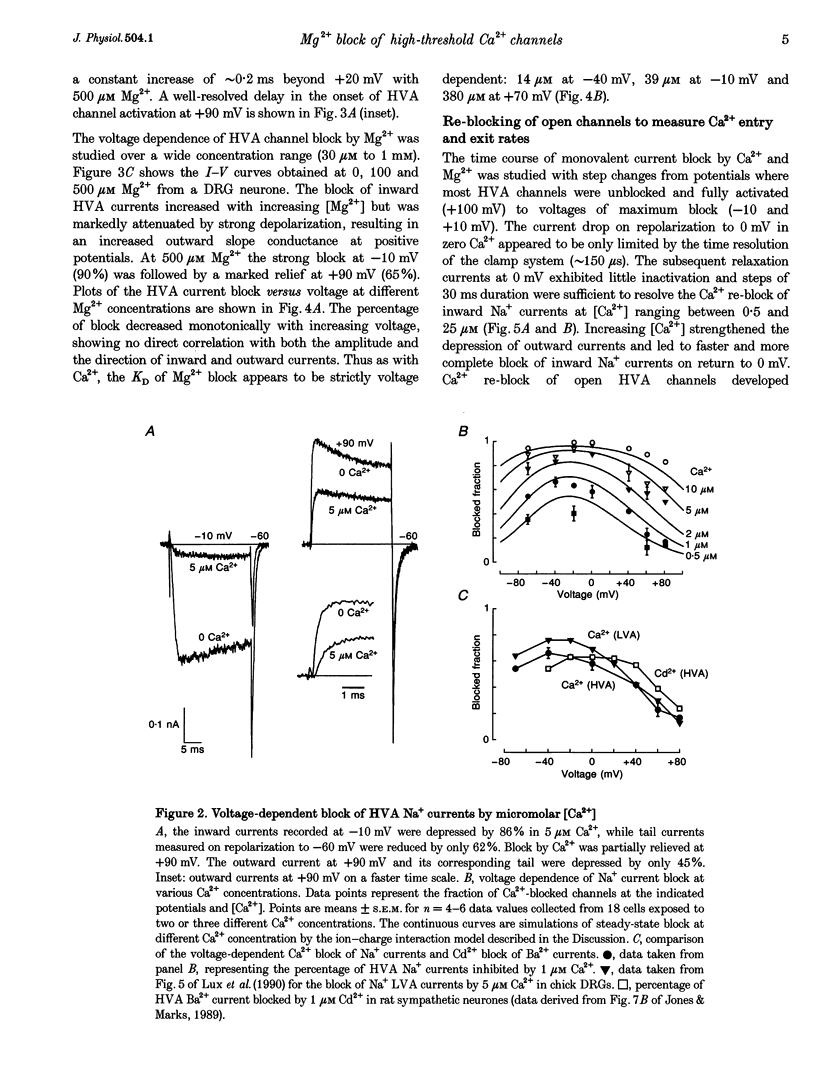
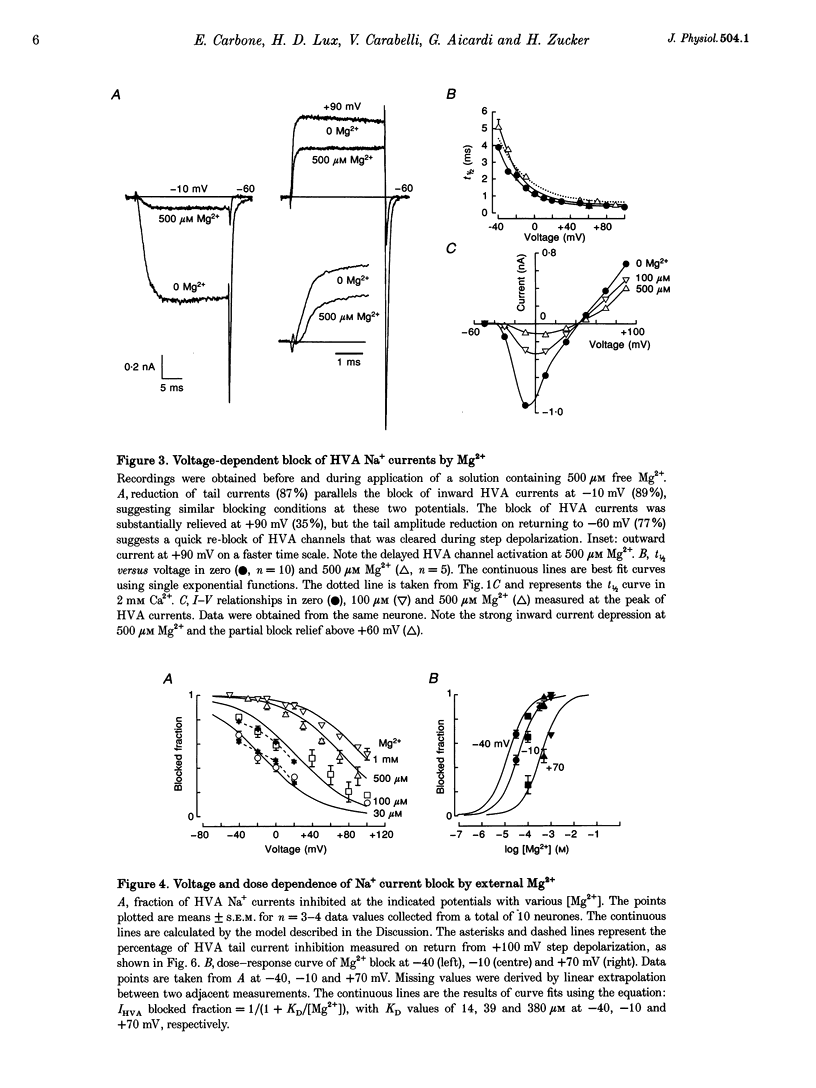
1. The Mg2+ block of Na+ and Ca2+ currents through high-voltage activated (HVA; L- and N-type) Ca2+ channels was studied in chick dorsal root ganglion neurones. 2. In low extracellular [Ca2+] (< 10(-8) M) and with Na+o and Cs+i as the main charge carriers (120 mM), HVA Na+ currents started to activate at -40 mV, reached inward peak values near 0 mV and reversed at about +40 mV. 3. Addition of 30-500 microM Mg2+ to the bath caused a strong depression of inward Na+ currents that was voltage and dose dependent (KD = 39 microM in 120 mM Na+ at -10 mV). The block was maximal at negative potentials (< -70 mV) and decreased with increasing positive potentials, suggesting that Mg2+ cannot escape to the cell interior. 4. Block of Ca2+ currents by Mg2+ was also voltage dependent, but by three orders of magnitude less potent than with Na+ currents (KD = 24 mM in 2 mM Ca2+ at -30 mV). The high concentration of Mg2+ caused a prominent voltage shift of channel gating kinetics induced by surface charge screening effects. To compensate for this, Mg2+ block of inward Ca2+ currents was estimated from the instantaneous I-V relationships on return from very positive potentials (+100 mV). 5. Inward Na+ and Ca2+ tail currents following depolarization to +90 mV were markedly depressed, suggesting that channels cleared of Mg2+ ions during strong depolarization are quickly re-blocked on return to negative potentials. The kinetics of re-block by Mg2+ was too fast (< 100 microseconds) to be resolved by our recording apparatus. This implies a rate of entry for Mg2+ > 1.45 x 10(8) M-1 S-1 when Na+ is the permeating ion and a rate approximately 3 orders of magnitude smaller for Ca2+. 6. Mg2+ unblock of HVA Na+ currents at +100 mV was independent of the size of outward currents, whether Na+, Cs+ or NMG+ were the main internal cations. 7. Consistent with the idea of a high-affinity binding site for Ca2+ inside the channel, micromolar amounts of Ca2+ caused a strong depression of Na+ currents between -40 and 0 mV, which was effectively relieved with more positive as well as with negative potentials (KD = 0.7 microM in 120 mM Na+ at -20 mV). In this case, the kinetics of re-block could be resolved and gave rates of entry and exit for Ca2+ of 1.4 x 10(8) M-1 S-1 and 2.95 x 10(2) s-1, respectively. 8. The strong voltage dependence and weak current dependence of HVA channel block by divalent cations and the markedly different KD values of Na+ and Ca2+ current block by Mg2+ can be well described by a previously proposed model for Ca2+ channel permeation based on interactions between the permeating ion and the negative charges forming the high-affinity binding site for Ca2+ inside the pore (Lux, Carbone & Zucker, 1990).
Full text
PDF

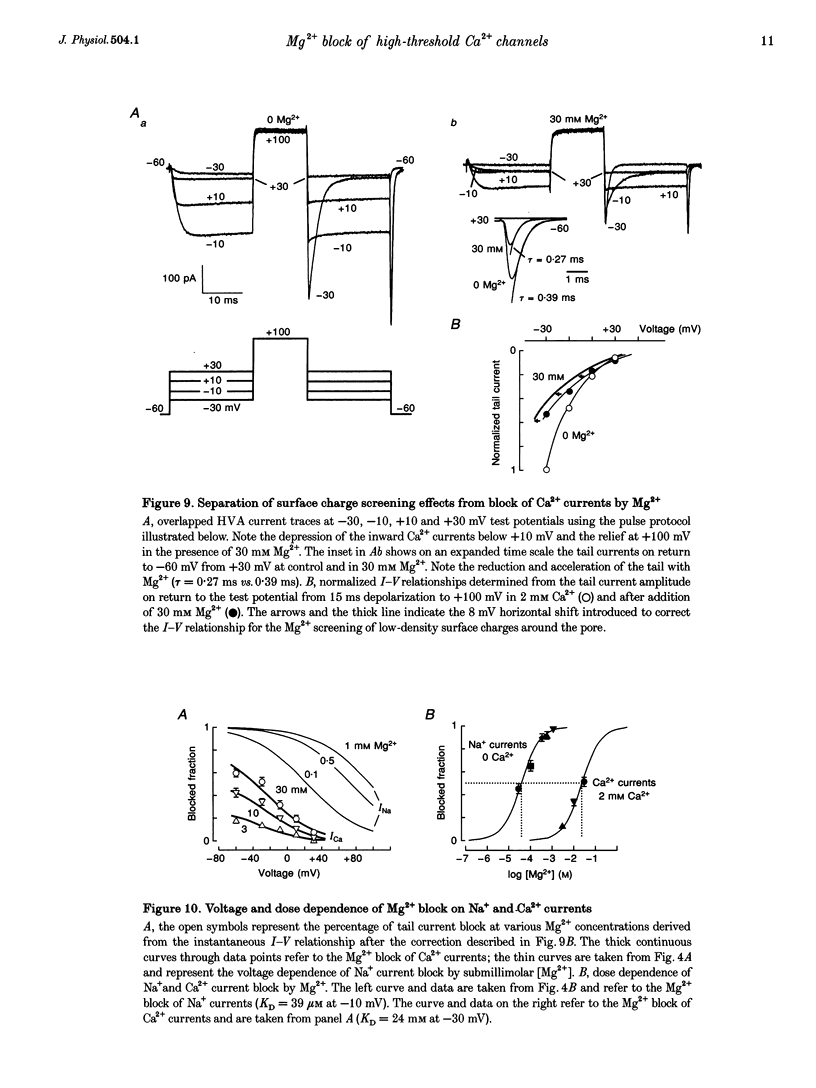




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W. Non-selective conductance in calcium channels of frog muscle: calcium selectivity in a single-file pore. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:585–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Neyton J. Ion permeation through calcium channels. A one-site model. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:18–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. Kinetics and selectivity of a low-voltage-activated calcium current in chick and rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:547–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Swandulla D. Neuronal calcium channels: kinetics, blockade and modulation. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54(1):31–58. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., Inesi G., MacLennan D. H. Location of high affinity Ca2+-binding sites within the predicted transmembrane domain of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):476–478. doi: 10.1038/339476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. H., Dunlap K. Pharmacological discrimination of N-type from L-type calcium current and its selective modulation by transmitters. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):906–914. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00906.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinor P. T., Yang J., Sather W. A., Zhang J. F., Tsien R. W. Ca2+ channel selectivity at a single locus for high-affinity Ca2+ interactions. Neuron. 1995 Nov;15(5):1121–1132. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Tsien R. W. Voltage-gated calcium channels: direct observation of the anomalous mole fraction effect at the single-channel level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5207–5211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Currents carried by monovalent cations through calcium channels in mouse neoplastic B lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:255–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S. H., Terlau H., Stühmer W., Imoto K., Numa S. Calcium channel characteristics conferred on the sodium channel by single mutations. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):441–443. doi: 10.1038/356441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Marks T. N. Calcium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. I. Activation kinetics and pharmacology. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):151–167. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Bean B. P. G-protein modulation of ion permeation through N-type calcium channels. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):258–262. doi: 10.1038/365258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Hess P. A functional view of the entrances of L-type Ca2+ channels: estimates of the size and surface potential at the pore mouths. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90189-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Hess P. Block of the L-type Ca2+ channel pore by external and internal Mg2+ in rat phaeochromocytoma cells. J Physiol. 1993 Jul;466:683–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Hess P. Characterization of the high-affinity Ca2+ binding sites in the L-type Ca2+ channel pore in rat phaeochromocytoma cells. J Physiol. 1993 Jul;466:657–682. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Hess P. Ion permeation through the L-type Ca2+ channel in rat phaeochromocytoma cells: two sets of ion binding sites in the pore. J Physiol. 1993 Jul;466:629–655. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansman J. B., Hess P., Tsien R. W. Blockade of current through single calcium channels by Cd2+, Mg2+, and Ca2+. Voltage and concentration dependence of calcium entry into the pore. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):321–347. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Carbone E., Zucker H. Na+ currents through low-voltage-activated Ca2+ channels of chick sensory neurones: block by external Ca2+ and Mg2+. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:159–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mironov S. L. Conformational model for ion permeation in membrane channels: a comparison with multi-ion models and applications to calcium channel permeability. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):485–496. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81628-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent L., Gopalakrishnan M. Glutamate substitution in repeat IV alters divalent and monovalent cation permeation in the heart Ca2+ channel. Biophys J. 1995 Nov;69(5):1801–1813. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80050-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Conti F., Stühmer W. Intracellular magnesium blocks sodium outward currents in a voltage- and dose-dependent manner. Biophys J. 1989 Jun;55(6):1267–1271. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82922-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M. Open-channel block of Na+ channels by intracellular Mg2+. Eur Biophys J. 1990;18(6):317–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00196922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swandulla D., Armstrong C. M. Calcium channel block by cadmium in chicken sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1736–1740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Reynolds J. A., Johnson E. A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump: a model for Ca2+ binding and Ca2+-coupled phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7094–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thévenod F., Jones S. W. Cadmium block of calcium current in frog sympathetic neurons. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81575-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. L., Morimoto K., Tsuda Y., Brown A. M. Interaction between calcium ions and surface charge as it relates to calcium currents. J Membr Biol. 1983;72(1-2):117–130. doi: 10.1007/BF01870319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Ellinor P. T., Sather W. A., Zhang J. F., Tsien R. W. Molecular determinants of Ca2+ selectivity and ion permeation in L-type Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):158–161. doi: 10.1038/366158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue D. T., Marban E. Permeation in the dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel. Multi-ion occupancy but no anomalous mole-fraction effect between Ba2+ and Ca2+. J Gen Physiol. 1990 May;95(5):911–939. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.5.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou W., Jones S. W. Surface charge and calcium channel saturation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Apr;105(4):441–462. doi: 10.1085/jgp.105.4.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


