Abstract
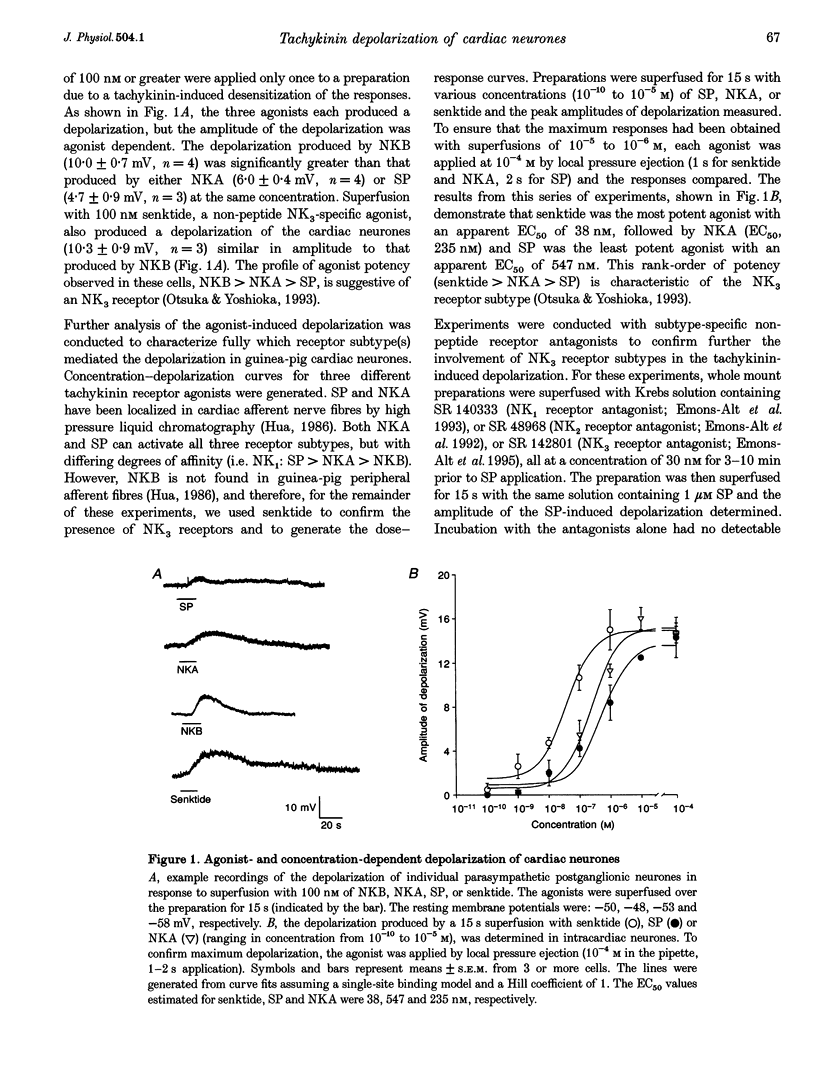
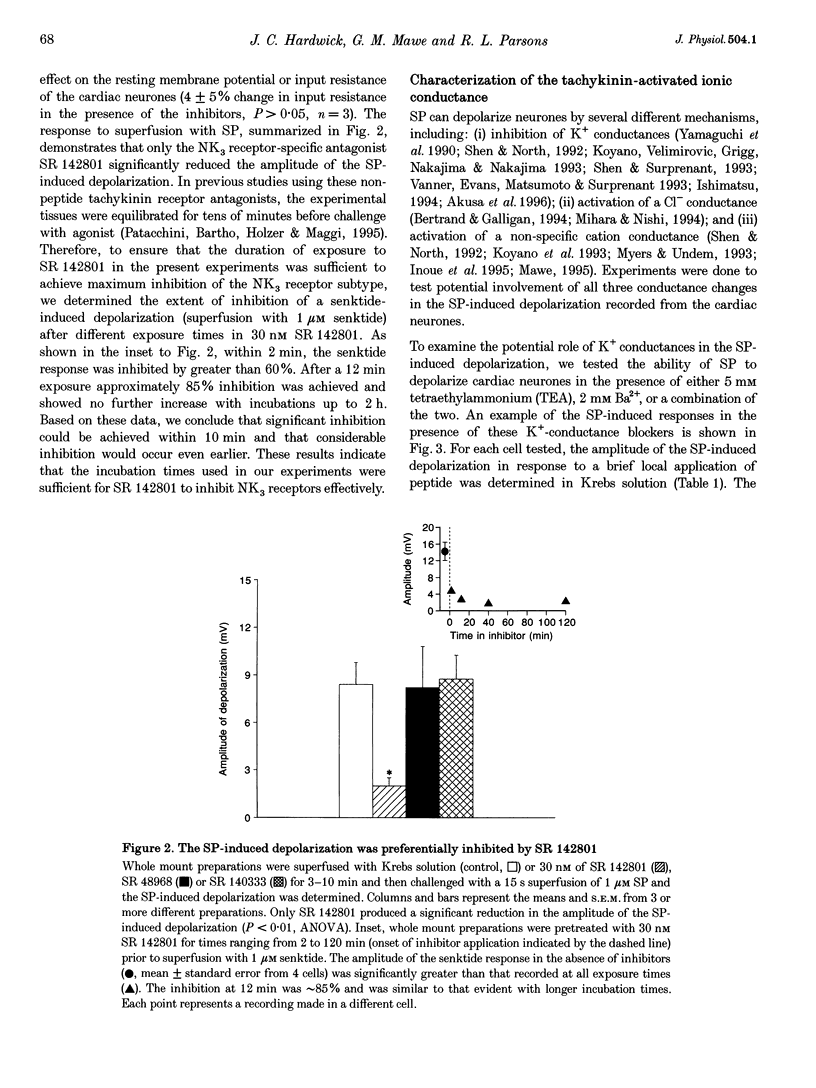
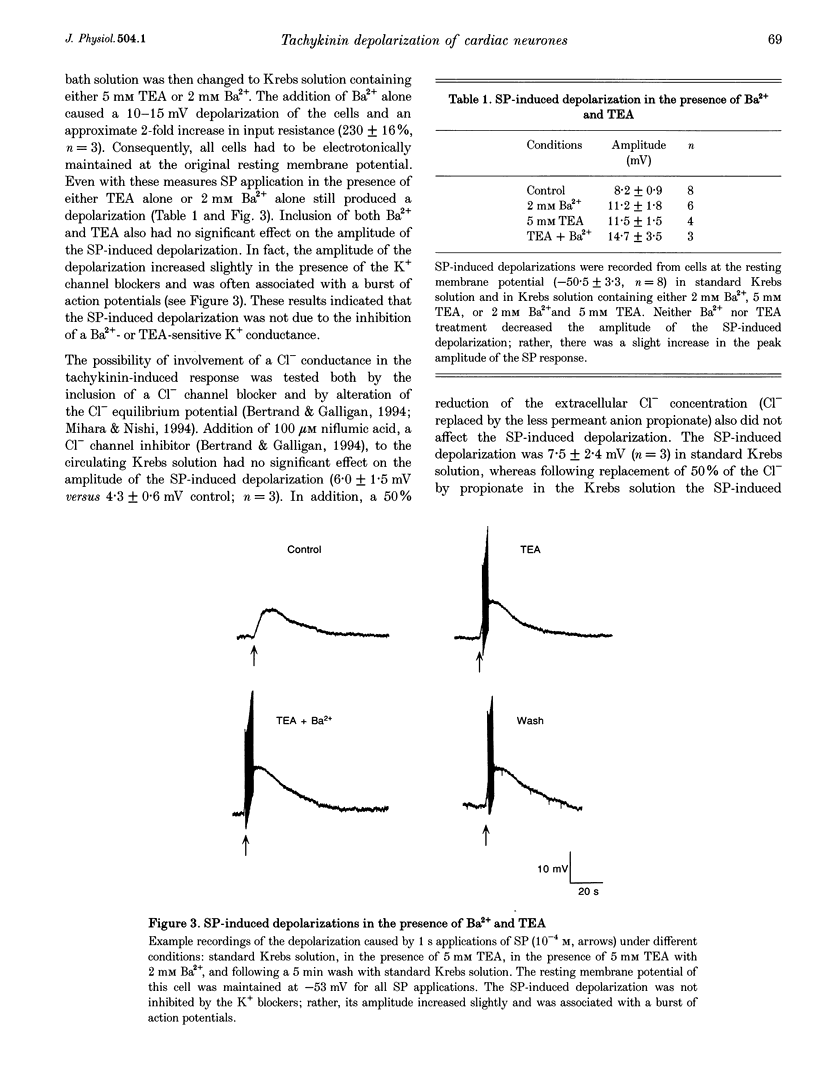
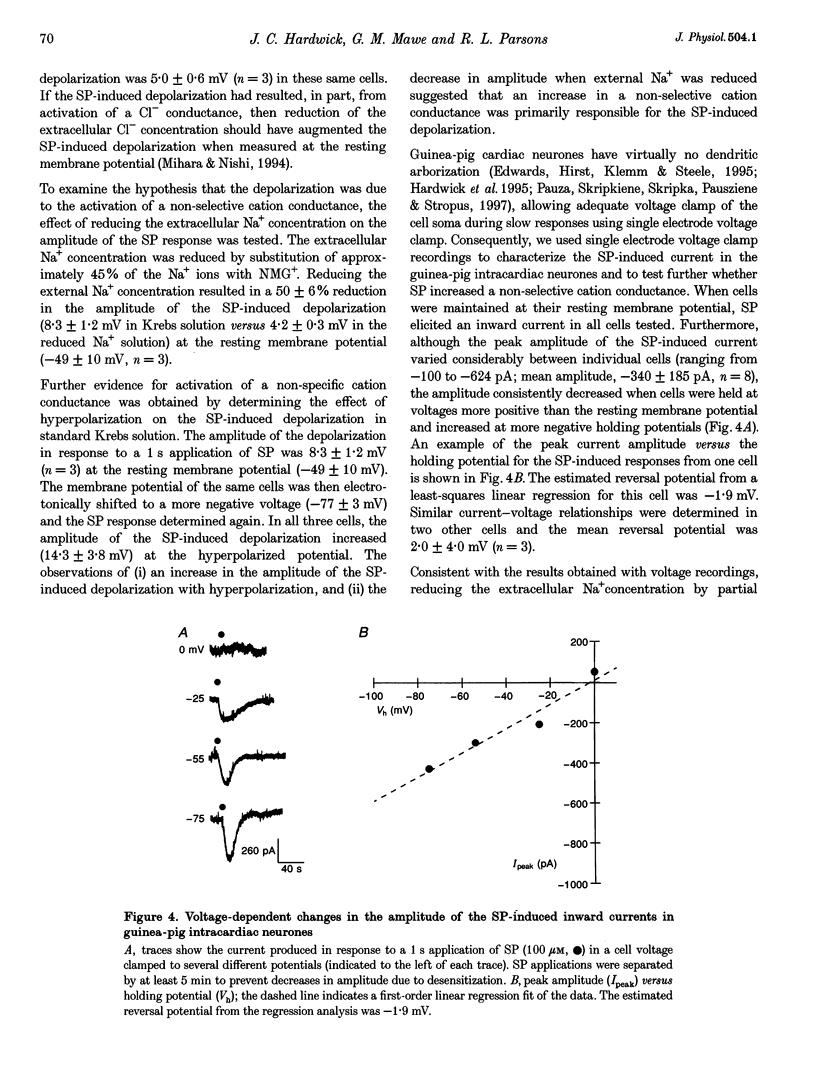
1. Whole mount preparations from guinea-pig hearts were used to characterize the receptors and ionic mechanisms mediating the substance P (SP)-induced depolarization of parasympathetic postganglionic neurones of the cardiac ganglion. 2. Measurement of the amplitude of depolarization in response to superfusion of different tachykinin agonists (neurokinins A (NKA) and B (NKB), SP, and senktide) gave a rank-order potency of NKB = senktide > NKA > SP, indicating involvement of an NK3 receptor. The use of the selective tachykinin receptor antagonists SR 140333, SR 48986, and SR 142801 demonstrated that only the NK3 receptor antagonist SR 142801 inhibited the SP-induced depolarization. 3. The SP-induced depolarization was not inhibited by Ba2+, TEA, or niflumic acid, or altered by reduced Cl- solutions, but was attenuated in reduced Na+ solutions. Single electrode voltage clamp studies demonstrated that the SP-induced inward current increased in amplitude at more negative potentials, had a reversal potential of approximately 0 mV, and was reduced in amplitude in reduced Na+ solutions. 4. We conclude that the SP-induced depolarization in guinea-pig postganglionic parasympathetic neurones of the cardiac ganglion is due to NK3-mediated activation of a non-selective cation conductance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akasu T., Ishimatsu M., Yamada K. Tachykinins cause inward current through NK1 receptors in bullfrog sensory neurons. Brain Res. 1996 Mar 25;713(1-2):160–167. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)01506-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand P. P., Galligan J. J. Contribution of chloride conductance increase to slow EPSC and tachykinin current in guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1994 Nov 15;481(Pt 1):47–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. J., Barber L. A., Dymshitz J., Vasko M. R. Peptidase inhibitors improve recovery of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide release from rat spinal cord slices. Peptides. 1996;17(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(95)02091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. R., Hirst G. D., Klemm M. F., Steele P. A. Different types of ganglion cell in the cardiac plexus of guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1995 Jul 15;486(Pt 2):453–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonds-Alt X., Doutremepuich J. D., Heaulme M., Neliat G., Santucci V., Steinberg R., Vilain P., Bichon D., Ducoux J. P., Proietto V. In vitro and in vivo biological activities of SR140333, a novel potent non-peptide tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec 21;250(3):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90027-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonds-Alt X., Vilain P., Goulaouic P., Proietto V., Van Broeck D., Advenier C., Naline E., Neliat G., Le Fur G., Brelière J. C. A potent and selective non-peptide antagonist of the neurokinin A (NK2) receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(15):PL101–PL106. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90352-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbins I. L., Furness J. B., Costa M., MacIntyre I., Hillyard C. J., Girgis S. Co-localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity with substance P in cutaneous, vascular and visceral sensory neurons of guinea pigs. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jun 12;57(2):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady E. F., Baluk P., Böhm S., Gamp P. D., Wong H., Payan D. G., Ansel J., Portbury A. L., Furness J. B., McDonald D. M. Characterization of antisera specific to NK1, NK2, and NK3 neurokinin receptors and their utilization to localize receptors in the rat gastrointestinal tract. J Neurosci. 1996 Nov 1;16(21):6975–6986. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-21-06975.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. C., Mawe G. M., Parsons R. L. Evidence for afferent fiber innervation of parasympathetic neurons of the guinea-pig cardiac ganglion. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1995 Jun 25;53(2-3):166–174. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(94)00182-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua X. Y. Tachykinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide in relation to peripheral functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1986;551:1–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Nakazawa K., Inoue K., Fujimori K. Nonselective cation channels coupled with tachykinin receptors in rat sensory neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Feb;73(2):736–742. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.73.2.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimatsu M. Substance P produces an inward current by suppressing voltage-dependent and -independent K+ currents in bullfrog primary afferent neurons. Neurosci Res. 1994 Feb;19(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(94)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyano K., Velimirovic B. M., Grigg J. J., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y. Two signal transduction mechanisms of substance P-induced depolarization in locus coeruleus neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Sep 1;5(9):1189–1197. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawe G. M. Tachykinins as mediators of slow EPSPs in guinea-pig gall-bladder ganglia: involvement of neurokinin-3 receptors. J Physiol. 1995 Jun 1;485(Pt 2):513–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., Nishi S. Neurokinin A mimics the slow excitatory postsynaptic current in submucous plexus neurons of the guinea-pig caecum. Neuroscience. 1994 Oct;62(4):1245–1255. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. C., Undem B. J. Electrophysiological effects of tachykinins and capsaicin on guinea-pig bronchial parasympathetic ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:665–679. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Yoshioka K. Neurotransmitter functions of mammalian tachykinins. Physiol Rev. 1993 Apr;73(2):229–308. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patacchini R., Barthò L., Holzer P., Maggi C. A. Activity of SR 142801 at peripheral tachykinin receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 May 4;278(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza D. H., Skripkiene G., Skripka V., Pauziene N., Stropus R. Morphological study of neurons in the nerve plexus on heart base of rats and guinea pigs. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1997 Jan 12;62(1-2):1–12. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1838(96)00102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabrook G. R., Bowery B. J., Hill R. G. Pharmacology of tachykinin receptors on neurones in the ventral tegmental area of rat brain slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan 24;273(1-2):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)00681-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., North R. A. Substance P opens cation channels and closes potassium channels in rat locus coeruleus neurons. Neuroscience. 1992 Sep;50(2):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., Surprenant A. Common ionic mechanisms of excitation by substance P and other transmitters in guinea-pig submucosal neurones. J Physiol. 1993 Mar;462:483–501. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban L., Papka R. E. Origin of small primary afferent substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the guinea-pig heart. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1985 Apr;12(4):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(85)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanner S., Evans R. J., Matsumoto S. G., Surprenant A. Potassium currents and their modulation by muscarine and substance P in neuronal cultures from adult guinea pig celiac ganglia. J Neurophysiol. 1993 May;69(5):1632–1644. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.69.5.1632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Stanfield P. R. Modulation of inwardly rectifying channels by substance P in cholinergic neurones from rat brain in culture. J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:499–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao F. Y., Saito K., Yoshioka K., Guo J. Z., Murakoshi T., Konishi S., Otsuka M. Tachykininergic synaptic transmission in the coeliac ganglion of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Aug;118(8):2059–2066. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



