Abstract
Purpose
Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Institute (EMRI) in 25th anniversary prompt to highlight the educational activities on capacity building and research in prevention and education of diabetes field. In recent decades, this academic institute arranges for opportunities to catch new ways to encounter non-communicable diseases especially diabetes to advantage both diabetes health care providers and people with diabetes. This review aims to overview the educational activities of EMRI on diabetes.
Methods
In this conventional review and Scientometrics, the studies affiliated with EMRI on diabetes education were explored in Scopus, PubMed, Google Scholar, and SID, without any restriction on time and language. All papers published up to 2020 were analyzed and visualized with the VOS viewer Software program.
Results
Total number of 12 documents retrieved from various databases. Patient education, diabetes type 2, health, and self-care are the most frequent keywords in the published paper. Several perspectives of diabetes education have been addressed in two main categories include public and patient education and professional education.
Conclusion
It is notable that, the national strategic planning to establish courses and produce materials and programs to empower health care providers and patients with diabetes and families. According to the strategic plan, further research and infrastructures are required for various aspects of diabetes prevention and education.
Keywords: Education, Diabetes mellitus, Iran
Introduction
Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Institute (EMRI) was designated as a World Health Organization (WHO) Collaborating Centre for Research & Education on the management of diabetes since 2007. It has been re-designated in this regard to 2023. Accordingly, one of the main focuses of this institute is to foster and create the opportunity for education on different aspects of diabetes except for complications.
Developing a national action plan for NCDs’ entitled “National Action Plan for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases” and the related risk factors in Iran (2015–2025) were developed by considering our country’s priorities, the burden of diseases, and WHO global targets. Along with WHO targets, a 25% reduction in the risk of premature death from diabetes is considered as a target [1].
Diabetes education potentially improves diabetes self-care with consequent advantages in different areas such as metabolic outcomes, costs, and quality of life [2]. A patient suffering from Diabetes encounters various care requirements in different life stages [3]. Since patients with diabetes need education and adjustment of treatment once first diagnosed and an on-going basis [4]. EMRI through training the well-educated and high-qualified health care provides a prominent impression in the patients’ outcomes. EMRI, effort to empower patients with diabetes and their families and health care providers in the field of diabetes through general and specialized education programs.
This review aims to overview the educational activities of EMRI on diabetes. Remarkably, many scholars, centers, and universities have been attempted to promote the sciences in this field, but we are going to inspect the main achievement of EMRI in the field of diabetes education and prevention.
Method
In this used the combination of conventional review and Scientometrics method to respond the main purpose of this paper, to introduce all educational activities of EMRI during 25 years past.
Scientometrics method
The electronic databases including Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus were searched for published articles in international databases. Other sources such as Magiran and SID were also searched as internal databases for Persian language publications. Search strategy conducted by using MESH and EMTREE terms for diabetes“ and “education concepts. Synonyms and related terms also applied to retrieve all of the documents. Keywords related to affiliation and address of EMRI such as “EMRI”, “Endocrinology”, “institute” and “Tehran” was also included for searching the terms. There was no restriction to the time of publication and language. All the papers were searched with at least one affiliation of EMRI published in the diabetes education field.
All sources were imported to the Endnote software and after merging duplicate items, the papers were reviewed by two independent researchers to exclude the non-related articles. In case of any disagreement between the two researchers, a third-person reexamined the papers to achieve a consensus. We described the characteristics and details of the documents retrieved from the various databases and analyzed and visualized the publications indexed and obtained from the Web of Science database with VOS viewer Software program 1.6.15. Also, ScientoPy v2.0.3 was used to analyze the trend of keyword presence in studies to reports the top topics (based on authors or index keywords), authors, and countries from bibliographic data (Table 1).
Table 1.
Details of 12 articles produced be researchers of EMRI in the education field
| No | Title | Authors | Year | Indexing | Journal | IF | SJR | Citation/ Scopus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | World diabetes day: celebrating two decades of Progress in combating diabetes and its complications in Iran | Bandarian F, Larijani B. | 2019 | ISI/PUBMED/SCOPUS | Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders | – | 0.69 | 2 |
| 2 | Conceptual map of diabetes education: the necessity of establishing Iran diabetes academy | Sanjari M, Aalaa M, Amini MR, Mehrdad N, Adibi H, Esfahani EN, et al. | 2019 | ISI/PUBMED/SCOPUS | Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders | – | 0.69 | 2 |
| 3 | A peer support intervention in improving glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes | Peimani M, Monjazebi F, Ghodssi-Ghassemabadi R, Nasli-Esfahani E. | 2018 | ISI/PUBMED/SCOPUS | Patient education and counseling. | – | 1.24 | 10 |
| 4 | Using virtual social networks for case finding in clinical studies: An experiment from adolescence, brain, cognition, and diabetes study | Pourabbasi A, Farzami J, Shirvani M-SE, Shams AH, Larijani B. | 2017 | ISI/PUBMED/SCOPUS | International journal of preventive medicine | – | 0.51 | 2 |
| 5 | Iran diabetes research roadmap (IDRR) study; patient education in diabetes: a review article | Peimani M, Bandarian F, Aalaa M, Kouhnavard M, Nasli-Esfahani E, Larijani B. | 2017 | ISI/SCOPUS | Iranian Journal of Public Health | 1.291 | 0.32 | 5 |
| 6 | Diabetic foot workshop: Improving technical and educational skills for nurses | Aalaa M, Sanjari M, Shahbazi S, Shayeganmehr Z, Abooeirad M, Amini MR, et al. | 2017 | SCOPUS/PUBMED | Medical journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran | – | 0.27 | 2 |
| 7 | The effectiveness of a peer coaching education on control and management of type 2 diabetes in women: a protocol for a randomized controlled trial | Aalaa M, Sanjari M, Meybodi HRA, Amini MR, Qorbani M, Adibi H, et al. | 2017 | SCOPUS/PUBMED | International journal of community-based nursing and midwifery | – | 0.41 | 2 |
| 8 | The conceptual framework for developing a diabetes information network | Riazi H, Langarizadeh M, Larijani B, Shahmoradi L. | 2016 | PUBMED/SCOPUS | Acta Informatica Medica | 0.24 | 1 | |
| 9 | Effectiveness of short message service-based intervention (SMS) on self-care in type 2 diabetes: A feasibility study | Peimani M, Rambod C, Omidvar M, Larijani B, Ghodssi-Ghassemabadi R, Tootee A, et al. | 2016 | ISI/PUBMED/SCOPUS | Primary care diabetes | 2.052 | 0.78 | 27 |
| 10 | Diabetic foot workshop to apply interactive learning method for nurses: working with the real patient as a teaching strategy | Amini MR, Mehrdad N, Sanjari M, Aalaa M, Shahbazi S, Shaygabmehr Z, et al., | 2016 | Abstract book | 18th European Congress of Endocrinology; 2016: BioScientifica | – | – | – |
| 11 | Persian diabetes self-management education (PDSME) program: evaluation of effectiveness in Iran | Shakibazadeh E, Bartholomew LK, Rashidian A, Larijani B. | 2015 | ISI/PUBMED/SCOPUS | Health promotion international | 1.98 | 0.79 | 9 |
| 12 | review of web-assisted interventions for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus | Aalaa M, Peimani M. A | 2014 | EMBASE/CINAHL/ MAGIRAN | Iranian journal of Diabetes and Metabolism | – | – | – |
Conventional review method
Also, other educational activities that are not reflected in the papers provide in different (Tables 2 and 3) in order to cover all educational activities of diabetes education. The data was obtained from the EMRI website, EMRI strategic plan, official reports of WHO, MOH, and also diabetes world day ceremonies. The remaining activities were reviewed and categorized into two subjects: i. public and patient education ii. Professional education.
Table 2.
Selected capacity building programs on public and patient education
| Capital category | Activity | Implementation description |
|---|---|---|
| Actual education | World Diabetes Day campaign | International Diabetes Federation (IDF) announced the World Diabetes Day (WDD) in 1991 in response to the alarming increasing prevalence of diabetes and diabetic complications all over the world. EMRI is celebrated WDD every year [5] which includes various activities and ceremonies to public awareness improving, contributing to government and policymakers to implement applicable national strategies, and promoting the vigilance of clinicians. |
| Monthly Diabetes Education for patients and their families | In order to promote the abilities of diabetes management, diabetes Education sessions are conducted for patients and their families by the Diabetes Specialty Clinic regularly. Overview of diabetes, nutrition, counting carbohydrates, diabetes treatment consists of oral agents and insulin therapy, overcoming barriers to diabetes control, blood glucose monitoring, stress management, physical activity, and foot care are considered as educational topics in these educational sessions. | |
| Diabetes patient decision aid guideline | Diabetes self-management guidelines according to a patient’s decision would be an effective way to standardize the quality of service provision to patients with diabetes. In this regard, diabetes care health providers help patients to set priorities give information to prevent and, manage diabetes complications. They focus on the demands of patients in health care goals; along with clarifying the treatment process, laboratory results, benefits, and side effects of various medications. | |
| Virtual Education | Online learning platform | An online learning platform prepared by The Iranian Diabetes Academy (IDA) considers as a novel educational strategy helped all diabetes care team members especially people with diabetes. Electronic material on the website such as educational short films, health messages about healthy lifestyle, calculation of Body Mass Index (BMI) to awareness about metabolic syndrome, carbohydrate calculation for the patient with diabetes and diabetes at risk questionnaire to diabetes risk assessment for people prepared by IDA [6]. |
Table 3.
Selected capacity building programs on medical and professional education
| Capital category | Activity | Implementation description |
|---|---|---|
| Actual education | Comprehensive Course of Diabetes Management |
Annually the Diabetes Comprehensive Training Courses aiming at updating health care providers on the most recent advances in different fields of diabetes is held. Team-based learning as foremost educational strategy designs and implements to implement a multifaceted approach to diabetes care by different health care professionals including general practitioners, as well as nurses and nutritionists. Subsequent to the theoretic course, the practical periods being held at diabetes clinics of EMRI for a total length of 12 working days (2 consecutive weeks). The participants get the Continuing Medical Education (CME) credit, which is approved by the Ministry of Health of I.R. of Iran. |
| Diabetic Foot Workshop with real patient technique |
In this workshop which was endorsed by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF 2014–2017) and the European Wound Management Association (EWMA 2017–2019), nurses, practitioners and physicians are qualified about Diabetic Foot to render their services at diabetes foot clinics. Be noted that the program of this workshop. The core topics in this workshop are prepared as lectures, hands-on training, and teamwork activities. Diabetic foot prevention, management, rehabilitation as lectures tracked by teamwork and educational case questions. Moreover, educational films, and visual demonstration on diabetic foot ulcers in patients were presented [7, 8]. |
|
| Comprehensive Course of diabetic foot Management | The comprehensive training courses planned for two weeks are held every year since 2018 in order to update clinicians and researchers on the recent advances in various areas of diabetic foot. It is held to authorize the theoretical and practical skills of all health care providers engaging in the diabetic foot prevention and management process. The mentioned course could be beneficial to implement the localized guideline of IWGDF by all trained Diabetic Foot team members. | |
| Virtual education | Iran Diabetes Academy |
The Iran diabetes Academy of EMRI committed to enhancing the health of patients and at-risk people in the community also promoting the knowledge of health care providers in the field of Diabetes and its complications. The IDA provides knowledge in conventional and novel strategies for empowering the future of health care providers to deliver appropriate care to patients with diabetes. This electronic educational center with the mission to train health care providers involved in diabetes prevention and management provides the opportunity to improve the health and quality of life of communities through sharing knowledge of diabetes care with other medical sciences, teaching and applying evidence in different fields of medicine, family, and community [6]. |
Result
Scientometrics analysis
First, we analyzed the 12 documents retrieved from various databases and the following table shows the details of these articles that are related to the education concept and topic produced by EMRI researchers.
Based on the data that has shown in this table, there are 7 articles of 12 documents that are indexed in the web of science database. Among these papers, the “Effectiveness of short message service-based intervention (SMS) on self-care in type 2 diabetes: A feasibility study” article, has the most citations (27 citations) among the other articles (Table 1).
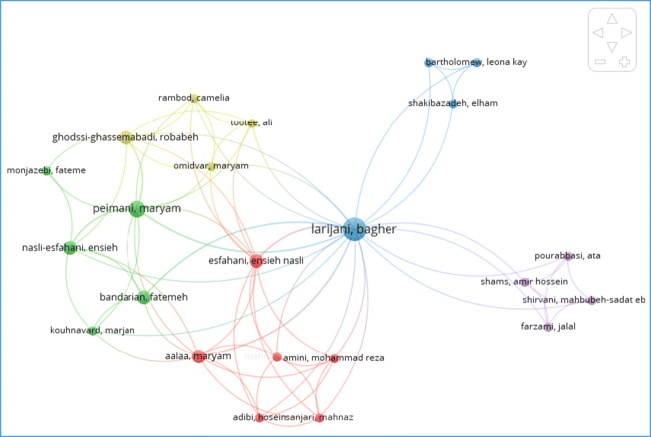
We also analyzed and visualized the 7 articles indexed and published in the Web of Science database which is related to the education topic and produced by EMRI scientists to find out more details about these articles. In Fig. 1 the co-authorship network among the researchers has shown. There are 5 clusters in this analysis and among 23 authors that collaborated in producing these publications, Larijani has the most collaboration, then Peimani and Nasli-Esfahani are followed (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Network Visualization of Co-authorship for the produced articles about education with EMRI affiliation in Web of Science database
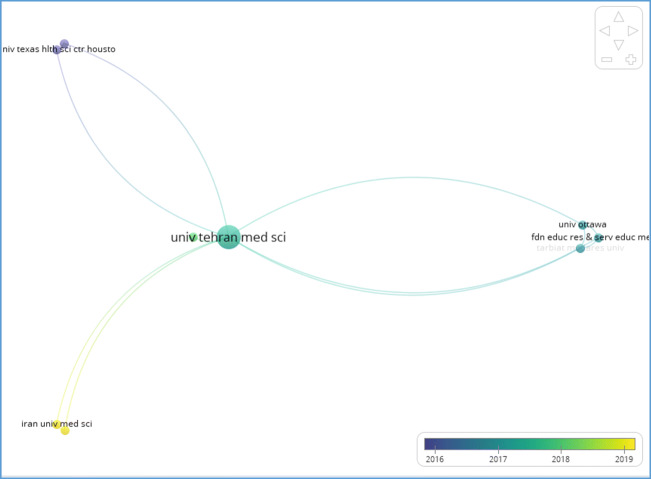
In another figure that is overlay visualization, we can see the 9 organizations that have cooperation in producing these documents. After TUMS, the fdn educ res & serv educ med… then Tarbiat modares univ. have most collaboration (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Network Visualization of organizations that produced articles about education with EMRI affiliation in Web of Science database
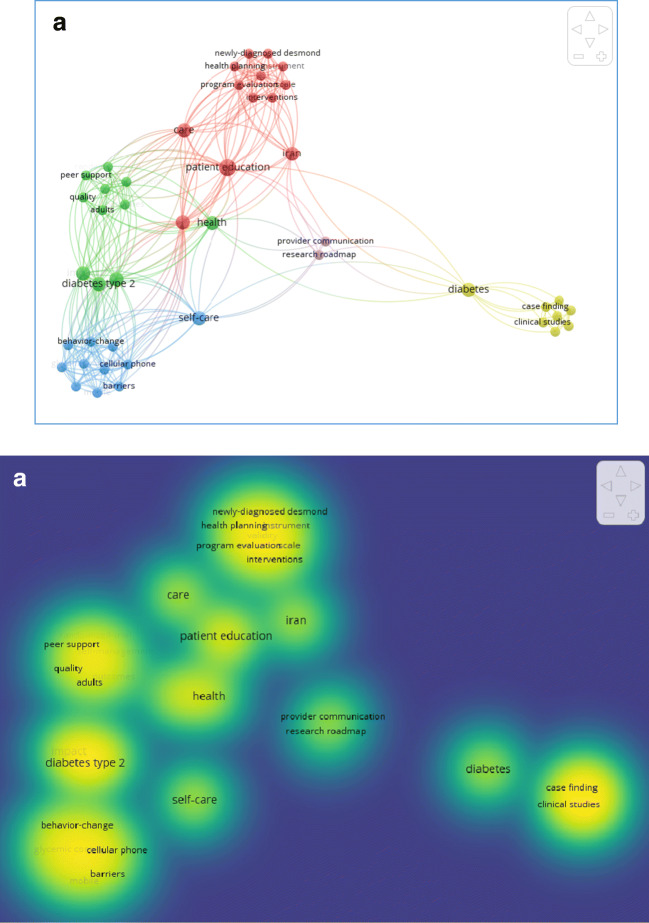
In Fig. 3a, the network of keywords assigned to these papers has shown. As data illustrated, the most keyword used and applied in these articles among 45 keywords, first was “patient education” and then “diabetes type 2” (Fig. 3a). Other figures for illustration of these keywords also show these keywords in density visualization and have more clarification (Fig. 3b).
Fig. 3.
a Network Visualization of Co-occurrence of keywords assigned for the produced articles about education with EMRI affiliation in Web of Science database. b density Visualization of Co-occurrence of keywords assigned for the produced articles about education with EMRI affiliation in Web of Science database
Content and papers analysis
According to the strategic plan of EMRI some researches have been done to bring more attention to education and prevention of diabetes in patients and their families’ population. In 2017, one study was conducted for the purpose to design a patient education road map in diabetes. The result of this study showed that the publication on patient education is relatively increasing with time and self-care training and model-based interventions are the foremost effective methods of education [9].
Some research was conducted in the area of effective interventions on self-care. Results of one systematic review showed that goal-setting, adapted coaching, collaborative feedback, and online peer support groups would be some of the successful approaches in diabetes education in patients with type 2 diabetes. Besides, both robust theoretical background and a longer duration of intervention were detected as an effective strategy [10]. The result of the study showed that 12 weeks of use of short message service-based intervention (SMS), with conventional diabetes treatment cause to improve glycemic control and Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS), triglyceride, and BMI significantly reduced in both SMS groups [11]. Another study was conducted on families of children with diabetes to use a combination of phone calls (90 days) and telegram (30 days) as educational strategies. The result showed that, even though the telegram method was shorter than the phone call, there were no significant differences in educational scores compared with the ones being phone called [12]. An additional study about Persian Diabetes Self-Management Education (PDSME) program effective in improving self-management cognitive and clinical outcomes, revealed that diabetes knowledge enhanced in PDSME patients treated with oral antidiabetic agents also this program escalated self-care behaviors, health beliefs, attitudes toward diabetes, stigma, self-efficacy and patient satisfaction. PDSME program was [13].
As well, two studies were conducted on peer support education. One of these studies was protocol for a randomized controlled trial investigating the effectiveness of a peer coaching education on type 2 diabetes management in women. The primary outcomes considered FBS and HbA1c measured at baseline and in 3,6 and 12 months to provide more evidence about the peer-coaching model [14]. The results of a different study about peer support disclosed that after 6 months, peer support leads to a decline significantly in mean HbA1c, diabetes self-management scores, self-efficacy scores, and mean the quality of life scores in the peer support groups [15].
Professional education is the main part of the conceptual map of diabetes management according to the strategic plan of EMRI. The studies in this field are less than in comparison with patient education. These reports will be delivered in two categories include professional education and medical education.
The result of the study on the necessity diabetes information network demonstrated that all required items were identified as essential or semi-essential by clinicians [16]. The EMRI proposed a conceptual framework for supporting diabetes care, which would be possible by using the DIANET framework. Moreover, in one commentary article about improving technical and educational skills on diabetic foot, five steps including Goals definition, deciding about attendees, location selection, creating agenda, and developing a follow-up plan presented to design diabetic foot workshop [7].
Conventional review
This institute has endeavored to the management of diabetes and combat diabetes complications as the main issue of patients, families, communities, and health system, and policymakers. Numerous articles, books, and booklets as well as other activities have been produced that we are not able to include in this brief paper. This article will be delivered in two categories include “public and patient education” and also “medical and professional education”.
Public and patient education
The general education is provided for the patient with diabetes, family members, at-risk patients, and the public. These activities are carried out in the form of face to face and virtual education. These educational activities consist of two major categories, capacity building program and research activities (Table 2).
Medical and professional education
The EMRI sponsors plentiful national and international academic events to keep informed Iranian health care providers and scientists on the latest advances in the field of endocrinology and metabolic diseases. The specific education is presented in the form of international congresses, seminars, and conferences and workshops for specialists involved in diabetes care (Table 3).
Discussion
The result of the study shows a significant contribution of EMRI in diabetes education filed as a main arm in the prevention of diabetes and diabetes complications during the last 25 years. The most of the papers published since 2014. The infrastructure and educational achievements such as patients’ education programs and were stablished from beginning the research center initiation. The most frequent subjects were investigated by EMRI included: care, behavior change, self-care, facilitator and barriers of education.
The education is an ongoing process to access the outcomes for patients and providers. The EMRI were planned the future programs to achieve this goal. This consideration will be discussed in different aspects of infrastructures, facilities, and research priorities.
Future horizons on capacity building
Establishment of Iran diabetes education Centre
The people with diabetes require diabetes education and adjustment of treatment not only when first diagnosed, but on an on-going basis. Hence, EMRI leans towards establishing the “Iran Diabetes Education Centre” through training the well-educated and high-qualified health care provides a prominent impress in the patients’ outcomes. The “Iran Diabetes Education Centre” provides information and skill for planning and empowering the future of health care providers to deliver proper care to patients with diabetes. The mission of this project would be to train the expert and efficient graduate specialists who have an effective role to improve the health and quality of life of the community through sharing knowledge of diabetes care with other medical sciences, teaching and applying evidence in various fields of medicine, family and community.
Diabetes vocational training course: Online and face-to-face program
This program focuses on developing the knowledge and skills of general practitioners, nurses, and nutritionists to be able to work in multidisciplinary teams and display a collaborative approach towards the management of diabetes. The professionals will gain the skills and experiences required to understand and manage people with diabetes. This project encompasses the combination of a virtual program, face to face training program, and internship program. This multi-disciplinary course grows appropriately qualified health care providers for work as health professionals in the area of diabetes management in a variety of settings.
Podiatrist course
The care quality and control of diabetes complications despite the high prevalence of diabetes and its complications such as diabetic foot is not acceptable. Actually, the lack of podiatrists in the diabetic foot care team in Iran is evident. The EMRI tends to design Podiatric Program in form of the comprehensive course considered basic medical and clinical sciences to train the physicians, nurses, and other primary health care with a broad base of podiatry knowledge and extensive clinical experience.
The graduates of this program can combine advanced foot care with other disciplines and affiliated specialties. They also have sufficient skills and knowledge in providing care for prevention, rehabilitation, and care of the patient, family, and society. They can identify the biological, psychological, social, and cultural needs of the patient at various levels of health through the application of the principles of human communication.
Future horizons on research activities
As mentioned, a wide range of priorities detected in the diabetes education field and required extended research. According to the Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020, further studies are needed in the area of collaborative patients’ education based on individual preferences, providing decision support tools [17], initiate and develop the behavioral lifestyle intervention program modeled according to Iranian context, propagation of technology-assisted interventions within the community and families [18].
Limitations
Our study had some limitations. According to the result, most of the articles have the observational methodology or review, because it is less expensive, easier, and fast. It is recommended that to design experimental studies as the gold standard in education to assess impacts, cost-effectiveness, and audit the education in the field of diabetes.
Conclusion
A situation analysis of existing educational activities and facilities has been providing a detailed and realistic picture of the opportunities, resources, challenges, and barriers regarding diabetes education. The authors find gaps for establishing educational structures, developing educational facilities in both patient and professional settings, and run the national and international projects to meet the patient and professional requirements.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank scientists who have been engaged in the prevention and education activities on the diabetes field to collect the paper. Also, Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Institute full support in preparing articles.
Declaration
Ethics approval
No institutional review board was required.
Competing interests
None declared.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Peykari N, Hashemi H, Dinarvand R, Haji-Aghajani M, Malekzadeh R, Sadrolsadat A, et al. National action plan for non-communicable diseases prevention and control in Iran; a response to emerging epidemic. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2017;16(1):3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Thomas V. Investigating intervention strategies for the management of diabetes in South Africa: a system dynamics approach. 2019. (Doctoral dissertation, Stellenbosch: Stellenbosch University).
- 3.Association Ad. 6. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(Supplement 1):S55–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mj D, Dipankui M, Chipenda Dansokho S, Légaré F, Ho W. Diabetes-related complications: which research topics matter to diverse patients and caregivers? Health Expect. 2018;21(2):549–59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bandarian F, Larijani B. World diabetes day: celebrating two decades of progress in combating diabetes and its complications in Iran. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2019;18(2):743–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Sanjari M, Aalaa M, Amini MR, Mehrdad N, Adibi H, Esfahani EN, et al. Conceptual map of diabetes education: necessity of establishing Iran diabetes academy. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2019;18(2):729–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Aalaa M, Sanjari M, Shahbazi S, Shayeganmehr Z, Abooeirad M, Mr A, et al. Diabetic foot workshop: improving technical and educational skills for nurses. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2017;31:8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Amini MR, Mehrdad N, Sanjari M, Aalaa M, Shahbazi S, Shaygabmehr Z, et al. Diabetic foot workshop to apply interactive learning method for nurses: working with real patient as a teaching strategy. In: 18th European Congress of Endocrinology (Vol. 41). Bristol: BioScientifica; 2016.
- 9.Peimani M, Bandarian F, Aalaa M, Kouhnavard M, Nasli-Esfahani E, Larijani B. Iran diabetes research roadmap (Idrr) study; patient education in diabetes: a review article. Iran J Public Health. 2017;46(Supple 1):10–6. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Aalaa M, Peimani M. A review of web-assisted interventions for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Iran J Diabetes Metab. 2014;13(3):211–22. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Peimani M, Rambod C, Omidvar M, Larijani B, Ghodssi-Ghassemabadi R, Tootee A, et al. Effectiveness of short message service-based intervention (Sms) on self-care in type 2 diabetes: a feasibility study. Prim Care Diabetes. 2016;10(4):251–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pourabbasi A, Farzami J, M-Se S, Ah S, Larijani B. Using virtual social networks for case finding in clinical studies: an experiment from adolescence, brain, cognition, and diabetes study. Int J Prev Med. 2017;8:30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shakibazadeh E, Lk B, Rashidian A, Larijani B. Persian diabetes self-management education (Pdsme) program: evaluation of effectiveness in Iran. Health Promot Int. 2015;31(3):623–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Aalaa M, Sanjari M, Hra M, Mr A, Qorbani M, Adibi H, et al. The effectiveness of a peer coaching education on control and management of type 2 diabetes in women: a protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2017;5(2):153. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Peimani M, Monjazebi F, Ghodssi-Ghassemabadi R, Nasli-Esfahani E. A peer support intervention in improving glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Patient Educ Couns. 2018;101(3):460–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Riazi H, Langarizadeh M, Larijani B, Shahmoradi L. Conceptual framework for developing a diabetes information network. Acta Inform Med. 2016;24(3):186–92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Association Ad. 1. Improving care and promoting health in populations: standards of medical care in diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(Supplement 1):S7–S13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Association Ad. 3. Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(Suppl 1):S32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]